introduce
This article describes how to rk-boot Implement the server JWT verification logic.
What is JWT?
JSON network token is an Internet standard used to create data with optional signature or optional encryption so that claims can be safely represented between two parties. The token is signed with a private secret or public / private key.
In short, the JWT mechanism allows the client to encrypt the information through a key, add it to the Header of the HTTP request, and transmit it to the server, which verifies the legitimacy of the client.
Please refer to JWT official website
Many SAAS services use JWT as user authentication, such as github
Please visit the following address for a complete tutorial:
install
go get github.com/rookie-ninja/rk-boot
Quick start
Rk boot will enable gRPC gateway for gRPC service by default. The two protocols listen to the same port.
Therefore, JWT can be verified whether it is a gRPC request or a Restful request.
1. Create boot.yaml
The boot.yaml file tells rk boot how to start the gRPC service.
In the following YAML file, we declare three things:
- Enable commonService: an API like / rk / V1 / health is provided by default. details
- Enable enableRkGwOption: this Option can regulate the error type of gRPC - > restful API, otherwise the returned error will be gRPC error code. Recommended.
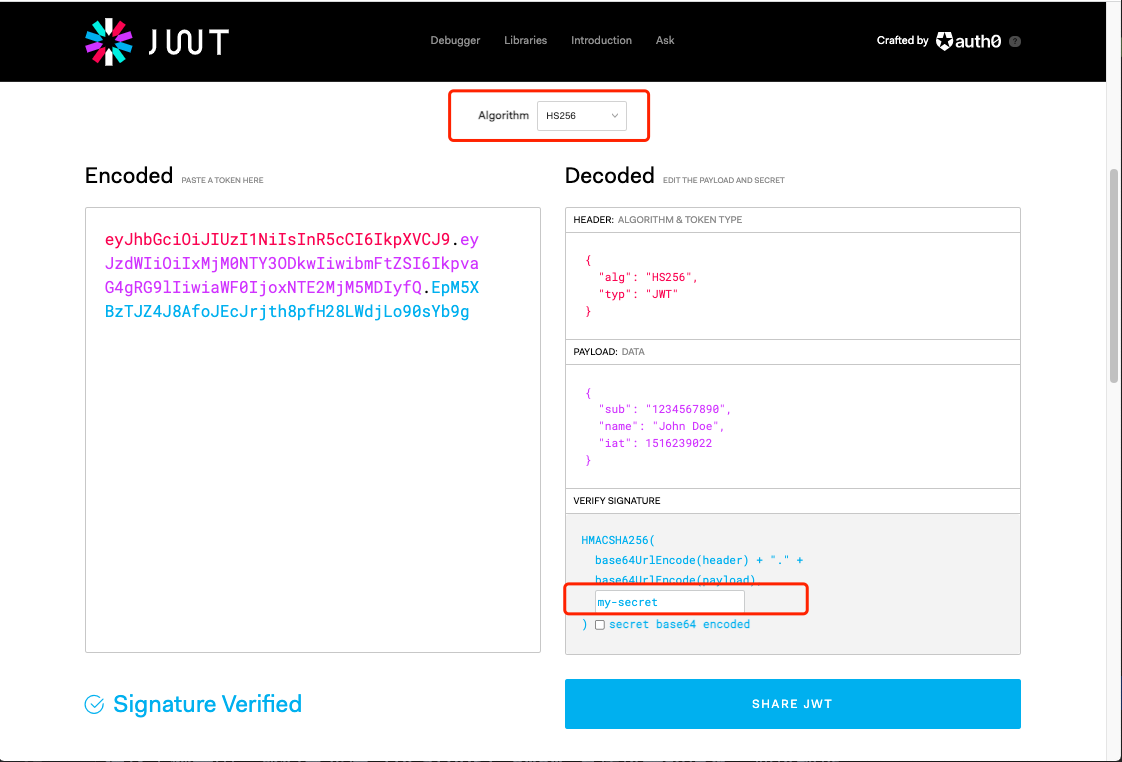
- Open the JWT interceptor and declare the JWT key as my secret as an example. The HS256 algorithm will be used in the background by default, or you can customize the algorithm, which will be described below.
Therefore, the boot.yaml file will tell rk boot to open port 8080, start gRPC service, and open commonService and JWT authentication interceptor.
---
grpc:
- name: greeter # Required
port: 8080 # Required
enabled: true # Required
enableRkGwOption: true # Optional
commonService:
enabled: true # Optional, default: false
interceptors:
jwt:
enabled: true # Optional, default: false
signingKey: "my-secret" # Required2. Create main.go
Since commonService is enabled, there is no need to add an API to gRPC for verification.
// Copyright (c) 2021 rookie-ninja
//
// Use of this source code is governed by an Apache-style
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
package rkdemo
import (
"context"
"github.com/rookie-ninja/rk-boot"
)
// Application entrance.
func main() {
// Create a new boot instance.
boot := rkboot.NewBoot()
// Bootstrap
boot.Bootstrap(context.Background())
// Wait for shutdown sig
boot.WaitForShutdownSig(context.Background())
}3. Create JWT Token
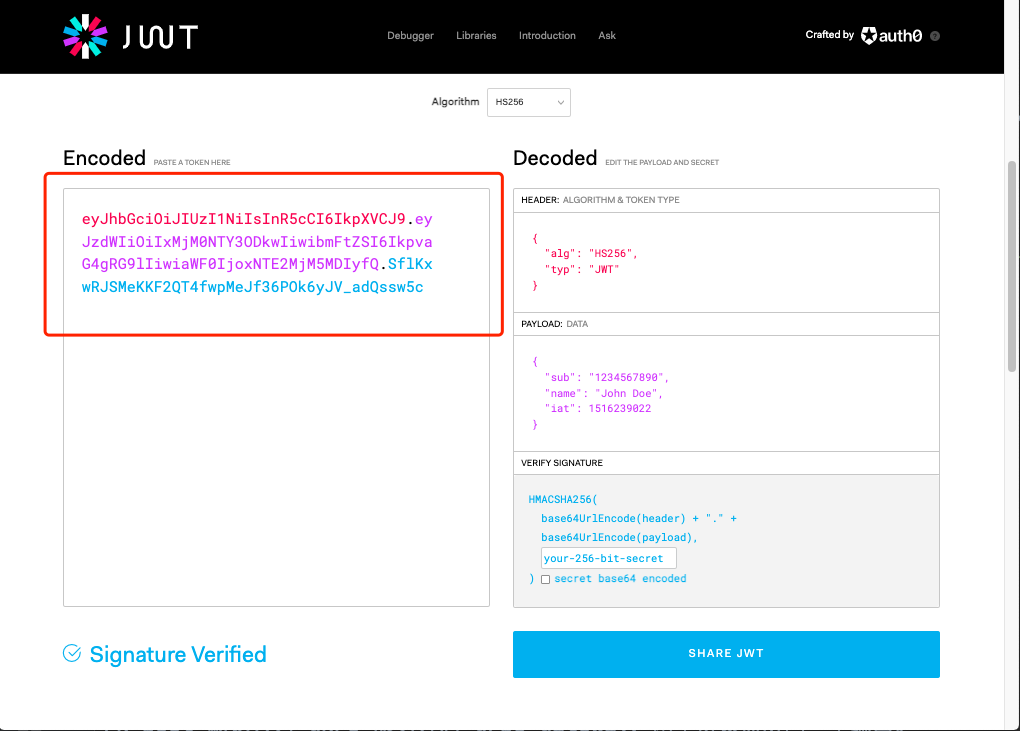
According to different languages, there are many open source libraries that can help us create JWT tokens. Please refer to Official website
Here, for convenience, we go directly from Official website Create a Token in. This Token uses my secret as the key and HS256 as the algorithm, which is the same as the configuration in boot.yaml.
4. Verification
- Send the request to / rk / V1 / health and provide the legal JWT Token created above.
$ curl localhost:8080/rk/v1/healthy -H "Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJzdWIiOiIxMjM0NTY3ODkwIiwibmFtZSI6IkpvaG4gRG9lIiwiaWF0IjoxNTE2MjM5MDIyfQ.EpM5XBzTJZ4J8AfoJEcJrjth8pfH28LWdjLo90sYb9g"
{"healthy":true}- Send a request to / rk / V1 / health to provide illegal JWT
$ curl localhost:8080/rk/v1/healthy -H "Authorization: Bearer invalid-jwt-token"
{
"error":{
"code":401,
"status":"Unauthorized",
"message":"invalid or expired jwt",
"details":[
{
"code":16,
"status":"Unauthenticated",
"message":"[from-grpc] invalid or expired jwt"
},
{
"code":2,
"status":"Unknown",
"message":"token contains an invalid number of segments"
}
]
}
}JWT interceptor options
Rk boot provides several JWT interceptor options. Unless there are special needs, the override option is not recommended.
option | describe | type | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|
grpc.interceptors.jwt.enabled | Start JWT interceptor | boolean | false |
grpc.interceptors.jwt.signingKey | If necessary, sign key | string | "" |
grpc.interceptors.jwt.ignorePrefix | JWT for a specific gRPC method is not validated | string | "" |
grpc.interceptors.jwt.signingKeys | Multiple sing keys are provided. Please refer to the following introduction | []string | [] |
grpc.interceptors.jwt.signingAlgo | For the signature algorithm, rk boot uses golang JWT / JWT as the dependency by default. Please refer to the following introduction for the supported algorithm types | string | HS265 |
grpc.interceptors.jwt.tokenLookup | Please refer to the following introduction for the interceptor's method of finding CSRF Token | string | "header:Authorization" |
grpc.interceptors.jwt.authScheme | Auth Scheme, that is, the Scheme followed by the Authorization header | string | Bearer |
Supported signature algorithms
HS256,HS384,HS512,RS256,RS384,RS512,ES256,ES384,ES512,EdDSA
tokenLookup format
gRPC only supports reading from the Header. If it is a request sent by gRPC protocol, the Header is grpc.metadata.
// Optional. Default value "header:Authorization". // Possible values: // - "header:<name>" // Multiply sources example: // - "header: Authorization"
Multiple signing keys
Please refer to RFC7515
Multiple signing keys are provided to separate Key and Value.
signingKeys: - "key:value"
gRPC protocol JWT example
In the previous example, we used the Restful API as a request example. This time, we use gRPC.
Or start the same gRPC service. This time we use grpcurl To call the gRPC service directly.
In order to use grpcurl, we need to start grpc reflection through enableReflection in boot.yaml.
- boot.yaml
---
grpc:
- name: greeter # Required
port: 8080 # Required
enabled: true # Required
enableRkGwOption: true # Optional
enableReflection: true # Optional
commonService:
enabled: true # Optional, default: false
interceptors:
jwt:
enabled: true # Optional, default: false
signingKey: "my-secret" # Required- Send a request to rk.api.v1.rkcommonservice.health and provide a legal JWT Token.
$ grpcurl -plaintext -H "Authorization:Bearer eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJzdWIiOiIxMjM0NTY3ODkwIiwibmFtZSI6IkpvaG4gRG9lIiwiaWF0IjoxNTE2MjM5MDIyfQ.EpM5XBzTJZ4J8AfoJEcJrjth8pfH28LWdjLo90sYb9g" localhost:8080 rk.api.v1.RkCommonService.Healthy
{
"healthy": true
}- Send a request to / rk / V1 / health to provide illegal JWT
$ grpcurl -plaintext -H "Authorization:Bearer invalid-jwt-token" localhost:8080 rk.api.v1.RkCommonService.Healthy Error invoking method "rk.api.v1.RkCommonService.Healthy": rpc error: code = Unauthenticated desc = failed to query for service descriptor "rk.api.v1.RkCommonService": invalid or expired jwt