This blog series is summarized here: Hibernate summary
Fetching strategies
Source project file: Hibernate 4.3_13
Fetching strategies
Select different strategies to query according to different needs, and the sql generated in the background is different
1. Multi to one single end grabbing
The first way
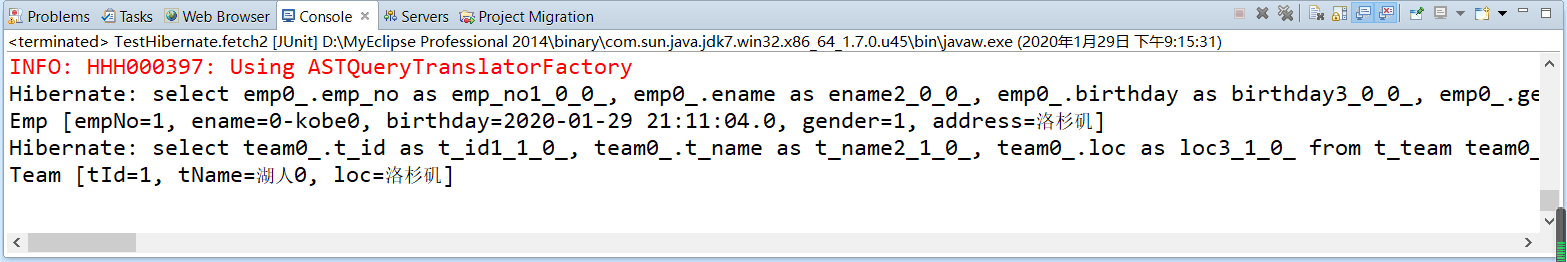
/** * Many to one single end grab fetch=join on many to one */ @Test public void fetch2() { Session session = HibernateUtils.getSession(); try { Emp emp = (Emp) session.load(Emp.class, 1); // Send a join query of two tables to query the data of emp and team System.out.println(emp); Team team = emp.getTeam(); // No hair sql System.out.println(team); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { HibernateUtils.closeResource(session); } }
The second way
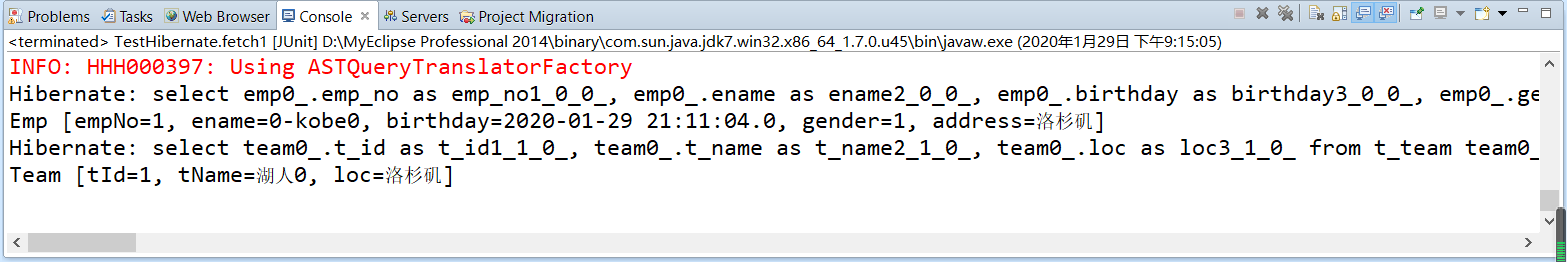
/** * fetch=select on many to one */ @Test public void fetch1() { Session session = HibernateUtils.getSession(); try { Emp emp = (Emp) session.load(Emp.class, 1); // Issue an sql to query emp according to emp ﹣ no System.out.println(emp); // No hair sql Team team = emp.getTeam(); // Issue a query to query the team's sql according to t_id System.out.println(team); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { HibernateUtils.closeResource(session); } }
2. One to many grabs
One end of one is a single object query
/** * One to many single object fetching set fetch=select (default) */ @Test public void fetch1() { Session session = HibernateUtils.getSession(); try { Team team = (Team) session.load(Team.class, 1); // Send out the sql to query the team according to t ﹣ ID System.out.println(team); Set<Emp> emps = team.getSet(); // Send out the sql to query emp employees according to team's t'id for (Emp e : emps) { System.out.println(e); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { HibernateUtils.closeResource(session); } } /** * One to many single object grabs fetch=join on set, no delay loading */ @Test public void fetch2() { Session session = HibernateUtils.getSession(); try { Team team = (Team) session.load(Team.class, 1); // Issue the sql to query the connection between the team and the employee according to a t_id System.out.println(team); Set<Emp> emps = team.getSet(); // No hair sql for (Emp e : emps) { System.out.println(e); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { HibernateUtils.closeResource(session); } } /** * One to many single object grabs the fetch=subselect on the set. If it is a single object query, it is exactly the same as select */ @Test public void fetch3() { Session session = HibernateUtils.getSession(); try { Team team = (Team) session.load(Team.class, 1); // Issue an sql to query the connection between the team and the employees according to the T ID System.out.println(team); Set<Emp> emps = team.getSet(); // No hair sql for (Emp e : emps) { System.out.println(e); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { HibernateUtils.closeResource(session); } }
One end is multiple object queries
/** * One end is multiple object queries, fetch=select */ @Test public void fetch4() { Session session = HibernateUtils.getSession(); try { String hql = "from Team"; Query query = session.createQuery(hql); // Issue sql to query all teams List<Team> teams = query.list(); for (Team team : teams) { System.out.println(team); Set<Emp> emps = team.getSet(); // Send out the sql to query the employees under the team according to the t_id for (Emp e : emps) { System.out.println(e); } } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { HibernateUtils.closeResource(session); } } /** * One end is multiple object queries, fetch=join, consistent with select */ @Test public void fetch5() { Session session = HibernateUtils.getSession(); try { String hql = "from Team"; Query query = session.createQuery(hql); // Issue sql to query all teams List<Team> teams = query.list(); for (Team team : teams) { System.out.println(team); Set<Emp> emps = team.getSet(); // Send out the sql to query the employees under the team according to the t_id for (Emp e : emps) { System.out.println(e); } } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { HibernateUtils.closeResource(session); } } /** * One end is multiple object queries, fetch=subselect */ @Test public void fetch6() { Session session = HibernateUtils.getSession(); try { String hql = "from Team"; Query query = session.createQuery(hql); // Issue sql to query all teams List<Team> teams = query.list(); for (Team team : teams) { System.out.println(team); Set<Emp> emps = team.getSet(); // The sql of a sub query queries all the players of all teams for (Emp e : emps) { System.out.println(e); } } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { HibernateUtils.closeResource(session); } }
If there is any mistake, please correct it!
Published 456 original articles, won praise 210, visited 80000+

