
crap
I really don't know what to do. I'd better touch the fish and write a blog. Next, it's pure dry goods. I don't like theoretical knowledge very much. I just start it directly.
No, look at the code at the end of this article. Download it yourself
story
Q: you have two systems a and B. at this time, system a needs the data of system B or system B needs to call the data of system A. what should you do
A: the common methods are nothing more than remote call and multiple data sources.
Multiple data sources: it roughly means a set of system. Generally speaking, we will create a database to store data, but sometimes we can see the configuration of multiple data sources in the system. Multiple data sources can access multiple databases in the same set of system. It can access the databases configured by other systems in your system, Although this has its advantages and disadvantages, I won't say them one by one. After all, today's focus is not here.
Remote invocation: this thing should be familiar to all, because it is very common under the continuous use of microservices. Roughly speaking, system A needs the data of system B. at this time, system B writes an interface to provide data to system A, and system A calls the interface of system B to obtain data. That's about it. Next, dry goods.
Prepare in advance
First of all, start a SpringBoot project and build an empty springbootweb project. You can add some tools you need according to your personal preference. Then start.
RestTemplate implementation
What is RestTemplate? Let's see what others say
RestTemplate is from spring 3 0 starts to support an HTTP request tool, which provides templates of common REST request schemes, such as GET request, POST request, PUT request, DELETE request and some general request execution methods exchange and execute. RestTemplate inherits from InterceptingHttpAccessor and implements RestOperations interface. RestOperations interface defines basic RESTful operations, which are implemented in RestTemplate.
How to use code directly:
1. First write the configuration of RestTemplate and handle it uniformly. New RestTemplateConfig
package com.example.transfercloud.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.http.client.ClientHttpRequestFactory;
import org.springframework.http.client.SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory;
import org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
/**
* @author user
*/
@Configuration
public class RestTemplateConfig {
@Bean
public RestTemplate restTemplate(ClientHttpRequestFactory factory) {
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate(factory);
// Support Chinese coding
restTemplate.getMessageConverters().set(1, new StringHttpMessageConverter(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
return restTemplate;
}
@Bean
public ClientHttpRequestFactory simpleClientHttpRequestFactory() {
SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory factory = new SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory();
//Unit: ms
factory.setReadTimeout(5000);
factory.setConnectTimeout(5000);
return factory;
}
}
2. Write a Test file to Test and write the following code
package com.example.transfercloud;
import com.example.transfercloud.entity.TestPOJO;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.http.*;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import org.springframework.util.LinkedMultiValueMap;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
class TestRestTemplate {
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@Test
void testRestTemplateOfGet() {
ResponseEntity<String> responseEntity = restTemplate.getForEntity("https://test.wslhome.top/api/getRecommendedGoods/v1?size=10", String.class);
log.info("\n code:{}\n header:{}\n body:{}\n",responseEntity.getStatusCodeValue(),responseEntity.getHeaders(),responseEntity.getBody());
// TestPOJO responseEntity0 = restTemplate.getForObject("https://test.wslhome.top/api/getRecommendedGoods/v1?size=10", TestPOJO.class);
// log.info("\n entity {}", responseEntity0);
//You need to create the corresponding entity class. Here, you can use GesonFormat reverse generation
ResponseEntity<String> responseEntity1 = restTemplate.getForEntity("https://test.wslhome.top/api/getRecommendedGoods/v1?size={1}", String.class,2);
log.info("\n code:{}\n header:{}\n body:{}\n",responseEntity1.getStatusCodeValue(),responseEntity1.getHeaders(),responseEntity1.getBody());
Map<String, String> params = new HashMap<>(4);
params.put("size","3");
ResponseEntity<String> responseEntity2 = restTemplate.getForEntity("https://test.wslhome.top/api/getRecommendedGoods/v1?size={size}", String.class,params);
log.info("\n code:{}\n header:{}\n body:{}\n",responseEntity2.getStatusCodeValue(),responseEntity2.getHeaders(),responseEntity2.getBody());
}
@Test
void testRestTemplateOfPost(){
LinkedMultiValueMap<String, Object> paramMap = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
paramMap.add("password","123");
paramMap.add("name","234");
paramMap.add("code","2131");
HttpEntity<LinkedMultiValueMap<String, Object>> param = new HttpEntity<>(paramMap, null);
ResponseEntity<String> responseEntity2 = restTemplate.postForEntity("https://test.wslhome.top/login/user/v1",param,String.class);
log.info("\n code:{}\n header:{}\n body:{}\n",responseEntity2.getStatusCodeValue(),responseEntity2.getHeaders(),responseEntity2.getBody());
}
@Test
void testRestTemplateOfDelete(){
Map<String,String> param = new HashMap<>(4);
param.put("id","34");
restTemplate.delete("https://test.wslhome.top/user/delCartByIds/v1", param);
ResponseEntity<String> result = restTemplate.exchange("https://test.wslhome.top/user/delCartByIds/v1" , HttpMethod.DELETE, null, String.class, param);
log.info("result{}",result);
//Set request header
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
//If the parameter data sent is json data, you need to add the following special request header
headers.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
//Or headers set("Content-Type", "application/json");
headers.add("Authorization", "shoppingkilleyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJ2ZXJpZnk6dXNlcjppZCI6MSwidmVyaWZ5OnVzZXI6ZmxhZyI6MTAsImV4cCI6MTYyMzc0Mjg4M30.joTLCSPy9gXlp0ABzbDlDr58hB1_wRToZaAMRVA4FqY");
HttpEntity<Map<String, String>> httpEntity = new HttpEntity<>(param, headers);
ResponseEntity<String> result1 = restTemplate.exchange("https://test.wslhome.top/user/delCartByIds/v1" , HttpMethod.DELETE, httpEntity, String.class);
log.info("result{}",result1);
}
}
The operation results are as follows:
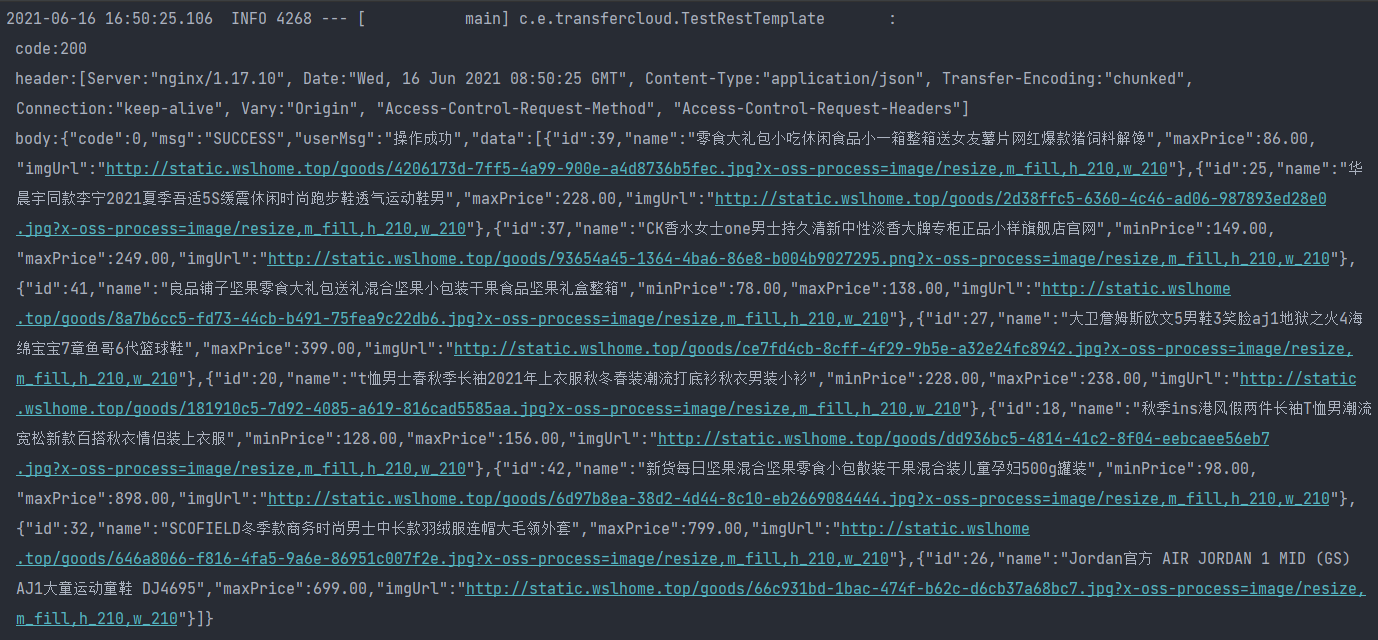
PS: the annotation part of the above code needs to create the corresponding entity class
TestPOJO responseEntity0 = restTemplate.getForObject("https://test.wslhome.top/api/getRecommendedGoods/v1?size=10", TestPOJO.class);
HttpClient implementation
What is httpClient? You can understand it as a toolkit. You can use it to simulate the browser's request with code
- The HttpClient library implements all available HTTP methods.
- The HttpClient library provides API s to protect requests using the secure socket layer protocol.
- Using HttpClient, you can establish a connection using a proxy.
Therefore, httpClient is also used for calls between interfaces
When using, first introduce dependencies
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId>
<artifactId>httpclient</artifactId>
</dependency>
Then go directly to the code
package com.example.transfercloud;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.http.HttpEntity;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.CloseableHttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpGet;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClientBuilder;
import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.Objects;
@Slf4j
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
class TestHttpClient {
/**
* GET---Nonparametric test
*
* @date 2018 At 4:18:50 pm on July 13
*/
@Test
void httpClientOfGet() {
//Create client
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().build();
// Create Get request
//HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost("https://test.wslhome.top/api/getAdvertiseForView/v1");
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet("https://test.wslhome.top/api/getAdvertiseForView/v1");
// Response model
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
try {
// Execute Get request
response = httpClient.execute(httpGet);
// Get response entity from response model
HttpEntity responseEntity = response.getEntity();
//code
final String s = EntityUtils.toString(responseEntity, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
log.info("\n text{}",s);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
// Release resources
if (Objects.nonNull(httpClient)) {
httpClient.close();
}
if (Objects.nonNull(response)) {
response.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
The implementation effect is shown in the figure:

PS: because there is little difference between get and post methods in httpClient, only get is used here for convenience. If post method is needed, just draw a gourd according to the gourd
Consumer + feign implementation
In microservices, we often use consumer + feign + hystrix to call and downgrade services. Then let's see how to use it.
1. After creating a springboot project, write a controller to provide an interface for another service
package com.example.cloudemo.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
@GetMapping("/getNum")
public String getNum() throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(10000L);
return "test get Request remote call";
}
@PostMapping("/postNum")
public String PostNum(){
return "test POST Request remote call";
}
@PostMapping("/postTest")
public String PostNums(@RequestParam Integer num){
if (num == 0){
return "Remote call test,Parameter 0";
}else if (num == 10){
return "Remote call test,Parameter 10";
}else {
return "Remote call parameters only support 0 and 10";
}
}
}
2. Introducing dependencies in both projects
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-consul-config</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-consul-discovery</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
3. Create a new bootstrap in the two projects YML file, write the following contents in the file
spring:
application:
name: feginTest
cloud:
consul:
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 8500
#Enable consumption
enabled: true
discovery:
# Enable service discovery
enabled: true
# Enable service registration
register: true
# Unregister when service stops
deregister: true
# Indicates that IP is used instead of hostname when registering
prefer-ip-address: true
# Frequency of monitoring checks
health-check-interval: 30s
# Set how long after the health check fails to cancel the registration
health-check-critical-timeout: 30s
# Turn on heartbeat detection
heartbeat:
enabled: true
# Path of health check
health-check-path: /test
# Service registration ID in the format of: application name + server IP + port
instance-id: ${spring.application.name}:${spring.cloud.client.ipaddress}:${server.port}
config:
# Enable the configuration center function of consumer. The default value is true
enabled: true
# There are four types of YAML PROPERTIES KEY-VALUE FILES, and the default is KEY-VALUE
format: YAML
#Configure the basic file. The default value is config
prefix: ${spring.application.name}
#Represents the development environment: dev/test/prepped, and the consumption server is deployed independently in the production environment
default-context: dev
#Represents the name of the configuration file above the consumer. Each developer manages its own configuration file
data-key: infokey
# The watch option is the configuration monitoring function, which mainly monitors the change of configuration
watch:
enabled: true
delay: 10000
wait-time: 30
feign:
hystrix:
enabled: true
hystrix:
shareSecurityContext: true
command:
default:
circuitBreaker:
requestVolumeThreshold: 1
sleepWindowInMilliseconds: 15000
forceOpen: false
forceClosed: false
execution:
isolation:
thread:
timeoutInMilliseconds: 5000
ribbon:
ConnectTimeout: 4000
ReadTimeout: 4000
PS1:spring.application.name is the service name. Two services should adopt different names. By the way, application The port number in YML should also be changed to a different port number.
PS: because I didn't create a new one, I went directly to application Write in YML, and then visit the registration center. It has always been localhost. No matter what address you fill in, it will not change. Then you are helpless and can't find a solution. Only the new bootstrap YML then it's normal.
4. Modify startup class
In the startup class application Add annotations to Java classes
@EnableDiscoveryClient @SpringBootApplication @EnableFeignClients
5. Start two projects in turn, and then go to your consumer to see if the service starts normally. You will see that the screenshot looks normal.
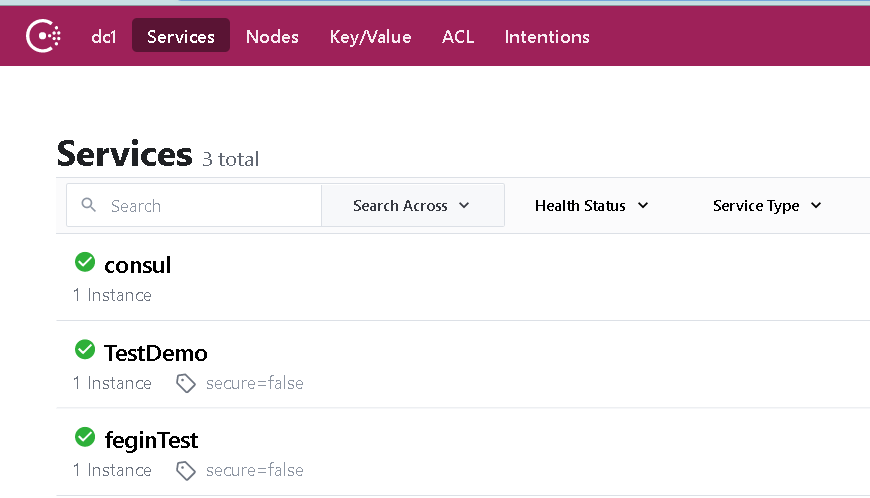
6. Start to write the interface call of the consumer
(1) Create an interface class for remote call, as follows
package com.example.transfercloud.rpc;
import com.example.transfercloud.rpc.callBack.TestCloudCallBackFactory;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
@FeignClient(value = "TestDemo",fallbackFactory = TestCloudCallBackFactory.class)
public interface TestCloud {
@GetMapping("/test/getNum")
String getTestNum();
@PostMapping("/test/postNum")
String getTestNumByPost();
@PostMapping("/test/postTest")
String getTestNumByPostParam(@RequestParam Integer num);
}
(2) Create a callBack file to implement the interface
package com.example.transfercloud.rpc.callBack;
import com.example.transfercloud.rpc.TestCloud;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class TestCloudCallBack implements TestCloud {
@Override
public String getTestNum() {
log.error("Call failed, service degraded");
return null;
}
@Override
public String getTestNumByPost() {
log.error("Call failed, service degraded");
return null;
}
@Override
public String getTestNumByPostParam(Integer num) {
log.error("Call failed, service degraded");
return null;
}
}
(3) Create FallbackFactory file processing service unavailable
package com.example.transfercloud.rpc.callBack;
import com.example.transfercloud.rpc.TestCloud;
import feign.hystrix.FallbackFactory;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class TestCloudCallBackFactory implements FallbackFactory<TestCloud> {
@Override
public TestCloud create(Throwable throwable) {
return new TestCloud() {
@Override
public String getTestNum() {
log.error("Callback failed 0");
return null;
}
@Override
public String getTestNumByPost() {
log.error("Callback failed 1");
return null;
}
@Override
public String getTestNumByPostParam(Integer num) {
log.error("Callback failed 2");
return null;
}
};
}
}
6. Write a test class to see if it succeeds
package com.example.transfercloud;
import com.example.transfercloud.rpc.TestCloud;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Slf4j
@SpringBootTest
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
public class TestColud {
@Resource
private TestCloud testCloud;
@Test
public void test(){
final String testNum = testCloud.getTestNum();
final String testNumByPost = testCloud.getTestNumByPost();
final String testNumByPostParam = testCloud.getTestNumByPostParam(10);
log.info("\n{}\n{}\n{}",testNum,testNumByPost,testNumByPostParam);
}
}
7. Results
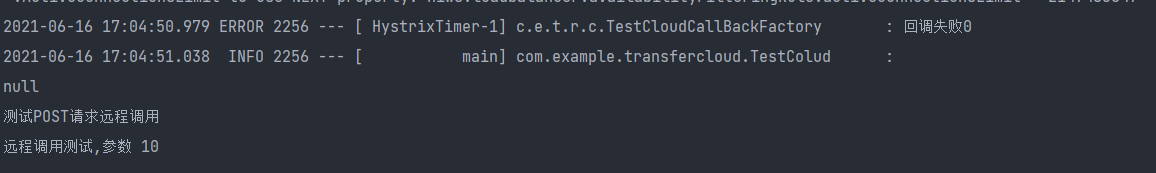
You can see that the first interface is degraded because of thread sleep(10000L); The second and third interfaces are called successfully
Code in the text
Colored eggColored eggColored eggColored eggColored eggColored eggColored eggColored eggColored eggColored eggColored eggColored egg
Article from personal blog[ hhtps://www.wslhome.top ]
Reprint please specify