How does Vue introduce BootStrap?
Installation of Node.JS
Because Vue relies on Node.JS, install Node.JS first (at least version 8.9)
Installation of VueCli Tools
- Command window input NPM install-g@vue/cli to install the latest version of VueCli tool
- Vue-V Viewable Vue Version
- NPM install-g@vue/cli-init retrievable old version
III. Creating Projects
- CD D:/VueProjects CD to the project directory to be created
- vue init webpack helloworld create helloworld project
- CD HelloWorld CD to project root directory
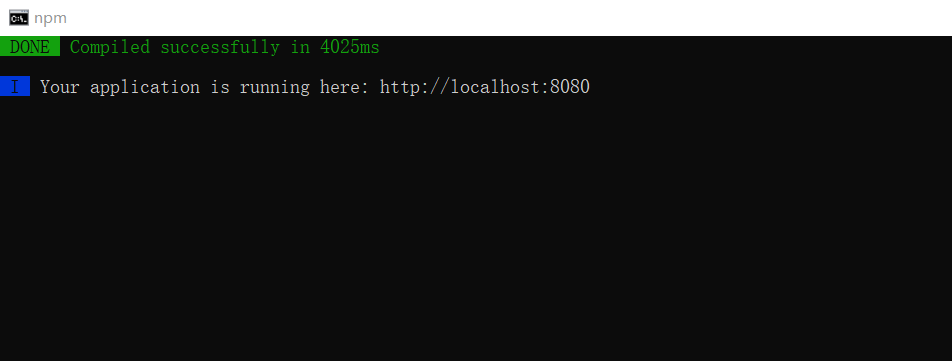
- npm install
- npm start startup project
BootStrap
1. Introducing Jquery
Because BootStrap relies on Jquery, you must first introduce Jquery to use BootStrap.
-
CD D:/VueProjects/helloworld CD to the project root directory
-
NPM install jquery-S download jquery
-
Find the webpack.base.conf.js file in the build directory
-
Add the following statement:
var webpack = require('webpack') //and // Add a plugins plugins: [ new webpack.ProvidePlugin({ $: "jquery", jQuery: "jquery" }) ], -
The following documents were added:
'use strict' const path = require('path') const utils = require('./utils') const config = require('../config') const vueLoaderConfig = require('./vue-loader.conf') var webpack = require('webpack') function resolve (dir) { return path.join(__dirname, '..', dir) } module.exports = { context: path.resolve(__dirname, '../'), entry: { app: './src/main.js' }, output: { path: config.build.assetsRoot, filename: '[name].js', publicPath: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' ? config.build.assetsPublicPath : config.dev.assetsPublicPath }, resolve: { extensions: ['.js', '.vue', '.json'], alias: { 'vue$': 'vue/dist/vue.esm.js', '@': resolve('src'), } }, module: { rules: [ { test: /\.vue$/, loader: 'vue-loader', options: vueLoaderConfig }, { test: /\.js$/, loader: 'babel-loader', include: [resolve('src'), resolve('test'), resolve('node_modules/webpack-dev-server/client')] }, { test: /\.(png|jpe?g|gif|svg)(\?.*)?$/, loader: 'url-loader', options: { limit: 10000, name: utils.assetsPath('img/[name].[hash:7].[ext]') } }, { test: /\.(mp4|webm|ogg|mp3|wav|flac|aac)(\?.*)?$/, loader: 'url-loader', options: { limit: 10000, name: utils.assetsPath('media/[name].[hash:7].[ext]') } }, { test: /\.(woff2?|eot|ttf|otf)(\?.*)?$/, loader: 'url-loader', options: { limit: 10000, name: utils.assetsPath('fonts/[name].[hash:7].[ext]') } } ] }, // Add a plugins plugins: [ new webpack.ProvidePlugin({ $: "jquery", jQuery: "jquery" }) ], node: { // prevent webpack from injecting useless setImmediate polyfill because Vue // source contains it (although only uses it if it's native). setImmediate: false, // prevent webpack from injecting mocks to Node native modules // that does not make sense for the client dgram: 'empty', fs: 'empty', net: 'empty', tls: 'empty', child_process: 'empty' } } -
Find the main.js file and add the following statement:
import $ from 'jquery' -
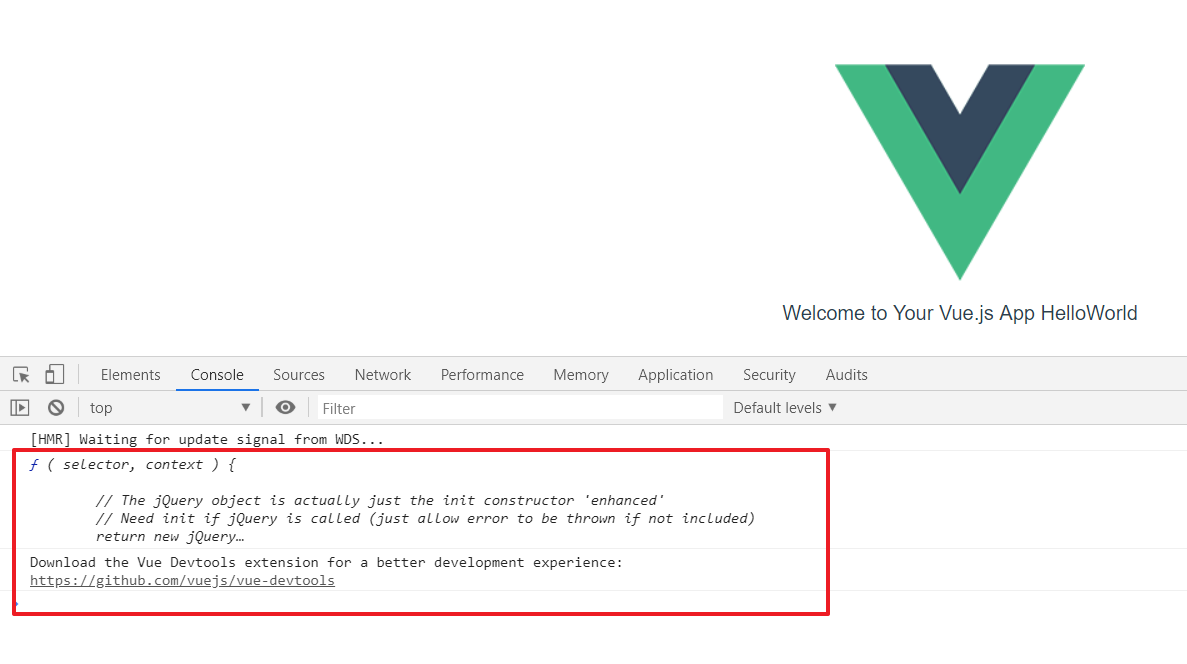
Test whether Jquery was installed successfully?
Add in HelloWorld.vue:
<script> export default { name: 'HelloWorld', data () { return { msg: 'Welcome to Your Vue.js App HelloWorld' } }, created(){ console.log($) } } </script>Startup project
Result:
2. Introducing BootStrap
-
npm install bootstrap --save-dev download bootstrap
-
Find main.js and add the following statement:
import 'bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css' import 'bootstrap/dist/js/bootstrap.min.js' -
You can happily use BootStrap in Vue.