1, Introduction to nginx
Nginx (engine x) is a high-performance HTTP and reverse proxy web server, which is characterized by less memory and strong concurrency. In fact, nginx performs better in the same type of web server.
Nginx is specially developed for performance optimization. Performance is its most important consideration. In fact, it pays great attention to efficiency and can withstand the test of high load. Some reports show that it can support up to 50000 concurrent connections.
2, Reverse proxy
1. Forward agency
Configure a proxy server on the client (browser) to access the Internet through the proxy server.
2. Reverse proxy
We only need to send the request to the reverse proxy server. The reverse proxy server selects the target server, obtains the data, and then returns it to the client. At this time, the reverse proxy server and the target server are external servers, exposing the proxy server address and hiding the real server IP address.
3, Load balancing
Increase the number of servers, and then distribute the requests to each server. Instead of concentrating the original requests on a single server, distribute them to multiple servers, and distribute the load to different servers, which is what we call load balancing.
4, Dynamic and static separation
In order to speed up the parsing speed of the website, dynamic pages and static pages can be parsed by different servers to speed up the parsing speed. Reduce the pressure of the original single server.
5, nginx common commands
1. Prerequisite for using nginx operation command: nginx directory must be
2. Check the version number of nginx
nginx -v
3. Start nginx
nginx
4. Turn off nginx
nginx -s stop
5. Reload nginx
nginx -s reload
6, Configuration file for nginx (nginx.conf)
The nginx configuration file consists of three parts
1. Global block
The content from the configuration file to the events block mainly sets some configuration instructions that affect the overall operation of the nginx server.
For example: Worker_ processes 1; worker_ The larger the processes value, the more concurrent processing can be supported.
2.events block
The instructions involved in the events block mainly affect the network connection between the nginx server and the user.
For example: worker_connection 1024; Maximum number of connections supported.
3.http block
The most frequent part of nginx server configuration, http block can also include http global block and server block.
7, nginx configuration image access path
Upload the image file to the server D:/images, and then access it through the IP address / upload / plus the image name.
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
#Access path splicing upload accesses a picture under the local absolute path
location /upload/ {
alias D:/images/;
autoindex on;
}
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}
Configure nginx Conf remember to restart the server. The effect is shown in the figure:
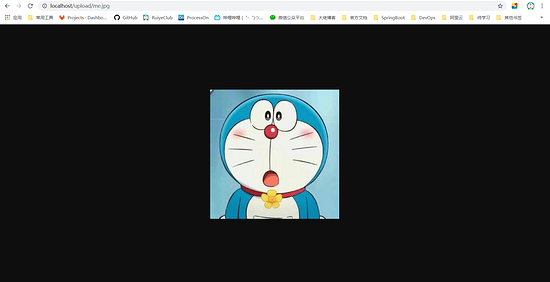
8, java background code
/**
* File upload
*/
@RestController
public class FileController {
@PostMapping(value = "/fileUpload")
public String fileUpload(@RequestParam(value = "file") MultipartFile file) {
if (file.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Please select a picture");
}
String fileName = file.getOriginalFilename(); // file name
String suffixName = fileName.substring(fileName.lastIndexOf(".")); // Suffix
String filePath = "D:/images/"; // Uploaded path
fileName = UUID.randomUUID() + suffixName; // New file name
File dest = new File(filePath + fileName);
if (!dest.getParentFile().exists()) {
dest.getParentFile().mkdirs();
}
try {
file.transferTo(dest);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//Return picture name
return fileName;
}
}
Here, upload the image to the D:/images folder. Because nginx is configured earlier, I test it locally. You can access it directly by using the image name returned by localhost/upload / +.
If you want to access through the project address plus the port number, you can configure a resource mapping path.
/**
* Resource mapping path
*/
@Configuration
public class MyWebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
registry.addResourceHandler("/upload/**").addResourceLocations("file:D:/images/");
}
}
like this!
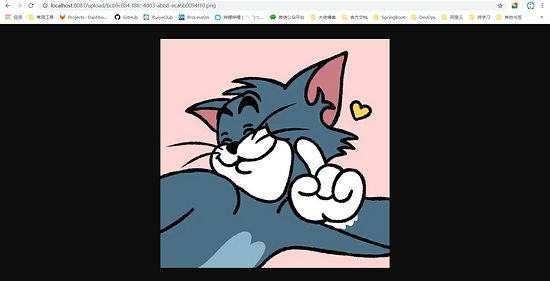
last
The space is limited. The front-end preliminary notes, learning roadmap and front-end interview questions in the article are OK Click here for free Full PDF (including answer analysis).
The content outline of the selected front-end interview questions in 2021 includes HTML, CSS, JavaScript, jQuery, browser, HTTP, React and applet
D-1627007626072)]
last
The space is limited. The front-end preliminary notes, learning roadmap and front-end interview questions in the article are OK Click here for free Full PDF (including answer analysis).
The content outline of the selected front-end interview questions in 2021 includes HTML, CSS, JavaScript, jQuery, browser, HTTP, React and applet
[external chain picture transferring... (img-NKwqH7nR-1627007626074)]