catalog
2.1 example 1 obtaining request parameters
2.2.2 modification Login.java code
2.3 example 3 request parameter return enumeration and Map object
3, Http ServletReques t (servletrequests sub interface)
3.1 example: get the URI of the client
This chapter is about the servet request. It is also an important chapter. ServletRequest can handle the request by its name.
1, Knowledge points
How to get request information in Serlvet:
1.Servlet Of service()Method to answer a request:Because every request calls service()method
public void service(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response ) throws ServletException, IOException ServletRequest:Encapsulates the request information. Any request information can be obtained from it. ServletResponse:It encapsulates the response information. If you want to give any response to the user, you can use the method of this interface to implement it.
The implementation classes of both interfaces are implemented by the server, and are passed in when the server calls the service method.
2.ServletRequest: encapsulates the request information. Any request information can be obtained from it.
1) Get request parameters:
String getParameter(string name): according to the name of the request parameter, the parameter value is returned nearly.
If the request parameter has multiple values (for example, checkbox), the method can only get the value of the first submission.
String[] getParametervalues(string name): according to the name of the request parameter, the string array corresponding to the last request parameter.
Enumeration getParameterNames(): returns the enumeration object corresponding to the parameter name,
Similar to the getInitParameterNames() method of serv1etconfig (or ServletContext).
Map getParameterMap(): returns the key value pair of the request parameter: key: parameter name, value: parameter value, String array type.
2) Get requested URL:
HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest = (HttpServ1etRequest) request; String requestURI = httpServ1etRequest.getRequestURI(); System.out.println(requestURI); // /day_ 29/1oginServ1et
3) Get request method:
String method = httpServletRequest.getMethod(); System.out.print1n(method); //GET
4) If - a GET request, GET the string corresponding to the request parameter, that is, the string after
String queryString = httpServletRequest.getQueryString(); //user=hua&password=123456&interesting=game&interesting=par System.out.print1n(querystring);
5) Get the mapping path of the requested Servlet
String servletPath = httpServletRequest.getServletPath(); System.out.print1n(servletPath); // /loginServ1et
6) Several methods related to attribute;
3. HttpServletRequest: a sub interface of ServletRequest. Defined for HTTP requests. It contains a large number of methods related to getting HTTP requests.
For more convenience, please check https://javaee.github.io/ ServletRequest interface in
2, Examples
All the following examples are the same. Under src, create a Login class and inherit the Servlet interface. The original code is as follows:
import javax.servlet.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Login implements Servlet {
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig servletConfig) throws ServletException {
}
@Override
public ServletConfig getServletConfig() {
return null;
}
@Override
public void service(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
@Override
public String getServletInfo() {
return null;
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}
web.xm Configure to add a route map as follows:
<servlet>
<servlet-name>login</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>Login</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>login</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/login</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
whole web.xlm The configuration is as follows: this configuration includes the web.xml to configure
<servlet>
<servlet-name>login</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>Login</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>login</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/login</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>t1</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>T1</servlet-class>
<!-- stay<servlet>Here is its secondary configuration-->
<init-param>
<param-name>user</param-name>
<param-value>hua</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>pwd</param-name>
<param-value>123</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
<!-- This is in<servlet>Outside, not its secondary configuration-->
<context-param>
<param-name>ctx</param-name>
<param-value>this is context-param value </param-value>
</context-param>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>t1</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/t1</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>2.1 example 1 obtaining request parameters
string getParameter(String name): returns the parameter value according to the name of the request parameter.
If the request parameter has multiple values (for example, checkbox), the method can only get the value of the first submission.
2.1.1 code
Login.java One of the codes is modified as follows:
@Override
public void service(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException {
String user = servletRequest.getParameter("user");
String pwd = servletRequest.getParameter("pwd");
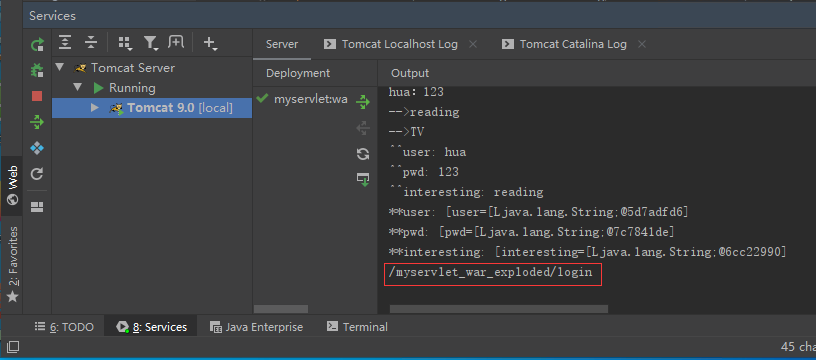
System.out.println(user+": "+pwd);
}
2.1.2 test results
According to HTML knowledge, you need to use "parameter name = value" or "parameter name 1 = value 1 & parameter name 2 = value 2.." to Get parameters
Open the end of the browser and add "/ login? User = Hua & PWD = 123", here I am
http://localhost:8080/myservlet_war_exploded/login?user=hua&pwd=123
After seeing the blank page, the ide output window is:
2.2 example 2 returns the string array corresponding to the request parameter according to the name of the request parameter
When do I return an array? Multiple choice
String[] getParameterValues(String name): returns the string array corresponding to the request parameter according to its name.
2.2.1 in index.jsp Write form
stay index.jsp Write the form with the following code:
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>test</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="login" method="post">
user: <input type="text" name="user" />
pwd: <input type="password" name="pwd" />
<br>
Hobbies:<br>
<input type="checkbox" name="interesting" value="reading" />read
<input type="checkbox" name="interesting" value="game" />game
<input type="checkbox" name="interesting" value="party" />party
<input type="checkbox" name="interesting" value="shopping" />shopping
<input type="checkbox" name="interesting" value="sport" />Sports
<input type="checkbox" name="interesting" value="TV" />television<br/>
<input type="submit" style="margin-left: 390px" value="Submit"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Run tomcat and automatically jump out of the browser. My is Firefox. The effect picture is as follows:

2.2.2 modification Login.java code
modify Login.java The code is as follows:
@Override
public void service(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException {
String user = servletRequest.getParameter("user");
String pwd = servletRequest.getParameter("pwd");
System.out.println(user+": "+pwd);
String[] interestings =servletRequest.getParameterValues("interesting");
for(String interest: interestings){
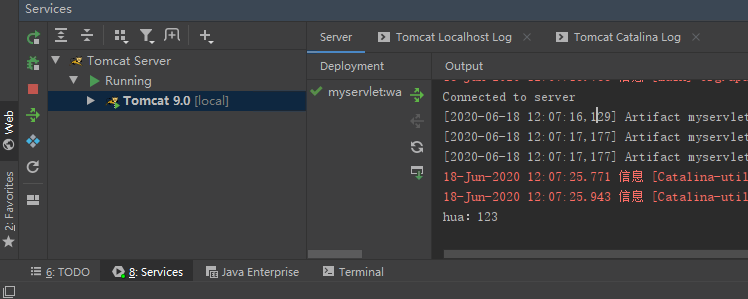
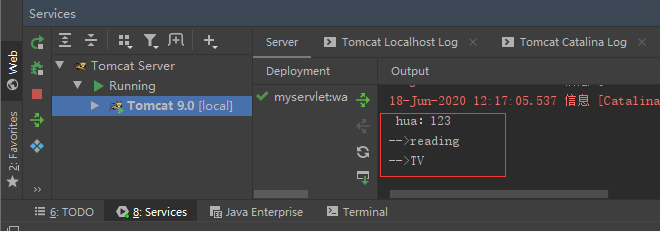
System.out.println("-->"+interest);
}
}
2.2.3 test results
Restart tomcat and enter the following in the browser:

Click "submit" and the ide will display the following results:
2.3 example 3 request parameter return enumeration and Map object
Enumeration getParameterNames(): returns the enumeration object corresponding to the parameter name,
Similar to the getInitPar ameterNames() method of ServletConfig (or ServletContext).
Map getParameterMap(): returns the key value pair of the request parameter: key: parameter name, value: parameter value, string array type
2.3.1 in Login.java Add code
stay Login.java Amend to read:
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Map;
@Override
public void service(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException {
String user = servletRequest.getParameter("user");
String pwd = servletRequest.getParameter("pwd");
System.out.println(user+": "+pwd);
String[] interestings =servletRequest.getParameterValues("interesting");
for(String interest: interestings){
System.out.println("-->"+interest);
}
Enumeration<String> names = servletRequest.getParameterNames();
while (names.hasMoreElements()){
String name = names.nextElement();
String val = servletRequest.getParameter(name);
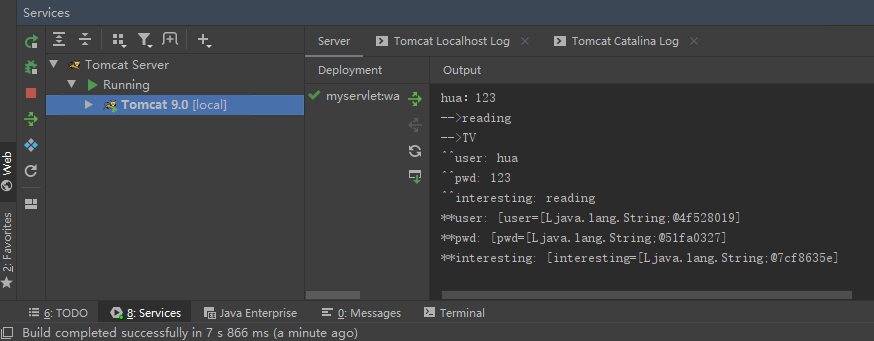
System.out.println("^^"+name+": "+val);
}
Map<String,String[]> map = servletRequest.getParameterMap();
for (Map.Entry<String,String[]> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println("**"+entry.getKey()+": "+ Arrays.asList(entry));
}
}
2.3.2 test results
Restart tomcat and enter the following in the browser:

Click "submit" and the ide will display:
3, Http ServletReques t (servletrequests sub interface)
The HttpServletRequest sub interface is more specific to the HTTP request aspect and encapsulates more HTTP methods than servlet s
HttpServletRequest object represents the client's request. When the client accesses the server through HTTP protocol, all the information in the HTTP request header is encapsulated in this object. Through the method provided by this object, all the information requested by the client can be obtained.
3.1 example: get the URI of the client
3.1.1 implementation code
stay Loin.java The service() method in the class directly adds the following
//This is the import class added at the top import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; //HttpServletRequest is a sub interface of ServletRequest, which can be forced into ServletRequest interface HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest=(HttpServletRequest) servletRequest; String requestURI = httpServletRequest.getRequestURI(); System.out.println(requestURI);
3.1.2 test results
Restart tomcat and enter the following in the browser:

Click "submit" and the ide will display: