Article directory
- Preface:
- 1, Huawei firewall dual hot standby overview
- 1.1 hot standby concept of firewall
- 1.2 hot standby features of firewall
- 1.3 Huawei firewall dual machine hot standby mode
- 1.4 state transition and working process of vgmp
- 1.5 working principle of vgmp (in main standby mode)
- 1.6 basic principles of HRP protocol
- 1.7 backup mode of HRP
- 1.8 backup channel status
- 1.9 core jumper
- 2, Hot standby experiment of firewall
Preface:
- In the traditional network, only one firewall is deployed at the exit. When the firewall breaks down, the communication between all the hosts with firewall as the default gateway and the external network is interrupted, so the communication reliability cannot be guaranteed.
- The emergence of dual computer hot backup technology has changed the awkward state that reliability is difficult to guarantee. By deploying two or more gateway devices at the exit of the network, the communication between the internal network and the external network is smooth.
- As a security device, USG firewall is usually deployed between the network to be protected and the unprotected network, that is, it is located on the business interface point. In this kind of business point, if only one USG firewall device is used, no matter how reliable it is, the system may bear the risk of network interruption due to single point of failure. In order to prevent the network business interruption caused by an unexpected failure of a device, two firewalls can be used to form a dual computer backup. Solve single point of failure, so as to realize smooth transition of business (the session table needs to be synchronized)
1, Huawei firewall dual hot standby overview
1.1 hot standby concept of firewall
- In general, multiple VRRP backup groups may have inconsistent status. Therefore, Huawei firewall introduces VGMP to realize the unified management of VRRP backup groups and ensure the consistency of multiple VRRP backup groups
-
VGMP (VRRP Group Management Protocol) group management protocol: due to the inconsistency of the back and forth paths when the device fails due to the dual machine hot standby, we add all VRRP backup groups on the firewall to a VGMP group, and the VGMP Group monitors and manages the status of all VRRP backup groups. If there is a VRRP backup group with status change, all VRRP backup groups will switch the status to ensure the consistency of the status of each VRRP backup group
- Realize the unified management of VRRP backup group
- Ensure the state consistency of devices in each backup group
- HRP (Huawei Redundancy Protocol): the protocol carries the transmission on the VGMP message, which is used to switch the standby equipment to the main equipment quickly when there is a problem in the main equipment, and at the same time ensures the synchronization of configuration commands and session table status information between the main equipment and the standby equipment.
- VGMP and HRP are private agreements of Huawei
1.2 hot standby features of firewall
- The state of the VGMP Group determines the state of the VRRP backup group
- The state of the VGMP group is determined by comparison priority
- By default, the priority of the VGMP group is 45000
- Negotiate VGMP status information through heartbeat line
- Once the status of the backup group is detected to be initialized, the priority of the VGMP group is automatically reduced by 2
1.2.1 priority of vgmp
- Middle and low end: Active device priority is 65001, Standby device priority is 6500
- High end: initial priority of VGMP group = number of cards on 45000+1000 LPU board + number of CPU s on 2SPU board
- USG6000, the initialization priority of NGFW Module is 45000
1.3 Huawei firewall dual machine hot standby mode
-
① Automatic backup
In this mode, the configuration commands related to dual hot standby can only be configured on the primary device and automatically synchronized to the standby device. The primary device automatically synchronizes the loading information to the standby device. This mode is the default open mode of Huawei firewall, mainly used for hot standby mode HRP auto sync
-
② Manual bulk backup
In this mode, all configuration commands and status information on the main equipment will be automatically synchronized to the standby equipment only when the batch backup command is executed manually. This mode is mainly used in the scenarios where the configuration of the main and standby equipment is not synchronized and needs to be synchronized immediately
-
③ Fast backup
In this mode, the configuration command is not synchronized, only the status information is synchronized. In the dual machine hot standby environment of load balancing mode, this mode must be started to quickly update the status information
1.4 state transition and working process of vgmp
- After the dual hot standby function is enabled, each VGMP group enters the Initialize state.
- When the Active group is enabled, the status of the Active group changes from Initialize to Active.
- When the Standby group is enabled, the status of the Standby group changes from Initialize to Standby.
- When the Interface monitored by the local VGMP group fails, the status switches from Active to A to S, and sends the VGMP request message to the VGMP group of the opposite device.
- The local VGMP group receives the VGMP request message from the opposite end and finds that its priority is high. Then it switches the status from Standby to active and sends the VGMP confirmation message to the VGMP group of the opposite end device.
- When the local VGMP group receives the VGMP confirmation message from the opposite end and confirms that the local end needs to switch the status, the local VGMP group status will be changed from A to S to Standby.
- If the peer VGMP group confirms that the local VGMP group does not need state switching or fails to respond to the local VGMP request message for three consecutive times, the local VGMP group state will be switched from A to S to Active.
- After the Interface monitored by the local VGMP group recovers from failure, if the local VGMP group priority is higher than that of the peer and the preemption function is configured, the status of the local VGMP group will be switched from Standby to S to A, and the VGMP request message will be sent to the peer.
- The local VGMP group receives the VGMP request message from the opposite end, and finds that the opposite end has a high priority, then switches the status from Active to Standby, and sends the VGMP confirmation message to the VGMP group of the opposite device.
- The local VGMP group receives the VGMP confirmation message from the opposite end and confirms that the local end needs to switch the state, then the local VGMP group state is switched from S to A to Active to complete the preemption process.
- If the peer VGMP group confirms that the local VGMP group does not need state switching or fails to respond to the local VGMP request message for three consecutive times, the local VGMP group state will be switched from S to A to Standby.
1.5 working principle of vgmp (in main standby mode)
- Specify devices as Active and Standby
- Set the status of all VRRP backup groups in the VGMP group to the specified Active standby (consistency of VRRP backup group status)
- Active device sends free ARP to refresh MAC address table of switch (guide traffic)
- Send HRP heartbeat message periodically (one second for death and three seconds for death), monitor Active and Standby
1.6 basic principles of HRP protocol
-
HRP protocol realizes backup session table and other state information and key configuration
-
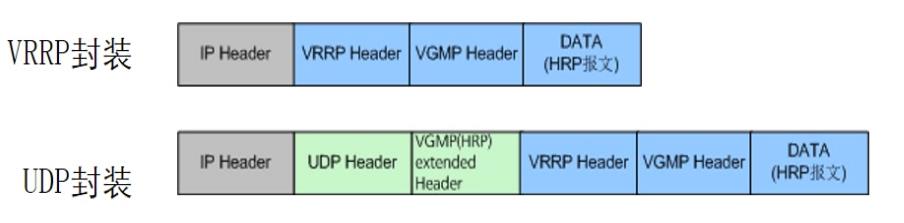
HRP message is actually a kind of VGMP message, which is carried in the Data area of VGMP message, that is, there are two encapsulation methods
-
The HRP message on the management interface will carry the following data types: specify automatic backup or batch backup, specify sending or response backup. The two methods are as follows
-
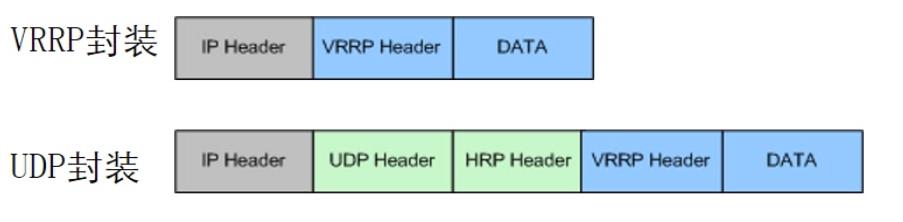
Two ways of forwarding
-
Encapsulate VRRP, multicast 224.0.0.18, do not need to consider security policy monitoring
-
Encapsulate UDP, unicast, need to consider security policy
-
When configuring the heartbeat line, you need to consider remote
1.7 backup mode of HRP
- Automatic backup, default
- Manual backup, batch mode (hrp sync config triggers batch backup manually)
- Fast backup for split load sharing
1.8 backup channel status
-
When heartbeat ports are configured on both sides of the device, the firewall will judge the physical and protocol status of the heartbeat interface. There are five states in the heartbeat link
① running: normal operation, able to send messages
② ready: normal operation, this interface is a backup channel, not currently used
③ peerdown: this section is normal, but the heartbeat message of the opposite end cannot be received
④ invaild: the IP address of the unspecified heartbeat address. The heartbeat port works on the second floor
⑤ DOWN: the physical state and protocol state of the heartbeat interface are DOWN
When there are multiple heart jumpers, which interface is configured first, i.e. which interface's state becomes ready first. When the heartbeat lines at both ends communicate, the interface that becomes ready first becomes running When the local running interface is down, the second ready interface will replace the down interface to become the running interface of the local device. The inheritance order is based on the time when it becomes ready, and there is no priority comparison. Just look at the time stamp. When there are more than one heartbeat at both ends, if the running port at both ends is not a link, it can also communicate normally
1.9 core jumper
-
In the dual machine hot standby network, the heartbeat line is the channel for two FW interactive messages to understand the peer status, backup configuration commands and various table items. The interface at both ends of the heartbeat line is usually called "heartbeat interface"
-
The heartbeat line mainly delivers the following messages:
Heartbeat message (hello message): two FW S send heartbeat messages to each other on a regular basis (default period is 1 second) to detect whether the opposite device is alive
VGMP message: understand the VGMP group status of the peer equipment, determine whether the current status of the local and peer equipment is stable, and whether a failover is required
Configuration and table item backup message: used for synchronous configuration command and status information of two FW S
Heartbeat link detection message: it is used to detect whether the heartbeat port of the opposite equipment can normally receive the messages of the local equipment, and determine whether there is a heartbeat interface that can be used
Configuration consistency check message: used to check whether the key configurations of two FW S are consistent, such as security policy, NAT, etc
2, Hot standby experiment of firewall
2.1 experimental topology
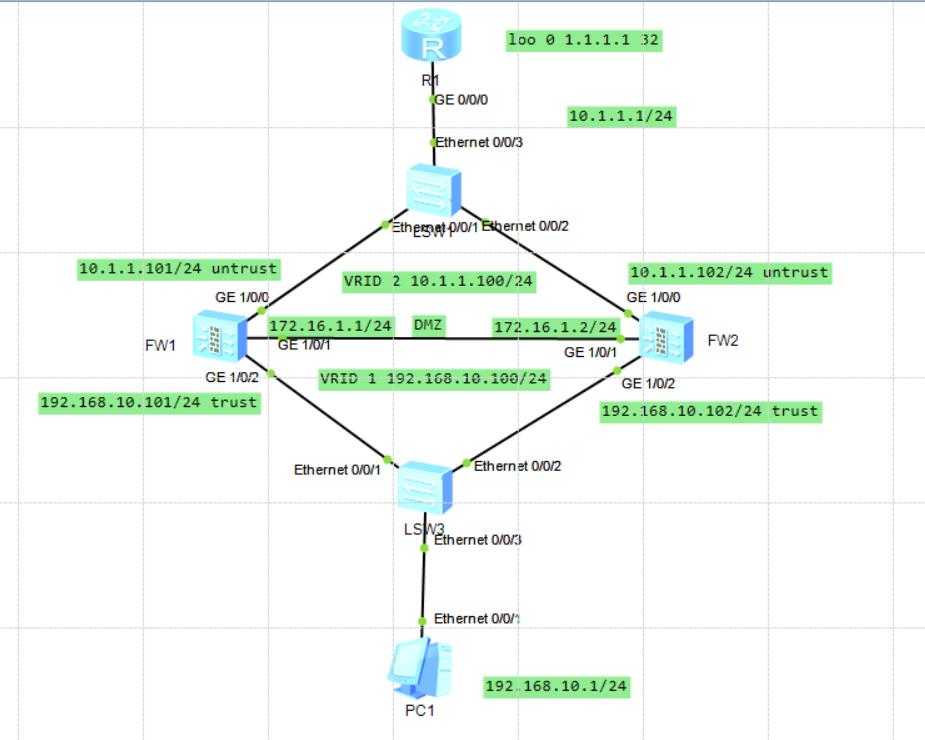
2.2 router R1 configuration
<Huawei>sys [Huawei]sysname R1 #Configure IP address of physical interface and loopback interface [R1]int g0/0/0 [R1-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 10.1.1.1 24 [R1-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]undo shut [R1-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]q [R1]int loo 0 [R1-LoopBack0]ip add 1.1.1.1 32 [R1-LoopBack0]q #Configuration point [R1]ip route-static 192.168.10.0 24 10.1.1.100
2.3 firewall FW1 configuration
<USG6000V1>sys [USG6000V1]sysname FW1 #Configure interface address [FW1]int g1/0/0 [FW1-GigabitEthernet1/0/0]ip add 10.1.1.101 24 [FW1-GigabitEthernet1/0/0]undo shut [FW1-GigabitEthernet1/0/0]q [FW1]int g1/0/2 [FW1-GigabitEthernet1/0/2]ip add 192.168.10.101 24 [FW1-GigabitEthernet1/0/2]undo shut [FW1-GigabitEthernet1/0/2]q [FW1]int g1/0/1 [FW1-GigabitEthernet1/0/1]ip add 172.16.1.1 24 [FW1-GigabitEthernet1/0/1]undo shut #Configure untrust area [FW1]firewall zone untrust #Add g1/0/0 interface to untrust area [FW1-zone-untrust]add in g1/0/0 #Configure dmz zone [FW1-zone-untrust]firewall zone dmz #Add g1/0/1 interface to dmz area [FW1-zone-dmz]add int g1/0/1 #Configure the trust area [FW1-zone-dmz]firewall zone trust #Add g1/0/2 interface to trust area [FW1-zone-trust]add in g1/0/2 [FW1-zone-trust]q #Configure a static route to the router [FW1]ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.1 #Configure security policy [FW1]security-policy #Definition rules (permit_heat)Heartbeat safety rules [FW1-policy-security]rule name permit_heat #Source region - Local [FW1-policy-security-rule-permit_heat]source-zone local #Destination area - DMZ [FW1-policy-security-rule-permit_heat]destination-zone dmz #let through [FW1-policy-security-rule-permit_heat]action permit [FW1-policy-security-rule-permit_heat]q #Define a rule (rule name: permit ﹣ trust ﹣ untrust [FW1-policy-security]rule name permit_trust_untrust #Source region -- trust [FW1-policy-security-rule-permit_trust_untrust]source-zone trust #Destination area - untrust [FW1-policy-security-rule-permit_trust_untrust]destination-zone untrust #let through [FW1-policy-security-rule-permit_trust_untrust]action permit [FW1-policy-security-rule-permit_trust_untrust]q #Define the VRRP primary group and virtual IP address of the lower interface [FW1-policy-security]int g1/0/2 [FW1-GigabitEthernet1/0/2]vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 192.168.10.100 active [FW1-GigabitEthernet1/0/2]undo shut [FW1-GigabitEthernet1/0/2]q #Define the VRRP primary group and virtual IP address of the upper interface [FW1]int g1/0/0 [FW1-GigabitEthernet1/0/0]vrrp vrid 2 virtual-ip 10.1.1.100 active [FW1-GigabitEthernet1/0/0]un shut [FW1-GigabitEthernet1/0/0]q #Configure heartbeat interface (address of remote remote connection is not 172.16.1.2) [FW1]hrp interface g1/0/1 remote 172.16.1.2 #Start dual hot standby [FW1]hrp enable #Define the hot standby mode of dual computers as automatic backup HRP_S[FW1]hrp auto-sync #View dual hot standby status information HRP_S[FW1]display hrp state 2020-02-26 04:05:06.200 Role: standby, peer: unknown Running priority: 45000, peer: unknown Backup channel usage: 0.00% Stable time: 0 days, 0 hours, 0 minutes Last state change information: 2020-02-26 4:04:29 HRP core state changed, old_s tate = initial, new_state = abnormal(standby), local_priority = 45000, peer_prio rity = unknown. #View heartbeat interface status information HRP_S[FW1]dis hrp int 2020-02-26 04:05:19.470 GigabitEthernet1/0/1 : negotiation failed
2.4 firewall FW2 configuration
<USG6000V1>sys [USG6000V1]sysname FW2 #Configure physical interface address [FW2]int g1/0/0 [FW2-GigabitEthernet1/0/0]ip add 10.1.1.102 24 [FW2-GigabitEthernet1/0/0]undo shut [FW2-GigabitEthernet1/0/0]q [FW2]int g1/0/1 [FW2-GigabitEthernet1/0/1]ip add 172.16.1.2 24 [FW2-GigabitEthernet1/0/1]undo shut [FW2-GigabitEthernet1/0/1]q [FW2]int g1/0/2 [FW2-GigabitEthernet1/0/2]ip add 192.168.10.102 24 [FW2-GigabitEthernet1/0/2]undo shut [FW2-GigabitEthernet1/0/2]q #Define firewall untrust area [FW2]firewall zone untrust #Add interface to untrust area [FW2-zone-untrust]add int g1/0/0 [FW2-zone-untrust]q #Define firewall dmz zone [FW2]firewall zone dmz #Add interface to dmz area [FW2-zone-dmz]add int g1/0/1 [FW2-zone-dmz]q #Define the trust area [FW2]firewall zone trust #Add the interface to the trust area [FW2-zone-trust]add in g1/0/2 [FW2-zone-trust]q #Configure static route to router [FW2]ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.1 #Define security policy [FW2]security-policy #Define the rule name) [FW2-policy-security]rule name permit_heat #Source region - Local [FW2-policy-security-rule-permit_heat]source-zone local #Target area -- dmz [FW2-policy-security-rule-permit_heat]destination-zone dmz #Permitted passage [FW2-policy-security-rule-permit_heat]action permit [FW2-policy-security-rule-permit_heat]q #Define the rule name (permit ﹣ trust ﹣ untrust) [FW2-policy-security]rule name permit_trust_untrust #Source region -- trust [FW2-policy-security-rule-permit_trust_untrust]source-zone trust #Target area - untrust [FW2-policy-security-rule-permit_trust_untrust]destination-zone untrust #Permitted passage [FW2-policy-security-rule-permit_trust_untrust]action permit [FW2-policy-security-rule-permit_trust_untrust]q #Define the VRRP primary group and virtual IP address of the upper interface [FW2-policy-security]int g1/0/2 #Define the VRRP primary group and virtual IP address (standby) [FW2-GigabitEthernet1/0/2]vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 192.168.10.100 standby [FW2-GigabitEthernet1/0/2]undo shut [FW2-GigabitEthernet1/0/2]q #Define the VRRP primary group and virtual IP address of the upper interface [FW2]int g1/0/0 [FW2-GigabitEthernet1/0/0]vrrp vrid 2 virtual-ip 10.1.1.100 standby [FW2-GigabitEthernet1/0/0]undo shut [FW2-GigabitEthernet1/0/0]q #Configure heartbeat interface (address of remote remote connection is not 172.16.1.1) [FW2]hrp int g1/0/1 remote 172.16.1.1 #Start dual hot standby [FW2]hrp enable #Define the hot standby mode of dual computers as automatic backup HRP_S[FW2]hrp auto-sync #View dual hot standby status information HRP_S[FW2]dis hrp state 2020-02-26 04:56:37.580 Role: standby, peer: active Running priority: 45000, peer: 45000 Backup channel usage: 0.00% Stable time: 0 days, 0 hours, 0 minutes Last state change information: 2020-02-26 4:56:21 HRP link changes to up. #View heartbeat interface status information HRP_S[FW2]dis hrp int 2020-02-26 04:56:54.370 GigabitEthernet1/0/1 : running
2.5 validation
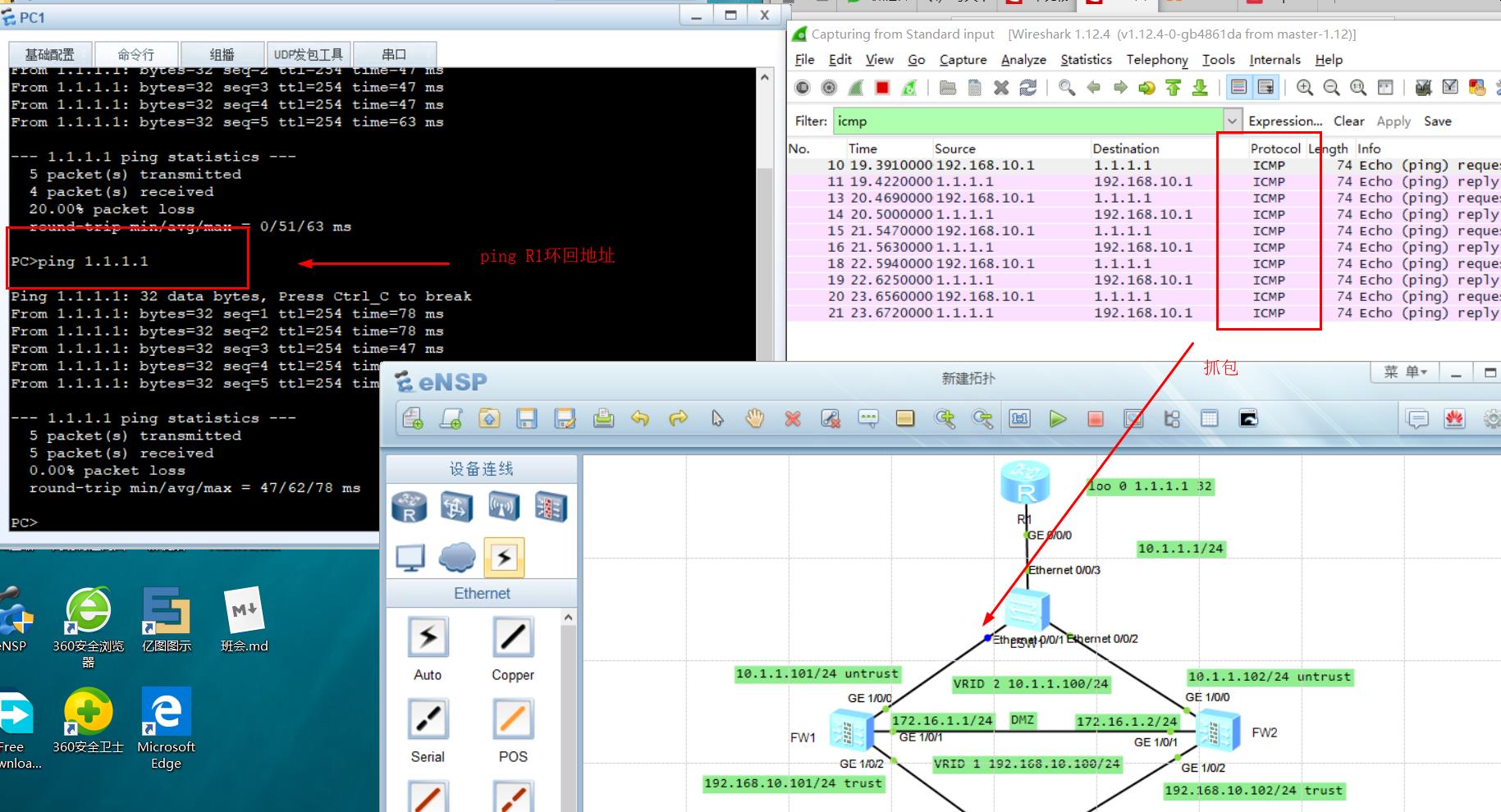
2.5.1 use PC1ping R1 loopback
-
First grab the packet at the e0/0/1 interface of LSW2
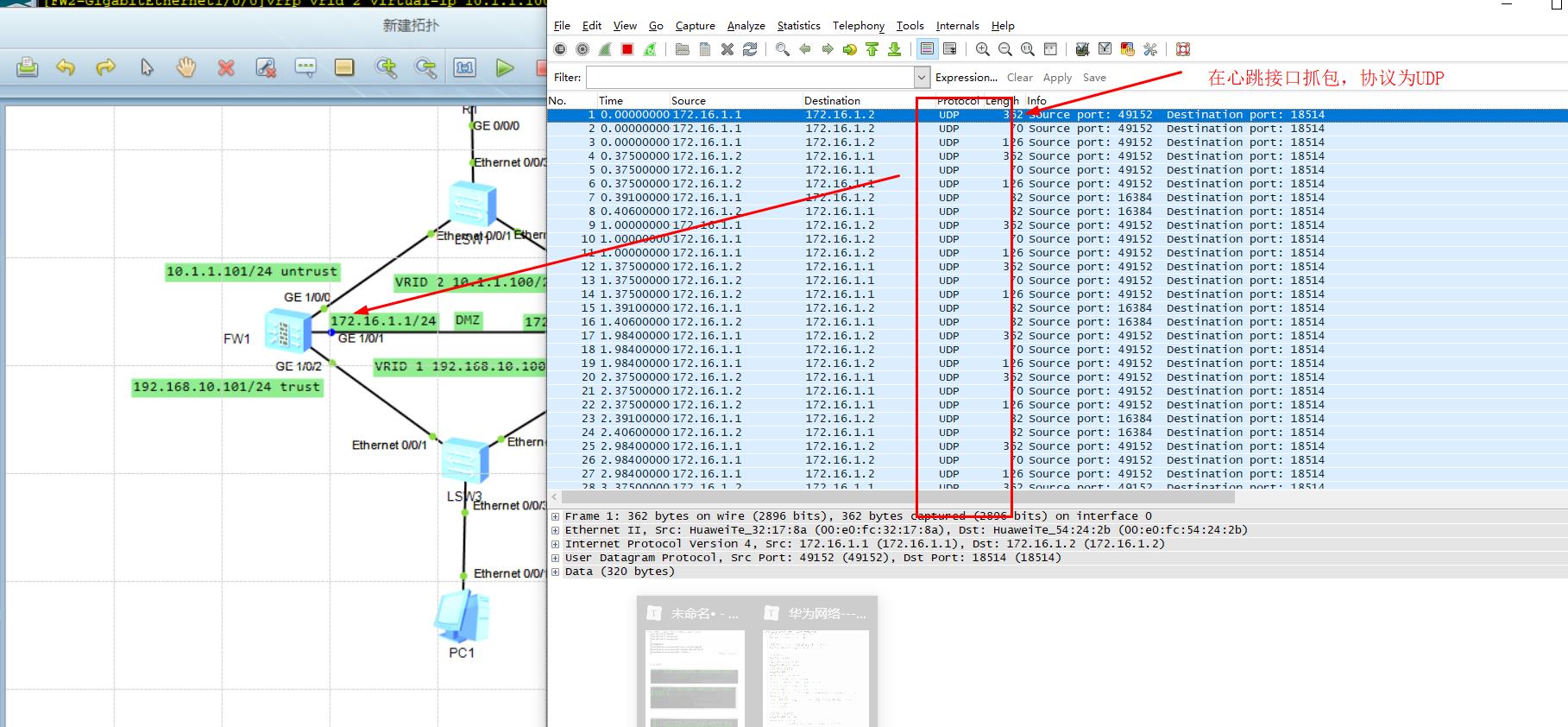
-
PC 1 PING R1e0/0/1 interface, view packet capturing information
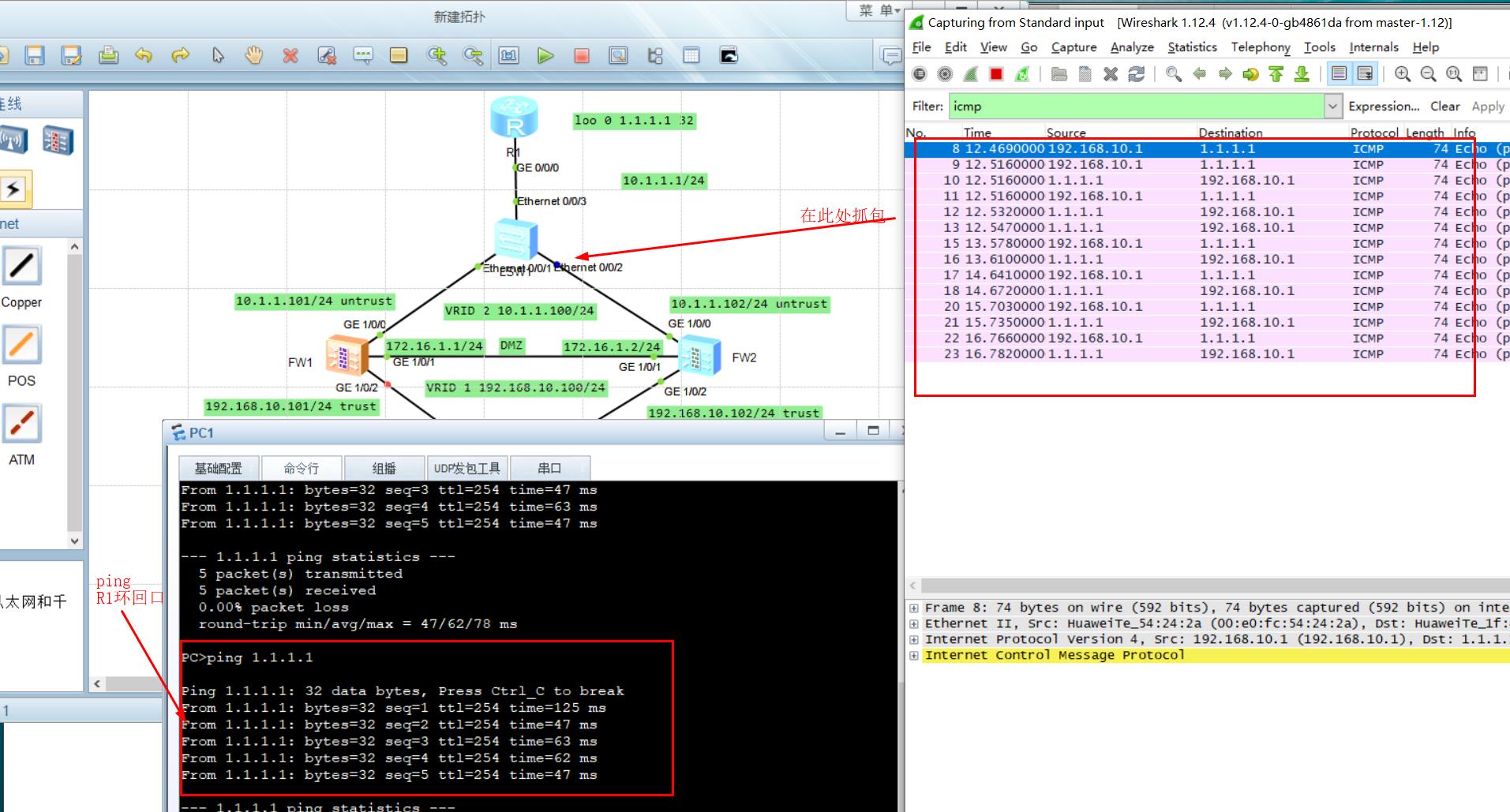
2.5.2 simulated fault
- Cut off the FW1 lower connector, and then use PC1 to Ping the R1 loopback
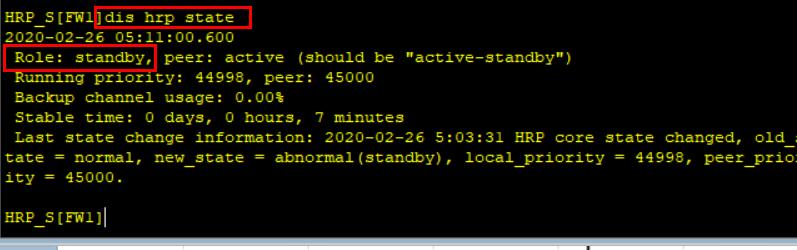
- View FW1 dual hot standby status
2.5.3 simulated fault repair
- Open and close the interface, simulate fault repair, and check the hot standby status of dual computers
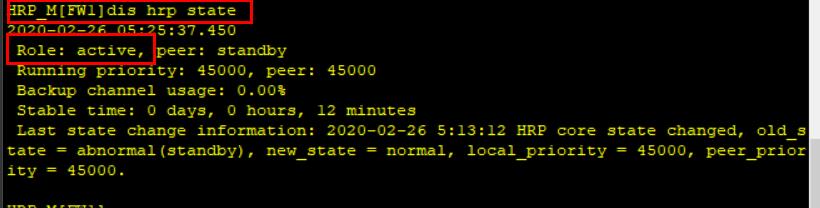
- After fault repair, FW1 changes from standby to active due to preemption mechanism

