FileInputStream and FileOutputStream classes
The FileInputStream and FileOutputStream classes are used to manipulate disk files. FileInputStream, FileOutputStream.
FileInputStream and FileOutputStream classes can read and write files.
First create the file object
public class Study2 { public static void main(String[] args) { //Create a file object File f = new File("word.txt"); } }
Create a FileOutputStream object to write information to a file
public class Study2 { public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a file object File f = new File("word.txt"); // Write information to a file FileOutputStream out = null; try { out = new FileOutputStream(f);// Create a FileOutputStream object byte b[] = "Holle Word!".getBytes();// Create byte array out.write(b);// Write information from the array to a file } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (out != null) {// Judge whether out is null. If it is not equal to null, you need to close the flow try { out.close();// Turn off flow } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
The word.txt file will appear in the project directory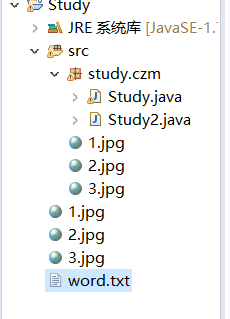
Punch in the file, and the sentence in byte array will be output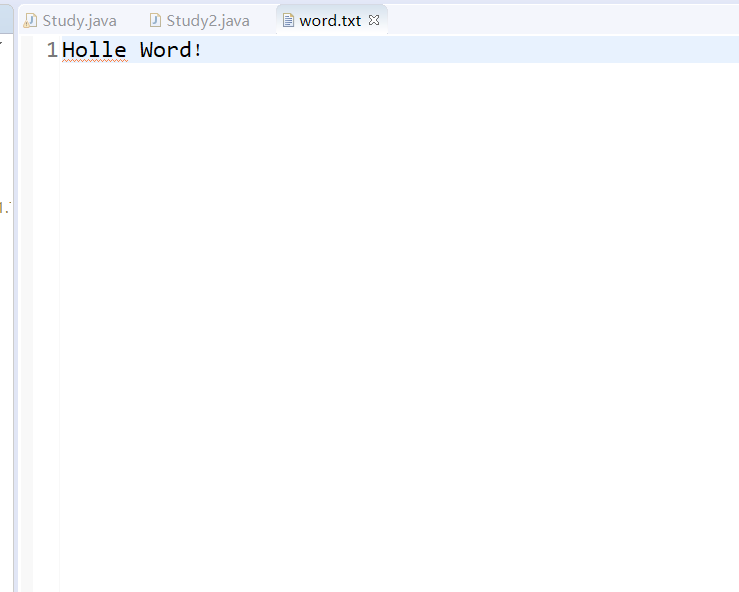
Create a FileInputStream object to read out the information in the file
// Read and output file information FileInputStream in = null; try { in = new FileInputStream(f);// Create FileInputStream object byte b1[] = new byte[1024];//Create byte array int len = in.read(b1);//Read information from file System.out.println("The information in the file is:" + new String(b1,0,len)); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (in != null) {// Determine whether in is a null value. If it is not equal to a null value, you need to close the flow try { in.close();// Turn off flow } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
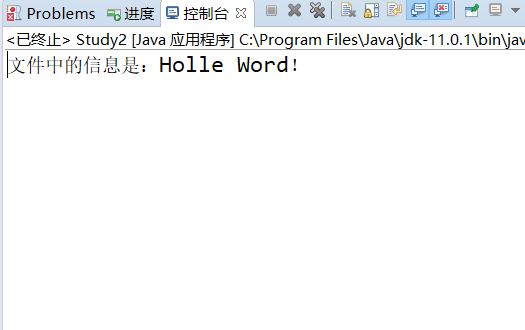
Full code:
public class Study2 { public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a file object File f = new File("word.txt"); // Write information to a file FileOutputStream out = null; try { out = new FileOutputStream(f);// Create a FileOutputStream object byte b[] = "Holle Word!".getBytes();// Create byte array out.write(b);// Write information from the array to a file } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (out != null) {// Judge whether out is null. If it is not equal to null, you need to close the flow try { out.close();// Turn off flow } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } // Read and output file information FileInputStream in = null; try { in = new FileInputStream(f);// Create FileInputStream object byte b1[] = new byte[1024];// Create byte array int len = in.read(b1);// Read information from file System.out.println("The information in the file is:" + new String(b1, 0, len)); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (in != null) {// Determine whether in is a null value. If it is not equal to a null value, you need to close the flow try { in.close();// Turn off flow } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
FileReader and FileWriter classes
Because FileInputStream and FileOutputStream only provide the method of reading byte or byte array, Chinese characters account for two bytes in bytes. If the reading is not good, there may be garbled code, so there are FileReader (file character input stream) and FileWriter (file character output stream) character streams.
They are the same in the same way.
The code is as follows:
public class Study2 { public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a file object File f = new File("word.txt"); // Write information to a file FileWriter out = null; try { out = new FileWriter(f);// Create a FileOutputStream object String str = "Holle Word!";// Create byte array out.write(str);// Write information from the array to a file } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (out != null) {// Judge whether out is null. If it is not equal to null, you need to close the flow try { out.close();// Turn off flow } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } // Read and output file information FileReader in = null; try { in = new FileReader(f);// Create FileInputStream object char c[] = new char[1024];// Create byte array int len = in.read(c);// Read information from file System.out.println("The information in the file is:" + new String(c, 0, len)); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (in != null) {// Determine whether in is a null value. If it is not equal to a null value, you need to close the flow try { in.close();// Turn off flow } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }

