BGP routing principle
When Huawei routers have multiple routes to the same destination, BGP selects routes according to the following policy sequence:
If the next hop of this route is unreachable, ignore this route
- The route with the highest PrefVal is preferred
- The route with the highest Local_Pref is preferred
- Local originating BGP routes are better than those learned from other peers. The priority of local originating routes is: manual aggregation > automatic aggregation > Network > Import > learned from peers.
- The route with the shortest AS_Path is preferred
- Compare the Origin attribute, and select the route with the Origin type of IGP, EGP and Incomplete in turn
- The route with the lowest MED value is preferred
- Routes learned from EBGP neighbors are preferred (EBGP routes have higher priority than IBGP routes)
- The route with smaller IGP Metric to the next hop is preferred
- Preferred Cluster_List shortest route
- The route published by the router with the smallest Router ID is preferred
- Compare the IP Address of the peer, preferably the route learned from the peer with a smaller IP Address
BGP equivalent routing implementation
When there are multiple equivalent routes to the same destination address, the purpose of balancing traffic can be achieved through BGP equivalent load sharing.
EBGP
The first 8 above can achieve equivalent load balancing. However, you need to start the maximum load balancing command
IBGP
The equivalent load balancing can only be achieved if all 11 items are the same. However, this kind of network does not exist in the actual network. What should I do?
IBGP uses virtual next hop to realize equivalent routing load balancing: iBGP selects the best route, and modifies the next hop of the route to a virtual address through policy. The virtual address is configured on two devices that need equivalence at the same time.
IBGP equivalent routing load experiment: virtual next hop
The interconnection link and loopback are all ISIS level 2.
BGP routing reflectors with RR of AR1, AR2, AR3 and AR4.
AR1 and AR2 announce BGP route 100.100.0/24 to RR
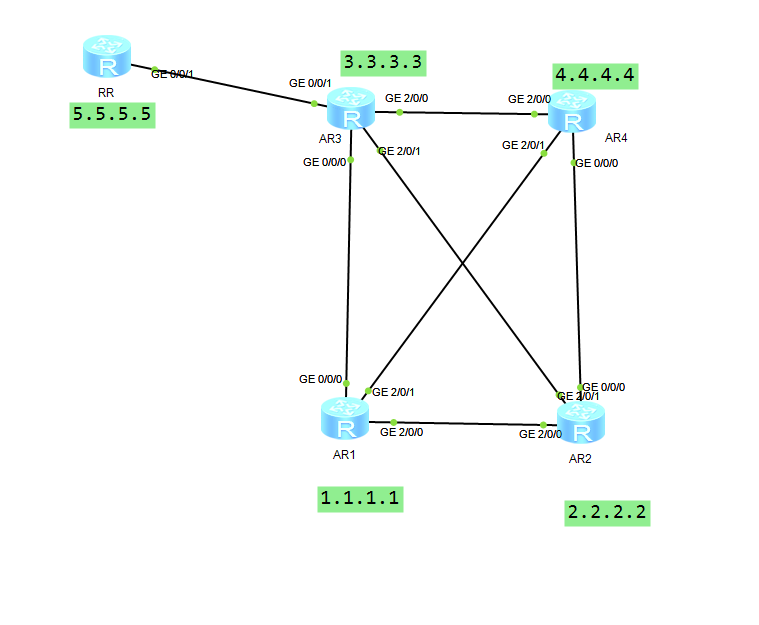
In terms of RR, only one route will be preferred: from peer 1.1.1.1 announcement, there is no preferred peer 2.2.2 announcement (the reason is not preferred for router ID, Article 10 of 11 routing rules). RR only advertises priority routes to 4 clients
[RR-bgp]dis bgp routing-table 100.100.100.0
BGP local router ID : 5.5.5.5
Local AS number : 100
Paths: 2 available, 1 best, 1 select
BGP routing table entry information of 100.100.100.0/24:
RR-client route.
From: 1.1.1.1 (1.1.1.1)
Route Duration: 00h07m35s
Relay IP Nexthop: 10.5.3.2
Relay IP Out-Interface: GigabitEthernet0/0/1
Original nexthop: 1.1.1.1
Qos information : 0x0
AS-path Nil, origin igp, MED 0, localpref 100, pref-val 0, valid, internal, bes
t, select, active, pre 255, IGP cost 20
Advertised to such 4 peers:
1.1.1.1
2.2.2.2
3.3.3.3
4.4.4.4
BGP routing table entry information of 100.100.100.0/24:
RR-client route.
From: 2.2.2.2 (2.2.2.2)
Route Duration: 00h07m19s
Relay IP Nexthop: 10.5.3.2
Relay IP Out-Interface: GigabitEthernet0/0/1
Original nexthop: 2.2.2.2
Qos information : 0x0
AS-path Nil, origin igp, MED 0, localpref 100, pref-val 0, valid, internal, pre
255, IGP cost 20, not preferred for router ID
Not advertised to any peer yet
On AR3, there is only one BGP route, because RR only reflects the optimal route preferred by RR
<AR3>dis bgp routing-table
BGP Local router ID is 3.3.3.3
Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped,
h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale
Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Total Number of Routes: 1
Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn
*>i 100.100.100.0/24 1.1.1.1 0 100 0 i
<AR3>This implementation configures virtual IP # 100.1.1.1 in AR1 and AR2 and releases it through IGP. realization
[AR1-LoopBack1]dis th
[V200R003C00]
#
interface LoopBack1
ip address 100.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
isis enable 1
#
return
[AR2-LoopBack1]dis th
[V200R003C00]
#
interface LoopBack1
ip address 100.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
isis enable 1
#
return
<AR3>dis ip routing-table 100.1.1.1
Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Routing Table : Public
Summary Count : 2
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface
100.1.1.1/32 ISIS-L2 15 10 D 10.1.3.1 GigabitEthernet0/0/0
ISIS-L2 15 10 D 10.2.3.1 GigabitEthernet2/0/1
<AR3>
//AR3 reaches 100.1.1.1 at this time. There are two routes, which are equivalent and balanced.