mini-vue
Implement a simple Vue js. To understand the principle of Vue response, mom doesn't have to worry that I won't use Vue anymore!
The technology is not yet mature and only a small part of functions are realized-- 2020/08/27
Technical implementation reference Pull hook education "big front end high salary training camp" 3-day experience course
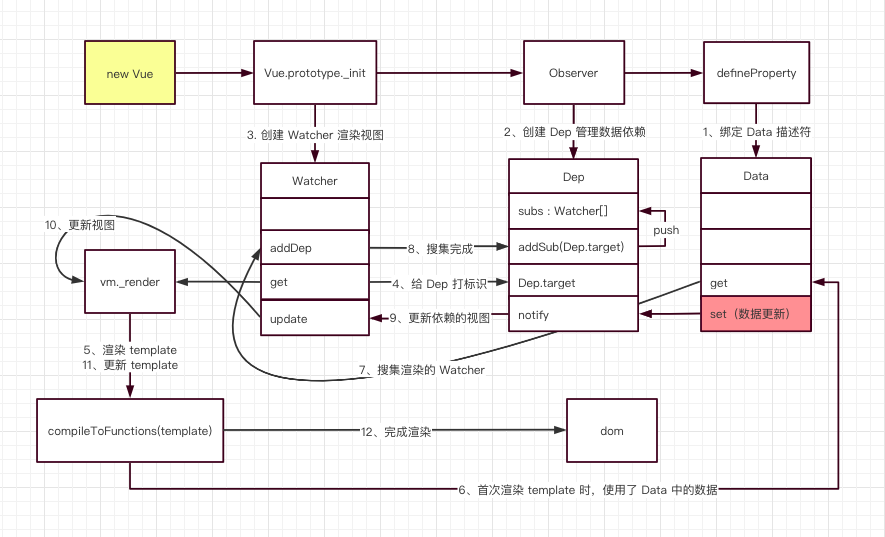
Full version of Vue responsive principle
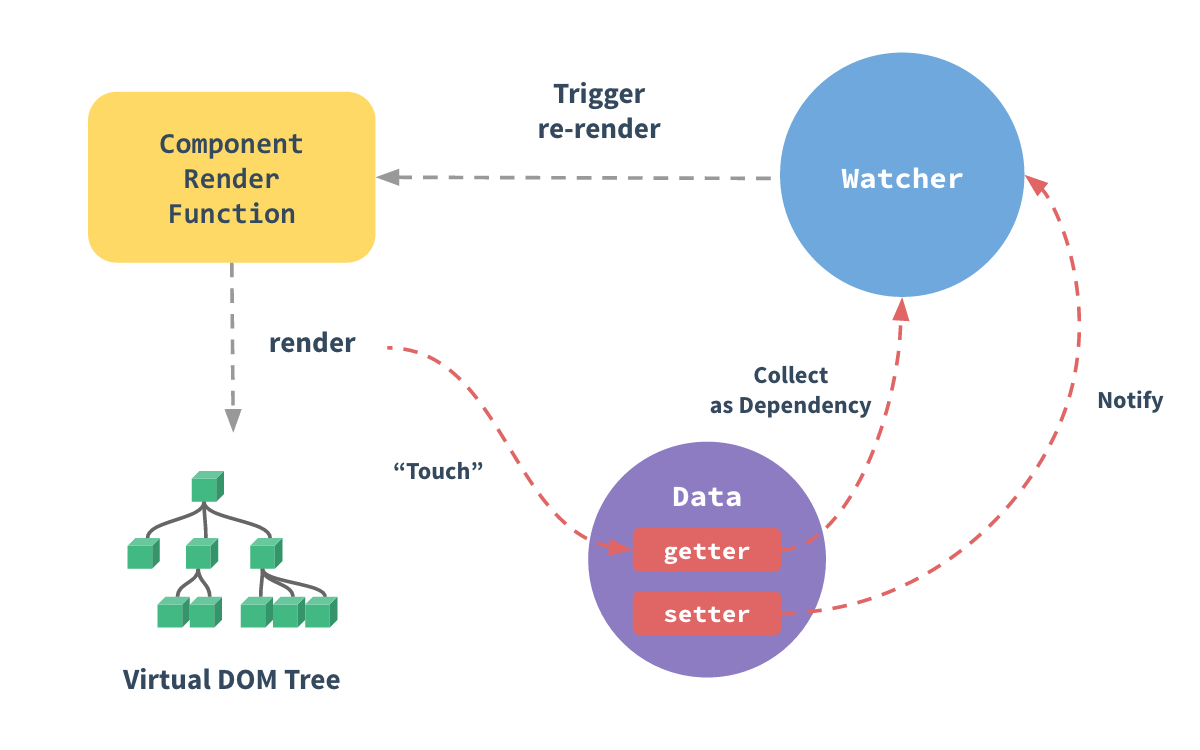
Picture quoted from Meng Sixing - schematic Vue response principle
Beggar Mini Vue
Before implementing Mini Vue, first look at the description on the official website. On Vue's official website, Deep response principle In, it is explained as follows:
Each component instance corresponds to a watcher instance, which will record the "contacted" data property as a dependency during component rendering. Then, when the setter of the dependency is triggered, it will notify the watcher to re render its associated components.
start
For technical reasons, instead of Virtual DOM and render, choose to directly operate DOM
In short, mini vue creates Vue instances
- Vue class is responsible for injecting the attributes in data into Vue instances and calling Observer class and Compiler class.
- The Observer class is responsible for data hijacking and converts each data into a getter and setter. Its core principle is through object Defineproperty implementation.
- The Compiler class is responsible for parsing instructions and interpolation expressions (Methods for updating views).
- The Dep class is responsible for collecting dependencies and adding observer patterns. Notify all observers corresponding to data Watcher to update the view. When the Observer class converts each data into a getter and setter, it will create a Dep instance to collect dependencies and send notifications. Collect dependencies in getters in each data. Notify the dependency in the setter, that is, notify all Watcher instances of the new view.
- The Watcher class is responsible for re rendering the associated view after data update.
Detailed comments have been added to the implementation code, which is non-toxic and harmless, and can be viewed at ease
Vue class
class Vue {
constructor(options) {
// 1. Save the data of options
this.$options = options || {}
this.$data = options.data || {}
this.$el = typeof options.el === 'string' ? document.querySelector(options.el) : options.el
// 2. To facilitate calling (vm.msg), convert the members in data into getter s and setter s and inject them into Vue instances
this._proxyData(this.$data)
// 3. Call the Observer class to listen for data changes
new Observer(this.$data)
// 4. Call compiler class to parse instructions and interpolation expressions
new Compiler(this)
}
_proxyData(data) {
Object.keys(data).forEach(key => {
Object.defineProperty(this, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get() {
return data[key]
},
set(newValue) {
if (newValue === data[key]) {
return
}
data[key] = newValue
}
})
})
}
}
Copy codeObserver class
class Observer {
constructor(data) {
this.walk(data)
}
// Traverse the attributes in data($data) and convert the attributes into responsive data
walk(data) {
if (!data || typeof data !== 'object') {
return
}
Object.keys(data).forEach((key) => {
this.defineReactive(data, key, data[key])
})
}
// Define responsive data
defineReactive(obj, key, value) {
const that = this
// Responsible for collecting dependencies and sending notifications
let dep = new Dep()
// Use recursion to convert deep (internal) attributes into responsive data
this.walk(value)
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get() {
// Collection dependency
Dep.target && dep.addSub(Dep.target)
return value
},
set(newValue) {
if (value === newValue) {
return
}
value = newValue
// If the newly set value is an object, it is also converted to responsive data
that.walk(newValue)
// Send notification
dep.notify()
}
})
}
}
Copy codeCompiler class
class Compiler {
constructor(vm) {
this.vm = vm
this.el = vm.$el
this.compiler(this.el)
}
// Compile templates to handle text nodes and element nodes
compiler(el) {
const childNodes = el.childNodes
Array.from(childNodes).forEach(node => {
// Processing text nodes
if (this.isTextNode(node)) {
this.compilerText(node)
} else if (this.isElementNode(node)) {
// Processing element nodes
this.compilerElement(node)
}
// Judge whether the node node has child nodes. If so, recursively call compile
if (node.childNodes.length) {
this.compiler(node)
}
})
}
// Compile element nodes, process instructions
compilerElement(node) {
// Traverse all attribute nodes
Array.from(node.attributes).forEach(attr => {
// Determine whether v-start instruction
let attrName = attr.name
if (this.isDirective(attrName)) {
// For more elegant handling of different methods, subtract v from the instruction-
attrName = attrName.substr(2)
const key = attr.value
this.update(node, key, attrName)
}
})
}
// Method of executing corresponding instruction
update(node, key, attrName) {
let updateFn = this[attrName + 'Updater']
// The corresponding method is executed only when there are instructions
updateFn && updateFn.call(this, node, this.vm[key], key)
}
// Processing v-text instructions
textUpdater(node, value, key) {
node.textContent = value
// Create a Watcher object to update the view when the data changes
new Watcher(this.vm, key, (newValue) => {
node.textContent = newValue
})
}
// Processing v-model instructions
modelUpdater(node, value, key) {
node.value = value
// Create a Watcher object to update the view when the data changes
new Watcher(this.vm, key, (newValue) => {
node.value = newValue
})
// Bidirectional binding
node.addEventListener('input', () => {
this.vm[key] = node.value
})
}
// Compile text nodes and process interpolation expressions
compilerText(node) {
const reg = /\{\{(.+?)\}\}/
let value = node.textContent
if (reg.test(value)) {
// Consider only one layer of objects, such as data MSG = 'hello world', nested objects are not considered. It is assumed that there is only one interpolation expression.
const key = RegExp.$1.trim()
node.textContent = value.replace(reg, this.vm[key])
// Create a Watcher object to update the view when the data changes
new Watcher(this.vm, key, (newValue) => {
node.textContent = newValue
})
}
}
// Determine whether an element attribute belongs to an instruction
isDirective(attrName) {
return attrName.startsWith('v-')
}
// Judge whether a node belongs to a text node
isTextNode(node) {
return node.nodeType === 3
}
// Judge whether the node book belongs to the element node
isElementNode(node) {
return node.nodeType === 1
}
}
Copy codeDep class
class Dep {
constructor() {
this.subs = []
}
// Add observer
addSub(sub) {
if (sub && sub.update) {
this.subs.push(sub)
}
}
// Send notification
notify() {
this.subs.forEach(sub => {
sub.update()
})
}
}
Copy codeWatcher class
class Watcher {
constructor(vm, key, cb) {
this.vm = vm
// Attribute name in data
this.key = key
// The callback function updates the view
this.cb = cb
// Record the watcher object into the static attribute target of the Dep class
Dep.target = this
// Trigger the get method, and addSub will be called in the get method
this.oldValue = vm[key]
Dep.target = null
}
// Update the view when the data changes
update() {
const newValue = this.vm[this.key]
// The data is returned directly without change
if (this.oldValue === newValue) {
return
}
// update the view
this.cb(newValue)
}
}
Copy codelast
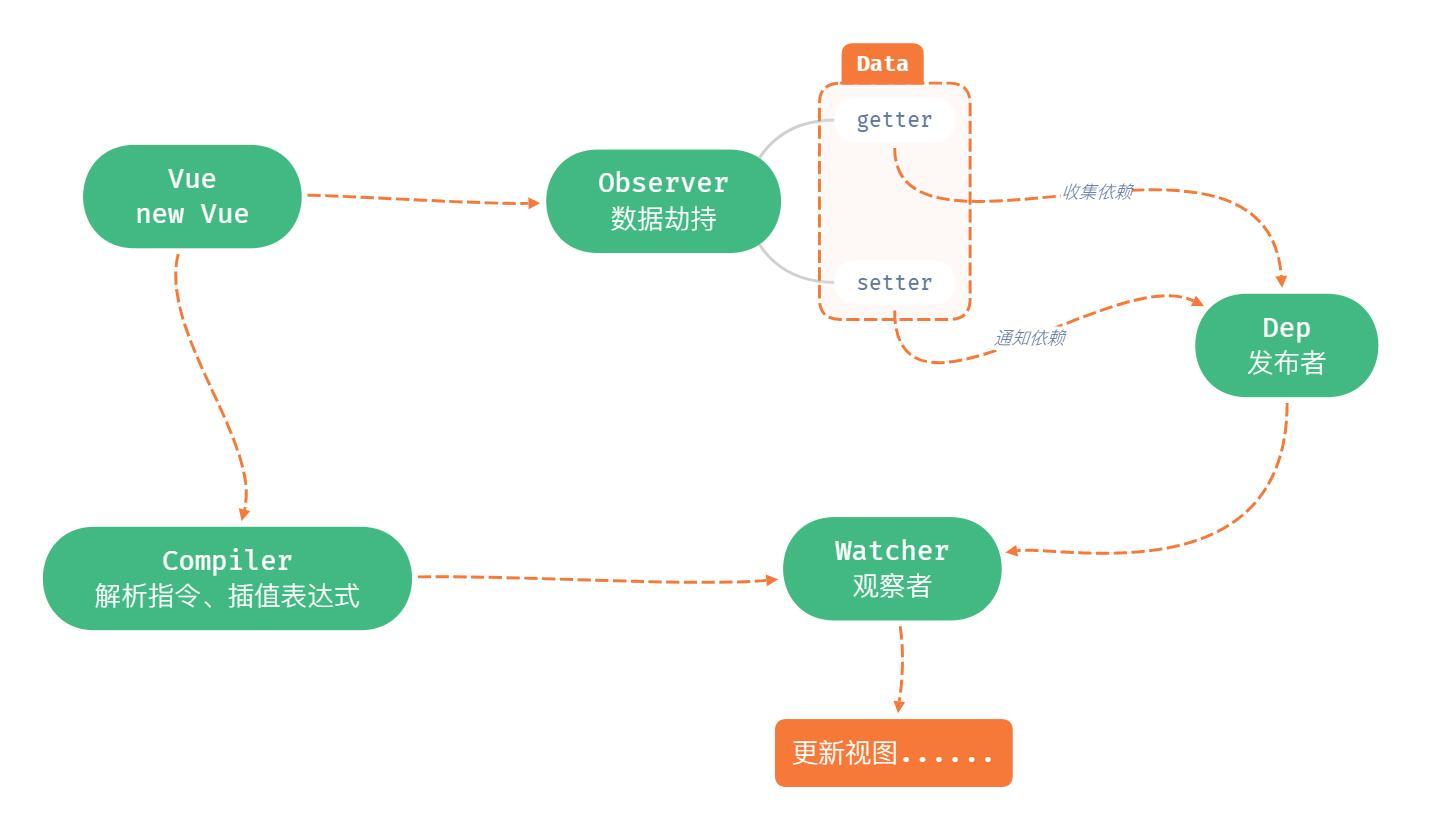
Full version of mind map

DEMO warehouse address
Listening for arrays
Here, getter s and setter s are directly added to each item of the array, so VM Items [1] = 'x' is also responsive.
Why not in Vue? reference resources Why does vue not provide listening for array properties