Just learning Python, making some gadgets to practice ( ̄▽  ̄)~*
1, Preparatory work
IDE: pycharm2019
Python: 3.7
And an Android phone (^ -)
Code git: Code address
2, Environment construction
one Install Android tools
First enter Google official website , download the corresponding SDK tools. Here I use Android SDK_ r24.4.1
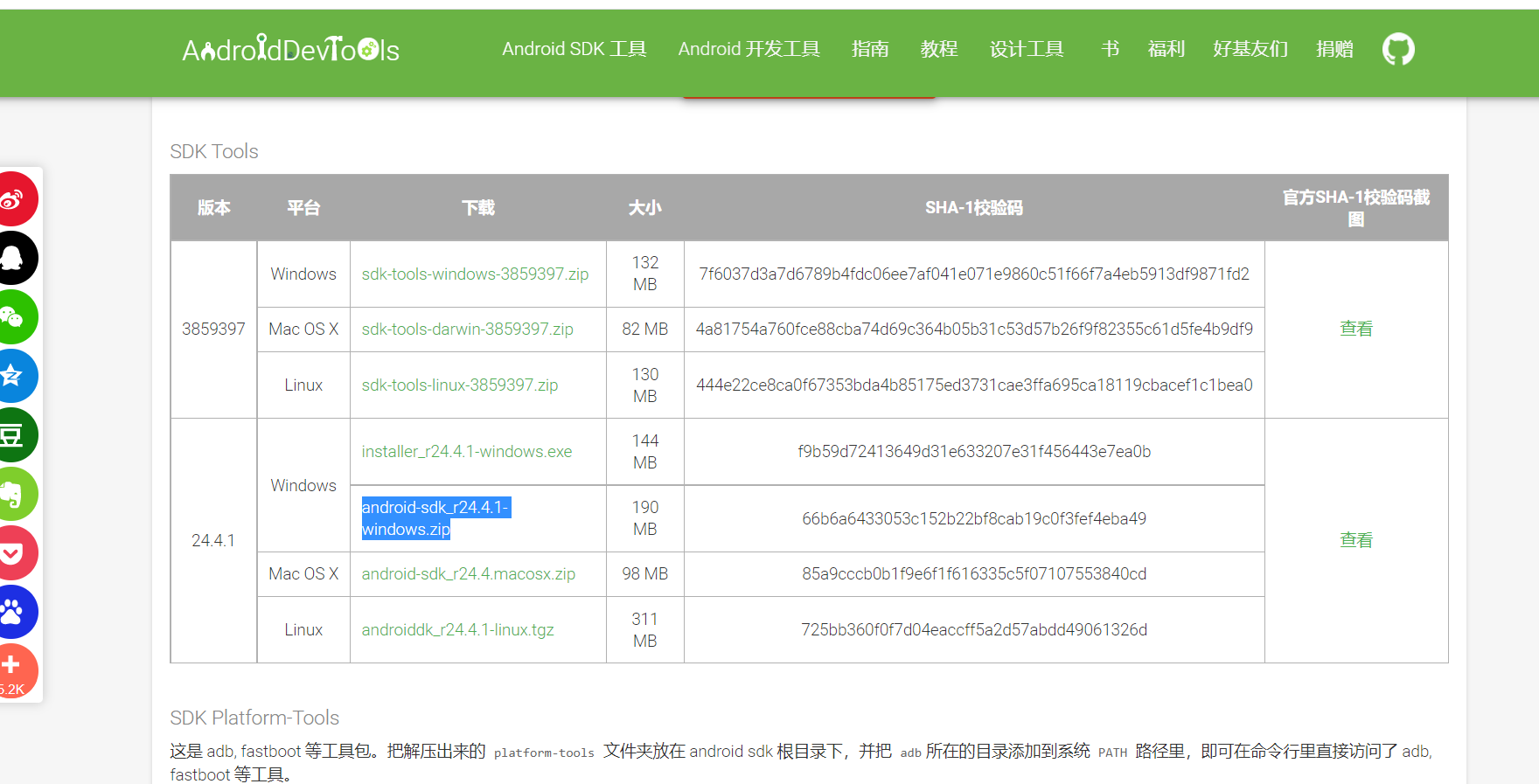
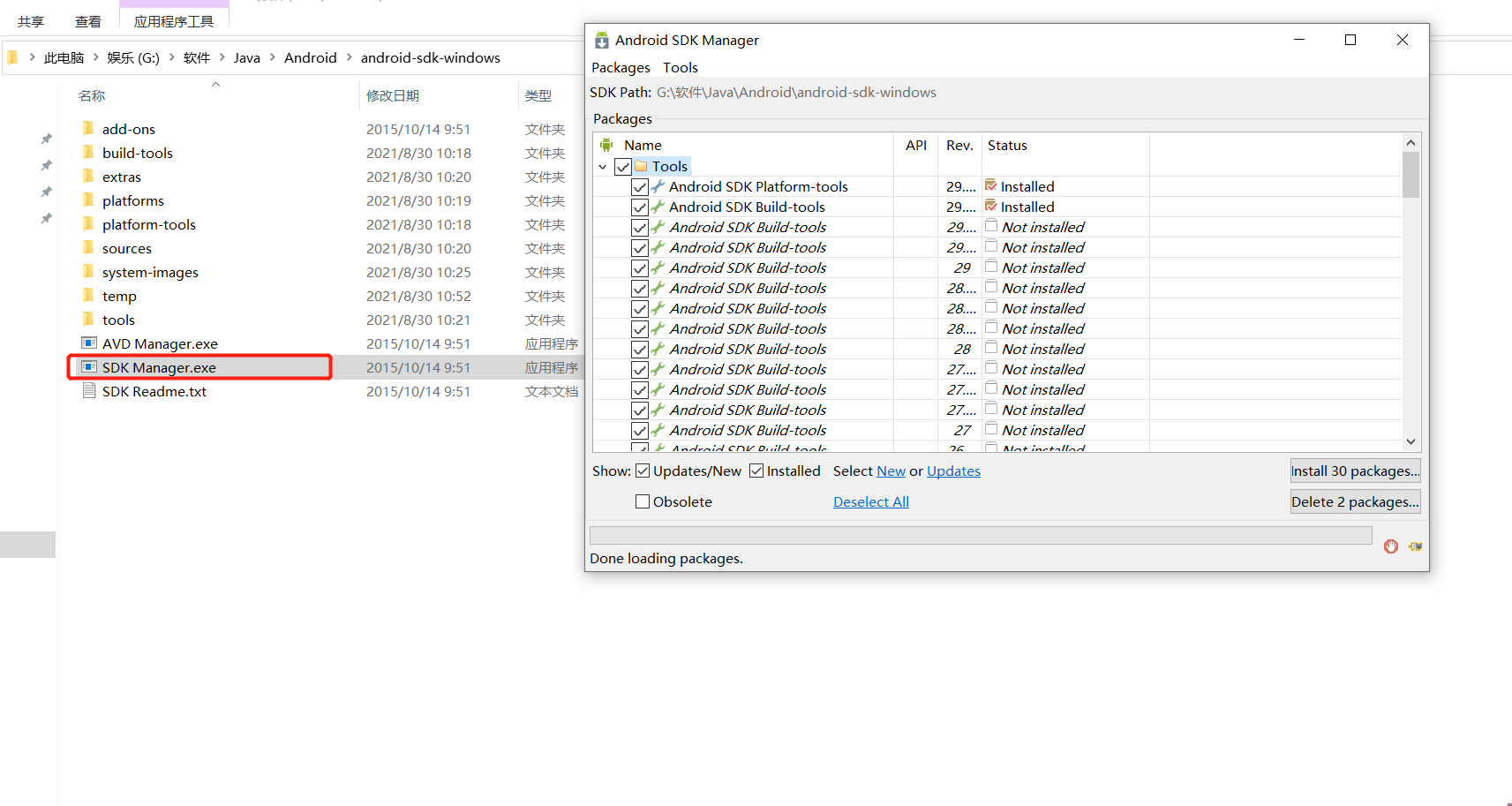
After downloading, unzip it, open the SDK Manager and install the corresponding tools (PS: Here I'll go straight to the next step)
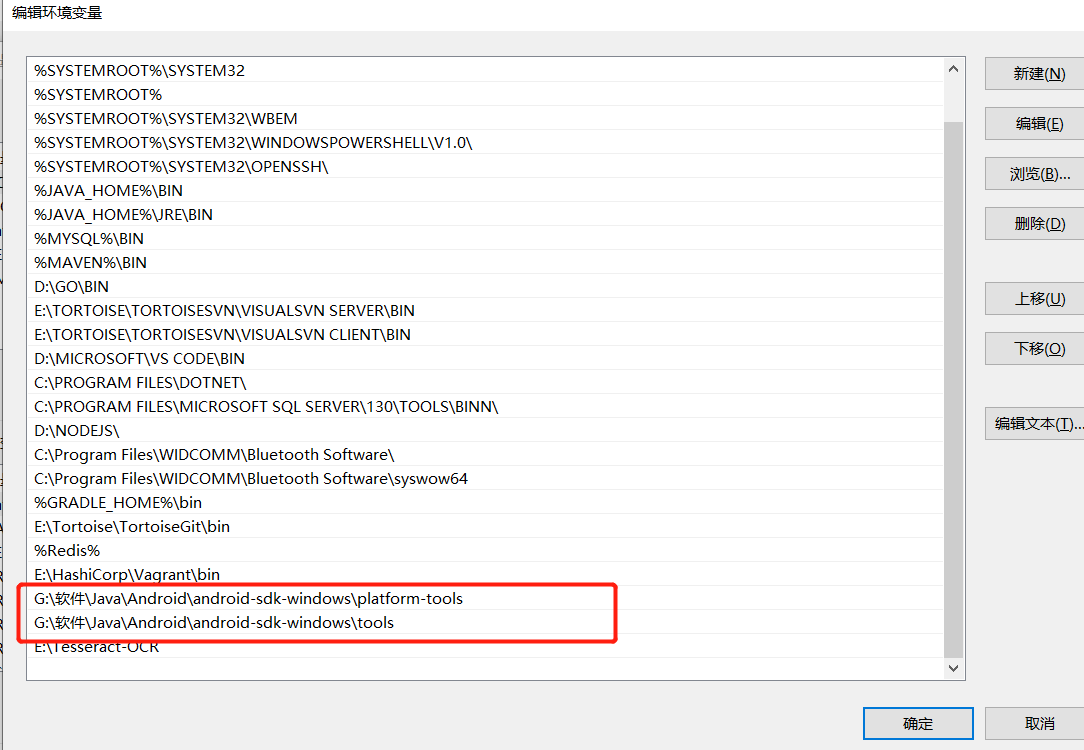
After installation, configure the environment variables and enter "adb" in the cmd interface to judge whether the installation is successful
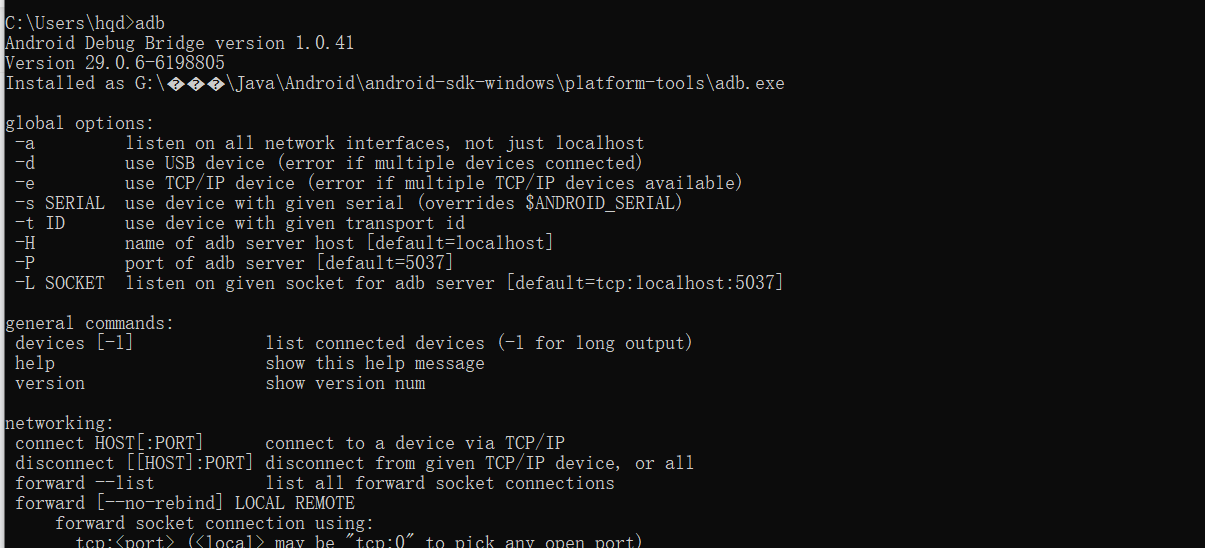
In this way, the SDK is installed
two UIAutomator2 installation
Directly execute the following command to install
pip3 install --pre -U uiautomator2
3. Configure mobile phone environment
Connect the mobile phone to the computer with USB, and turn on USB debugging at the mobile phone end. cmd input adb devices
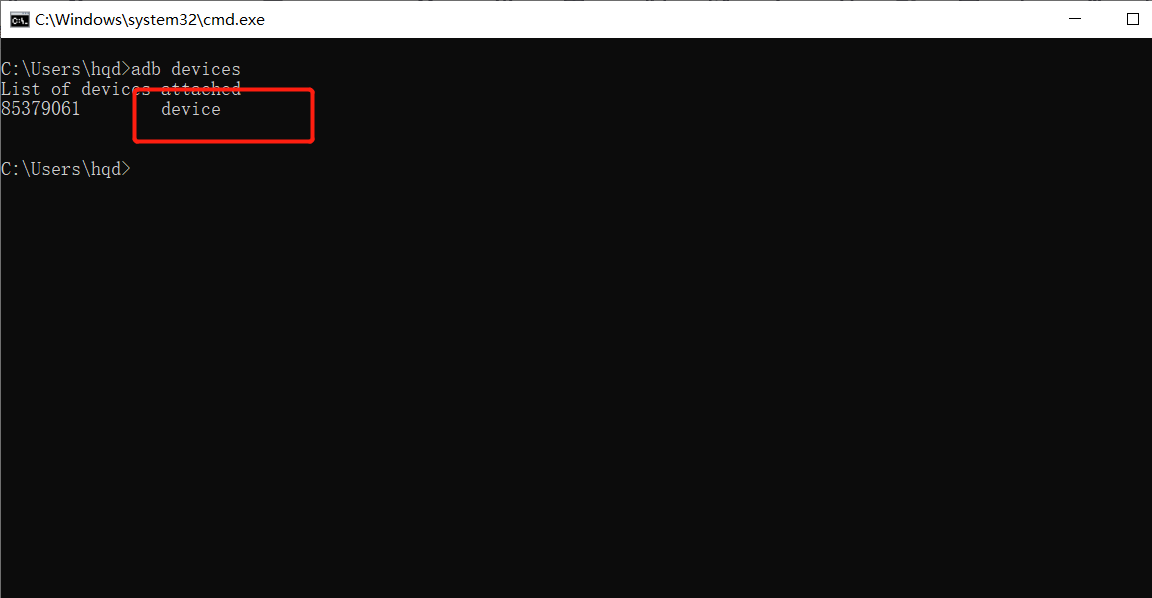
If device appears, the authorization is successful. If unauthorized occurs, it is unauthorized and requires mobile phone authorization
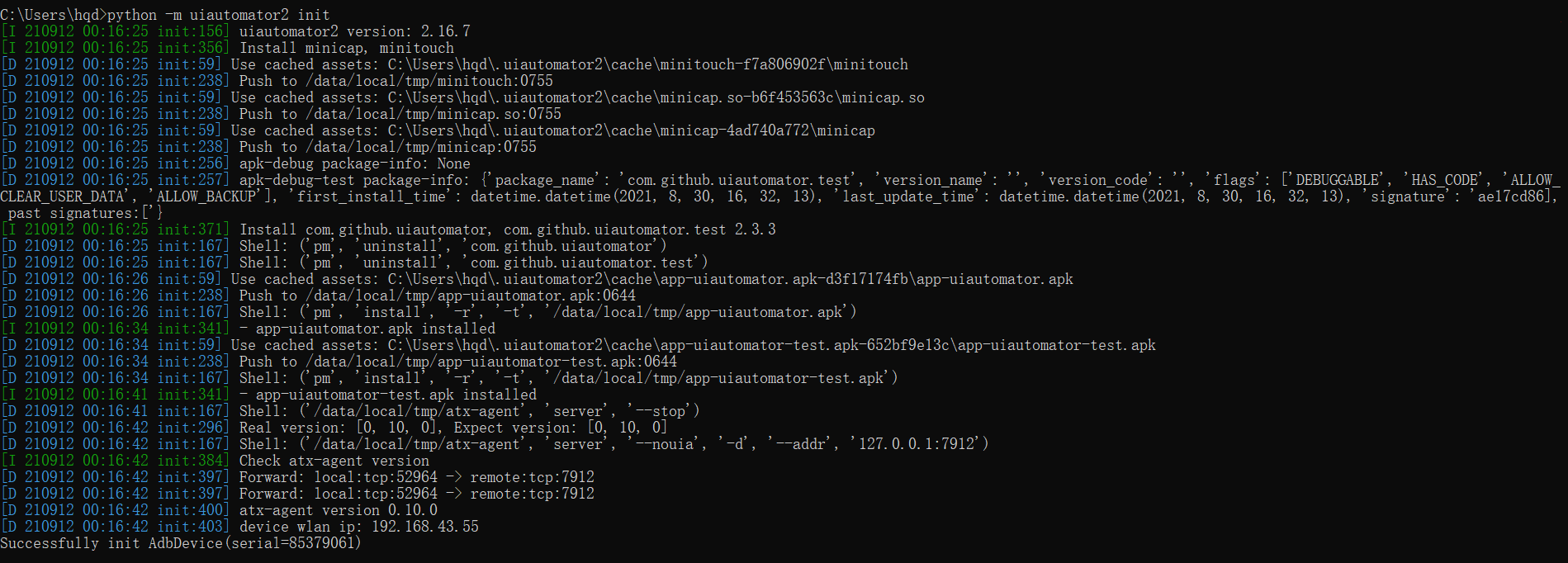
After the connection is successful, cmd enters the command to install the ATX agent to the mobile phone
python -m uiautomator2 init
The following figure shows that the installation is successful, and an ATX app will appear on the mobile terminal
Since the built-in SDK tool cannot input Chinese, it also needs a plug-in adbkeyboard.apk to support it
4. Install weditor
This plug-in allows us to locate mobile phone elements like web page elements, and execute the following commands to install them:
pip3 install --pre weditor
After the installation is successful, start with the following command:
python -m weditor
After successful startup, the effects are as follows:
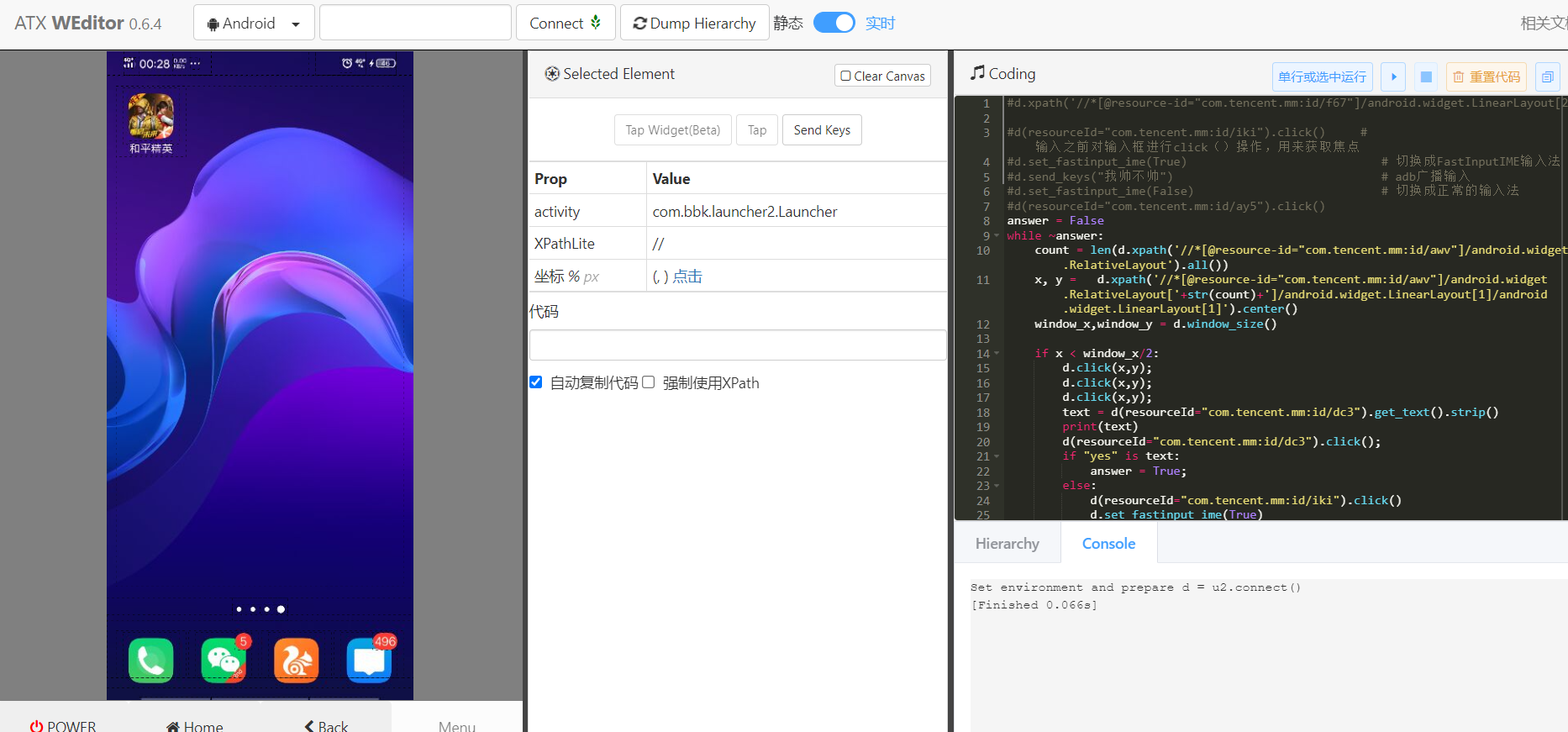
The environment is finally set up. Next, everything is ready, only due to the east wind
3, Program analysis
one Connect phone
There are two main ways to connect your mobile phone, one is through USB, and the other is through WiFi
USB connection:
This is relatively simple, just a data cable, and then turn on the USB debugging of the mobile phone
WiFi connection:
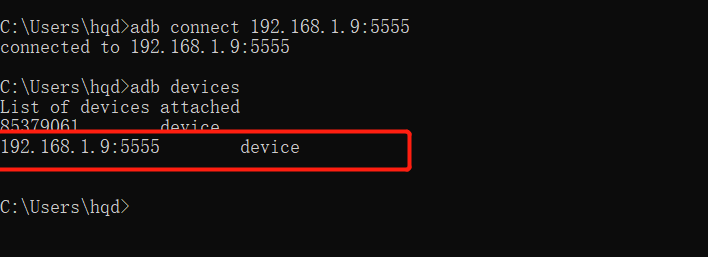
First connect the phone and computer to the same WiFi, and then execute the following command:
adb tcpip 5555
Then execute the following command to view:
adb devices
This was successful:
two Start weditor
Simply execute the following command:
python -m weditor
After successful startup:
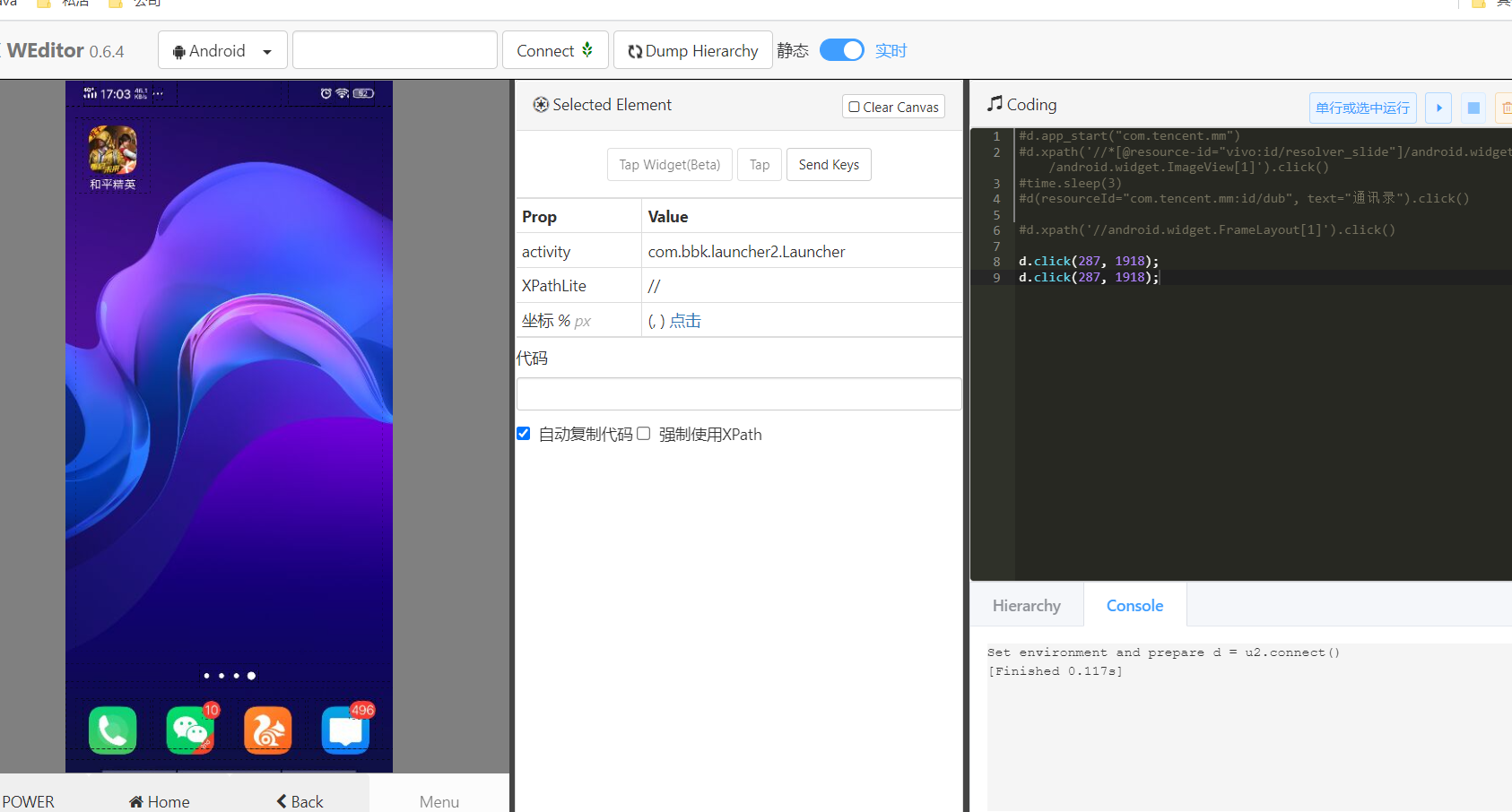
3. Organize ideas
Before you start writing code, let's sort out your ideas, mainly in the following steps:
- Open wechat
- Find contacts
- open a dialog box
- Get reply content
- Respond
Let's look at the next step. Open wechat. This is relatively simple. Just get the wechat package name and execute the following command:
adb shell pm list package -f |findstr tencent
The results are as follows:
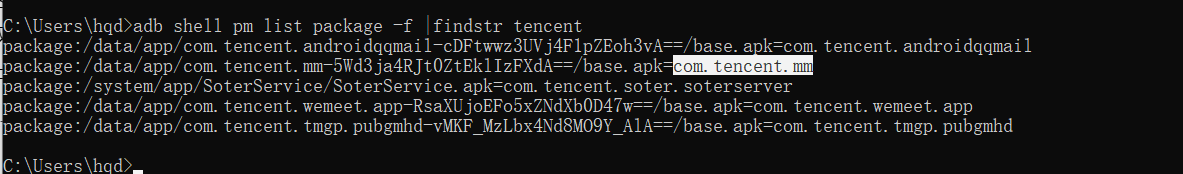
It's easy to get the package name. Run the code directly in webiter:
d.app_start("com.tencent.mm")The effects are as follows:
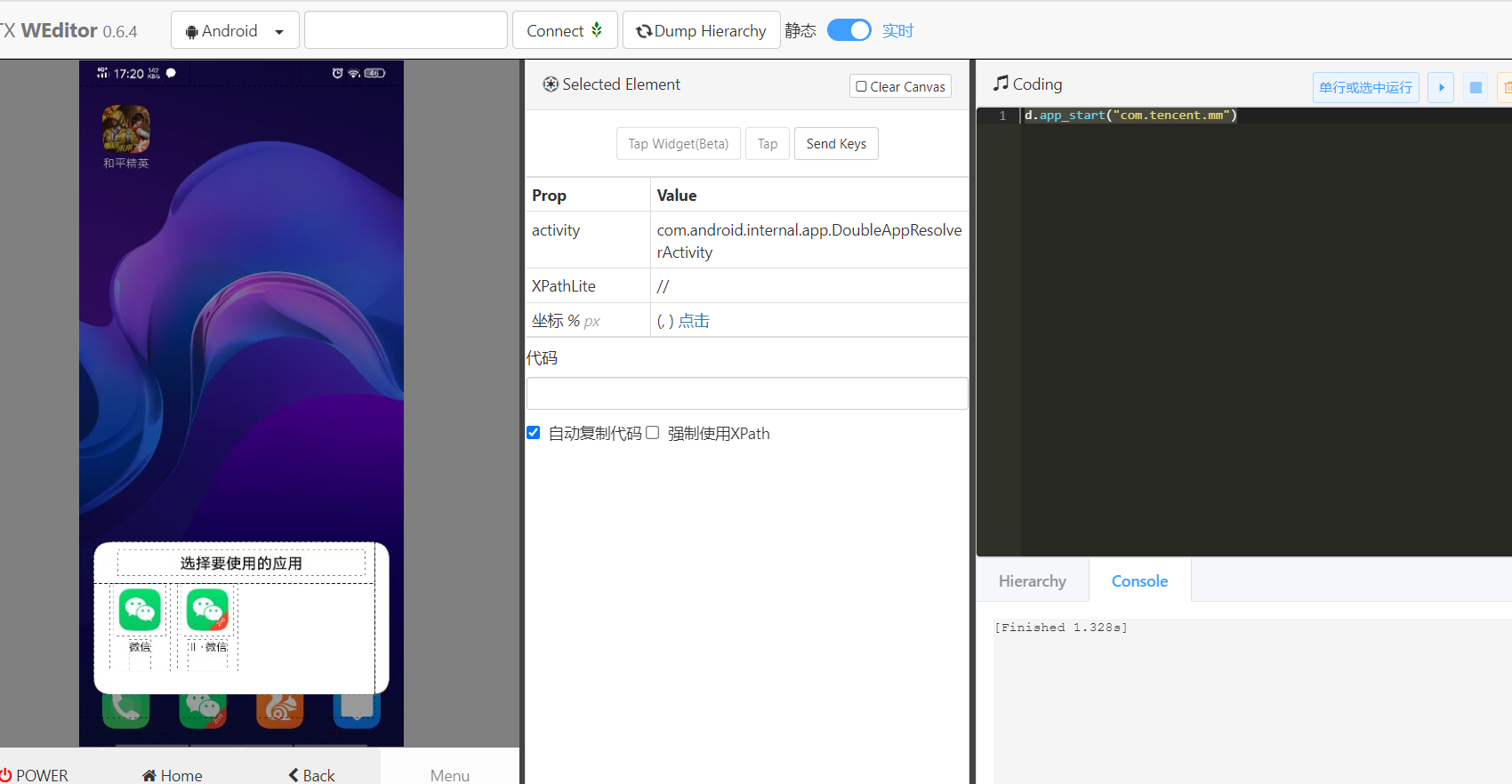
oh, I forgot that I have application separation. I have to add one more step. If there is no separation, I should be able to open it directly. Locate the wechat to be opened with webitor, and double click it to automatically generate code:
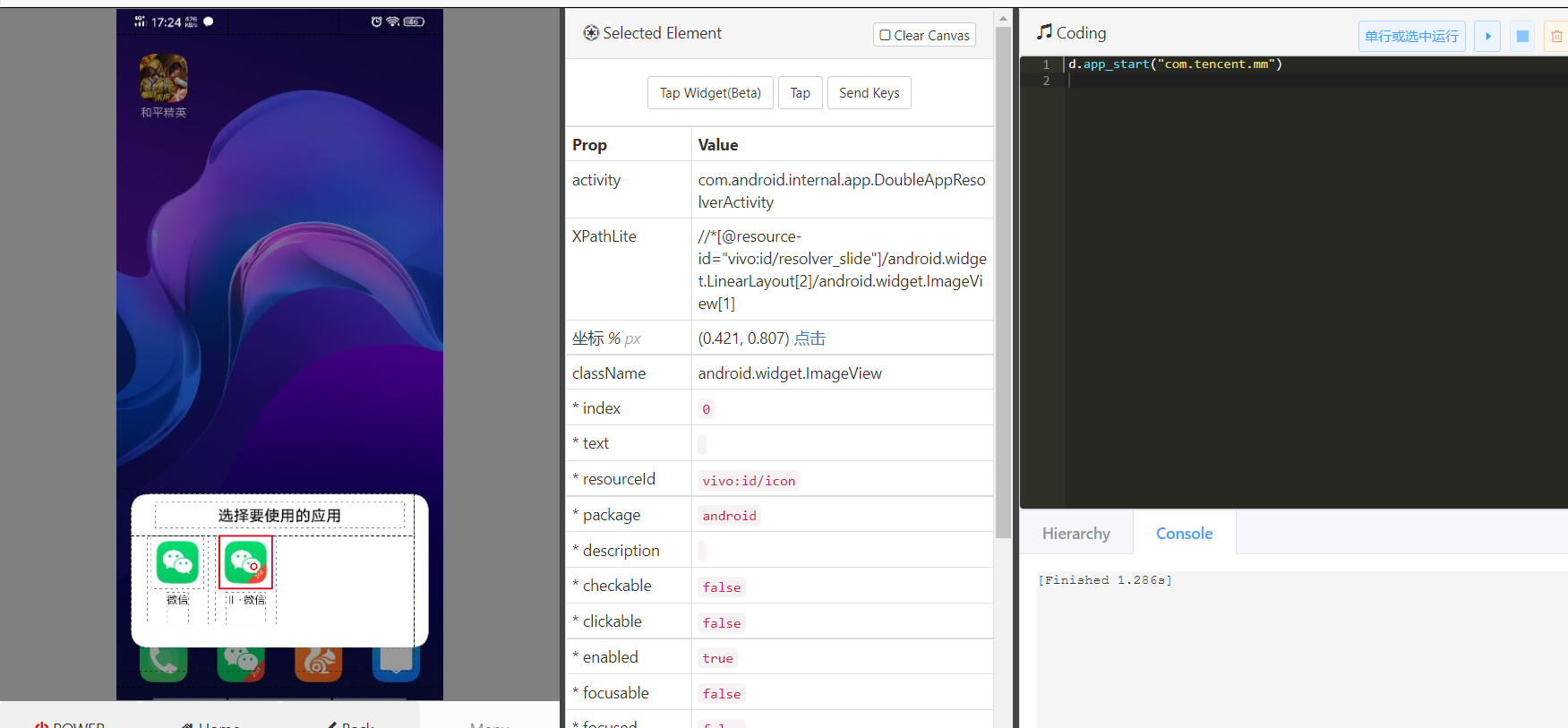
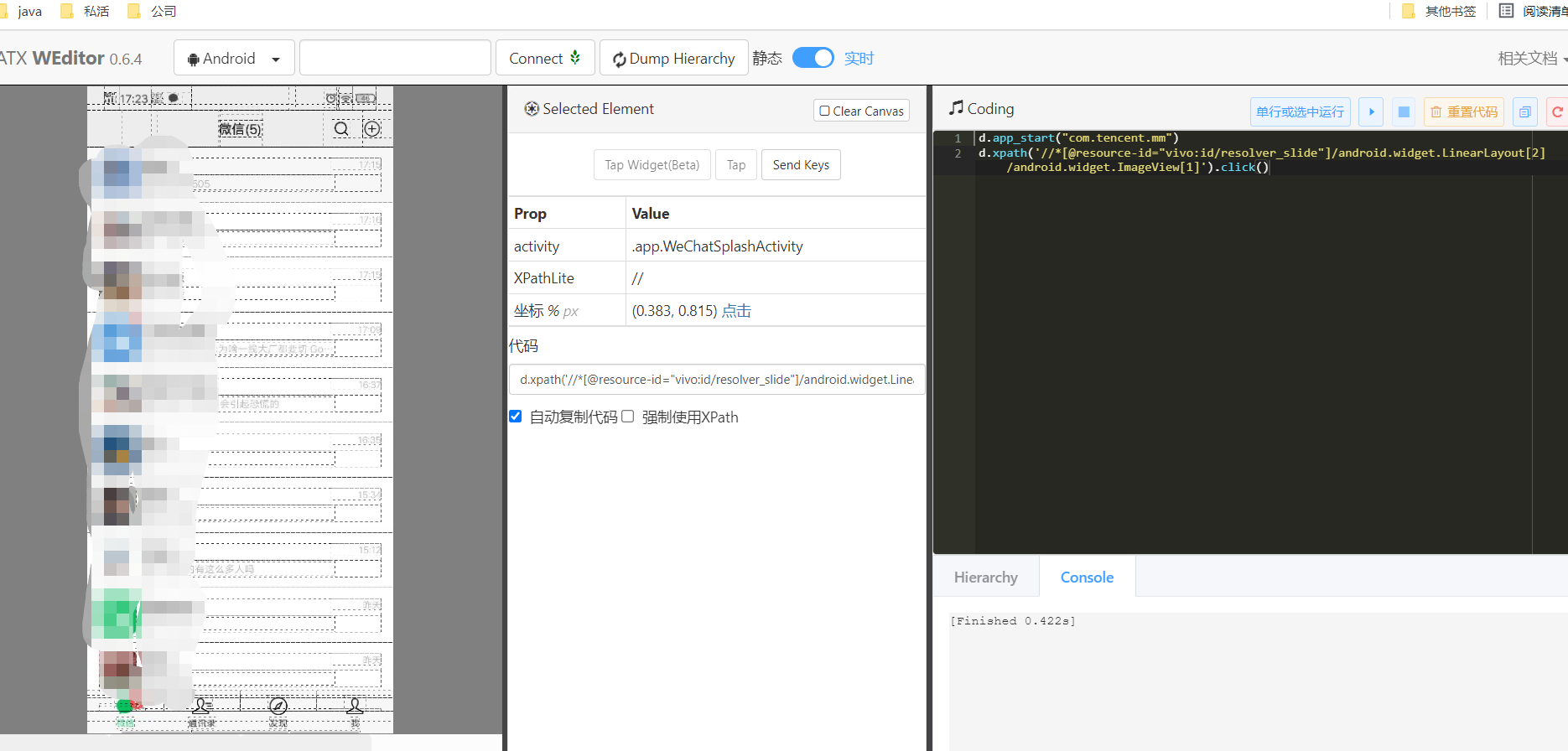
The first step is to open wechat. After that, let's see how to open the dialog box. Others are similar to those above. Do the same. Here you can directly locate the first contact. First locate the element:
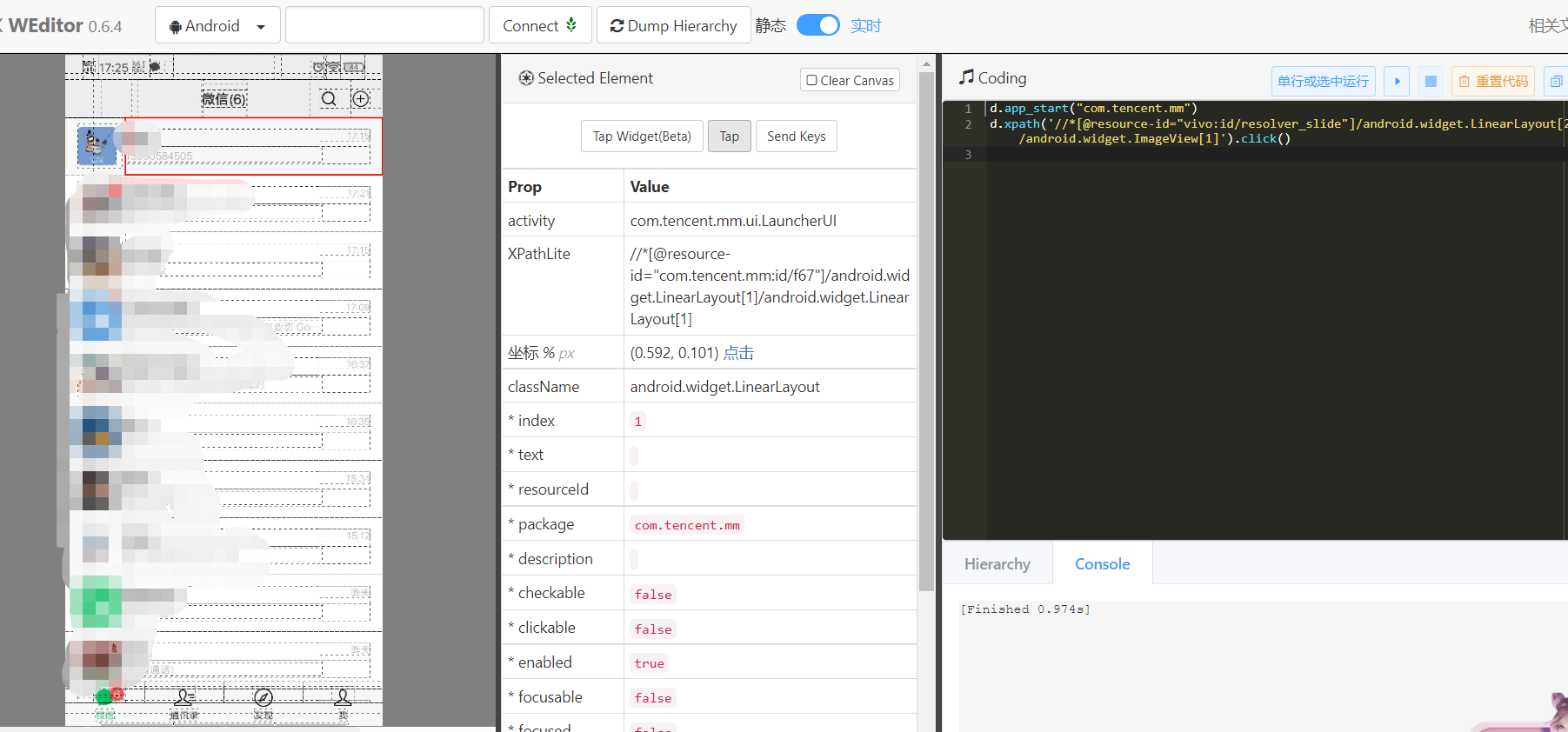
Double click on:
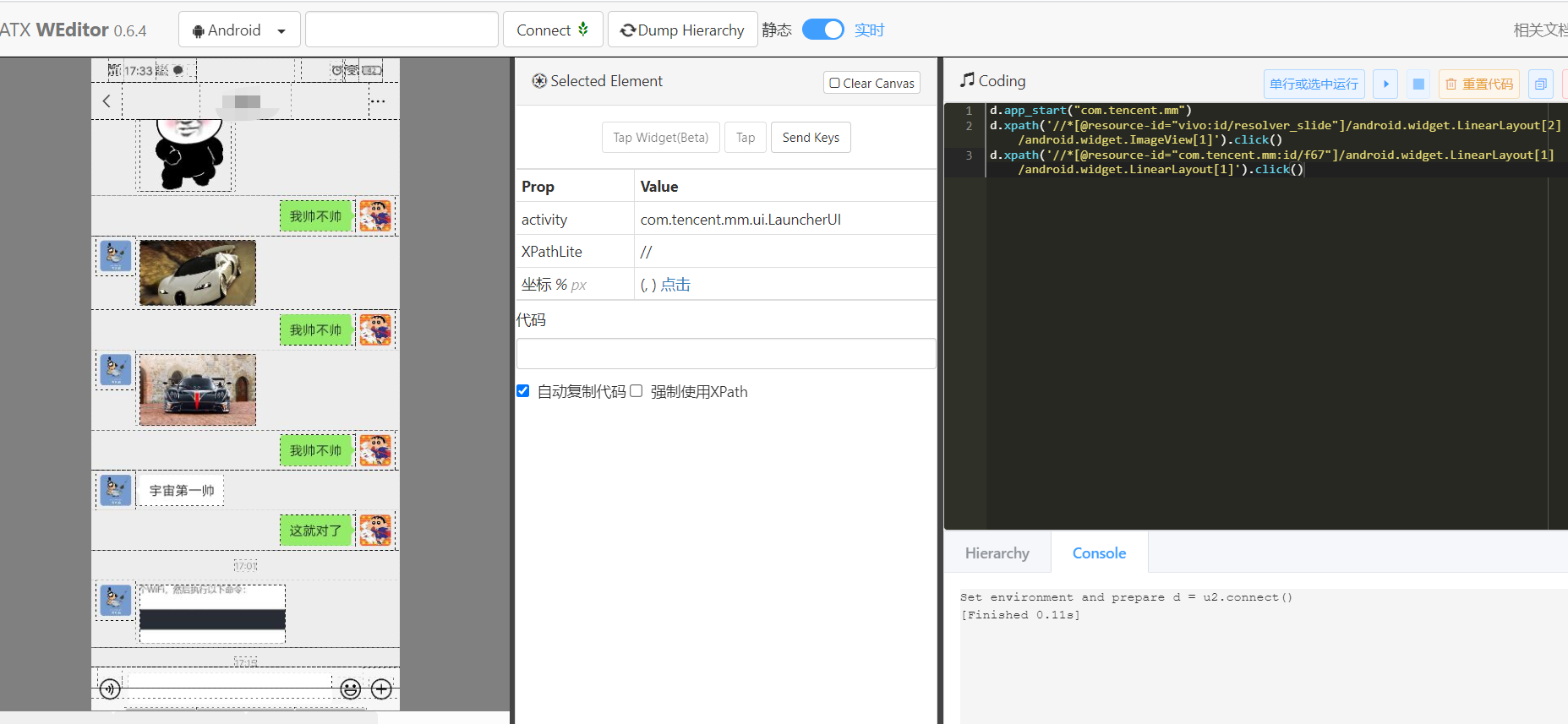
In this way, opening the chat box is also completed. The next step is to get the reply content. This is more troublesome. There are two main questions: one is how to distinguish the messages of the other party, and the other is how to obtain the content of the reply. Let's start with the first question
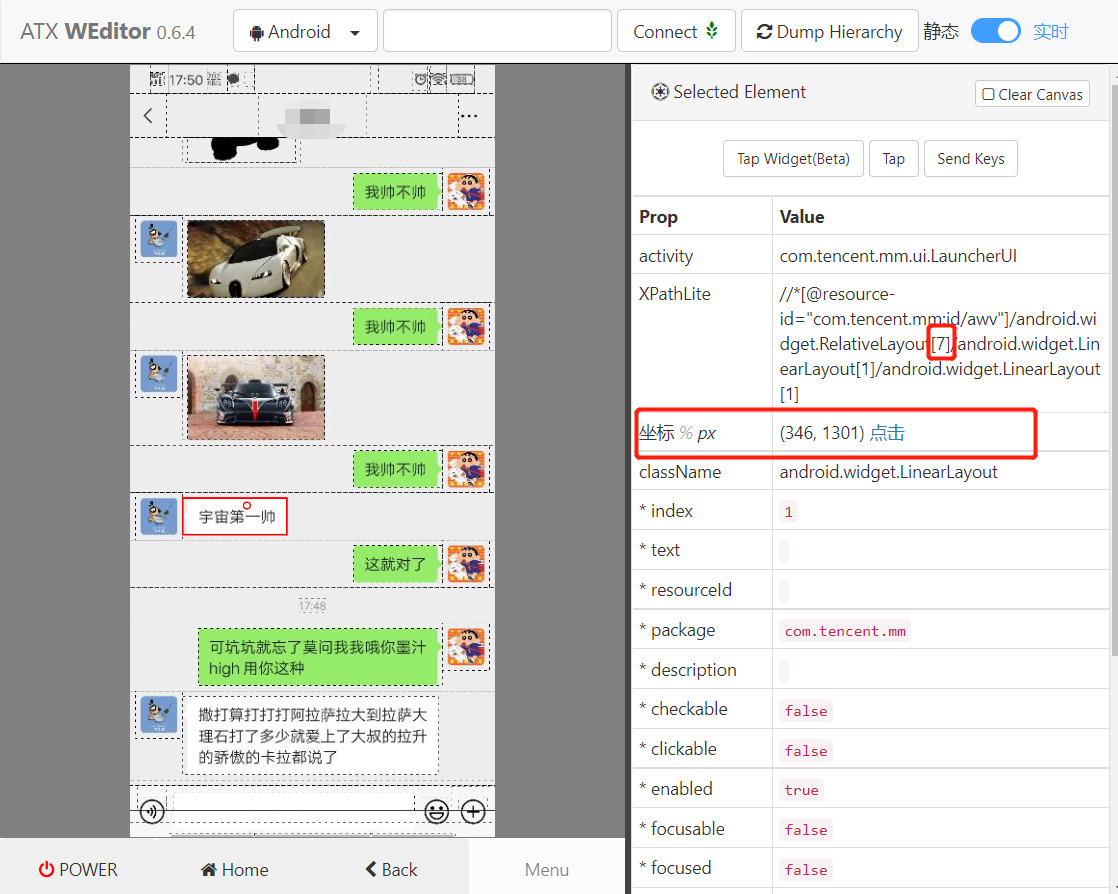
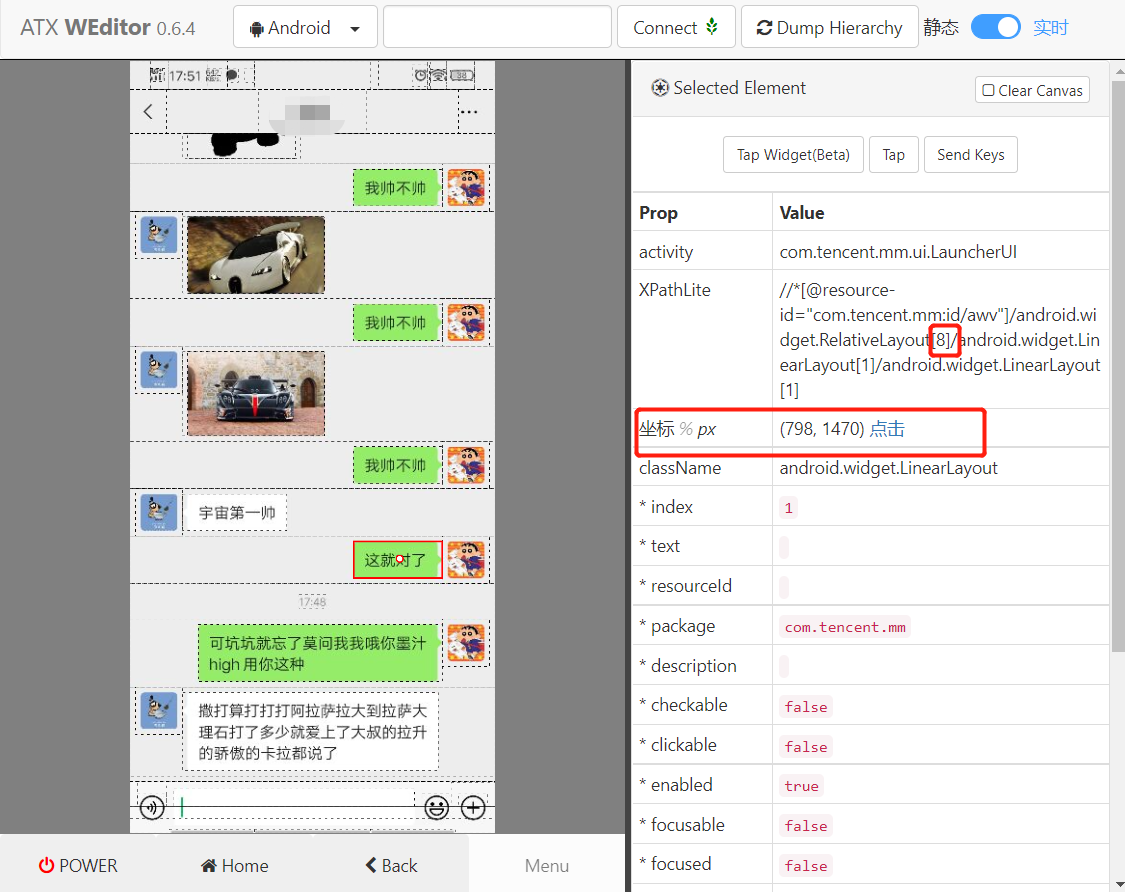
After comparing the two, it is found that only the middle number is different. What does this number represent? Let's count the chat records on the current screen, which is exactly 10, so we simply guess that it is the number of chat records .
Let's look at the coordinates of the two nodes. Can we judge by coordinates? There's another problem. What if you encounter a super long one? We can take the central coordinate of the element and compare it with the central coordinate of the mobile phone screen, so as long as it doesn't cover the whole width, it seems to be OK. Let's do an experiment to verify:
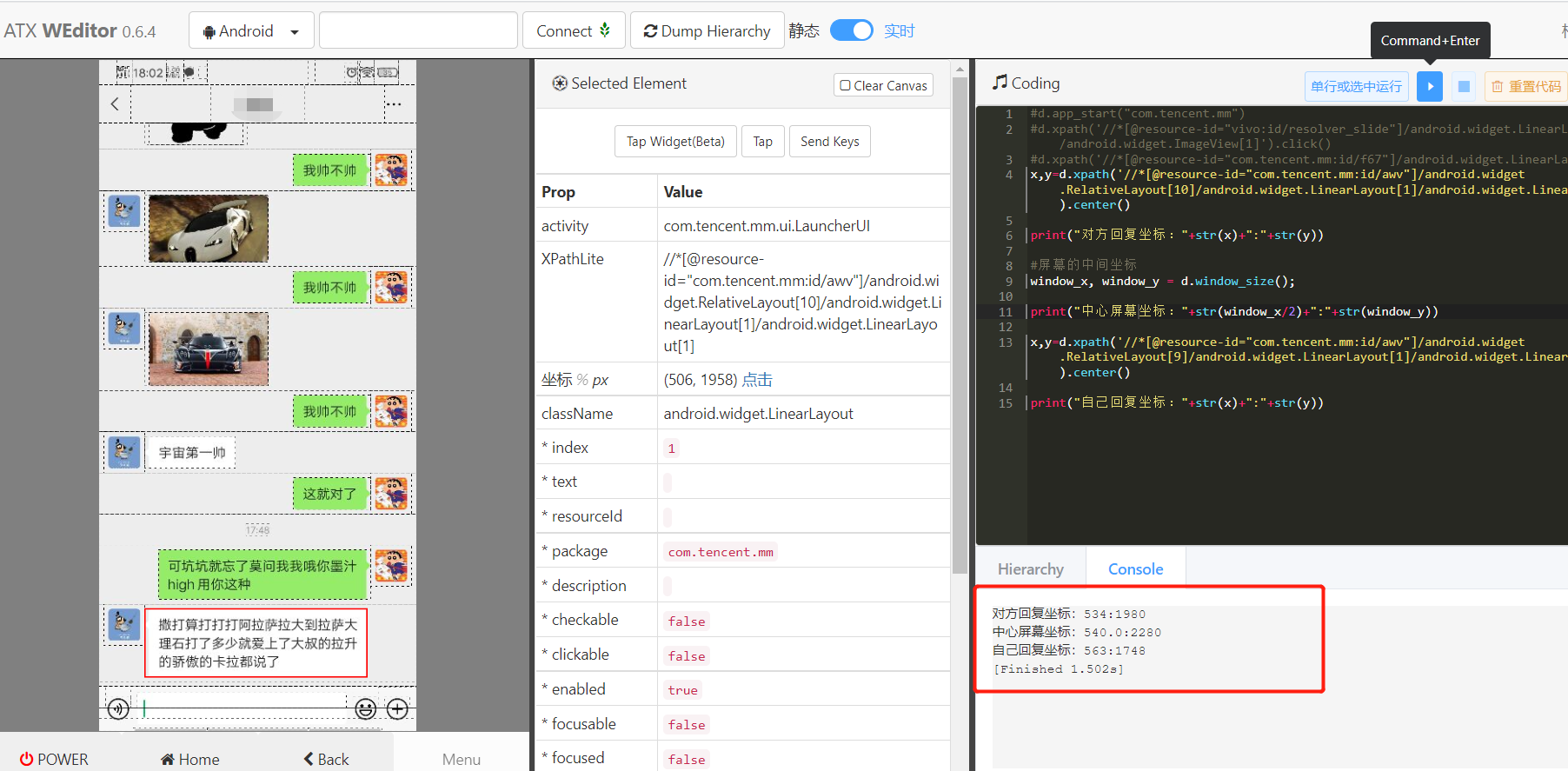
Look at the results, it seems OK
After obtaining the reply element of the other party, you can prepare to obtain the reply content. We were surprised to find that the text of the element was empty:
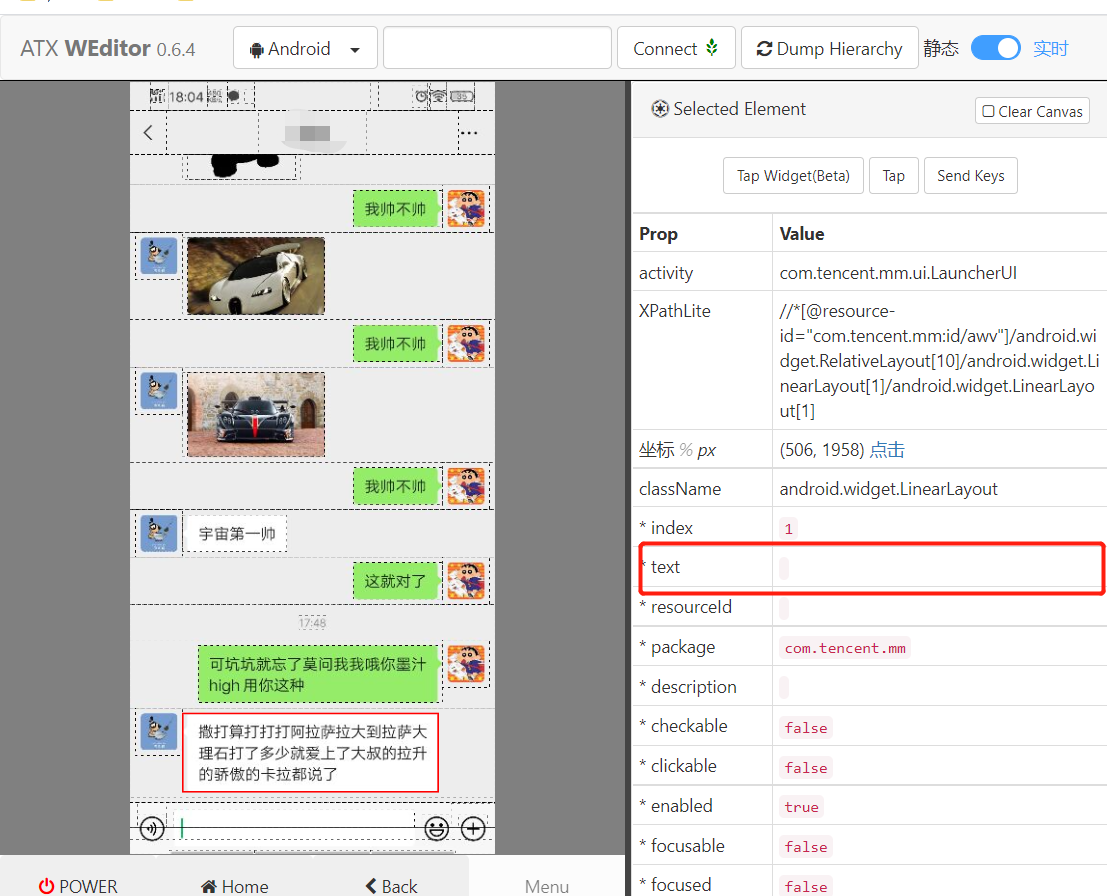
Well, it's difficult. If you can't get the content, how can you reply. Eh, double click. I found it can be enlarged
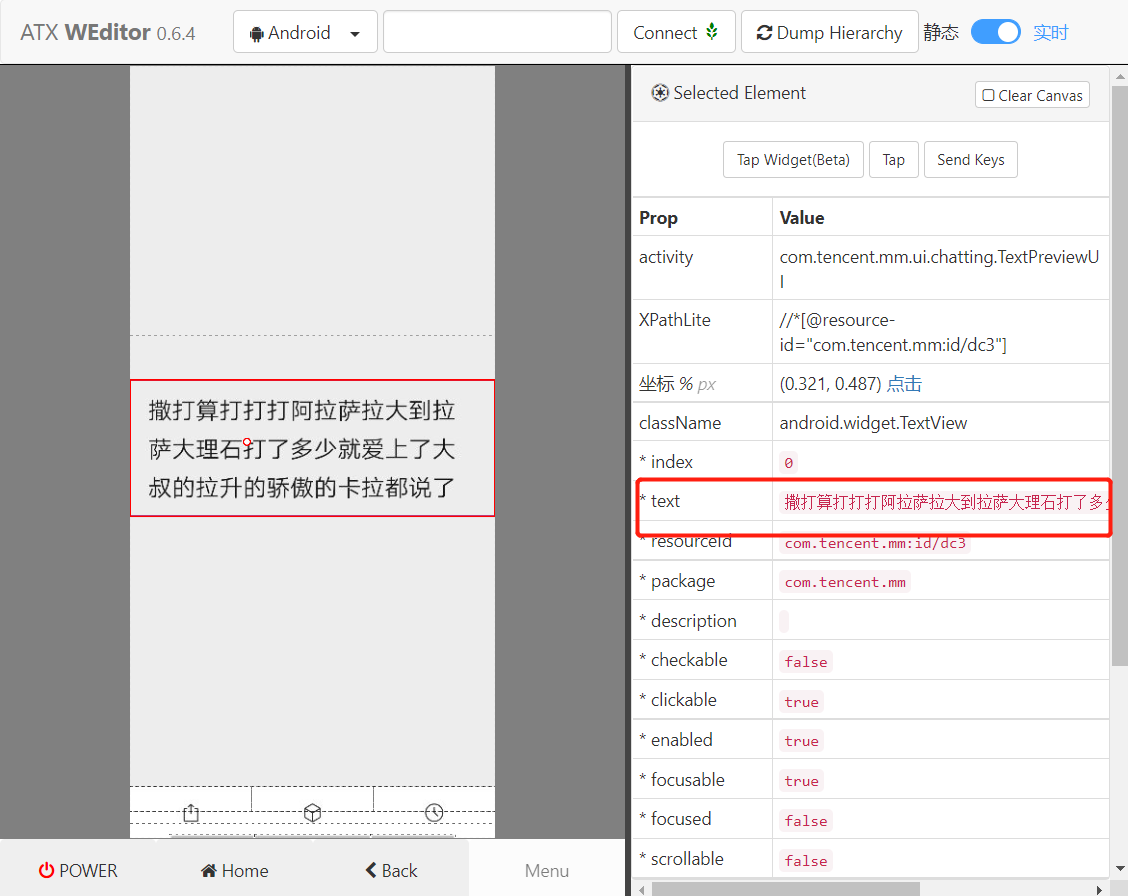
The mountain is poor and the water is suspicious. There is no way, and the willows are dark and the flowers are bright. Try to get the value as follows:
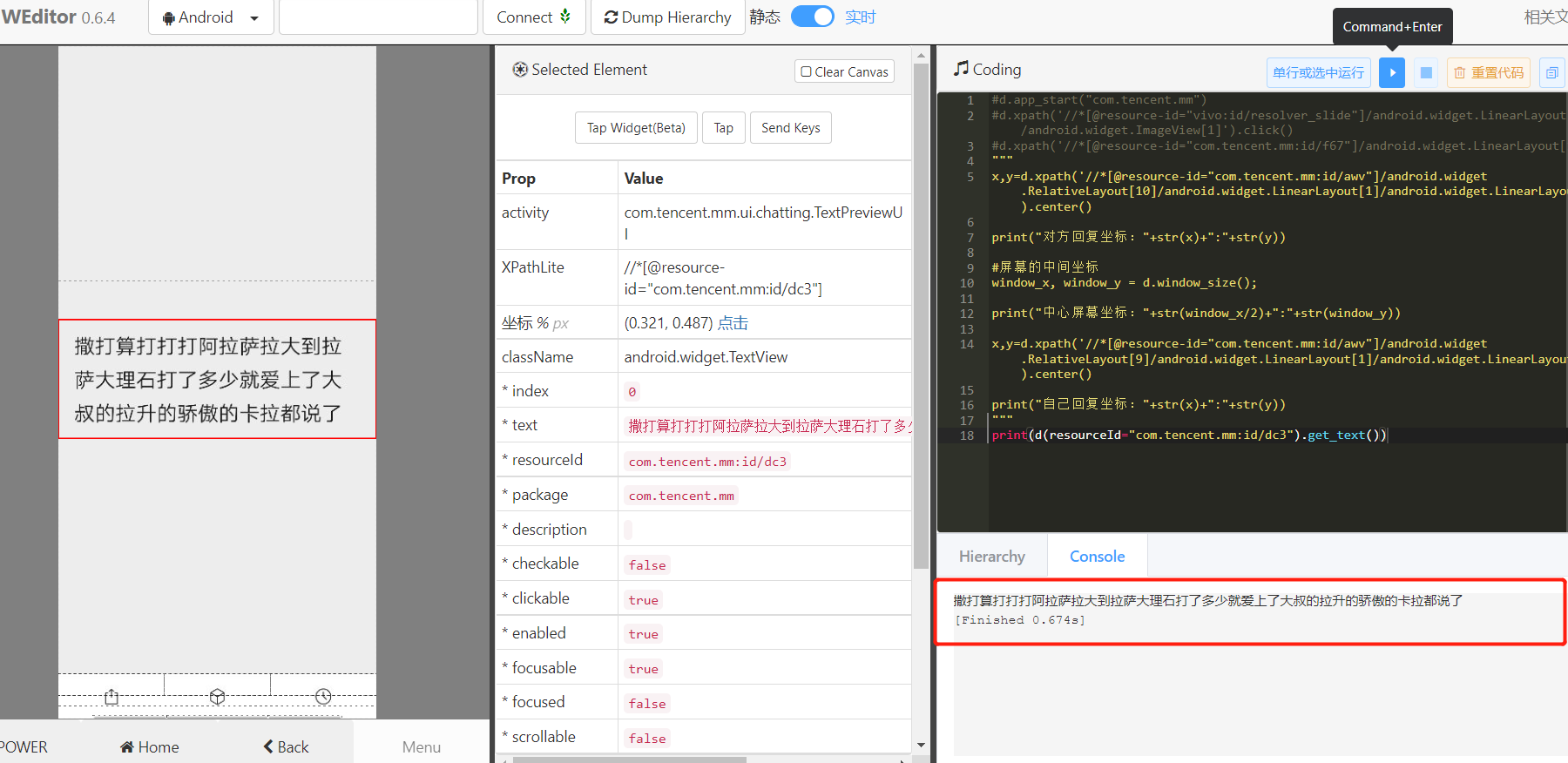
Oh, yeah! After getting the content, there is only one last step left, that is, reply to the message
First, set the input method we installed earlier, as follows:
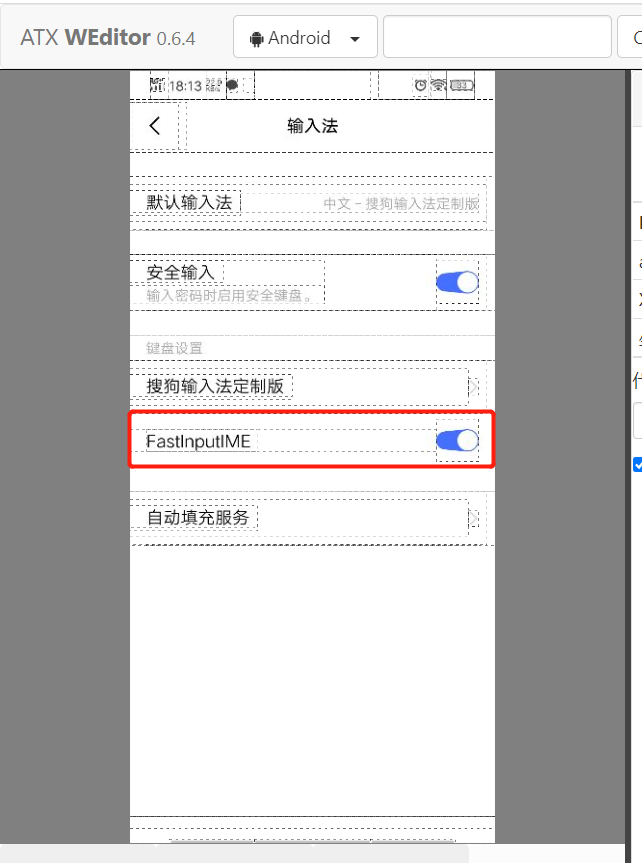
Write code to test:
# Click the dialog box
d(resourceId="com.tencent.mm:id/iki").click()
# Switching input method
d.set_fastinput_ime(True)
time.sleep(1)
# Input content
d.send_keys("I'm going to")
# d.set_fastinput_ime(False)
# send message
d(resourceId="com.tencent.mm:id/ay5").click()The effects are as follows:
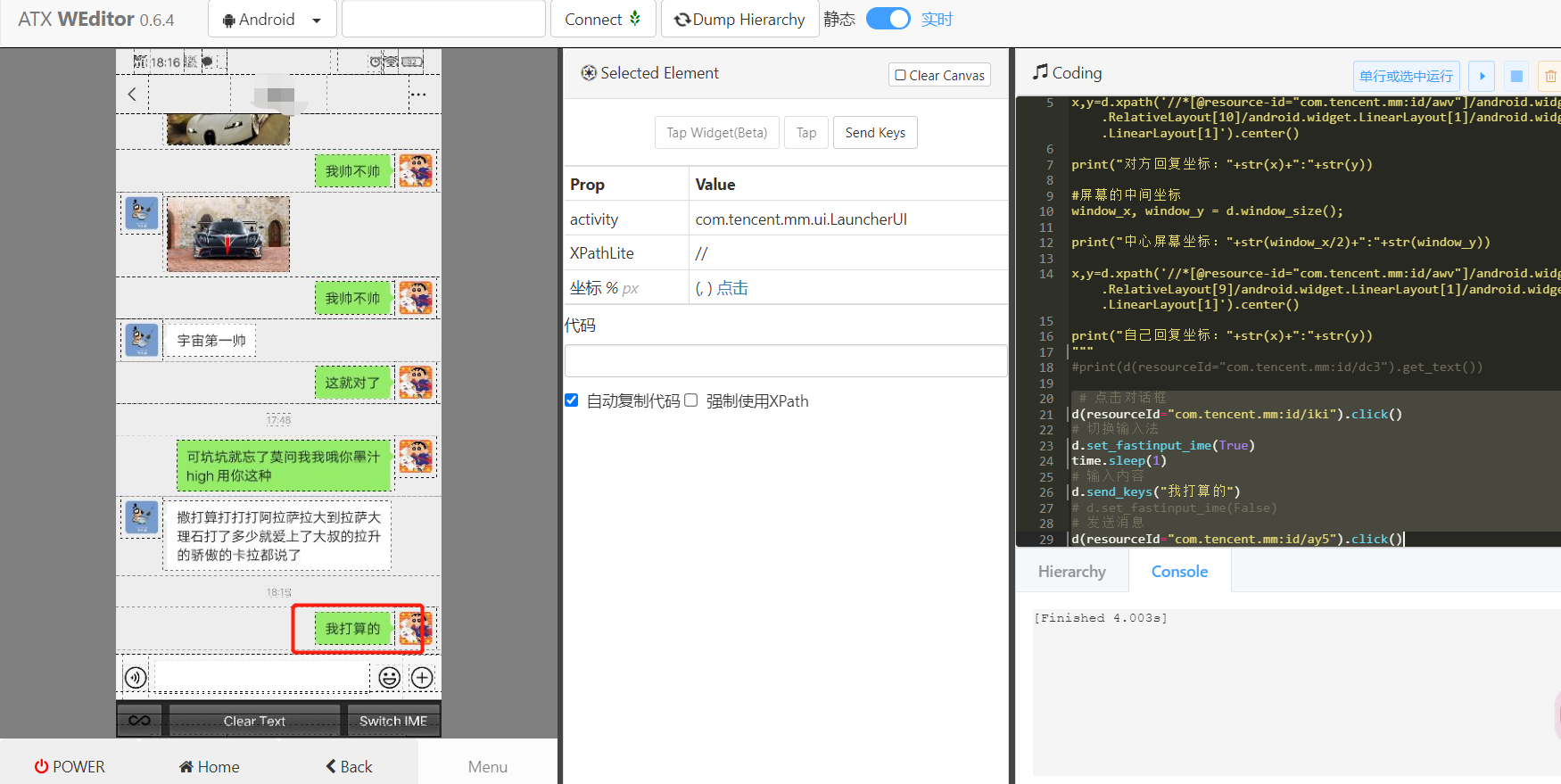
Well, all the problems have been solved at last. The next step is to realize ( ̄▽  ̄)~*
4, Code implementation
Here is just a simple sentence to repeat until you get the correct answer (PS: you wanted to access the Turing robot, but you found that you wanted money, so you gave up (╥╯╥╥). The complete code is as follows:
import time
import uiautomator2 as u2
answer_right_list = ["yes", "Handsome", "handsome guy", "yes", "yes", "Very handsome", "The most handsome in the universe"];
# USB connection
device = u2.connect();
# WiFi connection
# device = u2.connect_adb_wifi("192.168.1.9");
"""
send message
"""
def auto_answer(message="Am I handsome"):
# Click the dialog box
device(resourceId="com.tencent.mm:id/iki").click()
# Switching input method
device.set_fastinput_ime(True)
time.sleep(1)
# Input content
device.send_keys(message)
# d.set_fastinput_ime(False)
# send message
device(resourceId="com.tencent.mm:id/ay5").click()
"""
Open wechat
"""
def open_chat_window():
# Start wechat according to the package name
device.app_start("com.tencent.mm")
# Due to the application separation of mobile phones, one more step is needed
device.xpath(
'//*[@resource-id="vivo:id/resolver_slide"]/android.widget.LinearLayout[2]/android.widget.ImageView[1]').click()
time.sleep(3)
# d(resourceId="com.tencent.mm:id/dub", text = "address book"). click()
# Open the top chat box
device.xpath(
'//*[@resource-id="com.tencent.mm:id/f67"]/android.widget.LinearLayout[1]/android.widget.LinearLayout[1]').click()
def is_right_answer(context):
if context in answer_right_list:
return True;
return False;
"""
Get the latest content
"""
def get_newest_answer():
# Count all chat boxes
count = len(device.xpath('//*[@resource-id="com.tencent.mm:id/awv"]/android.widget.RelativeLayout').all());
# Get the bottom chat information
ele = device.xpath('//*[@resource-id="com.tencent.mm:id/awv"]/android.widget.RelativeLayout[' + str(
count) + ']/android.widget.LinearLayout[1]/android.widget.LinearLayout[1]');
x, y = ele.center();
window_x, window_y = device.window_size();
if x == window_x / 2: # Equality is an expression pack
ele = device.xpath('//*[@resource-id="com.tencent.mm:id/awv"]/android.widget.RelativeLayout[' + str(
count) + "]/android.widget.LinearLayout[1]/android.widget.LinearLayout[1]/android.widget.LinearLayout[1]/android.widget.FrameLayout[1]");
if ele.exists:
x, y = ele.center();
return x, y;
"""
Get recovery content
"""
def get_answer_content():
x, y = get_newest_answer();
#Here, due to the deviation, take the center point of 28 pixels again
cent_x = (x + (x - 28)) / 2;
cent_y = (y + (y - 28)) / 2;
device.click(cent_x, cent_y);
time.sleep(0.1)
device.click(cent_x, cent_y);
ele = device(resourceId="com.tencent.mm:id/dc3");
text = "";
if ele.exists:
text = str(device(resourceId="com.tencent.mm:id/dc3").get_text()).strip();
# Close the zoom in box
device(resourceId="com.tencent.mm:id/dc3").click();
else:
# Is it an expression pack
ele = device(resourceId="com.tencent.mm:id/ei");
if ele.exists:
device(resourceId="com.tencent.mm:id/ei").click();
text = "this" \
"It's an expression pack"
else:
# picture
device.click(x, y);
text = "This is a picture"
return text;
"""
Determine whether it is a reply
"""
def is_answer():
x, y = get_newest_answer();
window_x, window_y = device.window_size();
# If it is on the left side of the screen, it is a reply
if x < window_x / 2:
return True;
return False;
def start():
open_chat_window();
auto_answer();
if __name__ == '__main__':
start();
while True:
if is_answer():
text = get_answer_content();
print(text)
if is_right_answer(text):
break
else:
auto_answer();
#Check it in five seconds
time.sleep(5)
auto_answer("That's right")
device.set_fastinput_ime(False)
5, Effect display
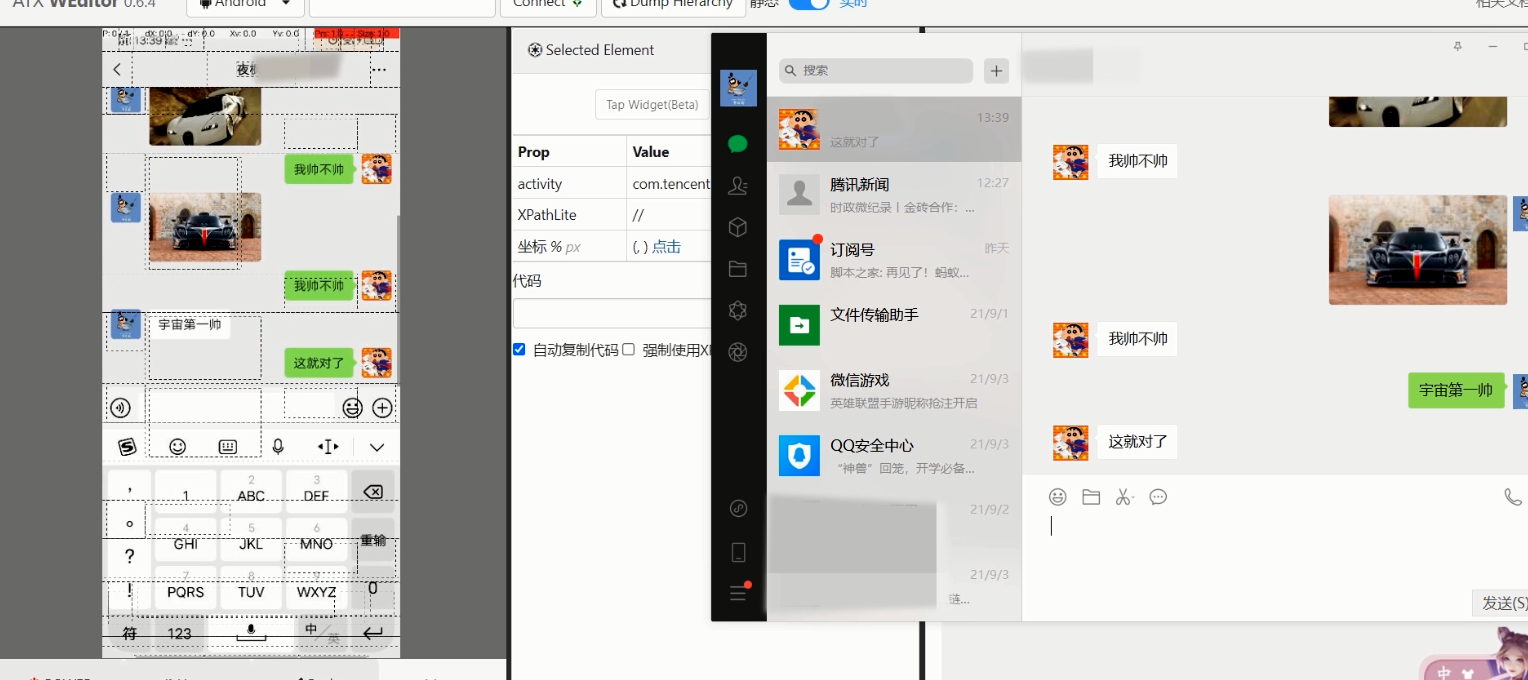
summary
Here uiautomator2 may have the problems of inaccurate positioning and too fast clicking. We need to try it ourselves.
Just started learning Python, welcome to correct the wrong places (✪ ω ✪)