Theoretical introduction
First, the map is used to illustrate how redis implements the delay queue
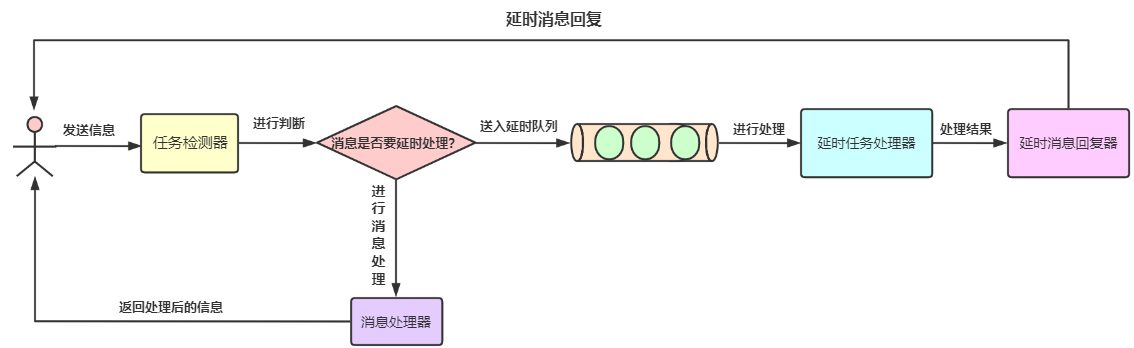
When the user sends a message request to the server background, the server will detect whether the message needs delay processing. If necessary, it will be put into the delay queue and detected and processed by the delay task detector. For tasks that do not need delay processing, the server will process the message immediately and return the processed results to the user.
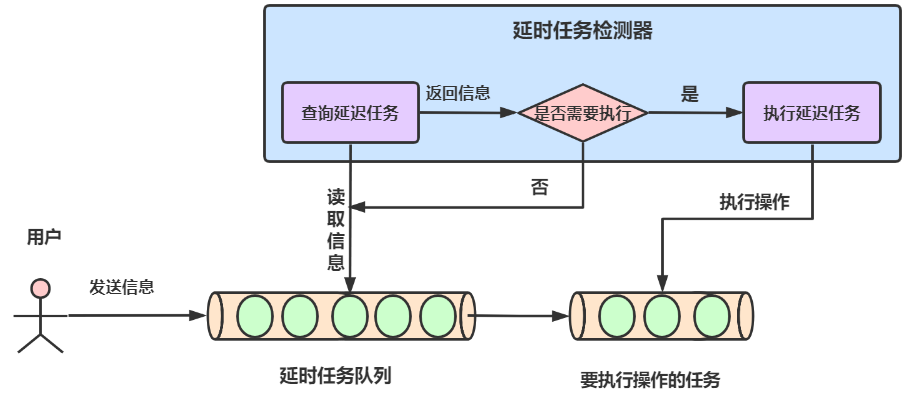
In the delayed task detector, there are two functions: querying delayed tasks and executing delayed tasks. The task detector will first go to the delayed task queue to read the information in the queue, judge which tasks in the current queue have expired, and output the expired tasks for execution (set a scheduled task).
At this time, we can think about the commands that can set the time flag in the Redis data structure?
Did you think of the zset command, which has the function of de reordering (fractional sorting). Yes, you're right!
We can use zset (sortedset) this command uses the set timestamp as the score for sorting. The zadd score1 value1... Command can be used to continuously produce messages into memory. Then, zrangebyscore can be used to query all the qualified tasks to be processed, and the queue tasks can be executed circularly. You can also query the earliest one through zrangebyscore key min max WithCores limit 0 1 A task to consume.
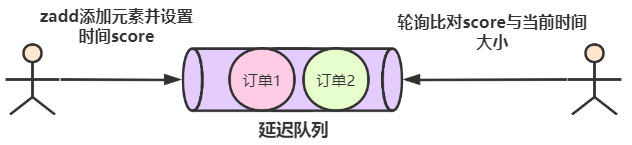
In general, you can do this in two ways:
(1) Use zrangebyscore to query all tasks in the current delay queue, find out all delay tasks that need to be processed, and operate in turn.
(2) Find the earliest task at present, and judge whether the execution time of the task is greater than that of the current system through the score value. For example, the earliest task execution time is 3:00 and the system time is 2:58), indicating that this should be executed immediately. The time is coming.
code implementation
RedisController for production messages
package testredis;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
/**
*
* @author nycp42j guobushi
* @version : RedisController.java, v 0.1 2021-12-25 4:56 PM guobushi Exp $$
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/redis")
public class RedisController {
@Autowired
private RedisUtil redisUtil;
private static String QUEUE_NAME = "redis_delay_queue";
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
// Imitation producer
@RequestMapping("/product")
public String product() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 1; i++) {
Calendar now = Calendar.getInstance();
now.setTime(new Date());
// Get the current seconds and set the consumption time to 20 seconds later than the current time
now.set(Calendar.SECOND, now.get(Calendar.SECOND) + 20);
System.out.println("Produced:" + i + "The current time is:" + simpleDateFormat.format(System.currentTimeMillis()) + "Consumption time:" + simpleDateFormat.format(now.getTime()));
// To queue_ Put i in the name collection and set score as the collation
redisUtil.opsForZsetAdd(QUEUE_NAME, i, now.getTime().getTime());
}
return "Producer production message succeeded";
}
}
Scheduled tasks for automatically executing consumption messages
package testredis;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
/**
*
* @author nycp42j guobushi
* @version : ConsumeConfiguration.java, v 0.1 2021-12-26 1:16 PM guobushi Exp $$
*/
// A scheduled task that starts when the project starts
//@Configuration
//@EnableScheduling
public class ConsumeConfiguration {
@Autowired
private RedisUtil redisUtil;
private static String QUEUE_NAME = "redis_delay_queue";
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
// Impersonate the consumer once per second
@Scheduled(cron = "*/1 * * * * * ")
public void consume(){
System.out.println("------------Waiting for consumption--------------");
// Take out the queue_ The score in the name collection is all values in the range of 0 - current timestamp
Set<Object> set = redisUtil.opsForZSetrangeByScore(QUEUE_NAME, 0, System.currentTimeMillis());
Iterator<Object> iterator = set.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Integer value = (Integer) iterator.next();
// Traverse and take out each score
Double score = redisUtil.opsForZSetScore(QUEUE_NAME, value);
// When the time is reached, consumption will be carried out
if (System.currentTimeMillis() > score) {
System.out.println("Consumed:" + value + "Consumption time:" + simpleDateFormat.format(System.currentTimeMillis()));
redisUtil.opsForZSetRemove(QUEUE_NAME, value);
}
}
}
}
If you don't want to automatically execute the scheduled task with the annotation of springboot, you can also use the manual method:
package testredis;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.scheduling.Trigger;
import org.springframework.scheduling.TriggerContext;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskScheduler;
import org.springframework.scheduling.support.CronTrigger;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledFuture;
/**
*
* @author nycp42j guobushi
* @version : Task.java, v 0.1 2021-12-26 2:31 PM guobushi Exp $$
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/task")
public class TaskScheduleController {
@Autowired
private ThreadPoolTaskScheduler threadPoolTaskScheduler;
@Autowired
private MyRunnable myRunnable;
private ScheduledFuture<?> future1;
@Bean
public ThreadPoolTaskScheduler threadPoolTaskScheduler() {
return new ThreadPoolTaskScheduler();
}
// Perform scheduled tasks manually
@RequestMapping("/startconsume")
public String startCron1() {
future1 = threadPoolTaskScheduler.schedule(myRunnable, new Trigger(){
@Override
public Date nextExecutionTime(TriggerContext triggerContext){
return new CronTrigger("0/1 * * * * *").nextExecutionTime(triggerContext);
}
});
return "Scheduled task started successfully!";
}
@RequestMapping("/stopconsume")
public String stopCron1() {
if (future1 != null) {
future1.cancel(true);
}
return "Scheduled task closed successfully!";
}
}
Custom Runnable interface for manually executing scheduled tasks
package testredis;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author nycp42j guobushi
* @version : MyRunnable.java, v 0.1 2021-12-26 2:33 PM guobushi Exp $$
*/
// @@ autowired can only take effect under Component
@Component
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
@Autowired
private RedisUtil redisUtil;
private static String QUEUE_NAME = "redis_delay_queue";
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
@Override
public void run() {
// Impersonate the consumer once per second
// Take out the queue_ The score in the name collection is all values in the range of 0 - current timestamp
Set<Object> set = redisUtil.opsForZSetrangeByScore(QUEUE_NAME, 0, System.currentTimeMillis());
Iterator<Object> iterator = set.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Integer value = (Integer) iterator.next();
// Traverse and take out each score
Double score = redisUtil.opsForZSetScore(QUEUE_NAME, value);
// When the time is reached, consumption will be carried out
if (System.currentTimeMillis() > score) {
System.out.println("Consumed:" + value + "Consumption time:" + simpleDateFormat.format(System.currentTimeMillis()));
redisUtil.opsForZSetRemove(QUEUE_NAME, value);
}
}
}
}
A customized RedisUtil tool is attached:
package testredis;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
*
* @author nycp42j guobushi
* @version : RedisTemplate.java, v 0.1 2021-12-25 3:02 PM guobushi Exp $$
*/
@Component
public class RedisUtil {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
//Add {value} to the sort collection at {key}, or update its {score} if it already exists
public <V>void opsForZsetAdd(String key, V value, double score){
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().add(key, value, score);
}
public Set<Object> opsForZSetrangeByScore(String key, double min, double max){
return redisTemplate.opsForZSet().rangeByScore(key, min, max);
}
// Gets the score of the specified key in zset
public Double opsForZSetScore(String key, Object score) {
return redisTemplate.opsForZSet().score(key, score);
}
// zset delete element
public void opsForZSetRemove(String key, Object value) {
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().remove(key, value);
}
}