Undertake the above Practice of delay queue based on redis and redisson Today, we will introduce rabbitmq, a delay plug-in based on rabbitmq_delayed_message_exchange implements deferred tasks.
1, Usage scenarios for delayed tasks
1. The order was placed successfully and was not paid for 30 minutes. Payment timeout, automatic cancellation of order
2. The order was signed, and no evaluation was conducted 7 days after signing. The order timeout is not evaluated, and the system defaults to high praise
3. The order was placed successfully, the merchant did not receive the order for 5 minutes, and the order was cancelled
4. Delivery timeout, push SMS reminder
5. A three-day trial period for members. After the expiration of the three-day trial period, users will be notified on time. The trial product has expired
......
For scenes with long delay and low real-time performance, we can use task scheduling to conduct regular polling. For example: XXL job.
Today, we will talk about the implementation of delay queue. There are many implementation methods of delay queue, such as:
- 1. For example, the queue ttl + dead letter routing strategy based on RabbitMQ: by setting a queue's timeout and non consumption time, and cooperating with the dead letter routing strategy, the message will be routed to the specified queue after the arrival time is not consumed
- 2. Rabbitmq delayed message exchange: when sending a message, you can delay the queue by adding a delay parameter (headers.put("x-delay", 5000)) to the request header. (by the way, Alibaba cloud's paid version of rabbitmq currently supports delayed messages within one day). Limitations: the current design of the plug-in is not really suitable for scenarios containing a large number of delayed messages (such as hundreds of thousands or millions). See #/issues/72 In addition, the plug-in relies on Erlang timers. After a certain number of long timers are used in the system, they begin to compete for scheduler resources.
- 3. Use the zset ordering of redis, poll each element in zset, and migrate the content to the queue to be consumed after arriving at the point (redisson has been implemented)
- 4. Use the expiration notification policy of redis's key, set the expiration time of a key as the delay time, and notify the client after expiration (this method relies on the redis expiration inspection mechanism. The delay will be serious if there are many keys; redis's pubsub will not be persisted, and the server will be discarded if it goes down).
2, Component installation
Installing rabbitMQ depends on the erlang language environment, so we need to download the erlang environment installer. There are many installation tutorials on the Internet, which will not be described here. It should be noted that the versions supported by the delay plug-in match.
Plug in Git official address: https://github.com/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-delayed-message-exchange
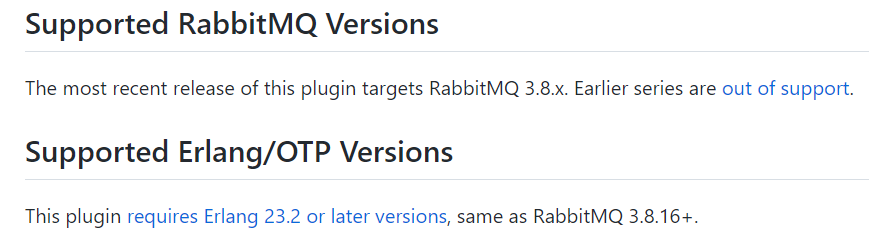
After you have successfully installed the plug-in, run rabbitmq management background. You can see that this option is added to the type type in the new exchange
3, Implementation of RabbitMQ delay queue plug-in
1. Basic principles
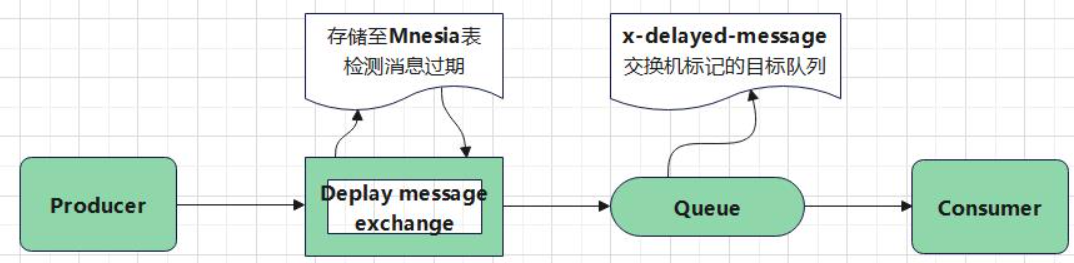
For the switch declared by x-delayed-message, its messages will not enter the queue immediately after publication. First, save the messages to Mnesia (a distributed database management system, which is suitable for telecommunications and other Erlang applications that need continuous operation and have soft real-time characteristics. At present, there are not many materials)
The plug-in will try to confirm whether the message has expired. First, ensure that the delay range of the message is delay > 0, delay = <? ERL_ MAX_ T (the range that can be set in Erlang is (2 ^ 32) - 1 ms). If the message expires and is delivered to the target queue through the switch marked with x-delayed-type, the whole message delivery process is completed.
2. Core component development starts
Introducing maven dependency
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId> </dependency>
application.yml simple configuration
rabbitmq:
host: localhost
port: 5672
virtual-host: /
RabbitMqConfig profile
package com.example.code.bot_monomer.config; import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding; import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder; import org.springframework.amqp.core.CustomExchange; import org.springframework.amqp.core.Exchange; import org.springframework.amqp.core.ExchangeBuilder; import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; /** * @author: shf description: date: 2022/1/5 15:00 */ @Configuration public class RabbitMQConfig { /** * ordinary */ public static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "test_exchange"; public static final String QUEUE_NAME = "test001_queue"; public static final String NEW_QUEUE_NAME = "test002_queue"; /** * delay */ public static final String DELAY_EXCHANGE_NAME = "delay_exchange"; public static final String DELAY_QUEUE_NAME = "delay001_queue"; public static final String DELAY_QUEUE_ROUT_KEY = "key001_delay"; //Because Ali rabbitmq There is an additional charge for adding queues, which is now used by all business delay tasks queue:delay001_queue //public static final String NEW_DELAY_QUEUE_NAME = "delay002_queue"; @Bean public CustomExchange delayMessageExchange() { Map<String, Object> args = new HashMap<>(); args.put("x-delayed-type", "direct"); //Custom switch return new CustomExchange(DELAY_EXCHANGE_NAME, "x-delayed-message", true, false, args); } @Bean public Queue delayMessageQueue() { return new Queue(DELAY_QUEUE_NAME, true, false, false); } @Bean public Binding bindingDelayExchangeAndQueue(Queue delayMessageQueue, Exchange delayMessageExchange) { return new Binding(DELAY_QUEUE_NAME, Binding.DestinationType.QUEUE, DELAY_EXCHANGE_NAME, DELAY_QUEUE_ROUT_KEY, null); //return BindingBuilder.bind(delayMessageQueue).to(delayMessageExchange).with("key001_delay").noargs(); } /** * Switch */ @Bean public Exchange orderExchange() { return ExchangeBuilder.topicExchange(EXCHANGE_NAME).durable(true).build(); //return new TopicExchange(EXCHANGE_NAME, true, false); } /** * queue */ @Bean public Queue orderQueue() { //return QueueBuilder.durable(QUEUE_NAME).build(); return new Queue(QUEUE_NAME, true, false, false, null); } /** * queue */ @Bean public Queue orderQueue1() { //return QueueBuilder.durable(NEW_QUEUE_NAME).build(); return new Queue(NEW_QUEUE_NAME, true, false, false, null); } /** * Switch and queue binding relationship */ @Bean public Binding orderBinding(Queue orderQueue, Exchange orderExchange) { //return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with("#.delay").noargs(); return new Binding(QUEUE_NAME, Binding.DestinationType.QUEUE, EXCHANGE_NAME, "test001_common", null); } /** * Switch and queue binding relationship */ @Bean public Binding orderBinding1(Queue orderQueue1, Exchange orderExchange) { //return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with("#.delay").noargs(); return new Binding(NEW_QUEUE_NAME, Binding.DestinationType.QUEUE, EXCHANGE_NAME, "test001_common", null); } }
MqDelayQueueEnum enumeration class
package com.example.code.bot_monomer.enums; import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; import lombok.Getter; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor; /** * @author: shf description: Delay queue service enumeration class * date: 2021/8/27 14:03 */ @Getter @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor public enum MqDelayQueueEnum { /** * Business 0001 */ YW0001("yw0001", "Test 0001", "yw0001"), /** * Business 0002 */ YW0002("yw0002", "Test 0002", "yw0002"); /** * Unique Key for delay queue service differentiation */ private String code; /** * Chinese description */ private String name; /** * The beans of the specific business implementation of the delay queue can be obtained through the context of Spring */ private String beanId; public static String getBeanIdByCode(String code) { for (MqDelayQueueEnum queueEnum : MqDelayQueueEnum.values()) { if (queueEnum.code.equals(code)) { return queueEnum.beanId; } } return null; } }
Template interface processing class: MqDelayQueueHandle
package com.example.code.bot_monomer.service.mqDelayQueue; /** * @author: shf description: RabbitMQ Delay queue scheme processing interface * date: 2022/1/10 10:46 */ public interface MqDelayQueueHandle<T> { void execute(T t); }
Specific business implementation processing class
@Slf4j @Component("yw0001") public class MqTaskHandle01 implements MqDelayQueueHandle<String> { @Override public void execute(String s) { log.info("MqTaskHandle01.param=[{}]",s); //TODO } }
Note: @ Component("yw0001") should be consistent with the corresponding beanId in the business enumeration class MqDelayQueueEnum.
Unified messaging body encapsulation class
/** * @author: shf description: date: 2022/1/10 10:51 */ @Data @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor @Builder public class MqDelayMsg<T> { /** * Unique key for business differentiation */ @NonNull String businessCode; /** * Message content */ @NonNull T content; }
Unified Consumer distribution processing Consumer
package com.example.code.bot_monomer.service.mqConsumer; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject; import com.example.code.bot_monomer.config.common.MqDelayMsg; import com.example.code.bot_monomer.enums.MqDelayQueueEnum; import com.example.code.bot_monomer.service.mqDelayQueue.MqDelayQueueHandle; import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils; import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; /** * @author: shf description: date: 2022/1/5 15:12 */ @Slf4j @Component //@RabbitListener(queues = "test001_queue") @RabbitListener(queues = "delay001_queue") public class TestConsumer { @Autowired ApplicationContext context; /** * RabbitHandler The message type is automatically matched (automatic message acknowledgement) * * @param msgStr * @param message */ @RabbitHandler public void taskHandle(String msgStr, Message message) { try { MqDelayMsg msg = JSONObject.parseObject(msgStr, MqDelayMsg.class); log.info("TestConsumer.taskHandle:businessCode=[{}],deliveryTag=[{}]", msg.getBusinessCode(), message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag()); String beanId = MqDelayQueueEnum.getBeanIdByCode(msg.getBusinessCode()); if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(beanId)) { MqDelayQueueHandle<Object> handle = (MqDelayQueueHandle<Object>) context.getBean(beanId); handle.execute(msg.getContent()); } else { log.warn("TestConsumer.taskHandle:MQ Deferred task does not exist beanId,businessCode=[{}]", msg.getBusinessCode()); } } catch (Exception e) { log.error("TestConsumer.taskHandle:MQ Delayed task Handle abnormal:", e); } } }
Finally, simply encapsulate a tool class
package com.example.code.bot_monomer.utils; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject; import com.example.code.bot_monomer.config.RabbitMQConfig; import com.example.code.bot_monomer.config.common.MqDelayMsg; import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.lang.NonNull; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.time.LocalDateTime; import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit; import java.util.Objects; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; /** * @author: shf description: MQ Distributed delay queue tool class date: 2022/1/10 15:20 */ @Slf4j @Component public class MqDelayQueueUtil { @Autowired private RabbitTemplate template; @Value("${mqdelaytask.limit.days:2}") private Integer mqDelayLimitDays; /** * Add deferred task * * @param bindId Business binding ID, used to associate specific messages * @param businessCode Unique identifier of business differentiation * @param content Message content * @param delayTime Set the delay time in milliseconds * @return Success: true; Failed false */ public boolean addDelayQueueTask(@NonNull String bindId, @NonNull String businessCode, @NonNull Object content, @NonNull Long delayTime) { log.info("MqDelayQueueUtil.addDelayQueueTask:bindId={},businessCode={},delayTime={},content={}", bindId, businessCode, delayTime, JSON.toJSONString(content)); if (StringUtils.isAnyBlank(bindId, businessCode) || Objects.isNull(content) || Objects.isNull(delayTime)) { return false; } try { //TODO If the delay time is more than 2 days, the database table records shall be added first, and then the scheduled task shall pull it twice a day to put the delay records less than 2 days into the database MQ Waiting for due execution if (ChronoUnit.DAYS.between(LocalDateTime.now(), LocalDateTime.now().plus(delayTime, ChronoUnit.MILLIS)) >= mqDelayLimitDays) { //TODO } else { this.template.convertAndSend( RabbitMQConfig.DELAY_EXCHANGE_NAME, RabbitMQConfig.DELAY_QUEUE_ROUT_KEY, JSONObject.toJSONString(MqDelayMsg.<Object>builder().businessCode(businessCode).content(content).build()), message -> { //Note that time can be used here long type,Millisecond units, setting header message.getMessageProperties().setHeader("x-delay", delayTime); return message; } ); } } catch (Exception e) { log.error("MqDelayQueueUtil.addDelayQueueTask:bindId={}businessCode={}abnormal:", bindId, businessCode, e); return false; } return true; } /** * Undo delay message * @param bindId Business binding ID, used to associate specific messages * @param businessCode Unique identifier of business differentiation * @return Success: true; Failed false */ public boolean cancelDelayQueueTask(@NonNull String bindId, @NonNull String businessCode) { if (StringUtils.isAnyBlank(bindId,businessCode)) { return false; } try { //TODO query DB,If the message still exists, it can be deleted } catch (Exception e) { log.error("MqDelayQueueUtil.cancelDelayQueueTask:bindId={}businessCode={}abnormal:", bindId, businessCode, e); return false; } return true; } /** * Modify delay message * @param bindId Business binding ID, used to associate specific messages * @param businessCode Unique identifier of business differentiation * @param content Message content * @param delayTime Set the delay time in milliseconds * @return Success: true; Failed false */ public boolean updateDelayQueueTask(@NonNull String bindId, @NonNull String businessCode, @NonNull Object content, @NonNull Long delayTime) { if (StringUtils.isAnyBlank(bindId, businessCode) || Objects.isNull(content) || Objects.isNull(delayTime)) { return false; } try { //TODO query DB,Message does not exist return false,There is a delay in judging the length of receipt or receipt mq //TODO If the delay time is more than 2 days, the database table records shall be added first, and then the scheduled task shall pull it twice a day to put the delay records less than 2 days into the database MQ Waiting for due execution if (ChronoUnit.DAYS.between(LocalDateTime.now(), LocalDateTime.now().plus(delayTime, ChronoUnit.MILLIS)) >= mqDelayLimitDays) { //TODO } else { this.template.convertAndSend( RabbitMQConfig.DELAY_EXCHANGE_NAME, RabbitMQConfig.DELAY_QUEUE_ROUT_KEY, JSONObject.toJSONString(MqDelayMsg.<Object>builder().businessCode(businessCode).content(content).build()), message -> { //Note that time can be used here long type,Millisecond units, setting header message.getMessageProperties().setHeader("x-delay", delayTime); return message; } ); } } catch (Exception e) { log.error("MqDelayQueueUtil.updateDelayQueueTask:bindId={}businessCode={}abnormal:", bindId, businessCode, e); return false; } return true; } }
Attach test class:
/** * description: Delay queue test * * @author: shf date: 2021/8/27 14:18 */ @RestController @RequestMapping("/mq") @Slf4j public class MqQueueController { @Autowired private MqDelayQueueUtil mqDelayUtil; @PostMapping("/addQueue") public String addQueue() { mqDelayUtil.addDelayQueueTask("00001",MqDelayQueueEnum.YW0001.getCode(),"delay0001 test",3000L); return "SUCCESS"; } }
Paste the field settings of the DB record table

Cooperate with XXL job to schedule tasks.
Since the delivered message cannot be modified, be careful when setting the delay message! It also needs to cooperate with the business party. For example, messages with a delay time of less than 2 days (the time and days can be adjusted, and you can also set the threshold unit to hours, depending on the business requirements) do not support modification and revocation. The delayed messages beyond 2 days support revocation and modification. It should be noted that the unique ID of the associated specific operation business needs to be bound to correspond to the revocation or modification of the associated operation. (PS: if the delay time is set beyond 2 days, it will be saved to the DB record table first, and the scheduled task will pull and release the data within 2 days to the delay column every day).
To be more secure, in order to prevent inconsistencies caused by operation time errors in messages entering the DB record, query the DB record table before consumption and distribution by the unified Consumer, and check whether the message has been undeleted (add a deletion mark field record), and the current time is greater than or equal to the due execution time of the records in the DB table before it can be distributed for execution, otherwise it will be discarded.
In addition, the dead letter queue mechanism of rabbitmq can also be used to delay tasks, and implementation cases can be attached when there is time.