Headless one-way acyclic linked list: it has a simple structure and is generally not used to store data alone. In fact, it is more used as a substructure of other data structures, such as hash bucket, adjacency table of graph and so on. In addition, this structure appears a lot in the written interview.
This linked list stores a data for each node and the address of the next node, which can string each node well.
Single linked list is created for the disadvantages of sequential list.
catalogue
Implementation of function interface
void SLTNodeDestroy(SLTNode** pphead)
SLTNode* BuyListNode(SLTDataType x)
void SLTNodePushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
void SLTNodePopBack(SLTNode** pphead)
void SLTNodePushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
void SLTNodePopFront(SLTNode** pphead)
void SLTNodePrint(SLTNode* pphead)
SLTNode* SLTNodeFind(SLTNode* pphead, SLTDataType x)
void SLTNodeInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
void SLTNodeErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos)
Single linked list complete code
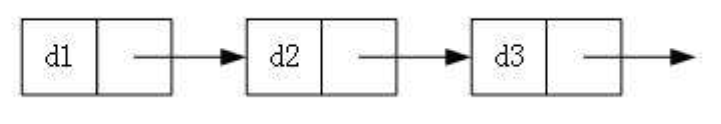
Structure creation
typedef int SLTDataType;
typedef struct SListNode
{
SLTDataType data;
struct SListNode* next;
}SLTNode;Implementation of function interface
//void SLTNodeInit(SLTNode** ps); // The single linked list does not need to be initialized //Destruction of single linked list void SLTNodeDestroy(SLTNode** pphead); //Tail insertion void SLTNodePushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x); //Tail deletion void SLTNodePopBack(SLTNode** pphead); //Head insert void SLTNodePushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x); //Header deletion void SLTNodePopFront(SLTNode** pphead); //Print single linked list void SLTNodePrint(SLTNode* pphead); //Find a data in the single linked list and return the address SLTNode* SLTNodeFind(SLTNode* pphead, SLTDataType x); //Insert a data before pos void SLTNodeInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x); //It is not the data change of pos position, and there is no need to transfer the secondary pointer //Delete pos location data void SLTNodeErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos);
Is it found that many function interfaces are passed secondary pointers. Why?
SLTNode* plist = NULL; // When testing the code, we initialize the first node and receive the pointer
SLTNodePushBack(&plist, 1); // Suppose we insert the header here, which may change the header node, plist It is a primary pointer. In order to change smoothly, we use a secondary pointer here (pointer variables are also variables).
Otherwise, sltnodepushback (plist, 1); The plist is received by the formal parameter after it is passed. There is no way to find the plist point here The address of that space. Although the space corresponding to the formal parameter is changed, the change of the formal parameter will not affect the argument. Plist actual The space pointed to has not changed.
void SLTNodeDestroy(SLTNode** pphead)
void SLTNodeDestroy(SLTNode** pphead)
{
SLTNode* cur = *pphead;
while (cur != NULL)
{
SLTNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = NULL;
cur = next;
}
}//Destroy the linked list of dynamically opened space
void SLTNodeDestroy(SLTNode** pphead) // The header pointer will be changed, so it is necessary to pass the secondary pointer
{
SLTNode* cur = *pphead; // Assign the value of the first element to cur
while (cur != NULL) // When cur is empty, the node is deleted
{
SLTNode* next = cur->next; // Delete from scratch. When deleting a header node, record the of the next node in advance Position to ensure that the following nodes can be found.
free(cur); // Release node
cur = NULL;
cur = next; // The head node position becomes the position recorded in advance
}
}
SLTNode* BuyListNode(SLTDataType x)
SLTNode* BuyListNode(SLTDataType x)
{
SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
else
{
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
}
return newnode;
}Dynamically open up a node size space to store data and the address of the next node
SLTNode* BuyListNode(SLTDataType x)
{
SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode)); // Dynamic development space
if (newnode == NULL) // If the development fails, end the process
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
else
{
newnode->data = x; // The location of a node stores a data
newnode->next = NULL; // The next address pointed to by the node is empty
}
return newnode; // Return the address of the opened node
}
void SLTNodePushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
void SLTNodePushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{
SLTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
*pphead = newnode;
}
else
{
//Find tail node
SLTNode* tail = *pphead;
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newnode;
}
}void SLTNodePushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{
SLTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x); // When inserting data, open up a space and use newnode to receive the data Open up a good space and an address
if (*pphead==NULL) //* pphead==NULL is empty, indicating that the first node has no data. When the linked list is empty
{
* pphead = newnode; // At this time, the newnode is assigned to the first empty node
}
else
{
// Find tail node
SLTNode* tail = *pphead; // Use a pointer to record the tail node to avoid modifying the head node
While (tail - > next! = null) / / if the next node is empty, the current node is not empty and is the last node
{
tail = tail->next; // The tail pointer constantly points to the address of the following node
}
tail->next = newnode; // The next node of the last node is assigned as the node to be inserted, which is equivalent to tail insertion
}
}
void SLTNodePopBack(SLTNode** pphead)
void SLTNodePopBack(SLTNode** pphead)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
if ((*pphead)->next == NULL)
{
SLTNode* cur = *pphead;
free(cur);
cur = NULL;
}
else
{
SLTNode* prev = NULL;
SLTNode* tail = *pphead;
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
prev = tail;
tail = tail->next;
}
free(tail);
tail = NULL;
prev->next = NULL;
}
}Delete the last node of the single linked list
void SLTNodePopBack(SLTNode** pphead)
{
assert(pphead);// Judge whether the received node is a valid address
assert(*pphead);// Judge whether the first node is empty. If it is empty, there is no node
If (* pphead) - > next = = null) / / judge whether there is only one node in the linked list
{
SLTNode* cur = *pphead;
free(cur); // Release the first node
cur = NULL;
}
else
{
SLTNode* prev = NULL; // Record the address of the previous node of the last node, and set it to null for the first time
SLTNode* tail = *pphead;// Record the last node
while (tail->next != NULL) // The tail finally points to the last node
{
prev = tail; //perv is assigned the address of (original) tail
tail = tail->next; // Tail points to the position of the next node
}
free(tail);
tail = NULL;
prev->next = NULL;// Prev stores the address of the penultimate node in the original linked list. At this time, it should be regarded as the tail node
}
}
void SLTNodePushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
void SLTNodePushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{
SLTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
*pphead = newnode;
}
else
{
newnode->next = *pphead;
*pphead = newnode;
}
}Insert a data before the first position in the linked list
void SLTNodePushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x) / / pass the secondary pointer. The first pointer may be modified Nodes
{
SLTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x); // Open up the nodes to join
if (*pphead == NULL) // Judge whether there are no nodes in the linked list
{
* pphead = newnode; // The first empty node is assigned newnode
}
else / / when there is at least one node in the linked list
{
newnode->next = *pphead;// The next node of the new node refers to the head node
* pphead = newnode;// When the head node becomes a new node, it is equivalent to inserting the head
}
}
void SLTNodePopFront(SLTNode** pphead)
void SLTNodePopFront(SLTNode** pphead)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
if ((*pphead)->next == NULL)
{
free(*pphead);
*pphead = NULL;
}
else
{
SLTNode* next = (*pphead)->next;
free(*pphead);
*pphead = next;
}
}Delete the first node in the linked list
void SLTNodePopFront(SLTNode** pphead)
{
assert(pphead);// Judge whether the received node is a valid address
assert(*pphead);// Judge whether the first node is empty. If it is empty, there is no node
If (* pphead) - > next = = null) / / when the next node of the chain header node is empty, there is only one node in the single chain table
{
free(*pphead); // Release header node
* pphead = NULL; // Head node null
}
else / / when the linked list has more than one node
{
SLTNode* next = (*pphead)->next;// Record the position of the next node of the header node in advance to prevent it from being found
free(*pphead);// Release the header node. If there is the previous step, you are not afraid that the following node cannot be found
* pphead = next; // At this time, the header node becomes the next node of the original node. At this time, the header is deleted
}
}
void SLTNodePrint(SLTNode* pphead)
void SLTNodePrint(SLTNode* pphead)
{
SLTNode* cur = pphead;
while (cur!= NULL)
{
printf("%d ", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}Print data in single linked list
void SLTNodePrint(SLTNode* pphead)
{
SLTNode* cur = pphead; // A pointer is used to represent the head node to avoid arbitrary change of the head node
While (cur! = null) / / stop when cur is empty, indicating that the data of nodes that are not empty have been printed
{
printf("%d ", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;// Cur keeps pointing to the next node
}
printf("\n");
}
SLTNode* SLTNodeFind(SLTNode* pphead, SLTDataType x)
SLTNode* SLTNodeFind(SLTNode* pphead, SLTDataType x)
{
SLTNode* cur = pphead;
while (cur != NULL)
{
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL; //Can't find
}Find a data in a single linked list
SLTNode* SLTNodeFind(SLTNode* pphead, SLTDataType x)
{
SLTNode* cur = pphead;// A pointer is used to represent the head node to avoid arbitrary change of the head node
While (cur! = null) / / stop when cur is empty, indicating that the data of the node that is not empty has been judged
{
If (cur - > data = = x) / / when the data to be searched is found
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL; // Can't find
}
void SLTNodeInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
void SLTNodeInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x) //It is not the data change of pos position, and there is no need to transfer the secondary pointer
{
assert(pphead);
assert(pos);
SLTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
if (*pphead == pos)
{
newnode->next = *pphead;
*pphead = newnode;
}
else
{
SLTNode* prev = *pphead;
while (prev->next != pos)
{
prev = prev->next;
}
prev->next = newnode;
newnode->next = pos;
}
}Insert a data before the pos position
void SLTNodeInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x) / / not for pos position If the data is changed, there is no need to transfer the secondary pointer
{
assert(pphead);
assert(pos); // Judge that the value passed from POS is not a valid value
SLTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);// Open up new nodes
if (*pphead == pos) / / when the first node is pos
{
newnode->next = *pphead;
*pphead = newnode;
}
else
{
SLTNode* prev = *pphead;
While (prev - > next! = pos) / / stop when the next node of pos is pos,
{
prev = prev->next;
}
prev->next = newnode;// At this time, prev records the previous node of pos, and the next node of prev points to the new node
newnode->next = pos;// The next node of the new node points to POS
}
}
void SLTNodeErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos)
void SLTNodeErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
assert(pos);
if (*pphead == pos)
{
SLTNodePopFront(pphead);
}
else
{
SLTNode* prev = *pphead;
while (prev->next != pos)
{
prev = prev->next;
}
prev->next = pos->next;
free(pos);
pos = NULL;
}
}Delete the node at pos position in the single linked list
void SLTNodeErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);// Judge whether the first node is empty. If it is empty, there will be no node and it cannot be deleted
assert(pos); // Judge that the value passed from POS is not a valid value
if (*pphead == pos) / / when the pos value is the header node, it is equivalent to header deletion
{
SLTNodePopFront(pphead); // Header deletion
}
else / / when pos does not point to the first node
{
SLTNode* prev = *pphead;// Record the previous node of pos, so that the front and rear nodes can be connected
While (prev - > next! = pos) / / prev event pos ends at the previous node
{
prev = prev->next;
}
prev->next = pos->next; // POS previous node POS next node
free(pos);// Release the POS node, so that the node at the POS position is deleted and the front and rear linked lists are connected
pos = NULL;
}
}
Single linked list complete code
SList.h
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef int SLTDataType;
typedef struct SListNode
{
SLTDataType data;
struct SListNode* next;
}SLTNode;
//void SLTNodeInit(SLTNode** ps); // The single linked list does not need to be initialized
//Destruction of single linked list
void SLTNodeDestroy(SLTNode** pphead);
//Tail insertion
void SLTNodePushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x);
//Tail deletion
void SLTNodePopBack(SLTNode** pphead);
//Head insert
void SLTNodePushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x);
//Header deletion
void SLTNodePopFront(SLTNode** pphead);
//Print single linked list
void SLTNodePrint(SLTNode* pphead);
//Find a data in the single linked list and return the address
SLTNode* SLTNodeFind(SLTNode* pphead, SLTDataType x);
//Insert a data before pos
void SLTNodeInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x); //It is not the data change of pos position, and there is no need to transfer the secondary pointer
//Delete pos location data
void SLTNodeErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos);SList.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"SList.h"
void SLTNodeDestroy(SLTNode** pphead)
{
SLTNode* cur = *pphead;
while (cur != NULL)
{
SLTNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = NULL;
cur = next;
}
}
SLTNode* BuyListNode(SLTDataType x)
{
SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
else
{
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
}
return newnode;
}
void SLTNodePushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{
SLTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
*pphead = newnode;
}
else
{
//Find tail node
SLTNode* tail = *pphead;
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newnode;
}
}
void SLTNodePopBack(SLTNode** pphead)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
if ((*pphead)->next == NULL)
{
SLTNode* cur = *pphead;
free(cur);
cur = NULL;
}
else
{
SLTNode* prev = NULL;
SLTNode* tail = *pphead;
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
prev = tail;
tail = tail->next;
}
free(tail);
tail = NULL;
prev->next = NULL;
}
}
void SLTNodePushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{
SLTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
*pphead = newnode;
}
else
{
newnode->next = *pphead;
*pphead = newnode;
}
}
void SLTNodePopFront(SLTNode** pphead)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
if ((*pphead)->next == NULL)
{
free(*pphead);
*pphead = NULL;
}
else
{
SLTNode* next = (*pphead)->next;
free(*pphead);
*pphead = next;
}
}
void SLTNodePrint(SLTNode* pphead)
{
SLTNode* cur = pphead;
while (cur!= NULL)
{
printf("%d ", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
SLTNode* SLTNodeFind(SLTNode* pphead, SLTDataType x)
{
SLTNode* cur = pphead;
while (cur != NULL)
{
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL; //Can't find
}
void SLTNodeInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x) //It is not the data change of pos position, and there is no need to transfer the secondary pointer
{
assert(pphead);
assert(pos);
SLTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
if (*pphead == pos)
{
newnode->next = *pphead;
*pphead = newnode;
}
else
{
SLTNode* prev = *pphead;
while (prev->next != pos)
{
prev = prev->next;
}
prev->next = newnode;
newnode->next = pos;
}
}
void SLTNodeErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
assert(pos);
if (*pphead == pos)
{
SLTNodePopFront(pphead);
}
else
{
SLTNode* prev = *pphead;
while (prev->next != pos)
{
prev = prev->next;
}
prev->next = pos->next;
free(pos);
pos = NULL;
}
}Code test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"SList.h"
void Test1()
{
SLTNode* plist = NULL;
SLTNodePushBack(&plist, 1);
SLTNodePushBack(&plist, 2);
SLTNodePushBack(&plist, 3);
SLTNodePushBack(&plist, 4);
SLTNodePushBack(&plist, 3);
SLTNodePushBack(&plist, 3);
SLTNodePopBack(&plist);
//SLTNodePopFront(&plist);
SLTNodePushFront(&plist, 10);
SLTNodePushFront(&plist, 20);
SLTNode* pos = SLTNodeFind(plist, 10); //No address
if (pos == NULL)
{
printf("Can't find\n");
}
else
{
SLTNodeInsert(&plist, pos, 100);
}
pos = SLTNodeFind(plist, 3);
//int i = 1;
//while (pos)
//{
// printf("address of the% d data to be searched:% P \ n", I, & (pos - > data));
// i++;
// pos = SLTNodeFind(pos->next, 3);
//}
if(pos!=NULL)
SLTNodeErase(&plist, pos);
SLTNodePrint(plist);
SLTNodeDestroy(&plist);
plist = NULL;
}
int main()
{
Test1();
return 0;
}The test results are as follows: