preface
Originally, I wanted to forget the previous chapters. If you take notes by watching videos, it is much better than the documents I found. Emphasize that I am not lazy or lazy
1, Having clause of group by
having Clause in select In the sentence and group by Clause, used to tell group by Clause which groups are included in the output, having about group by The function of is equivalent to where about select Is used to set conditions. use having Clause allows the result set to contain or remove an entire set of data
2, ALTER command
1. Add table fields
ALTER TABLE [table_name] ADD [column_name] [dataType];
2. Modify table fields
ALTER TABLE [table_name] MODIFY [column_name] varchar(200); ALTER TABLE [table_name] change [old_column_name] [new_column_name] varchar(200);
3. Delete table fields
ALTER TABLE [table_name] DROP [column_name]
4. Modify table name
ALTER TABLE [table_name] RENAME TO [new_table_name];
3, Index
1. Indexing principle:
Take the table of contents page (index) of a Chinese dictionary for example. We can quickly find the required words according to the table of contents (index) sorted by pinyin, strokes, partial radicals, etc.
2. Index data structure:
Any data structure is not created out of thin air. It must have its background and usage scenarios. Let's summarize what we need this data structure to do. In fact, it is very simple, that is, control the disk IO times in a small order of magnitude, preferably a constant order of magnitude, every time we look for data. So we think if a highly controllable multi-channel search tree can meet the demand? In this way, b + tree came into being.
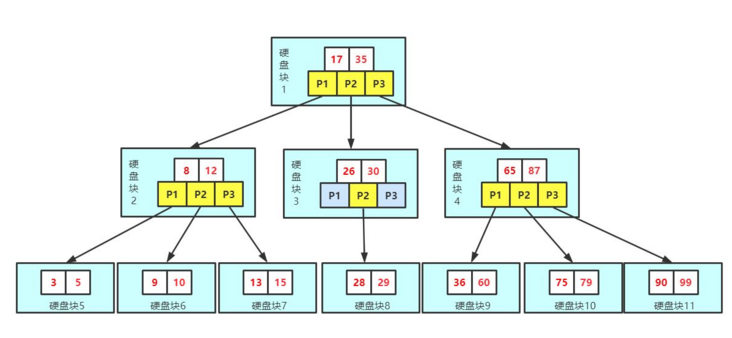
3. Category of index:
3.1. Index (general index)
ALTER TABLE [table_name] ADD INDEX index_name ( [column] );
3.2. Primary key index
ALTER TABLE [table_name] ADD PRIMARY KEY ( [column] );
3.3. Unique (unique index)
ALTER TABLE [table_name] ADD UNIQUE ([column]);
3.4. Fulltext (full text index)
ALTER TABLE [table_name] ADD FULLTEXT ([column]);
3.5. Multi column index
ALTER TABLE [table_name] ADD INDEX index_name ( [columns...,]);
4. Several cases of index invalidation
4.1 index field can be null
Using is null or is not null may invalidate the index
4.2 like wildcards may cause index invalidation
like queries that start with% will invalidate the index.
select * from [table_name] where [column_name] like '%name' ;
4.3 using built-in functions on index columns will certainly lead to index invalidation
select * from [table_name] where DATE_ADD(create_time, INTERVAL 1 DAY) = 7;
4, Characteristics of transactions

Atomicity: all operations in a transaction are either completed or not completed, and will not end in an intermediate link. If an error occurs during the execution of a transaction, it will be rolled back to the state before the start of the transaction, as if the transaction had never been executed.
Consistency: the integrity of the database is not destroyed before and after the transaction. This means that the written data must fully comply with all preset rules, including the accuracy and serialization of the data, and the subsequent database can spontaneously complete the predetermined work.
Isolation: the ability of a database to allow multiple concurrent transactions to read, write and modify their data at the same time. Isolation can prevent data inconsistency caused by cross execution when multiple transactions are executed concurrently. Transaction isolation is divided into different levels, including Read uncommitted, read committed, repeatable read, and Serializable.
Durability: after the transaction is completed, the modification of data is permanent and will not be lost even if the system fails.
1. Transaction operation

5, Difference between InnoDB and MyISAM
5.1 InnoDB supports transactions. MyISAM does not support transactions. This is one of the important reasons why MySQL changed the default storage engine from MyISAM to InnoDB
5.2 InnoDB Supports foreign keys, and MyISAM I won't support it. For a containing foreign keys InnoDB Table to MYISAM Will fail
6, Stored functions, stored procedures, triggers, views
6.1 common functions:
sum: sum
min: min
max: maximum count: statistics group_concat([column_name]): group and merge this field
substr([column_name],pos,len): intercepting string function
......
6.2 view
definition:
The stored query statement, when called, produces a result set, and the view acts as a virtual table
CREATE VIEW myview AS <selectSql>;
6.3 storage function
Define variables:
Using DECLARE to define local variables can only be used in stored procedures and stored functions
In the analysis of process statements, we use the declaration and setting of variables in stored procedures. Because these variables can only be used in stored procedures, they are also called local variables. The declaration of variables can use the following syntax:
DECLARE variable name [, variable name 2...] Data type [default value];
DECLARE num INT DEFAULT 10 ; -- Define variables num,Data type is INT Type, the default value is 10
DECLARE mult_a,mult_b int; //Define multiple variables
Assign values to variables:
1. Use set
set var =value;
2. Using select
select var := value;
Syntax format
CREATE FUNCTION function([Parameter type data type[,....]]) RETURNS Return type BEGIN SQL sentence..... RETURN (Returned data) END
[](https://blog.csdn.net/jikuicu...)
6.4 stored procedures
Input parameters, output parameters and input-output parameters
Input parameters: IN input parameters: OUT input output parameters: INOUT
Query stored procedure:
show procedure STATUS where Db='Database name' SHOW PROCEDURE STATUS //Query all stored procedures SHOW PROCEDURE STATUS LIKE 'pattern' //Query stored procedures required by symbols For example: SHOW PROCEDURE STATUS LIKE 'myuse' The name of the stored procedure is myuse Information
Query database character coding
show variables where Variable_name like 'collation%';
Delete stored procedure:
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS myuse //IF EXISTS, you'd better take it with you, or an error will be reported
Basic style for creating stored procedures:
Stored functions are somewhat similar to stored procedures. In short, they encapsulate a piece of sql code, complete a specific function, and return results. The syntax is as follows:
create procedure Stored procedure name (type of parameter, parameter 1 data type,
Parameter type parameter 2 data type...Type of parameter n (data type)
BEGIN
// Processing content, in which functions and conditional statements can be used
ENDgrammar
CREATE PROCEDURE Stored procedure name()
BEGIN
//sql
ENDDifference from storage function
1. Different from stored procedures, output parameter (OUT) and input / output parameter (INOUT) types cannot be specified IN stored functions. Storage functions can only specify input types and cannot take IN. At the same time, the storage function can RETURN the processing result to the caller through the RETURN command.
2. The storage function must be in the return after the parameter list and the data type returned by the instruction. The storage function must have a return value, and the stored procedure can have no return value.
3. The calling methods are different. The stored procedure uses select and the stored function uses call
4. Storage function parameters cannot use in, out or inout
6.5 trigger
definition:
A trigger is a database object related to a table. It is triggered when the defined conditions are met and executes the statement set defined in the trigger. This feature of trigger can help the application to ensure the integrity of data on the database side.
Trigger_event:
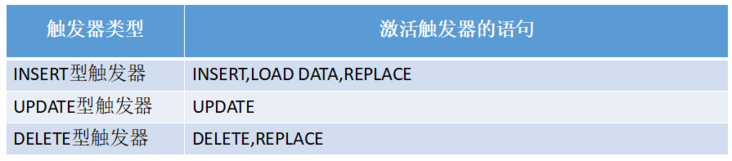
7, JDBC
6.1 name interpretation
Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) is an application program interface used in Java language to standardize how client programs access the database. It provides methods such as querying and updating data in the database. JDBC is also a trademark of Sun Microsystems. We usually say that JDBC is oriented to relational database.
6.2 JDBC programming steps
Load driver:
Class.forName(driverClass)
--->Specific use
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver") //Load MySql driver
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver")//Load Oracle driver Get database connection:
DriverManager.getConnection("<URL>", "account number", "password");
---- mysql Specific use
DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://< IP address >: < port > / < databasename > "," account "," password ");To create a Statement\PreparedStatement object:
conn.createStatement(); conn.prepareStatement(sql);//Get precompiled statement object [recommended]
6.2 important JDBC interfaces and APIs
PreparedStatement
| method | effect | Return results | remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| setBytes(int parameterIndex, byte x[]); | Set a value for the parameter column. The value type is byte array | void | ||
| setInt(int parameterIndex, int x); | Set a value for the parameter column. The value type is byte array | void | ||
| setLong(int parameterIndex, long x); | Set a value for the parameter column. The value type is long | void | ||
| setString(int parameterIndex, String x); | void | |||
| setBoolean(int parameterIndex, boolean x); | void | |||
| setNull(int parameterIndex, int sqlType); | void | |||
| setTime(int parameterIndex, java.sql.Time x) | void | |||
| setObject(int parameterIndex, Object x) ; | Set a value for the parameter column. The value type is object type | |||
| clearParameters() | Clear preprocessed parameters | void | ||
| addBatch(); | void | |||
| addBatch( String sql ); | Adds the given SQL command to this command list. The commands in this list can be executed in batch by calling methods. | void | ||
| executeBatch(); | Execute batch processing statements, generally adding, modifying and deleting | void | ||
| clearBatch() ; | Clear all objects in this batch mode | void | ||
| execute(); | CRUD is OK when any sql statement is executed. If it is a new, modified or deleted statement, you can use getUpdateCount() to view the affected lines. If it is a query statement, you can call getMoreResults() to get the search results | boolean | ||
| execute(String sql); | Execute the given SQL statement, which may return multiple results. In some (uncommon) cases, a single SQL statement may return multiple result sets and / or update counts. | boolean | ||
| getUpdateCount(); | Get the number of impacts | int | ||
| getMoreResults(); | boolean | |||
| executeQuery(); | Execute query operation | |||
| #### ResultSet | ||||
| executeUpdate(); | Perform update operation | boolean | ||
| getResultSet(); | Get query result set | |||
| #### ResultSet |
ResultSet
| method | effect | remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|
| next() | Moves the cursor forward one line from the current position. A ResultSet cursor is initially positioned before the first row; The first call to the method makes the first line the current line; This second call makes the second row the current row, and so on. | ||
| getString(int columnIndex) | The value of the specified column in the current row is of type String | ||
| getBoolean(int columnIndex) | The value of the specified column in the current row is of type Bool | ||
| getByte(int columnIndex) | The value of the specified column in the current row is of type byte | ||
| getBytes(int columnIndex) | The value of the specified column in the current row is a byte array type | ||
| getInt(int columnIndex) | |||
| getLong(int columnIndex) | |||
| getDouble(int columnIndex) | |||
| getTime(int columnIndex) | The value of the specified column in the current row is of type Time | The returned Time belongs to Java sql. In the bag | |
| getTimestamp(int columnIndex) | The value of the specified column in the current row is of type Timestamp | The returned Time belongs to Java sql. In the bag |
6.3 jdbc encapsulation
Purpose:
Generate and execute insert statements through entity object reflection
raw material:
0. Database sql
CREATE TABLE `t_book_info` ( `id` int(20) NOT NULL, `name` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL, `author` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL, `push_time` datetime DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
1. Entity object (TBookInfo)
package com.jdbc.demo;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* <ul>
* <li>Title: TBookInfo</li>
* <li>Description: TODO </li>
* </ul>
*
* @author Programmer ken
* @date 2021-12-22 16:11
*/
@TableName("t_book_info")
public class TBookInfo {
@TableField(name = "id",autoIncrement=true)
private int id;
@TableField(name = "name")
private String name;
@TableField(name = "author")
private String author;
@TableField(name = "push_time")
private Date pushTime;
//get set method omitted
}
2. Annotation class (TableName and TableField act on class and field respectively)
TableName class
package com.jdbc.demo;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.FIELD;
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.TYPE;
@Documented
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface TableName {
String value();
}
TableField class
package com.jdbc.demo;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Documented
@Target({ElementType.FIELD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface TableField {
String name();
boolean exist() default true;
boolean autoIncrement() default false;
}
3. Actual code (reflection mechanism is required)
package com.jdbc.demo;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
/**
* <ul>
* <li>Title: JdbcUtil</li>
* <li>Description: TODO </li>
* </ul>
*
* @author:Programmer ken
* @date 2021-12-22 15:55
*/
public class JdbcUtil {
private static String url ="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mytest?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&allowMultiQueries=true";
private static String user ="root";
private static String password ="123456";
//Method of obtaining connection
private static Connection getConnect() {
Connection con =null;
try {
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return con;
}
// Encapsulate the new unified
//sql statement is required for entity class = > generic T = > generation
/**
* Function Description:
* @param t
* @return: void
* @author:Programmer ken
* @date: 2021-12-22 16:08
*/
public static <T> void insert(T t) {
Class<?> aClass = t.getClass();
Field[] fields = aClass.getDeclaredFields();
String insertSqlTemp = "insert into #{tableName} (#{columns}) values(#{columnValues})";
StringBuffer columnsSbf = new StringBuffer();
StringBuffer columnValuesSbf = new StringBuffer();
TableName tableName = aClass.getAnnotation(TableName.class);
if(tableName!=null){
insertSqlTemp = insertSqlTemp.replace(" #{tableName}",tableName.value());
}
List<Field> fieldList =new ArrayList<Field>();
TableField tableField =null;
for (Field field : fields) {
tableField = field.getAnnotation(TableField.class);
if(tableField!=null && tableField.exist() && !tableField.autoIncrement()){
columnsSbf.append(","+tableField.name());
columnValuesSbf.append(",?");
fieldList.add(field);
}
field.setAccessible(true);
}
if(columnsSbf.length()>0){
insertSqlTemp =insertSqlTemp.replace("#{columns}",columnsSbf.delete(0,1)).replace("#{columnValues}",columnValuesSbf.delete(0,1));
}
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pst = null;
try {
conn = getConnect();
pst= conn.prepareStatement(insertSqlTemp);
int ind =1;
for (Field field : fieldList) {
field.setAccessible(true);
try {
pst.setObject(ind,field.get(t));
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
ind++;
}
int row = pst.executeUpdate();
System.out.println("Number of affected rows:"+row);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(pst!=null){
pst.close();
}
if(conn!=null){
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
Other examples
Batch precompiled statements
package com.ken.sys.common.util;
import com.ken.sys.common.entity.DbSettingInfo;
import com.ken.sys.common.ifs.PrepareFunction;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JdbcUtil {
private static Connection conn = null;
private static String finaUrl= "jdbc:mysql://192.168.0.118:3306/erp-sy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&allowMultiQueries=true";
private static String finaUser = "root";
private static String finaPass = "123456";
//The default is mysql
private static String driver ="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
//Default maximum number of submissions
private static final int COMMIT_MAX_COUNT = 20000;
static {
try {
String rootPath = JdbcUtil.class.getClassLoader().getResource("").getPath();
//Read the SQL configuration file. The configuration file is under src
InputStream in = new FileInputStream( rootPath+"jdbc.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(in);
//Get parameters
driver = properties.getProperty("jdbc.driver");
finaUrl = properties.getProperty("jdbc.url");
finaUser = properties.getProperty("jdbc.username");
finaPass = properties.getProperty("jdbc.password");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//The connection is established according to the configuration of the properties file
public static Connection getConnection(){
return getConnection(driver,finaUrl,finaUser,finaPass);
}
//The connection is established according to the configuration of the properties file
private static Connection getConnection(DbSettingInfo dbSettingInfo){
if(dbSettingInfo==null){
throw new Error("dbSettingInfo is not allowed to be null");
}
return getConnection(dbSettingInfo.getDriver(),dbSettingInfo.getDbUrl(),dbSettingInfo.getUserName(),dbSettingInfo.getPassword());
}
public static Connection getConnection(String driver,String url, String user, String pass){
try {
Class.forName(driver);
conn= DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,pass);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return conn;
}
public static void closeConnection(Connection conn, PreparedStatement stmt, ResultSet rs){
try {
if(rs!=null) {
rs.close();
}
if(stmt!=null) {
stmt.close();
}
if(conn!=null) {
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* Function Description: batch execute sql
* @param dbSettingInfo
* @param executeSql
* @param list
* @return: void
* @author:Programmer ken
* @date: 2021-12-09 10:44
*/
public static <T> void executeBatch(DbSettingInfo dbSettingInfo
,String executeSql, List<T> list){
executeBatch(dbSettingInfo,executeSql,list,COMMIT_MAX_COUNT,null);
}
/**
* Function Description: batch execute sql
* @param dbSettingInfo
* @param executeSql
* @param list
* @param commitMaxCount
* @return: void
* @author:Programmer ken
* @date: 2021-12-09 10:44
*/
public static <T> void executeBatch(DbSettingInfo dbSettingInfo
,String executeSql, List<T> list, int commitMaxCount){
executeBatch(dbSettingInfo,executeSql,list,commitMaxCount,null);
}
/**
* Function Description: batch execute sql
* @param dbSettingInfo database information
* @param executeSql Execute sql
* @param list data source
* @param commitMaxCount Maximum number of submissions
* @param prepareFunction Generally, preprocessing parameters can be used for external intervention
* @return: void
* @author:Programmer ken
* @date: 2021-12-09 10:44
*/
public static <T> void executeBatch(DbSettingInfo dbSettingInfo
,String executeSql, List<T> list, int commitMaxCount, PrepareFunction prepareFunction){
PreparedStatement pstmt =null;
Connection conn =null;
try {
commitMaxCount = commitMaxCount>0 && commitMaxCount<=COMMIT_MAX_COUNT ?commitMaxCount:COMMIT_MAX_COUNT;//The default maximum number of submissions is 2000
conn = getConnection(dbSettingInfo);
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(executeSql);
int ind =0;
boolean hand =true;
for (T t : list) {
if(prepareFunction!=null){
hand = prepareFunction.hand(t, pstmt);//Parameters are set here
}
//Do not execute this data
if(!hand){
continue;
}
pstmt.addBatch();
ind++;
if(ind==commitMaxCount){
pstmt.executeBatch();//Batch submission
pstmt.clearParameters();//Clear parameters
ind =0;
}
}
//The maximum number of submissions is insufficient. There are still inserts to submit
if(ind>0){
pstmt.executeBatch();//Batch submission
pstmt.clearParameters();//Clear parameters
}
//Commit, set transaction initial value
conn.commit();
conn.setAutoCommit(true);
} catch (Exception e) {
//Commit failed, execute rollback
try {
if(conn!=null){
conn.rollback();
}
} catch (SQLException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(pstmt!=null){
pstmt.close();
}
if(conn != null){
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
8, Database backup and restore
8.1 database backup (MySQL export data)
8.1.1 using select Into outfile statementexport data
Syntax:
select * from [table_name] INTO OUTFILE "[The specific location of the file is accurate to the file name]";
1. Note that double backslashes (\) are used for file backslashes (\)
2. Operations are performed in mysql, not on the command line, so they can be nested in the xml of mybatis
<update id="selectExport" >
SELECT * FROM [table_name] INTO OUTFILE "[Full path of specific export file]";
</update>[
](https://blog.csdn.net/hanshim...)
Errors encountered:
select * from t_project_info INTO OUTFILE "E:\\Database backup\\backup_data.txt" > 1290 - The MySQL server is running with the --secure-file-priv option so it cannot execute this statement > time: 0s
Solution:
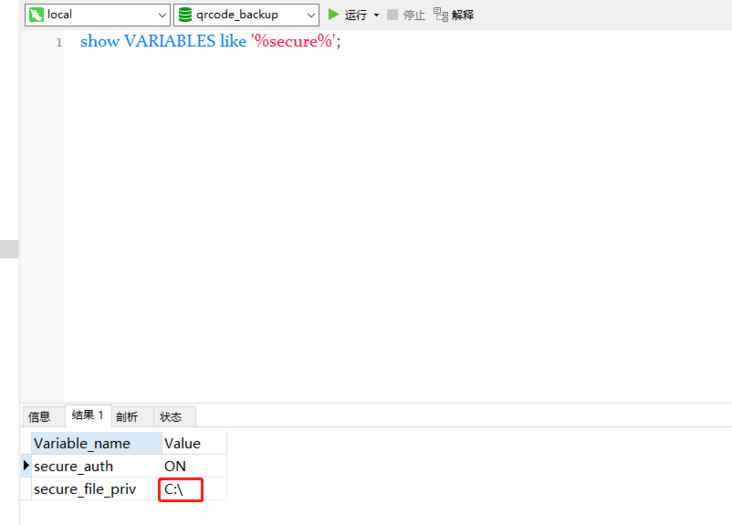 Use show VARIABLES like '%secure%'; Query secure_ file_ Whether priv is set. This value is the root directory of the exported file. The setting is shown in the figure, which means that the exported file can only exist under disk C. If you need to modify this reference, modify the mysql configuration file, which is generally named my ini .
Use show VARIABLES like '%secure%'; Query secure_ file_ Whether priv is set. This value is the root directory of the exported file. The setting is shown in the figure, which means that the exported file can only exist under disk C. If you need to modify this reference, modify the mysql configuration file, which is generally named my ini .
There are three cases for the value of secure file priv:
secure_file_prive=null ––limit mysqld Import and export not allowed secure_file_priv=/path/ – --limit mysqld The import and export of can only occur in the default/path/Directory secure_file_priv='' – --incorrect mysqld Import and export restrictions
[
](https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_...)
8.1.2 using the [mysqldump] command line
If you need to copy data to other MySQL servers, you can specify the database name and data table in the mysqldump command.
grammar
1. Export all table data of a single database
mysqldump -h [ipAddress] -u [user] -p[password] [database] --default-character-set=utf8 --hex-blob >[backUpPath][exportFileName]
Example
mysqldump -h 127.0.0.1 -u root -p123456 qrcode-beiyong --default-character-set=utf8 --hex-blob >E:\Database backup\qrcode_2021.sql
2. Export all table data of a single database
mysqldump -u [user] -p[password] [database] --tables table_name1 table_name2 table_name3 >[backUpPath][exportFileName]
Example
mysqldump -u root -p123456 qrcode-beiyong --tables t_project_info t_bid_auth_peopel_info >E:\Database backup\qrcode_2022.sql
2. Export all database and table data
mysqldump -u [user] -p[password] –all-databases >[backUpPath][exportFileName]
Example
mysqldump -u root -p123456 –all-databases>E:\Database backup\qrcode_2021.sql
Parameter description
| Parameter name | abbreviation | meaning |
|---|---|---|
| --host | -h | Server IP address |
| --port | -P | Server port number |
| --user | -u | MySQL user name |
| --pasword | -p | MySQL password |
| --databases | Specify the database to back up | |
| --all-databases | Back up all databases on the mysql server | |
| --compact | Compression mode produces less output | |
| --comments | Add comment information | |
| --complete-insert | Output completed insert statement | |
| --lock-tables | Lock all database tables before backup | |
| --no-create-db/--no-create-info | Prohibit generating database creation statements | |
| --force | Continue the backup operation when an error occurs | |
| --default-character-set | Specifies the default character set | |
| --add-locks | Locking database tables when backing up database tables |
be careful:
1. -- default character set = utf8 set the code set to utf8. You can customize the code set or not
2. -- hex blob is used to export binary data in the system. If there is no binary data, it can be removed
3.-h [ipAddress] represents the remote connection address. If there is no connection address, it is the connection host by default
4. – all databases stands for exporting all databases
5. Do not use spaces for host - p[password] -p and password. The password can be empty, but the command line may verify the password in the next step
8.2 database restore [import data]
8.2.1 LOAD DATA command import
Syntax:
LOAD DATA LOCAL INFILE '[Specific location of documents]' INTO TABLE [table_name];
Example:
LOAD DATA LOCAL INFILE 'C:\\ProgramData\\MySQL\\MySQL Server 5.6\\Uploads\\backup_data.txt' INTO TABLE t_project_info
be careful:
1. This is not executed on the mysql command line, but as a mysql statement. All can be embedded in the xml [map layer] tag
2. The data exported by mysqldump command is often used as the data source
8.2.2 mysql command import
Syntax:
mysql -u[user] -p[password] < [backUpPath][exportFileName]
Example:
mysql -uroot -p123456 qrcode-backup< E:\Database backup\qrcode_2021.sql
be careful:
1. This must be executed on the mysql command line
2. Often use Select The data exported by the into outfile statement is used as the data source
Video link:
Welcome to my official account: programmer ken, the way of procedure, let's explore together and make progress together.