Introduction to Linux distribution
Linux branch reference website: http://futurist.se/gldt/
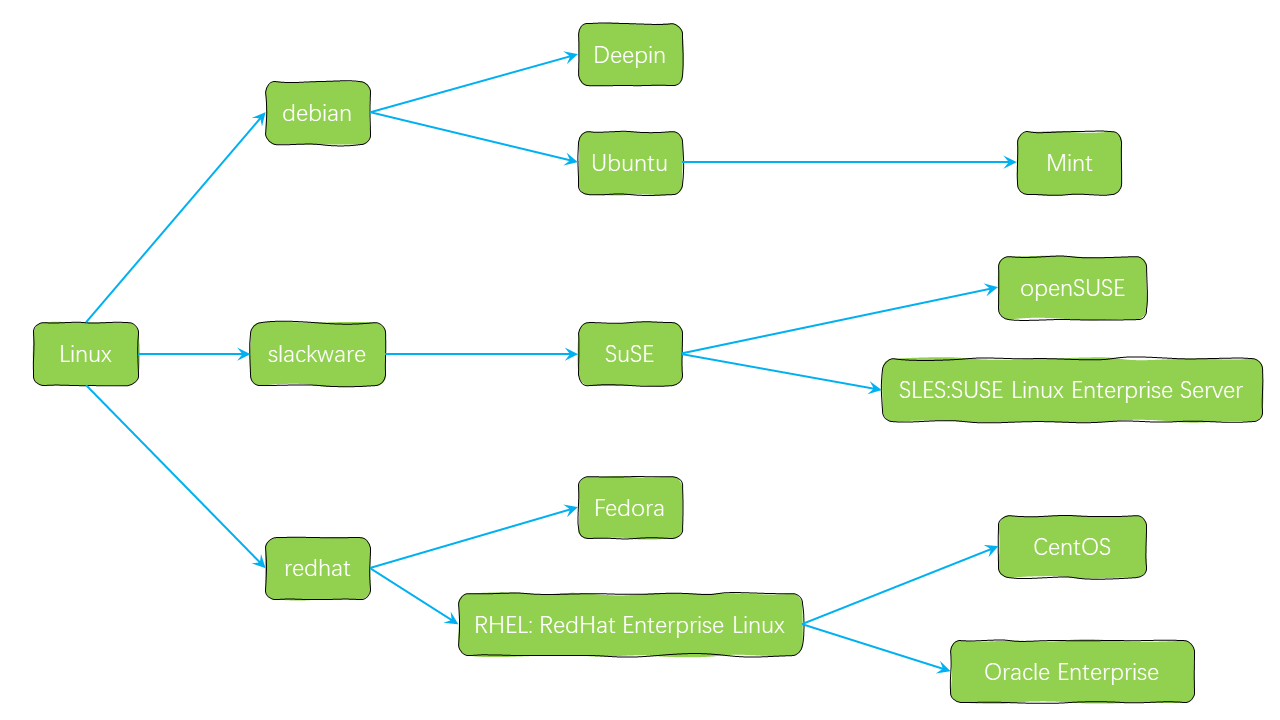
Common Linux distributions
- debian system: Ubuntu, Deepin, Mint
- **slackware: openSUSE
- redhat: Fedora, CentOS, RHEL, Oracle Enterprise
What Linux distributions have in common: the Linux kernel
Linux has many distributions, but they are all considered Linux. Why? The reason is that they all adopt the Linux kernel, which is the core of the operating system. It bridges the work of the system with the underlying hardware. It also includes many device drivers to support the use of various hardware
Differences between Linux distributions
Package manager
Each Linux distribution contains various ways to install software, but they all have an underlying package manager.
- On Debian based distributions such as Ubuntu and Linux Mint, dpkg can be accessed through the apt dependency parser.
- For Redhat systems, such as CentOS, RPM is the package manager, which relies on the yum command for parsing
Differences in other configurations
network configuration
- The CentOS default network configuration file is in the path / etc / sysconfig / network scripts /, usually ifcfg-[ifname]
- After Ubuntu 17, the default network configuration file is in / etc/netplan / path and ends with yaml. There is no special limit on the file name
Default firewall
- The default firewall of CentOS 6 is iptables, and the default firewall of CentOS 7 is firewall
- The default firewall for Ubuntu 20 is ufw
Installing a Linux distribution
Installing CentOS 7.9
VMware installing CentOS 7.9_Sky_Nemo's blog - CSDN blog
Install Ubuntu 20.04.2
Vmware installation Ubuntu 20.04.2_Sky_Nemo's blog - CSDN blog
Common settings after installation
The following settings apply to CentOS 7.9 Ubuntu 20.04.2
Set host name
[root@localhost ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname aiden # Effective after re login [root@aiden ~]#
Set time zone
[root@aiden ~]# timedatectl list-timezones | grep Shanghai Asia/Shanghai [root@aiden ~]# timedatectl set-timezone Asia/Shanghai
Set the number of history reserved entries and the command execution time
# Temporary settings
[root@aiden ~]# export HISTSIZE=3000
[root@aiden ~]# export HISTTIMEFORMAT="%Y-%m-%d %H-%M-%S "
# Permanent settings
[root@luna ~]# cat > /etc/profile.d/history_set.sh <<EOF
# history command set
export HISTSIZE=3000
export HISTTIMEFORMAT="%Y-%m-%d %H-%M-%S "
EOF
# Load for settings to take effect
[root@aiden ~]# source /etc/profile
# View effect
[root@aiden ~]# history | head -n3
1 2021-07-10 23-58-24 vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33
2 2021-07-10 23-58-24 systemctl restart network
3 2021-07-10 23-58-24 ping www.baidu.com
Linux Philosophy
- All files (including hardware)
- Small, single purpose program
- Link programs to complete complex tasks together
- Avoid confusing user interfaces
- The configuration data is stored in text
Common command formats for Linux
COMMAND [OPTIONS...] [ARGUMENTS...] COMMAND [COMMAND] [COMMAND] ....
COMMAND
**OPTIONS, OPTIONS: * * used to enable or disable one or more functions of the command
- Short options: UNIX style options, - c for example: - l, -h
- Long options: GNU style options, – word, for example: – all, --human
- BSD style option: a letter, for example: A, is relatively less used
**ARGUMENTS, parameter: * * the target of the command, such as file name, user name, etc
Example:
# Short options [root@aiden ~]# echo -e "1\t2" 1 2 # Long option [root@aiden ~]# date --utc Sat Jul 10 16:34:37 UTC 2021 # BSD style [root@aiden ~]# ps a PID TTY STAT TIME COMMAND 1351 tty1 Ss+ 0:00 -bash 10446 pts/1 Ss 0:00 -bash 10630 pts/1 R+ 0:00 ps a
System directory usage
Linux directory structure
[the external chain picture transfer fails. The source station may have an anti-theft chain mechanism. It is recommended to save the picture and upload it directly (img-DH5pRaO7-1625983984558)(.\pic\dir_struc.png)]
- Files and directories are organized into a single root inverted tree structure
- The file system starts from the root directory and is represented by /
- Root file system (rootfs): root file system
- Standard Linux file system (e.g. ext4). The file name is case sensitive, such as mail, mail, mail and mail The first file is hidden
- The symbol for path separation is/
- The maximum length of the file name is 255 bytes
- The maximum length of the file name including the path is 4095 bytes
- Blue – > directory, green – > executable, red – > compressed file, light blue – > linked file, gray – > other files
- All characters are valid except slash and NUL. However, directory names and files with special characters are not recommended. Some characters need to be quoted in quotation marks
- Each file has two types of related data: metadata, i.e. attribute, and data, i.e. file content
File system hierarchy of Linux: FHS file system Hierarchy Standard: https://www.pathname.com/fhs/
Common directory functions
/bin: Basic commands used by all users; Cannot be associated to a separate partition, OS Start the program that will be used
/boot: Boot file storage directory, kernel file(vmlinuz),boot loader (bootloader, grub)Are stored in this directory
/dev: Storage location of equipment files and special files
b: block device,Random access
c: character device,Linear access
/etc: Profile directory
/home/[USERNAME]: Home directory of ordinary users
/root: Administrator's home directory
/sbin: Basic commands of management class; Cannot be associated to a separate partition, OS Start the program that will be used
/tmp: Temporary file storage location
/usr: universal shared, read-only data
bin: Application program provided to ensure that the system has complete functions
sbin:
lib: 32 Bit usage
lib64: Only 64 bit systems exist
include: C Program header file(header files)
share: Structured independent data, e.g doc, man etc.
local: Installation location of third-party applications
bin, sbin, lib, lib64, etc, share
/var: variable data files
cache: Application cache data directory
lib: Application status information data
local: Dedicated to/usr/local Applications under store variable data
lock: Lock file
log: Log directory and files
opt: Dedicated to/opt Applications under store variable data
run: Running process related data,Typically used to store processes pid file
spool: Application data pool
tmp: Save temporary data generated between system restarts
/lib: The basic shared library files and kernel module files that the program depends on at startup(/lib/modules)
/lib64: Dedicated to x86_64 Secondary shared library file storage location on the system
/media: Portable mobile device mount point
/mnt: Temporary file system mount point
/opt: Installation location of third-party applications
/srv: Data used by services running on the system
/proc: Virtual file system for outputting kernel and process information
/sys: Used to output information about hardware devices on the current system virtual file system
/selinux: security enhanced Linux,selinux Storage location of relevant security policies and other information
Application common directories
Binary program:/bin, /sbin, /usr/bin, /usr/sbin, /usr/local/bin, /usr/local/sbin Library files:/lib, /lib64, /usr/lib, /usr/lib64, /usr/local/lib, /usr/local/lib64 Profile:/etc, /etc/DIRECTORY, /usr/local/etc Help files:/usr/share/man, /usr/share/doc, /usr/local/share/man, /usr/local/share/doc
Changes in directory structure after CentOS 7
Some directories are combined in the form of soft links
- /Bin and / usr/bin
- /sbin and / usr/sbin
- /lib and / usr/lib
- /Lib64 and / usr/lib64
[root@aiden ~]# ls -ild /bin /usr/bin 3505 lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 Mar 7 2019 /bin -> usr/bin 15 dr-xr-xr-x. 2 root root 36864 Jul 9 11:38 /usr/bin [root@aiden ~]# ls -ild /sbin /usr/sbin 33 lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 8 Mar 7 2019 /sbin -> usr/sbin 16 dr-xr-xr-x. 2 root root 20480 Feb 28 22:08 /usr/sbin [root@aiden ~]# ls -ild /lib /usr/lib 25 lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 Mar 7 2019 /lib -> usr/lib 17 dr-xr-xr-x. 30 root root 4096 Feb 28 22:27 /usr/lib [root@aiden ~]# ls -ild /lib64 /usr/lib64 27 lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 9 Mar 7 2019 /lib64 -> usr/lib64 24 dr-xr-xr-x. 51 root root 32768 Jun 15 19:04 /usr/lib64