Introduction to Netcat
Netcat (nc for short) is a powerful command line Network tool is used to establish TCP/UDP connection between two machines and read and write data through standard input and output
Netcat installation
Most Linux distributions will come with Netcat. You can use the nc command to check whether Netcat is installed in the system
$ nc usage: nc [-46AacCDdEFhklMnOortUuvz] [-K tc] [-b boundif] [-i interval] [-p source_port] [--apple-recv-anyif] [--apple-awdl-unres] [--apple-boundif ifbound] [--apple-no-cellular] [--apple-no-expensive] [--apple-no-flowadv] [--apple-tcp-timeout conntimo] [--apple-tcp-keepalive keepidle] [--apple-tcp-keepintvl keepintvl] [--apple-tcp-keepcnt keepcnt] [--apple-tclass tclass] [--tcp-adp-rtimo num_probes] [--apple-initcoproc-allow] [--apple-tcp-adp-wtimo num_probes] [--setsockopt-later] [--apple-no-connectx] [--apple-delegate-pid pid] [--apple-delegate-uuid uuid] [--apple-kao] [--apple-ext-bk-idle] [--apple-netsvctype svc] [---apple-nowakefromsleep] [--apple-notify-ack] [--apple-sockev] [--apple-tos tos] [--apple-tos-cmsg] [-s source_ip_address] [-w timeout] [-X proxy_version] [-x proxy_address[:port]] [hostname] [port[s]]
The above prompt message indicates that Netcat has been installed in the system. If it is not installed, you can use the following command to install it
$ wget https://sourceforge.NET/projects/netcat/files/netcat/0.7.1/netcat-0.7.1.tar.gz $ tar zxvf netcat-0.7.1.tar.gz $ cd netcat-0.7.1 $ ./configure $ make $ make install
Quick start
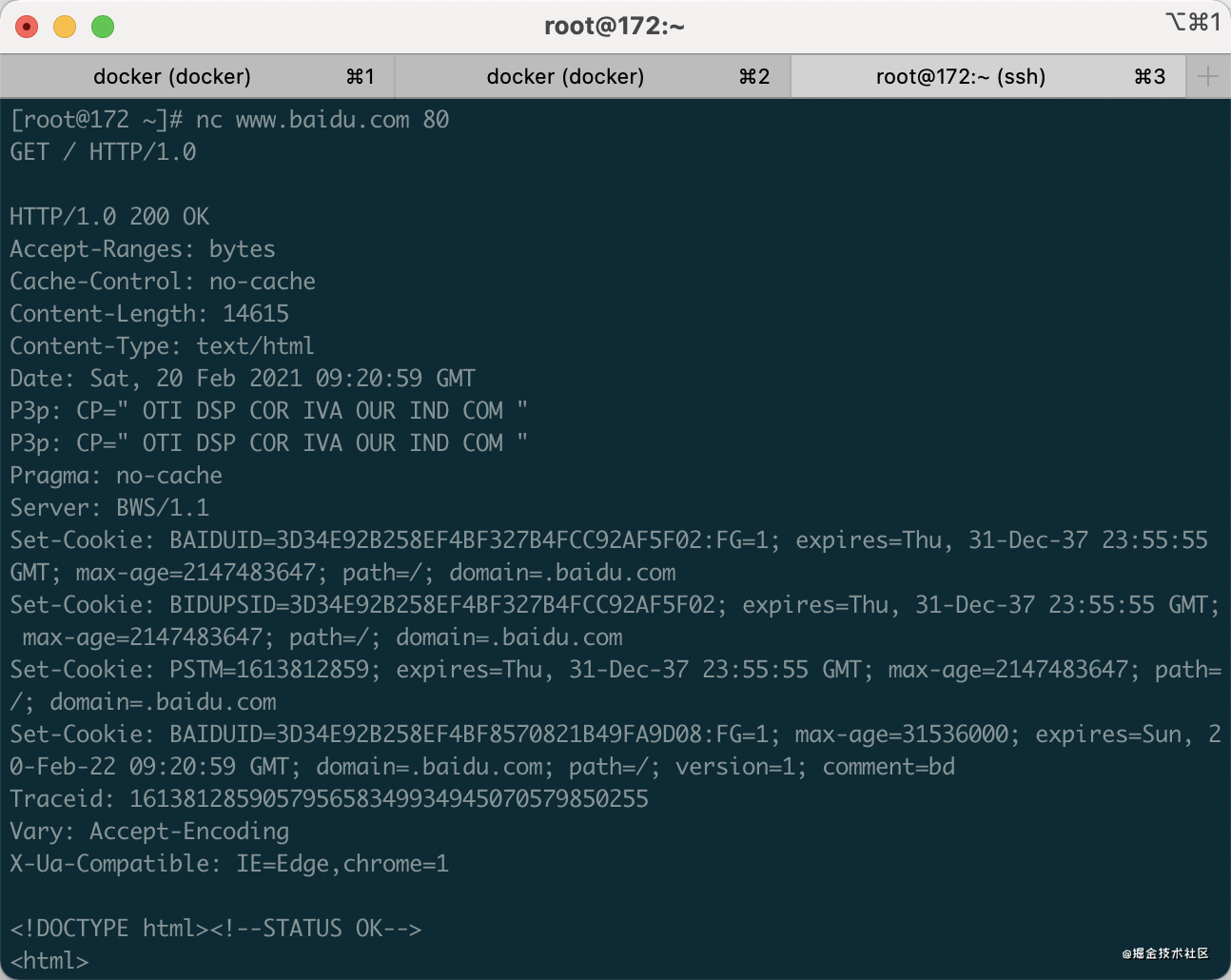
We can use Netcat to establish a connection with the HTTP server. Take Baidu as an example, use the following command to establish a TCP connection with Baidu
$ nc www.baidu.com 80
The first parameter is the address of the server to establish the connection, and the second parameter is the connection port. After the connection is successfully established, you will enter the input / output interface, where you can send / receive data to the TCP connection. If Baidu server sends a GET request, simulate the browser to visit Baidu home page, enter GET / HTTP/1.0 and press enter twice
$ nc www.baidu.com 80 GET / HTTP/1.0 (enter) (enter)
After sending the request, you will receive the following HTTP response
HTTP/1.0 200 OK Accept-Ranges: bytes Cache-Control: no-cache Content-Length: 14615 Content-Type: text/html ...
The complete process is as follows
Other usage scenarios
Port scan
Netcat can also be used for port scanning to find open ports on some machines
$ nc -zv localhost 9995-9999 nc: connect to localhost port 9995 (tcp) failed: Connection refused nc: connect to localhost port 9995 (tcp) failed: Connection refused nc: connect to localhost port 9996 (tcp) failed: Connection refused nc: connect to localhost port 9996 (tcp) failed: Connection refused nc: connect to localhost port 9997 (tcp) failed: Connection refused nc: connect to localhost port 9997 (tcp) failed: Connection refused nc: connect to localhost port 9998 (tcp) failed: Connection refused nc: connect to localhost port 9998 (tcp) failed: Connection refused nc: connect to localhost port 9999 (tcp) failed: Connection refused Connection to localhost 9999 port [tcp/*] succeeded!
-The z parameter indicates that the Zero-I/O mode is used, that is, input and output are prohibited during connection, and only check whether the port is turned on. It is very suitable for port scanning- The v parameter is used to display the detailed output information in the network connection. According to the output information, it can be seen that 9999 port can be connected, which proves that 9999 port is being developed
Chat tool
If you write a simple point-to-point chat program in C, you need at least 60-70 lines of code. Using Netcat to make two machines establish a TCP connection, you only need to execute two lines of commands to realize a simple chat function, such as on server 172.16.0.4
$ nc -l 9999
-l parameter, which means running Netcat in listening mode. Here, we are listening to port 9999, and then execute it on another server
$ nc 172.16.0.4 9999
After successful execution, the two servers establish a TCP connection, and then can send messages through the connection, such as sending Hello, I'm client on the client server
$ nc 172.16.0.4 9999 Hello, I'm client
The server can receive the message immediately
$ nc -l 9999 Hello, I'm client
Similarly, the client can also receive the message sent by the server
transfer files
Similarly, it is convenient to transfer files between two hosts by establishing A TCP connection. If you want to set test. On server A Txt is sent to server B (the IP address is 172.16.0.4) and executed on server B
nc -l 9999 > test.txt
Then execute on server A
$ nc 172.16.0.4 9999 < test.txt
In this way, the file can be sent
Forward shell
This is interesting. Using Netcat can achieve functions similar to ssh, that is, the shell terminal of the target machine is exposed on a port, and then the local machine can access the shell terminal of the target machine by connecting to the target machine using Netcat
Execute on target machine
$ nc -l 9999 | /bin/bash
Here, Netcat is used as the server to listen to 9999 port and send the received data to / bin/bash through the pipeline, which is equivalent to exposing / bin/bash to 9999 port and then executing on the local machine
$ nc 172.16.0.4 9999
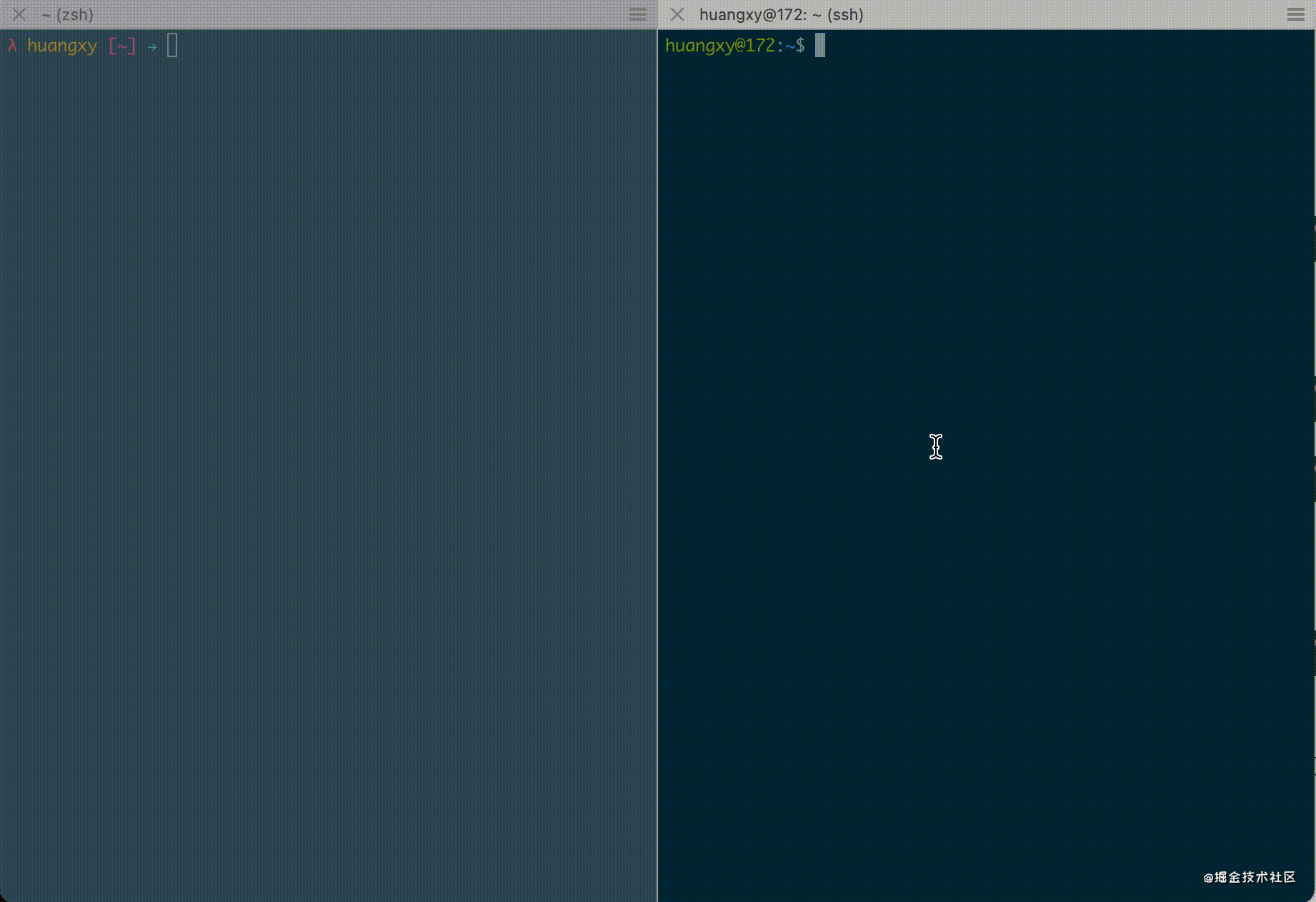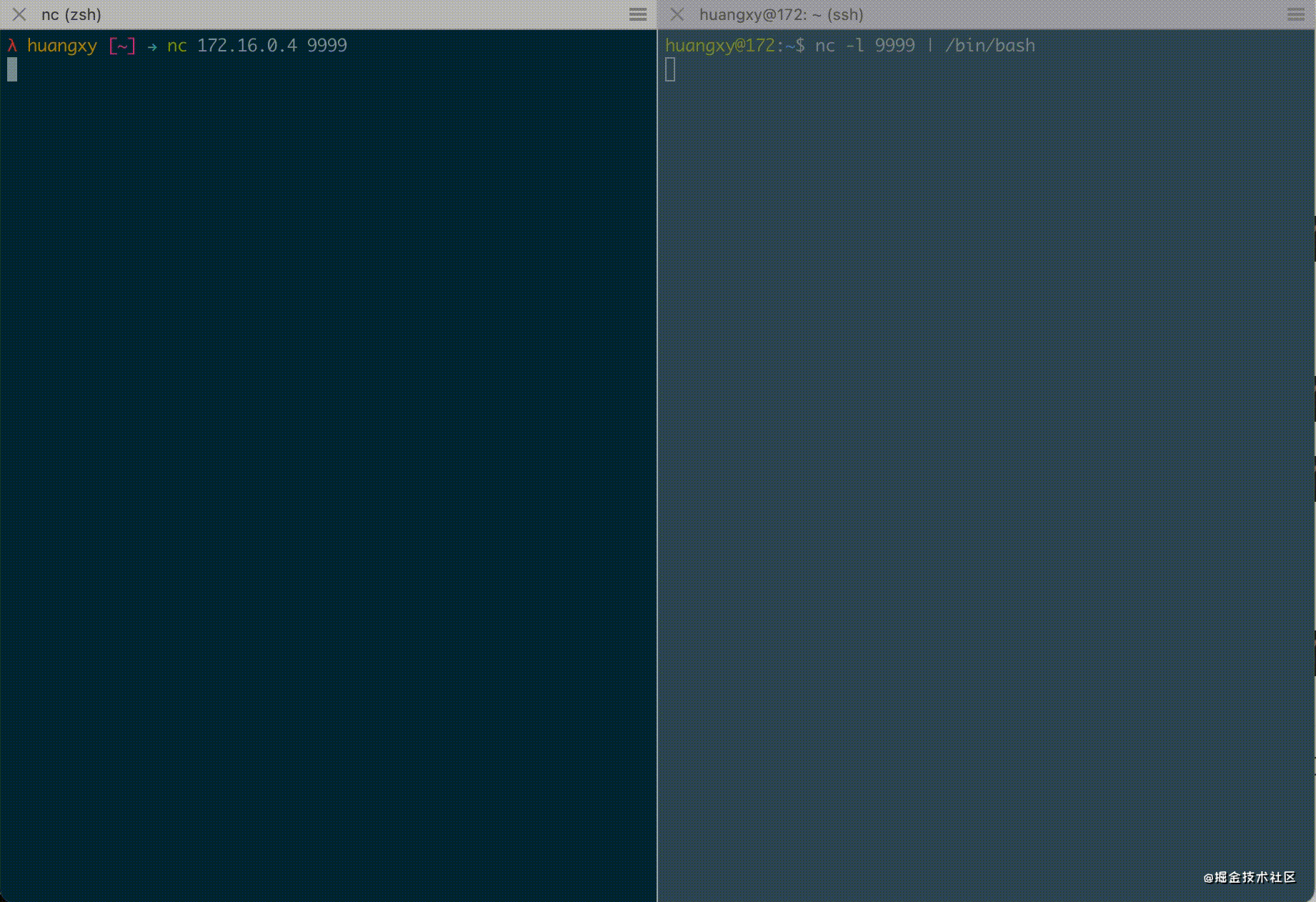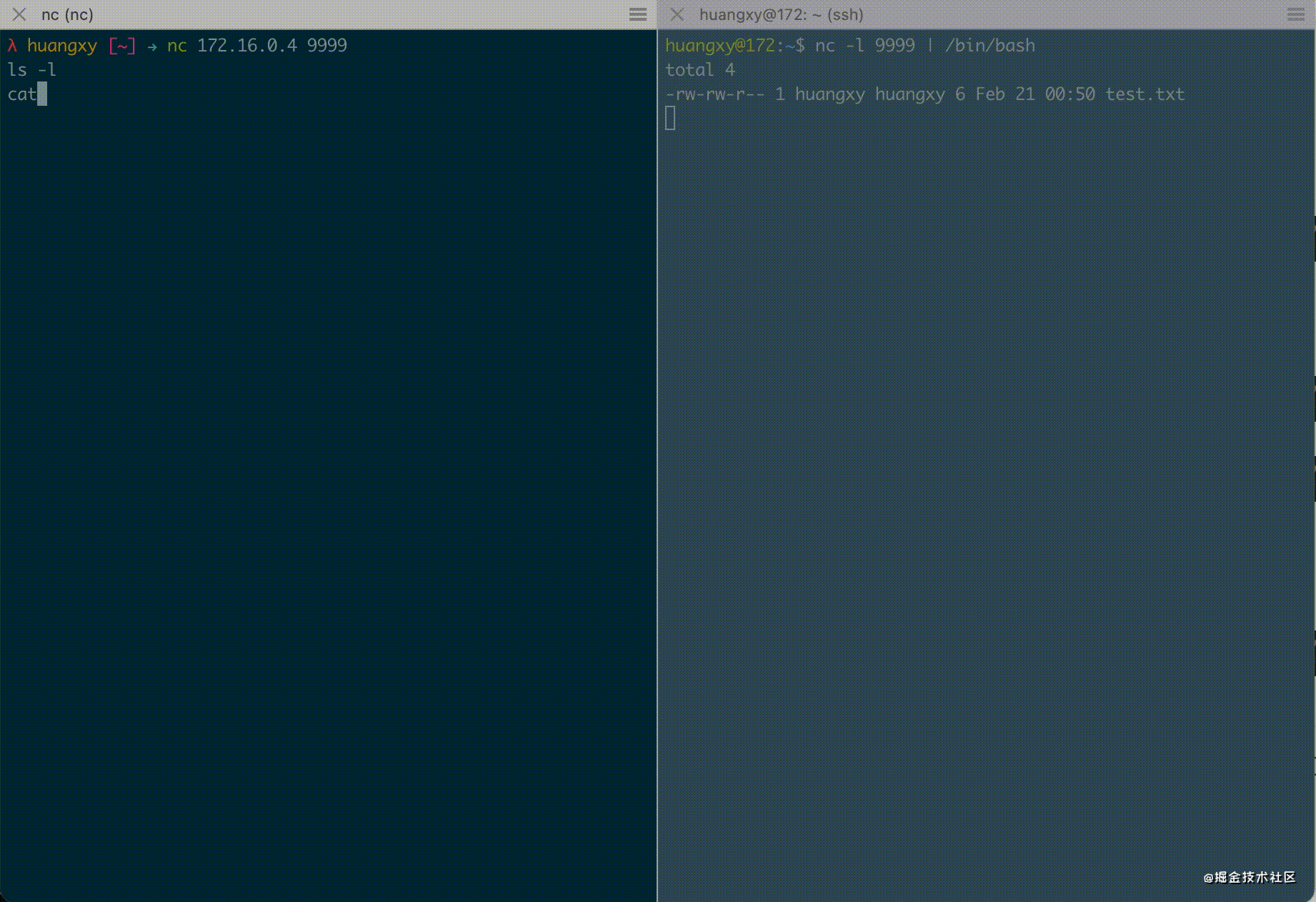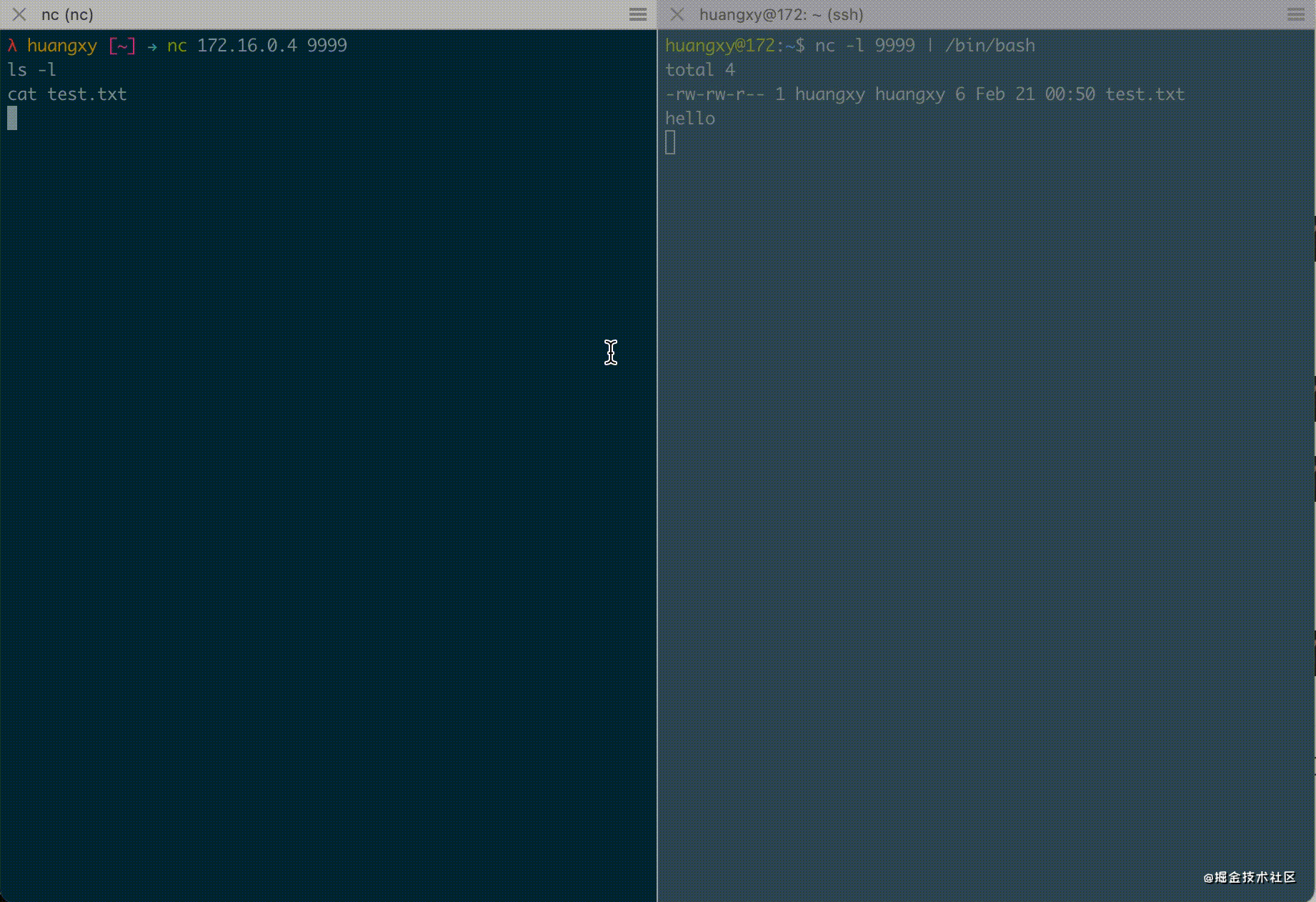
By establishing a connection through Netcat, you can access the / bin/bash terminal of the target machine on the local machine, such as executing the ls command on the local machine
$ nc 172.16.0.4 9999 ls -l
The target machine output is as follows
$ nc -l 9999 | /bin/bash total 4 -rw-rw-r-- 1 huangxy huangxy 6 Feb 21 00:50 test.txt
You can see that the commands we entered on the local machine have been successfully executed on the target machine
Although we can use the local machine to transmit commands to the target machine for execution, it is still a little different from ssh connection, because the execution results of commands cannot be seen on the local machine. Pipes can be used to solve this problem skillfully and execute on the target machine
$ mkfifo /tmp/pipe $ cat /tmp/pipe | /bin/bash 2>&1 | nc -l -p 9999 > /tmp/pipe
The main functions of the above two commands are as follows:
- Create a named pipe with the mkfifo command
- Then read the content of / tmp/pipe through cat command and send the content to / bin/bash through pipeline
- Send the execution result of / bin/bash to nc through pipeline
- nc saves the commands received from the local machine to / tmp/pipe
- /The command in tmp/pipe is read by cat and transferred to / bin/bash to complete the flow of the whole data at one time
Now you can receive the execution result of / bin/bash command on the local machine
$ nc 172.16.0.4 9999 ls -l total 4 -rw-rw-r-- 1 huangxy huangxy 6 Feb 21 00:50 test.txt
[external chain picture transfer failed. The source station may have anti-theft chain mechanism. It is recommended to save the picture and upload it directly (img-rqzs32x8-1613911304543)( https://p6-juejin.byteimg.com/tos-cn-i-k3u1fbpfcp/fe8cd64f9688438a8251b48df7290275 ~tplv-k3u1fbpfcp-watermark. image)]
Interaction with TCP server
Netcat can interact with any server using TCP protocol. For example, use netcat to execute PING command in Redis
$ printf "PING\r\n" | nc localhost 6379 +PONG
Equivalent to
$ nc localhost 6379 PING +PONG