Introduction to Apache working mode
1.Apache is the most widely used and stable open source server software for today's web servers
2. There are many working modes. When the source package installs httpd, you can view the httpd-mpm.conf file, which is located in the extra/conf directory
3. At present, there are two modes:
event mode: multiple threads in a process
prefork mode: a process contains a thread
worker mode: multiple threads in a process
event working mode introduction:
1.event is the latest working mode of Apache. It is very similar to worker mode. The difference is that it solves the problem that thread resources are wasted when keep alive long connection
2.event working mode will fail when encountering some incompatible modules, and will fall back to worker mode
3. The event working mode needs the support of epoll from Linux system (Linux 2.6 +) to enable. What needs to be added is HTTPS connection (SSL)
4. In the event mode, there will be some special threads to manage these keep alive threads
5. When a real request comes, the thread passing the request to the server is allowed to release after execution
6. In this way, a thread can handle several requests and realize asynchronous non blocking. This enhances request processing in high concurrency scenarios
event parameter explanation
In the httpd-mpm.conf configuration file, the following is the definition of the prefork module:
<IfModule mpm_event_module> StartServers 3 MinSpareThreads 75 MaxSpareThreads 250 ThreadsPerChild 25 MaxRequestWorkers 400 MaxConnectionsPerChild 0 </IfModule>
Parameter Description:
| parameter | Explain |
|---|---|
| StartServers | The initial number of processes when the service starts, default 3 |
| MinSpare Threads | Minimum number of idle subprocesses, default 75 |
| MaxSpare Threads | Maximum number of idle subprocesses, default 250 |
| ThreadsPerChild | The number of threads generated by each subprocess, the default is 25 |
| MaxRequestWorkers | Limit the maximum number of client access requests in the same time. The default is 400 |
| MaxConnectionsPerChild | The maximum number of requests allowed for each subprocess in its life cycle. If the total number of requests has reached this value, the subprocess will end. If it is set to 0, the subprocess will never end. Setting this value to a non-zero value can prevent memory leaks caused by running PHP |
event optimization suggestions
1. It can be debugged according to the production environment to determine the appropriate parameters
2. Optimization reference:
<IfModule mpm event module> ServerLimit 1000 StartServers 20 MinSpareThreads 25 MaxSpareThreads 1200 ThreadsPerChild 50 MaxRequestWorkers 2000 MaxC onnectionsPerChild 1000 </IfModule>
Introduction to the working mode of prefork
1.prefork is a multiprocessing module (MPM), which implements a process type, pre derived web server. It is suitable for a system without thread safety library and needs to avoid thread compatibility problems
2. It has good characteristics when each request is required to be independent from each other. If there is a problem with one request, other requests will not be affected
3. It has a strong self-regulation ability, and only needs a few configuration instructions to adjust it can be suitable for enterprise application requirements
4. The most important thing is to set MaxClients to a value that is large enough to handle the potential request peak. At the same time, it should not be too large to prevent the required memory from exceeding the size of physical memory
5. A separate control process (parent process) is responsible for generating child processes, which are used to listen to and respond to requests. Therefore, in memory, there will be one or more spare or idle child processes to respond to new requests, which can speed up the response speed
6. The parent process usually runs as root in order to bind port 80. The child process usually runs as a low privileged User, which can be configured through the User and Group of the configuration item
7. Users running subprocesses must have access to the content of the website, but they must have as few access to other resources as possible to ensure the security of the system
8. No working mode is specified during compilation and installation. The default mode is prefork, which can be viewed with httpd-l
Introduction to prefork parameters
In the httpd-mpm.conf configuration file, the following is the definition of the prefork module:
<IfModule mpm_ prefork module> StartServers 20 MinSpareServers 10 MaxSpareServers 50 MaxClients 150 MaxRequestsPerChild 0 </IfModule>
Parameter Description:
| parameter | Explain |
|---|---|
| ServerLimit | Maximum number of processes |
| StartServers | Number of processes created at startup |
| MinSpareServers | Least idle process |
| MaxSpareServers | Most idle processes |
| MaxClients | How many subprocesses can be created to process requests at most |
| MaxRequestsPerChild | The maximum number of requests processed by each process. When the number of requests is reached, the process is destroyed. If it is set to 0, the subprocess will never end |
prefork optimization suggestions
1. It can be debugged according to the production environment to determine the appropriate parameters
2. Optimization reference:
<IfModule mpm prefork module> ServerLimit 1000 StartServers 10 MinSpareServers 10 MaxSpareServers 30 MaxClients 1000 MaxRequestsPerChild 5000 </IfModule>
How the worker works
1. The number of threads that each process can own is fixed. The server will increase or decrease the number of processes according to the load
2. A separate control process (parent process) is responsible for the establishment of child processes. Each subprocess can establish a number of ThreadsPerChild service threads and a listening thread. The listening thread listens for the access request and passes it to the service thread for processing and answering
3.Apache always maintains a spare or idle pool of service threads. Clients can get services without waiting for new threads or new processes to be established
4. The parent process is generally started as root to bind port 80. Then, Apache establishes the child process and thread as a user with lower permission
5. The user and Group directives are used to configure the running user of the Apache subprocess The subprocess should have read permission to the web content, but should limit the permission as much as possible
Parameter Description:
| parameter | Explain |
|---|---|
| ServerLimit | Maximum number of processes, default is "16" |
| ThreadL imit | Maximum number of threads per subprocess, default is "64" |
| StartServers | The number of subprocesses established when the server starts. The default value is "3" |
| MaxClients | Maximum number of simultaneous access requests allowed (maximum number of threads) |
| MinSpare Threads | Minimum number of idle threads, default is "75" |
| MaxSpare Threads | Set the maximum number of idle threads. The default is "250" |
| ThreadsPerChild | The number of resident execution threads established by each subprocess. The default is 25 |
| MaxRequestsPerChild | Sets the maximum number of requests that each subprocess is allowed to serve during its lifetime. Set to '0', child processes will never end |
Apache directory properties
1. The permission settings of the directory use < directory directory path > and < / Directory > to set the permission of the main directory or virtual directory
2. They are a pair of container statements, which must appear in pairs. They encapsulate specific set directory permission statements, which only work on the set directory and its subdirectories
Directory property parameters:
| parameter | Effect |
|---|---|
| Options | Set which properties to use in a specific directory |
| AllowOverride | Allowed instruction types in. htaccess files |
| Require | Set access control for directories |
| Indexes | When the user accesses the directory, but does not specify which file to access, and there is no default web page in the directory, the list of files and subdirectories in the directory is returned |
| MultiViews | Multi view of content negotiation, an intelligent feature of Apache When accessing an object that does not exist in the directory |
| ExecCGI | Allow CGI script execution in this directory |
| FollowSymLinks | Allow file systems to use symbolic connections in this directory |
| Includes | Allow server side to include features |
| IncludesNoExec | Allow the server side to include functions, but prohibit the execution of CGI scripts |
| All | Contains All properties except MultiViews. If there is no Options statement, the default is All |
Demo1: Apache working mode (take prefork as an example here)
Step 1: compile and install Apache manually
[root@localhost ~]# smbclient -L //192.168.10.171/
Enter SAMBA\root's password:
OS=[Windows 10 Home China 18362] Server=[Windows 10 Home China 6.3]
Sharename Type Comment
--------- ---- -------
ADMIN$ Disk Remote management
C$ Disk Default sharing
D$ Disk Default sharing
F$ Disk Default sharing
IPC$ IPC Long-range IPC
rpm Disk
Connection to 192.168.10.171 failed (Error NT_STATUS_RESOURCE_NAME_NOT_FOUND)
NetBIOS over TCP disabled -- no workgroup available
[root@localhost ~]# mount.cifs //192.168.10.171/rpm /mnt
Password for root@//192.168.10.171/rpm:
[root@localhost ~]# cd /mnt
[root@localhost mnt]# ls
LAMP
[root@localhost mnt]# cd LAMP/
[root@localhost LAMP]# ls
apr-1.6.2.tar.gz ha.jpg
apr-util-1.6.0.tar.gz httpd-2.4.29.tar.bz2
awstats-7.6.tar.gz lf.jpg
cronolog-1.6.2-14.el7.x86_64.rpm mysql-5.6.26.tar.gz
Discuz_X2.5_SC_UTF8.zip nginx-1.12.0.tar.gz
error.png php-5.6.11.tar.bz2
[root@localhost LAMP]# tar jxvf httpd-2.4.29.tar.bz2 -C /opt/
[root@localhost LAMP]# tar zxvf apr-1.6.2.tar.gz -C /opt/
[root@localhost LAMP]# tar zxvf apr-util-1.6.0.tar.gz -C /opt/
[root@localhost LAMP]# cd /opt
[root@localhost opt]# ls
apr-1.6.2 apr-util-1.6.0 httpd-2.4.29 rh
[root@localhost opt]# mv apr-1.6.2/ httpd-2.4.29/srclib/apr
[root@localhost opt]# mv apr-util-1.6.0/ httpd-2.4.29/srclib/apr-util
[root@localhost opt]# yum install gcc gcc-c++ pcre pcre-devel zlib-devel expat-devel -y
[root@localhost opt]#cd httpd-2.4.29/
[root@localhost httpd-2.4.29]#./configure \
--prefix=/usr/local/httpd \
--enable-deflate \
--with-mpm=prefork \
--enable-expires \
--enable-so \
--enable-rewrite \
--enable-charset-lite \
--enable-cgi
[root@localhost httpd-2.4.29]# make && make install
[root@localhost httpd-2.4.29]# ln -s /usr/local/httpd/conf/httpd.conf /etc/httpd.conf
//Establish a soft connectionStep 2: modify the configuration file
[root@localhost httpd-2.4.29]# vim /etc/httpd.conf
//Enter / mpm to find this keyword and delete the previous comment
Include conf/extra/httpd-mpm.conf //Navigate to this line to delete the comment and enable the function
//Enter / Listen to find this keyword and modify the listening port
Listen 192.168.116.145:80 //This line of IPv4 monitoring is enabled, and the monitoring address is the IP address of the Linux system
#Listen 80 / / disable IPv6 listening in this line
//Enter / ServerName to find this keyword and modify the domain name
ServerName www.test.com:80 //Change domain name to www.test.com
//After modification, press Esc to exit the insertion mode, enter: wq to save and exit
[root@localhost httpd-2.4.29]# cd /usr/local/httpd/
[root@localhost httpd]# cd conf/
[root@localhost conf]# ls
extra httpd.conf magic mime.types original
[root@localhost conf]# cd extra/
[root@localhost extra]# ls
httpd-autoindex.conf httpd-languages.conf httpd-ssl.conf
httpd-dav.conf httpd-manual.conf httpd-userdir.conf
httpd-default.conf httpd-mpm.conf httpd-vhosts.conf
httpd-info.conf httpd-multilang-errordoc.conf proxy-html.conf
[root@localhost extra]# vim httpd-mpm.conf
//In this case, we will quit without making any changes. After implementation, we will compare the changes later
[root@localhost extra]# cd ../../bin/
[root@localhost bin]# ls
ab apu-1-config dbmmanage fcgistarter htdigest httxt2dbm
apachectl apxs envvars htcacheclean htpasswd logresolve
apr-1-config checkgid envvars-std htdbm httpd rotatelogs
[root@localhost bin]# ./apachectl start
[root@localhost bin]# netstat -ntap | grep 80
tcp 0 0 192.168.116.145:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 58773/httpd
[root@localhost bin]# lsof -i :80
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME
httpd 58773 root 3u IPv4 84859 0t0 TCP localhost.localdomain:http (LISTEN)
httpd 58775 daemon 3u IPv4 84859 0t0 TCP localhost.localdomain:http (LISTEN)
httpd 58776 daemon 3u IPv4 84859 0t0 TCP localhost.localdomain:http (LISTEN)
httpd 58777 daemon 3u IPv4 84859 0t0 TCP localhost.localdomain:http (LISTEN)
httpd 58778 daemon 3u IPv4 84859 0t0 TCP localhost.localdomain:http (LISTEN)
httpd 58779 daemon 3u IPv4 84859 0t0 TCP localhost.localdomain:http (LISTEN)
//root is the main process and the other five are the received subprocesses
[root@localhost bin]# cd ../conf/extra/
[root@localhost extra]# vim httpd-mpm.conf
<IfModule mpm_prefork_module>
StartServers 10 //The number of processes created at startup is changed to 10
MinSpareServers 10 //Idle minimum changed to 10
MaxSpareServers 20 //Max set to 20
MaxRequestWorkers 200 //Access set to 200
MaxConnectionsPerChild 0
</IfModule>
//After modification, press Esc to exit the insertion mode, enter: wq to save and exit
[root@localhost extra]# cd ../../bin/
[root@localhost bin]# ./apachectl stop
[root@localhost bin]# ./apachectl start
//Turn off the service again
[root@localhost bin]# lsof -i :80
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME
httpd 58933 root 3u IPv4 88357 0t0 TCP localhost.localdomain:http (LISTEN)
httpd 58937 daemon 3u IPv4 88357 0t0 TCP localhost.localdomain:http (LISTEN)
httpd 58938 daemon 3u IPv4 88357 0t0 TCP localhost.localdomain:http (LISTEN)
httpd 58939 daemon 3u IPv4 88357 0t0 TCP localhost.localdomain:http (LISTEN)
httpd 58940 daemon 3u IPv4 88357 0t0 TCP localhost.localdomain:http (LISTEN)
httpd 58941 daemon 3u IPv4 88357 0t0 TCP localhost.localdomain:http (LISTEN)
httpd 58942 daemon 3u IPv4 88357 0t0 TCP localhost.localdomain:http (LISTEN)
httpd 58943 daemon 3u IPv4 88357 0t0 TCP localhost.localdomain:http (LISTEN)
httpd 58944 daemon 3u IPv4 88357 0t0 TCP localhost.localdomain:http (LISTEN)
httpd 58945 daemon 3u IPv4 88357 0t0 TCP localhost.localdomain:http (LISTEN)
httpd 58946 daemon 3u IPv4 88357 0t0 TCP localhost.localdomain:http (LISTEN)
//Remove one main process, and the other subprocesses become 10
[root@localhost bin]# . / httpd -l / / view the working mode
Compiled in modules:
core.c
mod_so.c
http_core.c
prefork.c //At this time, it is in the prefork working modeDemo2: Directory properties
[root@localhost bin]# vim /etc/httpd.conf
//Enter / htdocs to find this keyword and find the following fields, two of which are supported:
DocumentRoot "/usr/local/httpd/htdocs"
<Directory "/usr/local/httpd/htdocs">
#
# Possible values for the Options directive are "None", "All",
# or any combination of:
# Indexes Includes FollowSymLinks SymLinksifOwnerMatch ExecCGI MultiViews
#
# Note that "MultiViews" must be named *explicitly* --- "Options All"
# doesn't give it to you.
#
# The Options directive is both complicated and important. Please see
# http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/mod/core.html#options
# for more information.
#
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
//1.Index: in the form of list
//2. Follow symlinks and support linked files
#
# AllowOverride controls what directives may be placed in .htaccess files.
# It can be "All", "None", or any combination of the keywords:
# AllowOverride FileInfo AuthConfig Limit
#
AllowOverride None
#
# Controls who can get stuff from this server.
#
Require all granted //Black-and-white list
</Directory>
#We can turn off the firewall and use the host's browser for verification
[root@localhost bin]# systemctl stop firewalld.service
[root@localhost bin]# setenforce 0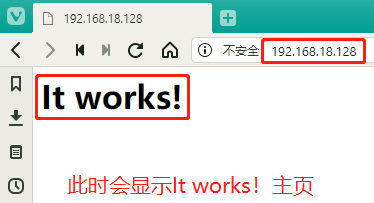
[root@localhost bin]# cd /usr/local/httpd/htdocs/ [root@localhost htdocs]# ls index.html [root@localhost htdocs]# cat index.html <html><body><h1>It works!</h1></body></html> [root@localhost htdocs]# ls index.html [root@localhost htdocs]# mv index.html a.html [root@localhost htdocs]# ls a.html [root@localhost htdocs]# touch b.html c.html d.html [root@localhost htdocs]# ls a.html b.html c.html d.html //At this time, it will be displayed in the form of file list. From another point of view, we can use this point to provide file download resources. At this time, we do not need home page identification

[root@localhost htdocs]# ln -s /usr/share/man/ ./ //Put the man manual in this folder to see if he can recognize the linked file [root@localhost htdocs]# ls a.html b.html c.html d.html man

