Docker's cognition
-
Core concept
docker is a linux container technology. The container effectively divides the resources managed by a single operating system into isolated groups, so as to better balance the conflicting resource use requirements between groups. It can be simply understood as a sandbox. An application runs in each container. Different containers are isolated from each other, and a communication mechanism can be established between containers. The creation and stop of containers are very fast, and the resource requirements are much lower than those of virtual machines.
Docker can make full use of the server through the isolation mechanism. -
Developed based on GO language.
-
Official website address: https://www.docker.com/
Document address: https://docs.docker.com/
Warehouse address: https://hub.docker.com/ -
difference
-
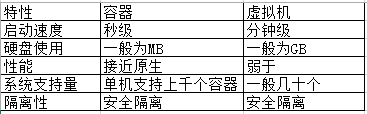
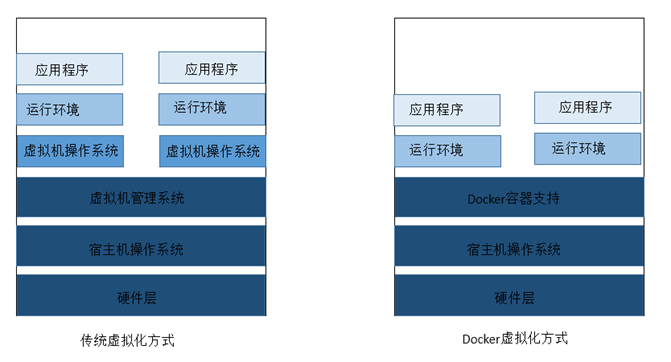
Traditional virtual machine, virtual out of a hardware, running a complete operating system
-
The applications in the container run directly on the host computer. The container does not have its own kernel or virtual hardware
Each container is isolated from each other. Each container has its own file system and complementary effects
5.docker and virtualization -
Virtualization is a resource management technology, which abstracts and transforms various physical resources of the computer, such as server, network and memory, so that users can apply these resources in a better way. The goal of virtualization is often to run multiple systems or applications on the same host, so as to improve resource utilization, reduce cost, facilitate management and fault tolerance.
-
Operating system level virtualization: the kernel isolates different processes by creating multiple virtual operating system instances (kernel and Library). docker and other container technologies belong to this category.
-
The traditional way of virtualization is to realize virtualization at the hardware level, which requires additional virtual machine management application and virtual machine operating system layer. The docker container is virtualized at the operating system level, directly reusing the local host operating system, which is lighter.
- effect
1. Applications can be delivered and deployed more quickly
2. The use of tiered storage and mirroring technology makes it easier to upgrade and expand, and easy to migrate and expand
3. Simpler system operation and maintenance, simple update management
4. More efficient utilization of computing resources
5. Can efficiently build applications.
6. Faster startup time, because it runs directly in the host kernel, there is no need to start the complete operating system
Multiple container instances can run on a virtual machine - structure
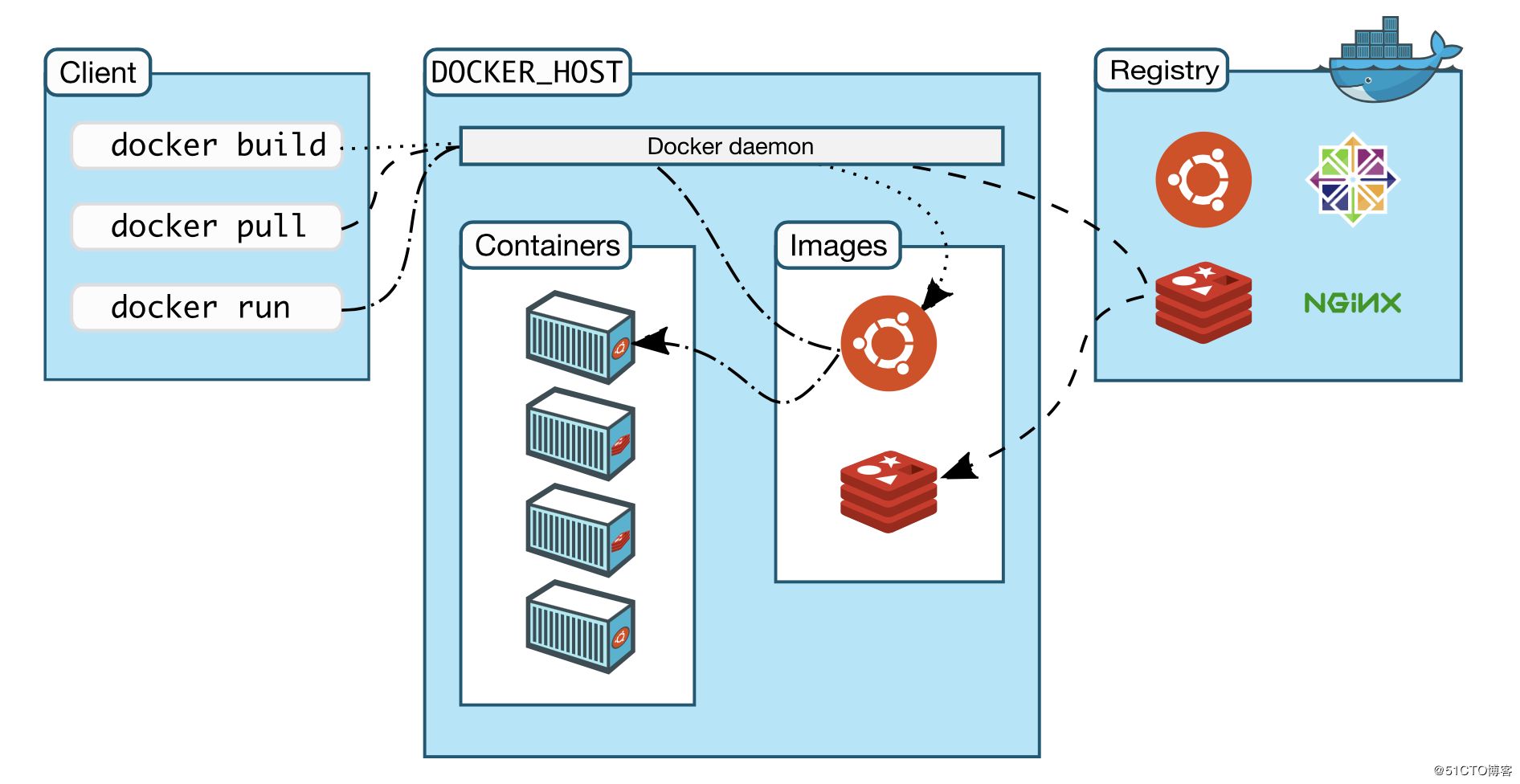
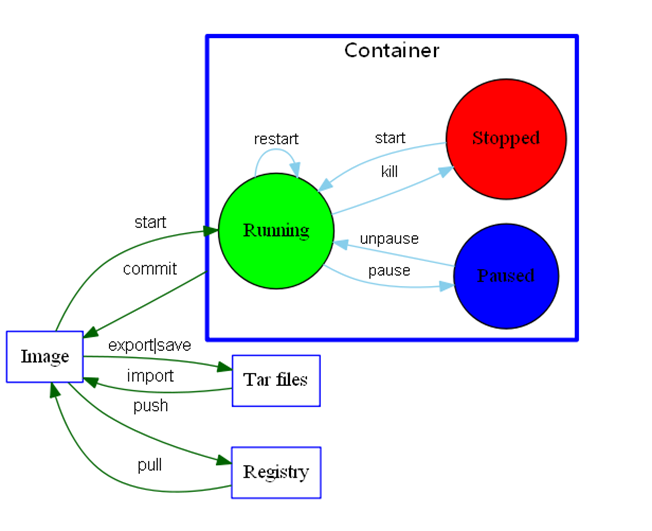
image: it can be regarded as a template through which container services can be created
container: run one or a group of applications independently and create them through image, which is equivalent to an instance
repository: the place where images are stored
Install Docker
- Uninstall old version
$sudo yum remove docker \
docker-client \
docker-client-latest \
docker-common \
docker-latest \
docker-latest-logrotate \
docker-logrotate \
docker-engine
- install
sudo yum install -y yum-utils
- Set mirror address
sudo yum-config-manager \ --add-repo \ http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo - Alibaba cloud image is recommended #https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo --Foreign mirror image
- Update software index
sudo yum makecache fast
- Install docker related content
docker -ce Community Edition
docker -ee enterprise
sudo yum install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
- Start Docker
sudo systemctl start docker
- Get the version of docker
docker versiondock
- test
docker run hello-world
- View the downloaded Hello world image
[root@localhost ~]# docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE hello-world latest feb5d9fea6a5 2 months ago 13.3kB nacos/nacos-server 2.0.1 90c4c6c5d925 7 months ago 1.04GB
Uninstall Docker
- Unload dependency
yum remove docker -ce docker -ce-cli containerd,io
- Delete resource
rm -rf /var/lib/docker ---Default working path
Alibaba cloud image acceleration
- Alicloud container service
- Mirror accelerator
- Configuration use
sudo mkdir -p ./etc/docker
sudo tee ./etc/docker/daemon.jsin<<-'EOF'
{
"registry-mirrors":["address"]
}
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl restart docker
Common commands of Docker
Help command
docker version #Displays the version information of docker docker info #The system information of docker, including the number of images and containers docker help #Help order
Help document address: https://docs.docker.com/reference/
Mirror command
docker images View mirrors on all local hosts
#explain
REPOSITORY Mirrored warehouse source
TAG Mirrored label
IMAGE ID mirrored ID
CREATE Creation time of the image
SIZE Mirror size
#Optional
-a, --all List all mirrors
--digests Show digests
-f, --filter filter Filter output based on conditions provided
--format string Pretty-print images using a Go template
--no-trunc Don't truncate output
-q, --quiet Show only mirrored ID
docker search Search image example: docker serach mysql Add parameters:--filter=STARS=3000 # The searched image STARS is greater than 3000
docker pull mysql #Download the latest version by default Equivalent to: docker pull docker.io/library/mysql:latest Add parameter: tag #Add version information Federated file system
docker rmi -f image ID #delete mirror docker rmi -f $(docker images -aq) #Recursively delete all mirrors
Container command
#Start container docker run[Optional parameters] image #Parameter description --name= "Container name" Container name, used to distinguish containers -d Run in background mode -it Run in interactive mode and enter the container to view the content -p Specifies the port of the container -P Randomly assigned port example ##Start and enter the container docker run -it Container name /bin/bash ##Exit and stop the container exit ##The container does not stop exiting Ctrl + P + Q
#View running containers docker ps #View containers that have been run docker ps -a #Displays recently created containers -n = ? #Displays only the number of the container -q
#Delete container (you cannot delete a running container, add rf -f) docker rm Container ID #Delete all containers docker rm -f ¥(docker ps -aq) docker ps -a -q|xargs docker rm
#Start container docker start container ID #Restart container docker restart container ID #Stop the currently running container docker stop container ID #Q force stop of current container docker kill Container ID
Other container commands
docker run -d Image name Question: docker ps The mirror is found to have stopped reason: docker When the container runs in the background, there must be a foreground process, docker If no application is found, it will stop automatically as nginx After the container is started, Faxiang will stop immediately if it does not provide services
#view log docker logs -f -t --tail t Number of containers ID
#Viewing container process information docker top container ID
#View information inside the container docker inspect Container ID
#View information inside the container docker inspect Container ID
#View status docker stats
Enter the currently running container
#We usually use the background mode to run the container, and we need to enter the container #command Method 1: after entering the container, open a new terminal, which can be operated inside docker exec -it Container ID bashShell example: [root@localhost ~]# docker exec -it 90185ae982b0 /bin/bash root@90185ae982b0:/apache-zookeeper-3.6.0-bin# Mode 2: enter the terminal where the container is executing, and no new process will be started docker attach Container ID
#Copy files from the container to the host docker cp Container ID:Path within container path to target host
practice
Installing Nginx
docker search nginx #search docker pull nginx #Pull docker run -d --name nginx01 -p :3344:80 nginx #start-up -d Background operation -p Host port: container internal port The burst port is on the host curl localhost:3344 #test #Enter container [root@localhost ~]# docker exec -it nginx01 /bin/bash root@4200055aa7ae:/# whereis nginx nginx: /usr/sbin/nginx /usr/lib/nginx /etc/nginx /usr/share/nginx root@4200055aa7ae:/# cd /etc/nginx root@4200055aa7ae:/etc/nginx# ls conf.d fastcgi_params mime.types modules nginx.conf scgi_params uwsgi_params
Install tomcat
docker run -it --rm tomcat:9.0 This command indicates delete after use, which is generally used for testing docker pull tomcat docker run -d -p 3355:8080 --name tomcat01 tomcat docker exec -it tomcat01 /bin/bash
Found 1: the linux command is missing 2: there is no webapps
Reason: alicloud image is the smallest image by default, and all unnecessary images are eliminated
resolvent:
docker exec -it tomcat01 /bin/bash cp -r webapps.dist/* webapps
Deploy es
[root@localhost ~]# docker run -d --name elasticsearch -p 9200:9200 -p 9300:9300 -e "discovery.type=single-node" elasticsearch:7.16.2
[root@localhost ~]# curl localhost:9200
{
"name" : "12c7a95dad74",
"cluster_name" : "docker-cluster",
"cluster_uuid" : "OqhjqILdQ3SetCie7pnOSg",
"version" : {
"number" : "7.6.2",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "docker",
"build_hash" : "ef48eb35cf30adf4db14086e8aabd07ef6fb113f",
"build_date" : "2020-03-26T06:34:37.794943Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "8.4.0",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "6.8.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "6.0.0-beta1"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
-e Add environment configuration
[root@localhost ~]# docker run -d --name elasticsearch02 -p 9200:9200 -p 9300:9300 -e "discovery.type=single-node" -e ES_JAVA_OPTS="-Xms64m -Xmx512m" elasticsearch:7.16.2
Configuration visualization (pointainer)
docker run -d -p 8088:9000\ --restart=always -v /var/run/docker.sock:var/run/docker.sock --name portainer1 --privileged=true portainer/portainer