JavaScript
Introducing JavaScript
- Internal label
<script>
//...
</script>
External reference
<script src="js File path"></script>
html file
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<!--Internal reference-->
<!--script Inside label JavaScript code-->
<script>
alert("hello world");
</script>
<!--External reference-->
<script src="js/JavaScript01.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
It can also be written here js code
</body>
</html>
JavaScript 01.js file
alert("hello world");
Basic grammar
notes:
A single line comment begins with / /.
Any text between / / and the end of the line is ignored by JavaScript (not executed).
Multiline comments begin with / and end with /.
Any text between / * and * / is ignored by JavaScript.
Variable:
JavaScript uses the var keyword to declare variables.
Output:
alert(score);
console.log(score); Output in browser console
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<!--JavaScript Strictly case sensitive-->
<script>
//1. Define variable type variable name = variable value;
var score = 71;
// alert(score);
//2. Condition control
if (score>60 && score<70){
alert("pass");
}else if (score>70 && score<80){
alert("secondary");
}else {
alert("excellent");
}
//console.log(score); Output in browser console
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
data type
variable
var Variable name;
number
js does not distinguish between decimal and integer
10//integer 10.1//Floating point number 1.01e3//Scientific counting method -10//negative NaN//Not a Number Infinity//Represents infinity
character string
- The string is wrapped in single quotation marks or double quotation marks, and the value is obtained through subscript. It cannot be assigned, and the string is immutable
- Note the escape string\
\' \n \t \u4e2d \u#### unicode characters \x41 Ascll character
- Multiline string writing
var msg = `
hello
world
Hello
`
- Template string
'use strict';
let name = 'sgl';
var msg = `How do you do! ${name}`
- String length
str.length
- toggle case
//Note that this is a method, not an attribute str.toUpperCase() str.toLowerCase()
- Gets the subscript of the character in the string
str.indexOf('a')
- substring
[) str.substring(1) //Intercept from the first string to the last string str.substring(1,3)//[) intercept characters from 1 to 3, including 1 but not 3
Note: the variability of string is immutable!!!
Boolean value
true,false
Logical operator
&& Both are true and the result is true || One is true and the result is true ! True is false, false is true
Comparison operator
= assignment == Equal to (if the type is different and the value is the same, it will also be judged as true) === Absolutely equal to (same type, same value, judged as true)
null and undefined
- Null: null
- Undefined: undefined
array
Java values must be objects of the same type, which is not required in js
//To ensure the readability of the code, try to use [] var arr = [1,2,3,'hello',null,true]; //Value or assignment by subscript new Array(1,2,3,'hello',null,true);
If the array subscript is out of bounds: display undefined
Array can contain any data type
- Array length
arr.length
Note: if arr.length is assigned, the array size will change. If the assignment is too small, the elements will be lost
- indexOf gets the subscript index through the element
arr.indexOf(2)
Note: the "2" of the string is different from the number 2
- slice () intercepts part of the Array and returns a new Array, similar to substring in String
- push() pop() tail
push:Press in to the rear pop:Pop up an element at the end
- Unshift() head
unshift:Press into the head shift:Pop up an element in the header
-
sort() sort reverse() reverse
concat() splicing does not modify the array, but returns a new array
join() connector
var arr = ['A','C'];
arr.push('B')
3
arr
(3) ["A", "C", "B"]
arr.sort();
(3) ["A", "B", "C"]
arr.reverse()
(3) ["C", "B", "A"]
arr.concat([1,2,3])
(6) ["C", "B", "A", 1, 2, 3]
arr.join('-') //As you can see, the array is not modified
"C-B-A"
- Multidimensional array
arr = [[1,2],[3,4],["5","6"]] arr[1][1] 4
object
All keys in JavaScript are strings, and values are arbitrary objects
Format: several key value pairs
var Object name = {
Attribute name:Attribute value,
Attribute name:Attribute value,
Attribute name:Attribute value,
}
Each attribute is separated by commas, and the last one does not need to be added
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script>
//Java object definition person = new person ()
var person = {
name:"sgl",
age:22,
tags:['js','css','html']
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
- Object Assignment
person.name="coco"; "coco" person.name; "coco"
- If you use a non-existent object attribute, no error will be reported! undefined
person.hh undefined
- For dynamic deletion of attributes, delete the attributes of the object through delete; for dynamic addition, directly add values to the new attributes
person.name="coco"; "coco" person.name; "coco" delete person.name; true person.haha="haha" "haha"
- Judge whether the value of the attribute exists in this object! xxx in xxx
'age' in person true //Inheritance, so it's right 'toString' in person true
- To determine whether a property is owned by the object itself, use hasOwnProperty()
person.hasOwnProperty('age')
true
person.hasOwnProperty('toString')
false
Strict inspection mode
-
’use strict 'strictly check the mode to prevent some problems caused by the randomness of JavaScript;
-
It must be written in the first line of JavaScript code;
-
let definitions are recommended for local variables
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<!--
premise:IDEA Need support ES6 grammar
'use strict';Strict inspection mode and Prevention JavaScript Some problems caused by the randomness of
Must be written in JavaScript First line of code
Local variables are recommended let definition
-->
<script>
'use strict'
//local variable
let b = 1;
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
Process control
if judgment
var score = 71;
// alert(score);
//2. Condition control
if (score>60 && score<70){
alert("pass");
}else if (score>70 && score<80){
alert("secondary");
}else {
alert("excellent");
}
while loop to avoid dead loop
var age = 0;
while (age<100){
age = age + 1;
console.log(age)
}
do {
age = age + 1;
alert(age);
}while (age<100)
for loop
for (let i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
alert(i); //Browser pop-up output
//console.log(i); console output
}
forEach loop
var arr = [12,23,123,45,67,89]
//function
arr.forEach(function (value){
console.log(value);
})
for in
Index represents the index of array arr elements
arr[index] output the value of array arr
for of
Value outputs the value of array arr
var arr = [12,23,123,45,67,89]
for (var index in arr){
console.log(index); //Index represents the index of array arr elements
console.log(arr[index]); //Output the value of array arr
for (var value of arr){
console.log(value); //Output the value of array arr
Map and Set
Map:
var map = new Map([['tom',100],['jack',99],['lucy',98]]);
var name = map.get('tom'); //Get value through key
map.set('linda',88); //Add or modify
map.delete("jack");//delete
Set: unordered non repeating set
let set = new Set([3,2,1,2,3]); //set can be de duplicated set.add(4); set.delete(1) console.log(set.has(3))
iterator
iterator iterates over Map and Set
var map = new Map([['tom',100],['jack',99],['lucy',98]]);
for (let value of map) {
console.log(value);
}
let set = new Set([7,8,9]);
for (let value2 of set) {
console.log(value2);
}
function
Function definition
Definition method I
function Function name(Attribute value){
//Function body
}
Absolute value function
function abs(x){
if(x>=0){
return x;
}else{
return -x;
}
}
Once executed, return represents the end of the function and returns the result!
If return is not executed, the result will also be returned after the function is executed. The result is undefined
Definition mode 2
var Function name = function(Attribute value){
//Function body
}
Absolute value function
var abs = function(x){
if(x>=0){
return x;
}else{
return -x;
}
}
Call function
abs(-10); //10 abs(10); //10
Parameter problem: JavaScript can pass any parameter or no parameter
abs(); //NaN abs(10,29,10); //10
Throwing an exception manually solves the problem of passing any parameters
var abs = function(x){
if (typeof x!=='number'){
throw 'Not a Number';
}
if(x>=0){
return x;
}else{
return -x;
}
}
abs(); Uncaught Not a Number
arguments
arguments represents all parameters passed in. It is an array
var abs = function(x){
console.log("x-->"+x);
for (let i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
console.log(arguments[i]);
}
if (typeof x!=='number'){
throw 'Not a Number';
}
if(x>=0){
return x;
}else{
return -x;
}
}
Console operation results:
abs(25,23,65,98,65); x-->25 //x points to the first parameter 25 //arguments[i] output 23 65 98 65 25 //Output of if statement 25
rest
rest gets the remaining parameters
function fun(a,b,...rest){
console.log("a-->"+a);
console.log("b-->"+b);
console.log(rest);
}
Operation results of console:
fun(1,2,3,6,7); a-->1 b-->2 (3) [3, 6, 7] Remaining parameters
Note: the rest parameter can only be written at the end and must be identified with
Scope of variable
In JavaScript, variables defined by var are actually scoped
If it is declared in the function body, it cannot be used outside the function. Otherwise, an error is reported: X is not defined
function qj() {
var x = 1;
x = x + 1;
}
x = x + 2; //Uncaught ReferenceError: x is not defined
If two functions use the same variable name, there is no conflict as long as they are inside the function
function qj() {
var x = 1;
x = x + 1;
}
function qj2() {
var x = A;
x = x + 1;
}
Internal functions can access functions of external members, not vice versa
function qj() {
var x = 1;
function qj2() {
var y = x + 1; //2
}
var z = y + 1; //console.log(z); Uncaught ReferenceError: z is not defined
}
Suppose that the internal function variable and the external function variable have the same name
function qj() {
var x = 'A';
function qj2() {
var x = 'B'; //2
console.log('inner:'+x); //outer:A
}
console.log('outer:'+x); //inner:B
qj2();
}
qj();
Suppose that in JavaScript, the function searches for variables from itself, from "inside" to "outside". If there is a function variable with the same name outside, the internal function will shield the variables of the external function.
Specification: all variable definitions are placed at the head of the function to facilitate code maintenance
function f(){
var x = 1,
y = x + 1,
z,i,a; //undef
//You can use it later
}
global variable
//global variable
x = 1;
function f(){
console.log(x);
}
f();
console.log(x);
Global object window
var x = 1; alert(x); alert(window.x);
The alter() function itself is also a window variable
var x = 1;
window.alert(x);
let alert_01 = window.alert;
alert_01(x);
window.alert = function () {
}
//alert failed
window.alert(123);
//recovery
window.alert = alert_01;
window.alert(456);
JavaScript actually has only one scope. Any variable (a function can also be regarded as a variable) will be searched outward if it is not found within the scope of the function. If it is not found in the global scope, an error referenceError will be reported
standard
Since all our global variables will be bound to our window, if different js files use the same global variables, how to reduce conflicts
//Unique global variable
var sgl = {};
//Define global variables
sgl.name = 'coco';
sgl.add = function(a,b){
return a+b;
}
Put all your code into the unique space name defined by yourself to reduce the problem of global naming conflict
Local scope let
function aaa() {
for (var i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
console.log(i);
}
console.log(i+1); //101 I out of scope, you can also use
}
let keyword to solve the problem of local scope conflict
function aaa() {
for (let i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
console.log(i);
}
console.log(i+1); //Uncaught ReferenceError: i is not defined
}
Constant const
var PI = '3.14'; console.log(PI); //3.14 PI = '111'; //You can change this value console.log(PI); //111
The constant const is introduced
const PI = '3.14'; //read-only variable console.log(PI); PI = '111'; //Direct error: unable typeerror: assignment to constant variable
method
Definition method
**The method is to put the function in the object. The * * object has only two things: attributes and methods
var sgl = {
name: 'GANGLONG',
birth: 2000,
//method
age:function() {
//This year - year of birth
let now = new Date().getFullYear();
return now - this.birth;
}
}
//attribute
sgl.birth;
//Method must be called in parentheses ()
sgl.age();
open
function getAge() {
//This year - year of birth
let now = new Date().getFullYear();
return now - this.birth;
}
var sgl = {
name: 'GANGLONG',
birth: 2000,
age:getAge
}
//sgl.age(); sure
//getAge() NaN window
this cannot be pointed to. It points to the object that calls it by default
apply
You can control the direction of this in js
getAge.apply(sgl,[])
function getAge() {
//This year - year of birth
let now = new Date().getFullYear();
return now - this.birth;
}
var sgl = {
name: 'GANGLONG',
birth: 2000,
age:getAge
}
getAge.apply(sgl,[]);//this points to sgl and the parameter is null
Internal object
Standard object
typeof 123
"number"
typeof NaN
"number"
typeof '123'
"string"
typeof true
"boolean"
typeof []
"object"
typeof {}
"object"
typeof Math.abs
"function"
typeof undefined
"undefined"
Date
Basic use
var now = new Date(); //console.log(now);
//VM81:1 Tue Sep 07 2021 21:42:17 GMT+0800 (China Standard Time) current time
//Output on console
now.getFullYear();//year
now.getMonth();//Month 0 ~ November represents month
now.getDate();//day
now.getDay();//What day is today?
now.getHours();//Time
now.getMinutes();//branch
now.getSeconds();//second
now.getTime();//Timestamp 1970.1.1 00:00:00 milliseconds 163102248114
console.log(new Date(1631022468114)) //Time stamp to time
Conversion (console output)
var now = new Date();
console.log(new Date(1631022468114))
Tue Sep 07 2021 21:47:48 GMT+0800 (China Standard Time)
now.toLocaleDateString //Note that the call is a method, not a property
ƒ toLocaleDateString() { [native code] }
now.toLocaleDateString();
"07/09/2021"
now.toLocaleString()
"07/09/2021, 21:47:48"
now .toGMTString()
"Tue, 07 Sep 2021 13:47:48 GMT"
JOSN
What is JOSN
- JSON (JavaScript object notation) is a lightweight data exchange format
- The concise and clear hierarchy makes JSON an ideal data exchange language
- It is easy for people to read and write, but also easy for machine analysis and generation, and effectively improves the network transmission efficiency
In JavaScript, any type supported by js can be represented by JOSN; number ,string …
Format:
- All objects use {}
- Arrays all use []
- All key value pairs use key:value
Conversion of JOSN and js objects
var user = {
name:'sgl',
age:21,
sex:'boy'
}
//Object is converted to JSON string, and the parameter is user's attribute {name: "sgl", age: 21, sex: "boy"}
var jsonUser = JSON.stringify('{name: "sgl", age: 21, sex: "boy"}')
//Convert the JSON string to an object, and the parameters are JSON strings
var json01 = JSON.parse('{name: \\"sgl\\", age: 21, sex: \\"boy\\"}');
The difference between JSON and js
var user = {name:'sgl',age:21,sex:'boy'}
var json = {'{name: \\"sgl\\", age: 21, sex: \\"boy\\"}'}
object-oriented programming
Prototype object
- Classes: template prototype objects
- Objects: concrete instances
Prototype: you can point to multiple objects with the last as the prototype
var Student = {
run:function () {
console.log(this.name+"run....")
}
}
var sgl = {
name:'sgl'
}
//The prototype object is Student
sgl.__proto__=Student;
var Bird = {
fly:function () {
console.log(this.name+"fiy....")
}
}
//The prototype object of sgl is Bird
sgl.__proto__=Bird;
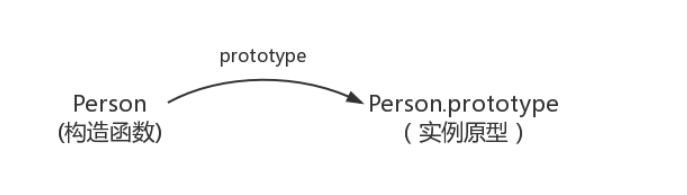
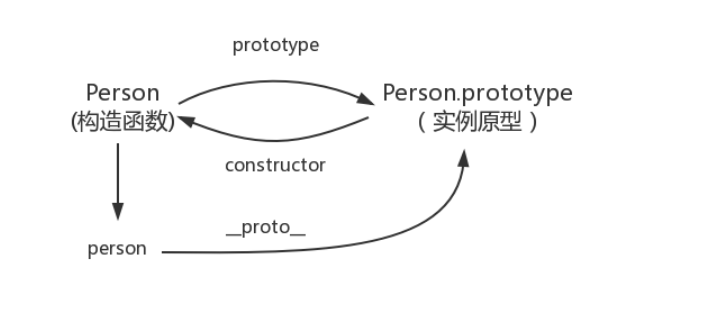
Description: the prototype of the function points to an object, which is the prototype of the instance created when calling the constructor, that is, the prototypes of person1 and person2.
Concept of prototype: when each javascript object (except null) is created, it will be associated with another object. This object is what we call the prototype, and each object will "inherit" properties from the prototype.
function Person(age) { //Initial class definition
this.age = age
}
//Add a new method to Person
Person.prototype.hello = function (){
alert("hello");
}
Person.prototype.name = 'kavin'
var person1 = new Person()
var person2 = new Person()
console.log(person1.name) //kavin
console.log(person2.name) //kavin
console.log(person1.hello()); //hello
console.log(person2.hello()); //hello
Represents the relationship between the constructor and the instance prototype:
class
class keyword
class Student{
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
hello(){
alert("hello");
}
}
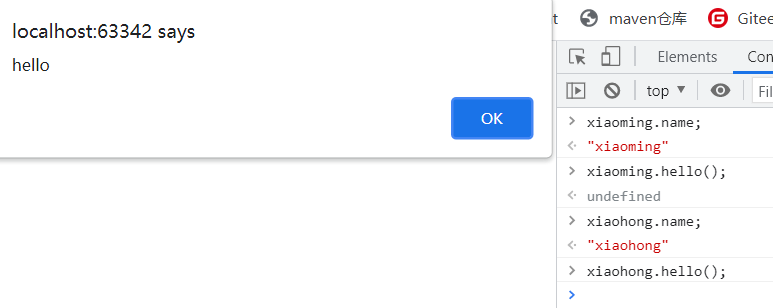
var xiaoming = new Student("xiaoming");
var xiaohong = new Student("xiaohong");
Console output:
inherit
class Student{
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
hello(){
alert("hello");
}
}
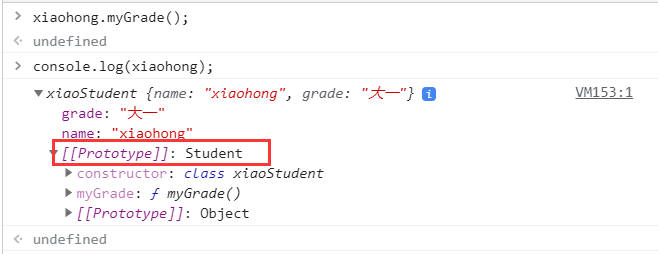
class xiaoStudent extends Student{
constructor(name,grade) {
super(name);
this.grade = grade;
}
myGrade(){
alert("I was just a freshman");
}
}
var xiaoming = new Student("xiaoming");
var xiaohong = new xiaoStudent("xiaohong","Freshman");
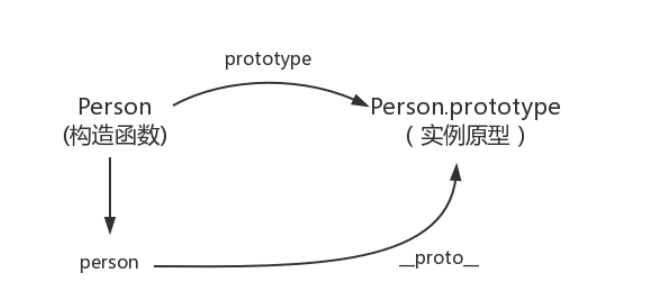
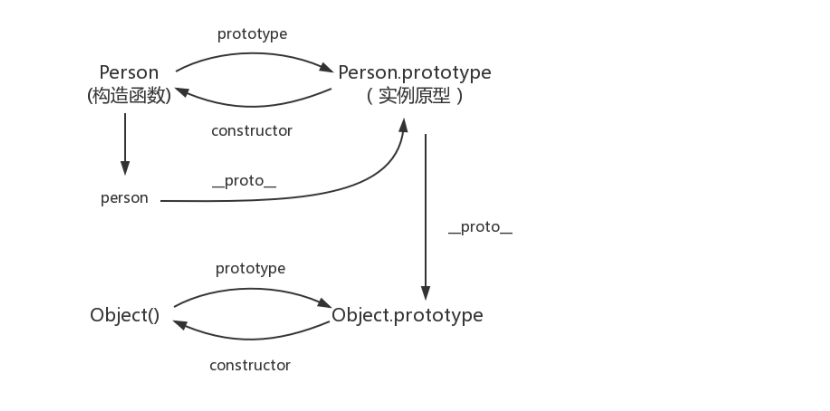
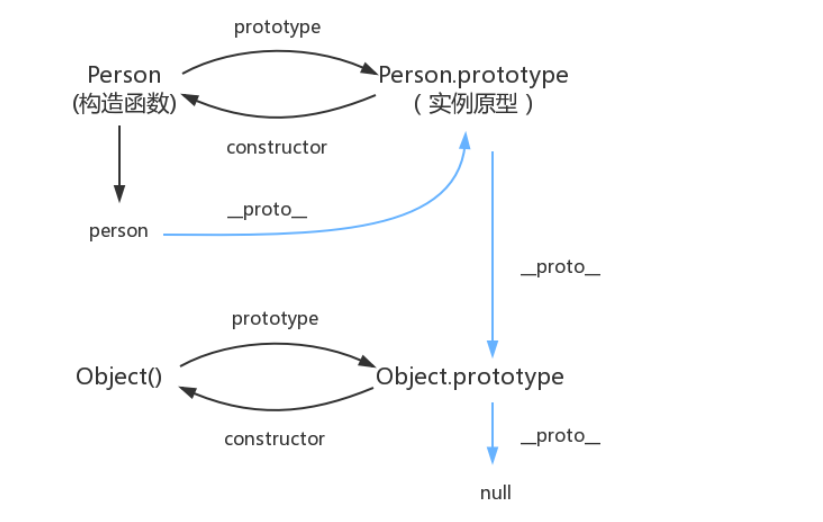
__ proto __ : This is a property that every object (except null) has, called__ proto __, This property points to the prototype of the object.
class Person{
}
var person = new Person();
console.log(person.__proto__ === Person.prototype); // true
Diagram:
constructor
Each prototype has a constructor attribute that points to the associated constructor.
class Person() {
}
console.log(Person===Person.prototype.constructor) //true
Diagram
The prototype Object of the prototype is generated through the Object constructor, combined with the examples mentioned earlier__ proto __ Prototype pointing to constructor
General drawing:
Manipulate BOM objects***
BOM: Browser Object Models
window ***
Window stands for browser window
window.alert(1); undefined window.innerHeight; 524 window.innerWidth; 790 window.outerHeight; 822
Navigator
Navigator encapsulates the browser's information
navigator.appName; "Netscape" navigator.appVersion; "5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/92.0.4515.107 Safari/537.36" navigator.userAgent; "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/92.0.4515.107 Safari/537.36" navigator.platform; "Win32"
Navigator objects are generally not used
screen
Screen stands for screen
screen.width; 1536 screen.height; 864
location ***
location represents the URL information of the current page (console input)
host: "www.baidu.com"
href: "https://www.baidu.com/"
protocol: "https:" //agreement
reload: ƒ reload() //Refresh page
location.assign("https://blog.csdn.net/m0_53821599?spm=1000.2115.3001.5343 "); / / set a new address and run to jump to the address
document
document represents the current web page, HTML DOM tree
document.title; "Baidu once, you know" document.title='Mad God' //Modify title "Mad God"
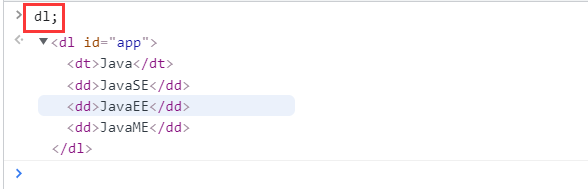
Get the specific document tree node var dl = document.getElementById("app");
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<dl id="app">
<dt>Java</dt>
<dd>JavaSE</dd>
<dd>JavaEE</dd>
<dd>JavaME</dd>
</dl>
<script>
var dl = document.getElementById("app");
</script>
</body>
</html>
Get cookie
document.cookie;
history
History represents the history of the browser
history.back(); history.forward();
Manipulating DOM objects***
DOM: Document Object Model
core
The browser web page is a Dom tree structure
- Update: updating Dom nodes
- Traverse Dom node: get Dom node
- Delete: deletes a Dom node
- Add: adds a new node
To operate a Dom node, you must first obtain the Dom node
Get Dom node
<div id="father">
<h1>Title I</h1>
<p id="p1">p1</p>
<p class="p2">p2</p>
</div>
<script>
//Corresponding css selector
var h1 = document.getElementsByName('h1');
var p1 = document.getElementById('p1');
var p2 = document.getElementsByClassName('p2');
var father = document.getElementById('father');
//father.firstChild;
//father.lastChild;
</script>
Native code, followed by jQuery
Update Dom node
<div id="div">
<script>
var div = document.getElementById('div');
</script>
Operation text:
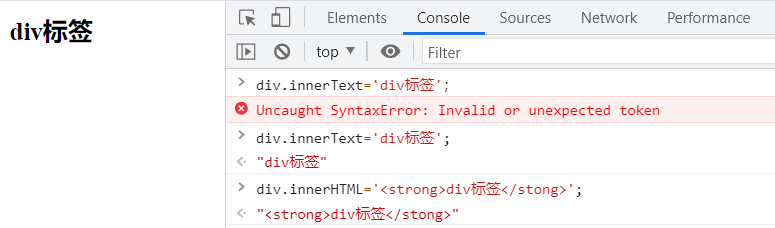
div.innerText and div.innerHTML
- div.innerText='div tag '; modify the value of the text
- Div.innerhtml = '< strong > div tag < / stong >'; tags that can parse HTML text
Operation JS
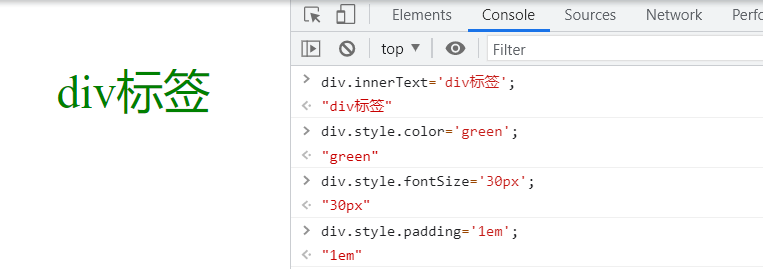
Property wrap with string - turn to hump naming
div.style.color='green'; div.style.fontSize='30px'; div.style.padding='1em';
Delete Dom node
Format: p1.parentElement;
Step: get the parent node first and delete yourself through the parent node
<div id="father">
<h1>Title I</h1>
<p id="p1">p1</p>
<p class="p2">p2</p>
</div>
<script>
var p1 = document.getElementById('p1');
var element = p1.parentElement; //Get parent node
element.removeChild(p1); //Delete the node that gets the parent node
/* Console operation
* //Deletion is a dynamic process
element.removeChild(father.children([0]));
element.removeChild(father.children([1]));
element.removeChild(father.children([2]));
* */
Note: when deleting multiple nodes, children change from time to time. Pay attention when deleting nodes!
Insert Dom node
Get the Dom node. Assuming that the Dom node is empty, we can add an element through innerHTML, but the Dom node already has elements, so we can't do so because it will generate overrides
Add:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
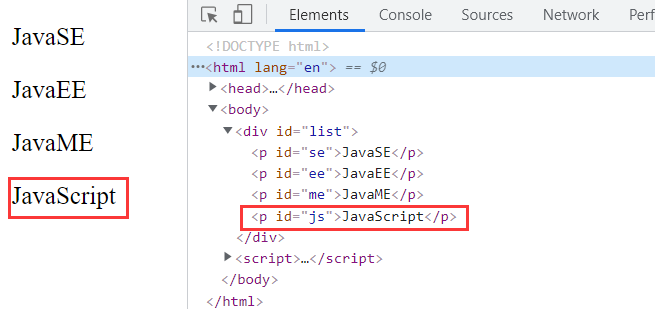
<p id="js">JavaScript</p>
<div id="list">
<p id="se">JavaSE</p>
<p id="ee">JavaEE</p>
<p id="me">JavaME</p>
</div>
<script>
var js = document.getElementById('js');
var ee = document.getElementById('ee');
var list = document.getElementById('list');
// Node to include. insertBefore(newNode,targetNode)
list.insertBefore(js,ee);
</script>
</body>
</html>
effect:
Create a new label to insert
Format: document.createElement('p ');
Test 1:
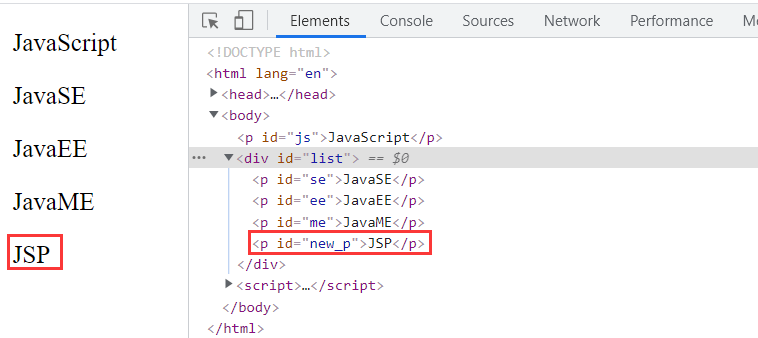
<body>
<p id="js">JavaScript</p>
<div id="list">
<p id="se">JavaSE</p>
<p id="ee">JavaEE</p>
<p id="me">JavaME</p>
</div>
<script>
var js = document.getElementById('js');
var list = document.getElementById('list');
//Create a new node
var new_p = document.createElement('p');
new_p.id = 'new_p';
new_p.innerText = 'JSP';
list.append(new_p);
</script>
effect:
Test 2:
With this property, you can set any value
setAttribute('type','text/javascript')
setAttribute('type','text/css');
<p id="js">JavaScript</p>
<div id="list">
<p id="se">JavaSE</p>
<p id="ee">JavaEE</p>
<p id="me">JavaME</p>
</div>
<script>
var js = document.getElementById('js');
var list = document.getElementById('list');
//Create a new node
var new_p = document.createElement('p');
new_p.id = 'new_p';
new_p.innerText = 'JSP';
list.append(new_p);
//Create a label node
var myScript = document.createElement('script');
myScript.setAttribute('type','text/javascript')
list.append(myScript);
//Create a Style label
var myStyle = document.createElement('style');
myStyle.setAttribute('type','text/css');
myStyle.innerHTML = 'body{background-color: yellow;}' //Equivalent to label selector body {background color: Yellow}
document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0].append(myStyle);
</script>
effect:
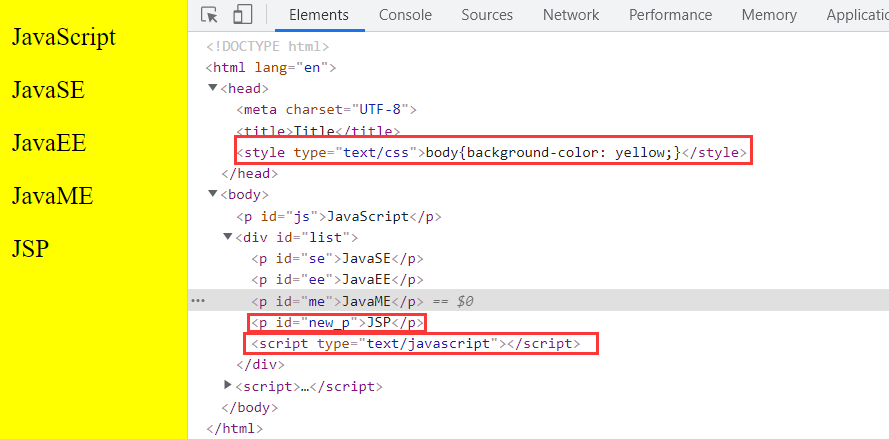
insertBefore
<p id="js">JavaScript</p>
<div id="list">
<p id="se">JavaSE</p>
<p id="ee">JavaEE</p>
<p id="me">JavaME</p>
</div>
<script>
var js = document.getElementById('js');
var ee = document.getElementById('ee');
var list = document.getElementById('list');
// Node to include. insertBefore(newNode,targetNode)
list.insertBefore(js,ee);
</script>
effect:

Action form (validation)
text box, drop-down box, select, radio box, checkbox, hidden field, password box, password
Purpose of the form: to submit information
Get form submission information
<form action="#" method='post'>
<p>
<span>user name:</span> <input type="text" id="username">
</p>
<p>
<span>Gender:</span>
<input type="radio" name="sex" value="man" id="boy">male
<input type="radio" name="sex" value="woman" id="girl">female
</p>
</form>
<script>
var input_text = document.getElementById('username');
var input_radio_boy = document.getElementById('boy');
var input_radio_girl = document.getElementById('girl');
//Get the value of the input box
input_text.value;
//Modify the value of the input box
input_text.value = '123';
//For fixed values such as radio boxes and multiple boxes, input_radio_boy.value can only get the current value
input_radio_boy.checked;//Check whether the returned result is true. If it is true, it will be selected
input_radio_girl.checked = true;//assignment
</script>
Submit form MD5 encryption
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<!--MD5 Tool class-->
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/blueimp-md5/2.10.0/js/md5.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!--
Form binding submission event
onsubmit = Bind a function to submit detection, true false
Return this result to the form, using onsubmit receive
οnsubmit="return fun()"
-->
<form action="https://www.baidu.com" method="post" onsubmit="return fun()">
<p>
<span>user name:</span> <input type="text" required id="username" name="username">
</p>
<p>
<span>password:</span> <input type="password" id="input_password">
</p>
<!--Real password (password hidden)-->
<input type="hidden" id="md5-password" name="password">
<!--Binding event onclick Be clicked-->
<!--<button type="submit" οnclick="fun()">Submit</button>-->
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
<script>
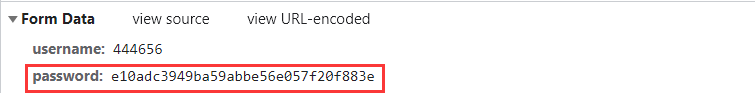
function fun() {
var uname = document.getElementById('username');
var pwd = document.getElementById('input_password');
var md5pwd = document.getElementById('md5-password');
//The password is encrypted by MD5 and assigned to md5pwd
md5pwd.value = md5(pwd.value)
//You can verify and judge the contents of the form. true means submitting, and false prevents submitting
return true;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
The password is encrypted
jQuery
jQuery is a library that contains a large number of JavaScript functions
Get jQuery
- External reference
<!--quote--> <script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/jquery/3.6.0/jquery.js"></script>
- Download jQuery from the official website and import
jQuery formula:
$(selector).action() selector is css selector. action refers to an event
Test:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<!--References can also be downloaded from the official website-->
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/jquery/3.6.0/jquery.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!--jQuery formula
$(selector).action()
selector namely css selector
action Refers to an event
-->
<a href="" id="jQuery">Point me</a>
<script>
$('#jQuery').click(function () {
alert('hello jQuery');
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
Selector selector
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/jquery/3.6.0/jquery.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//tag chooser
document.getElementsByTagName();
//id selector
document.getElementById();
//Class selector
document.getElementsByClassName();
//All selectors in jQuery CSS can be used
$('p').click(); //tag chooser
$('#id01').click(); //id selector
$('.class01').click(); //Class selector
</script>
</body>
</html>
action event
| Mouse event | Keyboard events | Form Events | Document / window events |
|---|---|---|---|
| click | keypress | submit | load |
| dblclick | keydown | change | resize |
| mouseenter | keyup | focus | scroll |
| mouseleave | blur | unload | |
| hover |
jQuery rookie tutorial has a detailed tutorial https://www.runoob.com/jquery/jquery-events.html
You can also go to jQuery to help the events in the document https://jquery.cuishifeng.cn/
Mouse movement test:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/jquery/3.6.0/jquery.js"></script>
<style>
#divMove{
width: 300px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!--Gets the current coordinate of the mouse-->
<p>Move to get mouse coordinates:</p>
<span id="mouseMove"></span>
<div id="divMove"></div>
<script>
//Respond to the event after the current web page is loaded
$(function () {
$('#divMove').mousemove(function (e) {
$('#mouseMove').text('x:'+e.pageX+'y:'+e.pageY)
})
});
</script>
</body>
</html>

jQuery operation Dom element
Node text operation
$('#id_ul li[name=javaee]').text(); // Get value
$('#id_ UL Li [name = JavaEE] '. Text ('set value')// Set value
$('#id_ul').html();// Get value
$('#id_ ul').html('<strong>123</strong>');// Set value
Test:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/jquery/3.6.0/jquery.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<ul id="id_ul">
<li class="class_se">JavaSE</li>
<li name="javaee">JavaEE</li>
</ul>
<script>
$('#id_ul li[name=javaee]').text();
$('#id_ul').html();
</script>
</body>
</html>

css operation:
$('#id_ul li[name=javaee]').css({ "color": "#ff0011", "background": "blue" });
<ul id="id_ul">
<li class="class_se">JavaSE</li>
<li name="javaee">JavaEE</li>
</ul>
<script>
$('#id_ul li[name=javaee]').text();
$('#id_ul').html();
//$('#id_ul li[name=javaee]').css({ "color": "#ff0011", "background": "blue" });
</script>

Display and hiding of elements: Essence display:none
$('#id_ul li[name=javaee]').show()
$('#id_ul li[name=javaee]').hide()