Introduction to JSON
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation), namely JavaScript object notation, is a lightweight and general text data format.
JSON syntax supports objects, arrays, strings, numbers (int/float), and true/false and null.
JSON has a strict format. The main formats are as follows:
- You can only use double quotation marks, not single quotation marks
- The elements are separated by commas. The last element cannot have commas
- Comments are not supported
- Chinese and other special characters shall be converted to ASCII code (\ uXXX format) during transmission
- Supports multi-layer nested objects or arrays
Sample format, file demo json:
{
"name": "Cactus",
"age": 18,
"skills": ["Python", "Java", "Go", "NodeJS"],
"has_blog": true,
"gf": null
}
Correspondence between JSON and Python data types
JSON corresponds to the dictionary and other types in Python one by one:
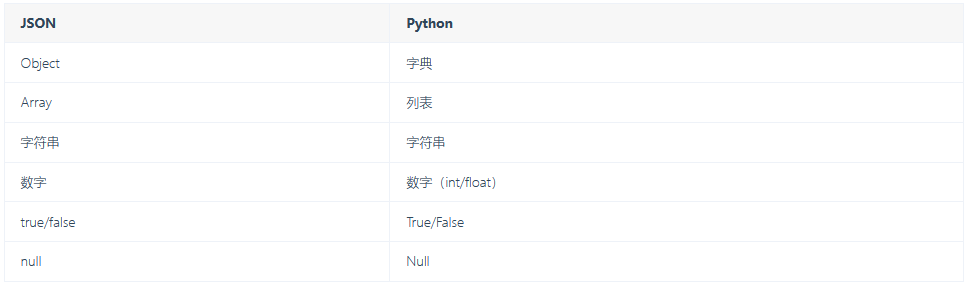
Note: in Python in, JSON Generally refers to compliance JSON A string in syntax format is actually a string, single line or multiple lines.
Conversion between string and Python dictionary
Why should we convert each other? JSON is a string, which is convenient for storage and transmission and inconvenient for extracting values; Dictionary is a data structure in memory, which is convenient for value taking and inconvenient for transmission and storage
Using Python's own JSON package can complete the conversion between dictionary and JSON string
- json. Dumps: converts a dictionary to a JSON string
- json.loads(JSON string): converts a JSON string into a dictionary. If the string is not in a legal JSON format, JSONDecodeError will be reported
Example 1: dictionary to JSON string
import json
dict_var = {
'name': 'Cactus',
'age': 18,
'skills': ['Python', 'Java', 'Go', 'NodeJS'],
'has_blog': True,
'gf': None
}
print(json.dumps(dict_var))
print(json.dumps(dict_var, indent=2,sort_keys=True, ensure_ascii=False))
json.dumps() supports parameters, indent is the number of indented spaces in multiple lines, sort_keys is whether to sort the keys, ensure_ascii=False means that ascii is not guaranteed, and special characters such as Chinese are not converted to \ uXXX, etc
Display results:
{"name": "Cactus", "age": 18, "skills": ["Python", "Java", "Go", "NodeJS"], "has_blog": true, "gf": null}
{
"age": 18,
"gf": null,
"has_blog": true,
"name": "Cactus",
"skills": [
"Python",
"Java",
"Go",
"NodeJS"
]
}
Example 2: JSON string - > dictionary
import json
json_str = '''{
"name": "Cactus",
"age": 18,
"skills": ["Python", "Java", "Go", "NodeJS"],
"has_blog": true,
"gf": null
}'''
print(json.loads(json_str))
Display results:
{'name': 'Cactus', 'age': 18, 'skills': ['Python', 'Java', 'Go', 'NodeJS'], 'has_blog': True, 'gf': None}
Conversion between JSON file and dictionary
In addition, you can directly save the dictionary as a JSON file or convert it from a JSON file to a dictionary
- json. Dump (Dictionary, f): convert dictionary to JSON file (handle)
- json.loads(f): turns the handle of the open JSON file into a dictionary
Example 3: Dictionary - > JSON file
'''
No one answers the problems encountered in learning? Xiaobian created a Python exchange of learning QQ Group: 725638078
Look for like-minded partners to help each other,There are also good videos and tutorials in the group PDF e-book!
'''
import json
dict_var = {
'name': 'Cactus',
'age': 18,
'skills': ['Python', 'Java', 'Go', 'NodeJS'],
'has_blog': True,
'gf': None
}
with open("demo2.json", "w", encoding='utf-8') as f:
# json.dump(dict_var, f) # Write as one line
json.dump(dict_var, f,indent=2,sort_keys=True, ensure_ascii=False) # Write as multiple lines
File demo2 JSON result:
{
"age": 18,
"gf": null,
"has_blog": true,
"name": "Cactus",
"skills": [
"Python",
"Java",
"Go",
"NodeJS"
]
}
Example 4: JSON file - > dictionary
import json
with open("demo2.json", encoding="utf-8") as f:
data = json.load(f)
pritn(data)
Display results:
{'age': 18, 'gf': None, 'has_blog': True, 'name': 'Cactus', 'skills': ['Python', 'Java', 'Go', 'NodeJS']}
Note: when the dictionary is converted to JSON, only nested dictionaries, lists, strings, numbers, True/False/None, etc. are supported, and date objects and other Python objects are not supported
To resolve complex nested JSON format, please use JSONPath