install
Just started R language, R (R language version) and RStudio (r compilation platform)
R: R
RStudio: Rstudio
Detailed installation process
R language is an object-oriented programming language
R language is more like python. The statement format is very similar to py. Use {} instead of: (colon)
The processing object of R language is vector, which calls the database frequently
Single line notes: # notes
Multiline comments: R does not provide multiline comments
Alternative method: RStudio select the code to be commented and press Ctrl+Shift+C
data type
The R language does not need to declare variables.
The R language allows the use of full and FALSE abbreviations T and F
typeof() #View data types #integer #integer #double #Decimal (floating point) (double by default) #character #String type #logical #Logical type mode() #View data structure #numeric #Numeric vector, numeric type, including integer, decimal and scientific counting #character #String vector #list #list #Matrix is also a kind of number vector #matrix #array
vector
Vector type is the core of R language. All types can be called vectors. A number (scalar) is also a vector with one element
R language numeric variables do not specify double precision "double" types, and 1:6 generates integers
Allow element duplication
Vector addition and deletion need to be re assigned to the vector
length(), get the length of the vector
#Assignment: > x<-3 > x[1] [1] 3 #x is also a vector with only one element #vector a<-c(1,3,5,7,9) > a[2] [1] 3 #Subscripts start at 1, not 0 > a[2:4] [1] 3 5 7 #Subscripts from 2nd to 4th #Change the vector and re assign the value > a<-c(a[1:3],66,18) > a [1] 1 3 5 66 18 #mean() find vector mean mean(x) #hist() draw histogram
Vector operation:
Vector addition, subtraction, multiplication and division, and the corresponding elements are added directly (in the same format)
Single vector x and vector A are added, subtracted, multiplied and divided, and each element of vector A corresponds to x operation respectively
Index, subscript starts from 1
> li
a
[1,] 1 1
[2,] 3 1
[3,] 5 1
[4,] 66 1
[5,] 18 1
> li + c(1,2)
a
[1,] 2 3
[2,] 5 2
[3,] 6 3
[4,] 68 2
[5,] 19 3
#Equivalent to:
> li + array(c(1,2),dim(li))
a
[1,] 2 3
[2,] 5 2
[3,] 6 3
[4,] 68 2
[5,] 19 3
> b <- c(1:9)
> b
[1] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
> b[-2:-4]
[1] 1 5 6 7 8 9 #R language indexes are closed intervals
seq(), generate an equal difference vector: seq(from=num1, to=num2, by=num3)
seq(from=num1, to=num2, length=num3)
req(), repeat subvector: req(x,times)
all(),any(), returns TRUE or FALSE
character string
String is actually a single element vector in character mode. Double quotation marks are used by default, and single quotation marks are also used for assignment.
The string in R language contains characters. It can also be said that a character is a string.
> st = 'my gril'
> st
[1] "my gril"
> mode(st)
#As long as one of the vectors is a string, the vector is a string vector
> ch = c('a',o,9,'45')
Error: object 'o' not found
> ch = c('a','one',9,'45')
> ch
[1] "a" "one" "9" "45"
> mode(ch)
[1] "character"
> length(ch)
[1] 4
String concatenation and separator

matrix
function matrix)Construction matrix(Two dimensional array)The construction form of the function is: matrix(data=NA,nrow=1,ncol=1,byrow=FALSE,dimnames=NULL) among data Is a vector data, nrol Is the number of rows of the matrix, ncol Is the number of columns of the matrix. When byrow=TRUE When, the data of the generated matrix is placed by row. By default, it is equivalent to byrow=FALSE,Data is placed in columns. dimname,Is the name of the array dimension. It is empty by default.
t(), matrix transpose
det(), find the determinant of a square matrix
dim(), number of rows and columns of the matrix
Two matrices are directly multiplied by A * B, and the corresponding elements are multiplied (the matrix must be similar)
**Vector inner product** A %*% B **Vector outer product (cross product)** A %o% B outer()It is a more powerful outer product operation function, outer(x,y)Compute vector two and y The outer product of, which is equivalent to A %o% B Function. outer()The general call format for is outer(A,B,fun="*") among A,B matrix(Or vector),fun Is a function for outer product operation. The default value is multiplication. function outer()Useful when drawing 3D surfaces, it generates a x and y Grid of.
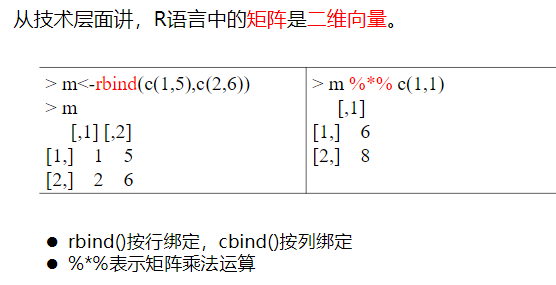
> m<-rbind(c(1,5),c(2,6))
> m
[,1] [,2]
[1,] 1 5
[2,] 2 6
> c = cbind(c(1,5),c(2,6))
> c
[,1] [,2]
[1,] 1 2
[2,] 5 6
#Matrix direct multiplication*
> m * c
[,1] [,2]
[1,] 1 10
[2,] 10 36
#Matrix inner product c
> m %*% c
[,1] [,2]
[1,] 26 32
[2,] 32 40
#Matrix outer product
> m %o% c
, , 1, 1
[,1] [,2]
[1,] 1 5
[2,] 2 6
, , 2, 1
[,1] [,2]
[1,] 5 25
[2,] 10 30
, , 1, 2
[,1] [,2]
[1,] 2 10
[2,] 4 12
, , 2, 2
[,1] [,2]
[1,] 6 30
[2,] 12 36
>mc<-m %o% c
> dim(mc)
[1] 2 2 2 2
#dim(mc) = c(dim(m), dim(c)) #Attention dimension
> mat <- matrix(1:9, nrow=3, dimnames=list(c('r1', 'r2', 'r3'), c('c1', 'c2', 'c3')))
> mat
c1 c2 c3
r1 1 4 7
r2 2 5 8
r3 3 6 9
#You can add rows and columns through rbind and cbind
> rbind(mat, c(12, 13, 14)) #Add a row after the original matrix mat
> rbind(mat, c(12, 13, 14))
c1 c2 c3
r1 1 4 7
r2 2 5 8
r3 3 6 9
12 13 14
list
Items in the list can be different data types
> li <- list(55,"34",c(3,5)) > li [[1]] [1] 55 [[2]] [1] "34" [[3]] [1] 3 5
Data frame
The database in R language can be regarded as a two-dimensional list
Data frames are usually created by reading files or databases
In R language, data frame uses data Frame() function. The format is as follows:
data.frame(col1, col2, ..., row.name=NULL, check.rows = FALSE, check.names=TRUE, stringsAsFactors = default.stringsAsFactors()) Among them, row.name It is used to specify the name of each row (sample). There is no name by default. Each row is identified by a self increasing sequence starting from 1; check.rows It is used to check whether the name and quantity of rows are consistent. The default value is FALSE; check.names To check whether the name of the variable (column) is unique and consistent with the syntax. The default is TRUE; It is used to describe whether to automatically convert a character vector into a factor. The default conversion is used if it is not changed stringsAsFactors = FALSE To specify.
You can add a new row or column to the data frame variable using the rbind() function and the cbind() function.
> arr1 = array(1:12,c(3,4))
> arr1
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
[1,] 1 4 7 10
[2,] 2 5 8 11
[3,] 3 6 9 12
> mode(arr1)
[1] "numeric"
> data.frame(arr1)
X1 X2 X3 X4
1 1 4 7 10
2 2 5 8 11
3 3 6 9 12
> mode(data.frame(arr1))
[1] "list"
> df1<-df1[-2,] #Delete line 2 data
> df1<-df1[,-c(1,3)] #Delete the data in columns and 3
#Add
> lis<-list(name=c("Zhang San","Fourth sister","Wang Wu"," Xiao Qi"), sex=c("male", "female", "male", "male"), score=c(ninety, eighty-five, eighty-two, ninety-three))
> df2 <- data.frame(lis)
> df2
name sex score
1 Zhang Sannan ninety
2 Fourth sister eighty-five
3 Wang Wunan eighty-two
4 Little seven man ninety-three
> lis2 <- list(name="myna",sex="male",score=ninety-two) #Create a new list
> df2<-rbind(df2, as.data.frame(lis2)) #Add list lis2 to df2
> df2
name sex score
1 Zhang Sannan 90
2 Fourth sister eighty-five
3 Wang Wunan eighty-two
4 Little seven man 93
5 Starling male ninety-two
> lis3<-list(height=c(one hundred and seventy,one hundred and seventy-eight,one hundred and eighty-five,190,178,one hundred and seventy-five)) #Create a new list and save the height
> lis3<-list(height=c(170,one hundred and sixty-eight,185,178,175)) #Create a new list and save the height
> df2
name sex score height
1 Zhang Sannan 90 170
2 Fourth sister 85 168
3 Wang Wunan 82 185
4 Little seven man 93 178
5 Starling male 92 175
function
#Vector summation
add<-function(x){ #x: Formal parameter, without type
sum<-0 #Initial value, assignment
#for loop:
for(i in x){
sum = sum + i #No sum+=i
}
return(sum)
}