1, What is istio
- Cloud platforms benefit companies that use them. But it is undeniable that going to the cloud will put pressure on the DevOps team. In order to be portable, developers must use microservices to build applications. At the same time, operation and maintenance personnel are also managing extremely large hybrid cloud and multi cloud deployment environments. Istio allows you to connect, protect, control and observe services.
- At a higher level, istio helps reduce the complexity of these deployments and reduces the pressure on the development team. It is a completely open source service grid, which is connected to the existing distributed applications as a transparent layer. It is also a platform with API interfaces that can integrate any logging, telemetry and policy systems. Istio's diverse features enable you to successfully and efficiently run a distributed microservice architecture and provide a unified way to protect, connect, and monitor microservices
Personal understanding: more and more applications / services are turning to microservices. When microservices reach a certain scale, the governance and control of microservices become a problem to be solved. istio just provides the governance ability of this kind of microservices, provides a unified method of protecting, connecting and monitoring microservices, reduces the complexity of these deployments, and reduces the pressure on the development team.
2, Why Istio?
Through load balancing, authentication between services, monitoring and other methods, Istio can easily create a network where services have been deployed, and the code of services only needs little or no change. Add Istio support to the service by deploying a special sidecar agent in the whole environment. The agent will intercept all network communication between micro services, and then use the functions of its control plane to configure and manage Istio, including:
- Automatic load balancing for HTTP, gRPC, WebSocket, and TCP traffic.
- Fine grained control of traffic behavior through rich routing rules, Retry, failover and fault injection.
- Pluggable policy layer and configuration API, supporting access control, rate restriction and quota.
- Automatic measurement, logging and tracking of all traffic within the cluster (including the entrance and exit of the cluster).
- Secure inter service communication is realized in a cluster with strong authentication and authorization based.
Istio is designed for scalability and can meet different deployment requirements.
3, Download Istio
visit Istio release Download the installation file corresponding to your operating system. I use
istio-1.6.13-linux-amd64.tar.gz
4, Installing Istio
1. Preparing the installation environment
1) . environmental information
| Node name | IP address |
|---|---|
| k8s-master1 | 192.168.227.131 |
| k8s-node1 | 192.168.227.132 |
| k8s-node2 | 192.168.227.133 |
2) . hardware environment information
| name | describe |
|---|---|
| Office computer | winxp10 |
| virtual machine | VMware® Workstation 15 Pro 15.5.1 build-15018445 |
| operating system | CentOS Linux 7 (Core) |
| linux kernel | CentOS Linux (5.4.123-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64) 7 (Core) |
| CPU | At least 2 cores (this version of k8s requires at least 2 cores, otherwise kubedm init will report an error) |
| Memory | 2G and above |
3) . cloud native k8s cluster installation
- For the installation of k8s cluster, please refer to my other blog, fool operation. When the hardware is ready, it can be installed in about half an hour
Link: kubernetes(k8s) quick installation guide on CentOS 7.
2. Install and deploy istio
1) Unzip the Istio installation file
[root@k8s-master1 ~]# mkdir istioinstall
Upload the Istio installation package to the installation directory istioinstall created above, and extract it
[root@k8s-master1 istioinstall]# tar -zxvf istio-1.6.13-linux-amd64.tar.gz
1) Configure Istio environment variables
[root@k8s-master1 istioinstall]# cd istio-1.6.13/bin/ [root@k8s-master1 bin]# pwd /root/istioinstall/istio-1.6.13/bin [root@k8s-master1 bin]# vi ~/.bashrc
Save and exit after adding the following contents
export PATH=/root/istioinstall/istio-1.6.13/bin:$PATH
Execute the following command to make the environment variable effective
[root@k8s-master1 bin]# source ~/.bashrc
Check the istio version and test whether the configuration is successful. The following message appears, indicating that the configuration is successful
[root@k8s-master1 bin]# istioctl version client version: 1.6.13 control plane version: 1.6.13 data plane version: 1.6.13 (3 proxies)
2) Start installing Istio
- Execute the following command to install the demo configuration:
istioctl manifest apply --set profile=demo
[root@k8s-master1 bin]# istioctl manifest apply --set profile=demo Detected that your cluster does not support third party JWT authentication. Falling back to less secure first party JWT. See https://istio.io/docs/ops/best-practices/security/#configure-third-party-service-account-tokens for details. ✔ Istio core installed ✔ Istiod installed ✔ Ingress gateways installed ✔ Egress gateways installed ✔ Addons installed ✔ Installation complete
- Verify that the installation was successful
- Add a namespace namespace of istio system
[root@k8s-master1 manifests]# kubectl get ns NAME STATUS AGE default Active 11d istio-system Active 8h kube-node-lease Active 11d kube-public Active 11d kube-system Active 11d prome-system Active 10d
- The Pod of the namespace namespace of istio system runs normally
[root@k8s-master1 manifests]# kubectl get pod -n istio-system NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE grafana-5dc4b4676c-d5l2r 1/1 Running 0 8h istio-egressgateway-6c59c897b-5xzv5 1/1 Running 0 8h istio-ingressgateway-69d64797d5-4s55m 1/1 Running 0 8h istio-tracing-8584b4d7f9-b2dwb 1/1 Running 0 8h istiod-67f5db7d47-k8mc6 1/1 Running 0 8h kiali-6f457f5964-24b9w 1/1 Running 0 8h prometheus-7c8bcc98c6-gtk27 2/2 Running 0 8h
5, Istio usage example
1. Introduction to Bookinfo sample application
Istio officially provides a sample application of Bookinfo,
The Bookinfo application is divided into four separate microservices:
- productpage. This microservice will call two microservices, details and reviews, to generate pages.
- details. This micro service contains information about books.
- reviews. This micro service contains book related comments. It also calls the ratings microservice.
- ratings. This micro service contains rating information composed of book reviews.
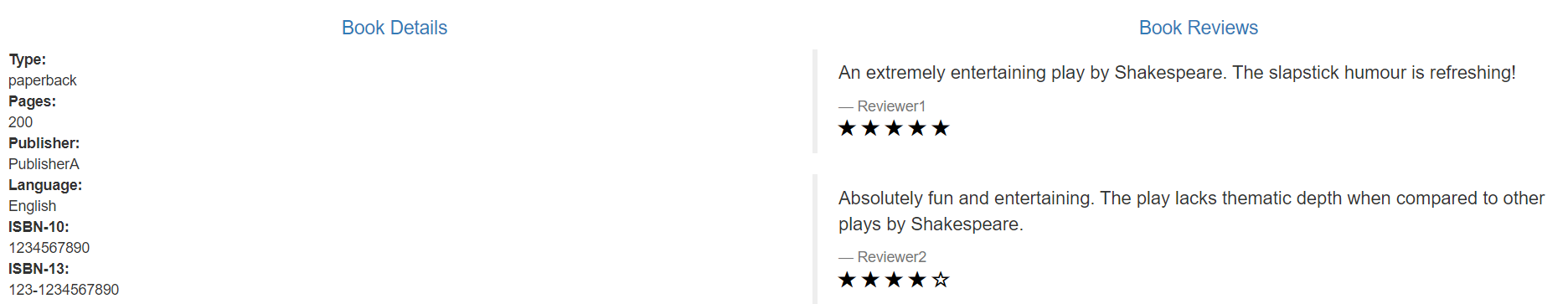
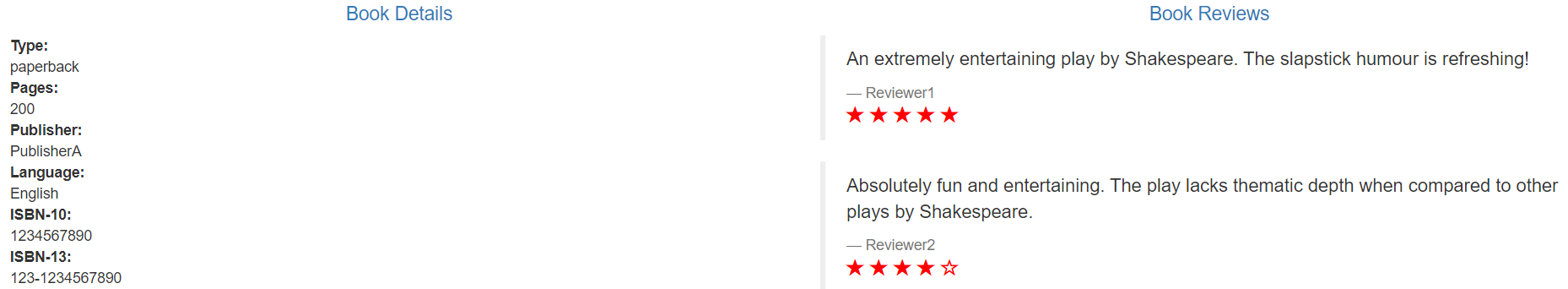
There are three versions of reviews micro service: - The v1 version does not call the ratings service.
- v2 version will call the ratings service and use 1 to 5 Black Star icons to display the rating information.
- The v3 version will call the ratings service and use 1 to 5 Red Star icons to display the rating information.
The architecture of the sample application of Bookinfo is shown in the figure below,
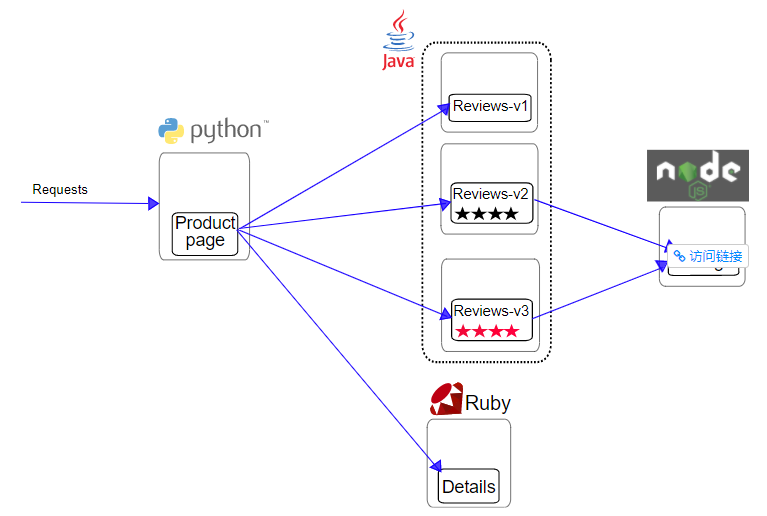 Several microservices in the Bookinfo application are written in different languages. These services do not depend on Istio, but constitute a representative example of service grid: it is composed of multiple services, multiple languages, and the reviews service has multiple versions.
Several microservices in the Bookinfo application are written in different languages. These services do not depend on Istio, but constitute a representative example of service grid: it is composed of multiple services, multiple languages, and the reviews service has multiple versions.
2. How does Istio manage Booinfo microservices?
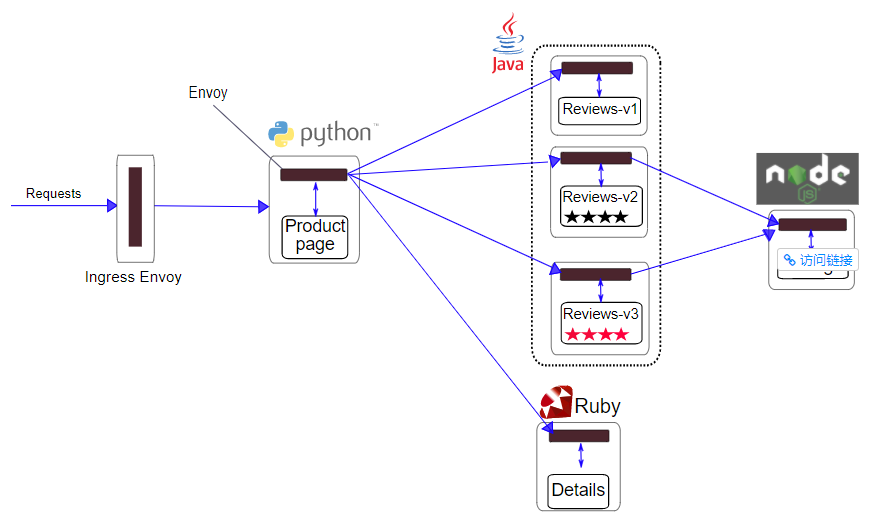
- The Bookinfo sample application runs in Istio. The application itself does not need to make any changes. Simply configure and run the service in Istio environment, specifically, inject Envoy sidecar into each service. The final deployment result is shown in the figure below:
3. Installing and deploying the Bookinfo sample application
1) Enter Istio installation directory
cd istio-1.6.13
2) Create the namespace in which the Bookinfo sample application runs
This step is not necessary, but can also be run in the default namespace. The officially provided installation method is deployed under default.
kubectl create ns bookinfo
3) Turn on Istio automatic injection Sidecar function
Label the namespace where the application runs istio injection = enabled istio automatically inject Sidecar by default Please label the default namespace istio injection = enabled
[root@k8s-master1 istio-1.6.13]# kubectl label namespace bookinfo istio-injection=enabled
3) Install bookinfo
[root@k8s-master1 istio-1.6.13]# kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml -n bookinfo service/details created serviceaccount/bookinfo-details created deployment.apps/details-v1 created service/ratings created serviceaccount/bookinfo-ratings created deployment.apps/ratings-v1 created service/reviews created serviceaccount/bookinfo-reviews created deployment.apps/reviews-v1 created deployment.apps/reviews-v2 created deployment.apps/reviews-v3 created service/productpage created serviceaccount/bookinfo-productpage created deployment.apps/productpage-v1 created
Check whether the deployment is successful
[root@k8s-master1 istio-1.6.13]# kubectl -n bookinfo get pod -o wide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES details-v1-5974b67c8-9r6dn 2/2 Running 0 5m54s 10.244.1.36 k8s-node1 <none> <none> productpage-v1-64794f5db4-k8t2s 2/2 Running 0 5m53s 10.244.1.34 k8s-node1 <none> <none> ratings-v1-c6cdf8d98-xgwqw 2/2 Running 0 5m53s 10.244.2.49 k8s-node2 <none> <none> reviews-v1-7f6558b974-phbsk 2/2 Running 0 5m53s 10.244.2.47 k8s-node2 <none> <none> reviews-v2-6cb6ccd848-zkn9w 2/2 Running 0 5m53s 10.244.2.48 k8s-node2 <none> <none> reviews-v3-cc56b578-whcv6 2/2 Running 0 5m53s 10.244.1.35 k8s-node1 <none> <none>
Create an Ingress gateway, otherwise the service cannot be accessed externally,
[root@k8s-master1 istio-1.6.13]# kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/networking/bookinfo-gateway.yaml -n bookinfo
Confirm the gateway and access address,
[root@k8s-master1 istio-1.6.13]# kubectl get gateways.networking.istio.io -n bookinfo NAME AGE bookinfo-gateway 50s [root@k8s-master1 istio-1.6.13]# kubectl get virtualservices.networking.istio.io -n bookinfo NAME GATEWAYS HOSTS AGE bookinfo [bookinfo-gateway] [*] 61s [root@k8s-master1 istio-1.6.13]# kubectl get svc -n istio-system|grep istio-ingressgateway istio-ingressgateway LoadBalancer 10.106.215.228 <pending> 15021:31689/TCP,80:32410/TCP,443:30289/TCP,31400:31641/TCP,15443:32757/TCP 3d4h [root@k8s-master1 istio-1.6.13]#
According to the description of the official document, when the EXTERNAL-IP of istio ingress gateway service is pending, you need to obtain the access address and port number in the following ways,
[root@k8s-master1 istio-1.6.13]# kubectl get po -l istio=ingressgateway -n istio-system -o jsonpath='{.items[0].status.hostIP}'
192.168.227.132
[root@k8s-master1 istio-1.6.13]# kubectl -n istio-system get service istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.spec.ports[?(@.name=="http2")].nodePort}'
32410
Then you can use the browser to access the application page,
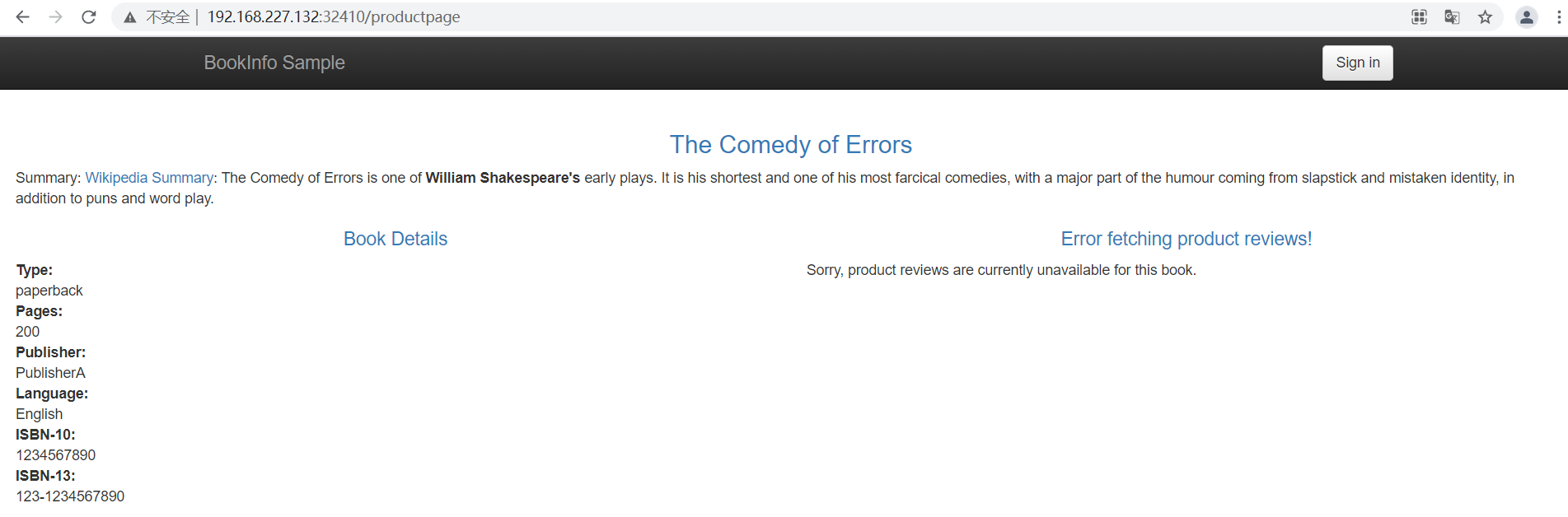
At this time, the requests of reviews can be refreshed to different versions of the service several times,