background
1. Receive serial port information

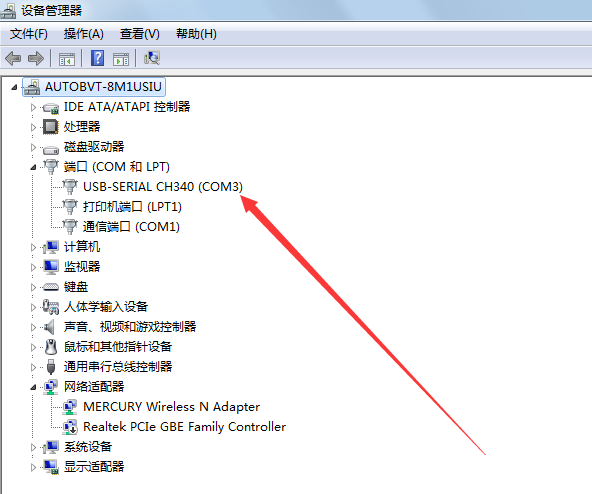
2. Make data into oscillogram
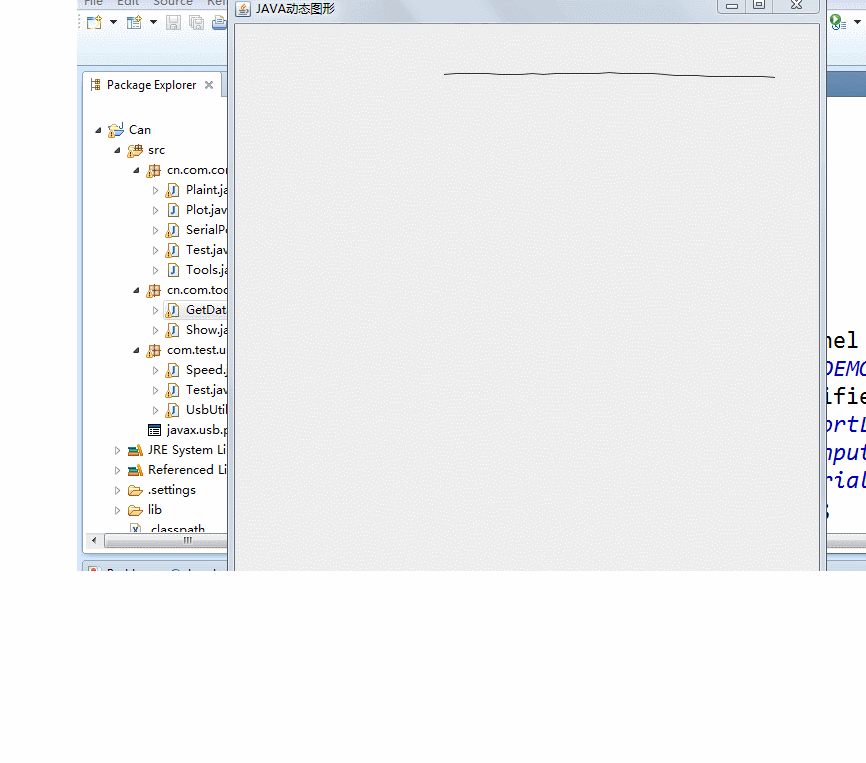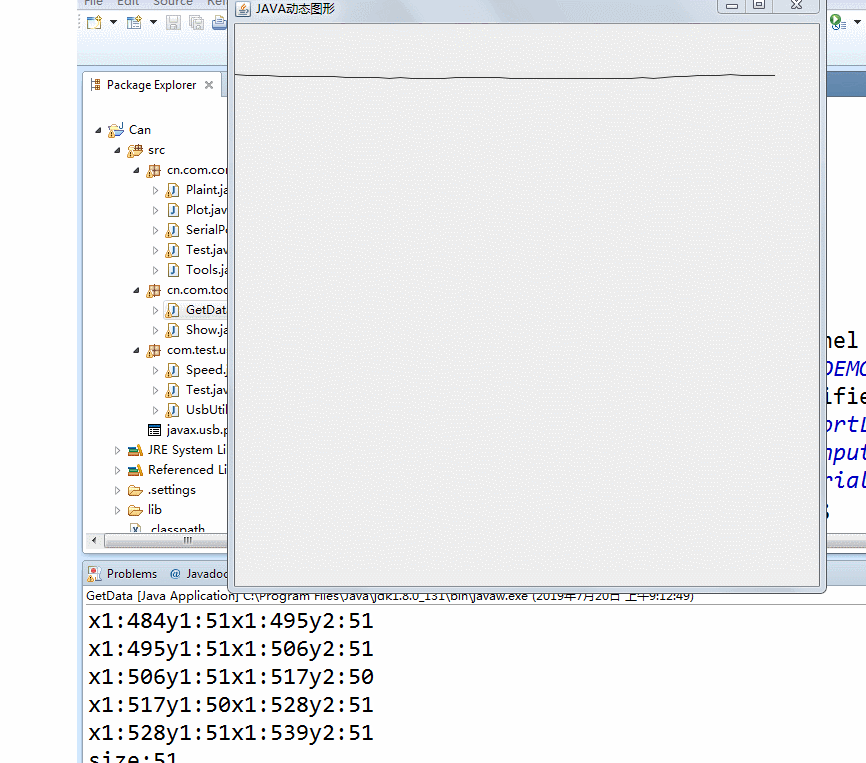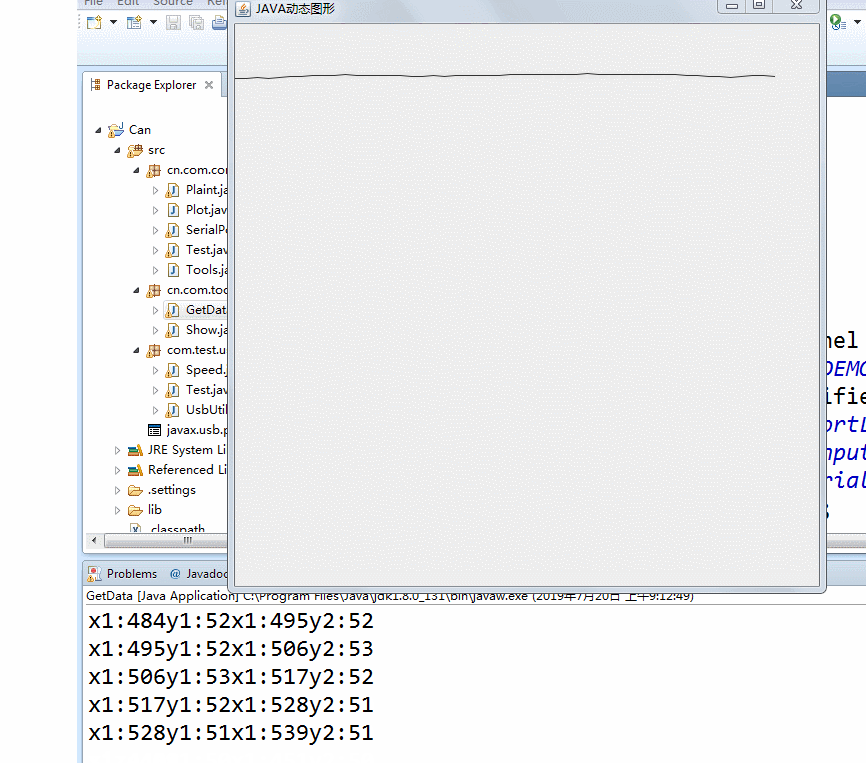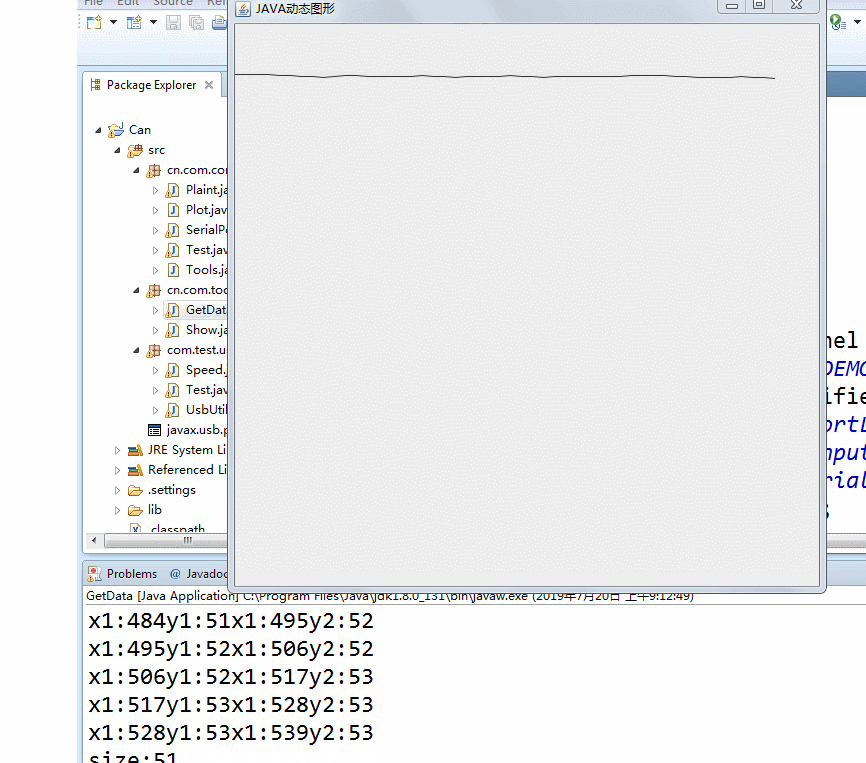
difficulty
1. The retain () method must be added to the Jrame to call the paintComponent(Graphics g) method.
2. Note the value type. If the y value is too small, it needs to be set to double. If it is of int type, it is 0. A line will be displayed at the top.
double y =getHeight()/value;
3. Understand the operation process
thinking
1. Single serial port receiving data https://blog.csdn.net/qq_37591637/article/details/96285961
2. Single implementation of java dynamic diagram https://blog.csdn.net/qq_37591637/article/details/96429855
3. Integration
The complete code is as follows (because I need to process the data, there are many codes)
package cn.com.tools;
import gnu.io.*;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.Graphics2D;
import java.awt.RenderingHints;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.TooManyListenersException;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import cn.com.com.Plot;
import cn.com.com.Tools;
/*author:Believers of destiny
*Purpose: serial communication
*Time: July 18, 2019
*/
public class GetData extends JPanel implements Runnable, SerialPortEventListener {
private static final String DEMONAME = "Serial port test";
private static CommPortIdentifier portId;
private static Enumeration portList;
private static InputStream inputStream;
private static SerialPort serialPort;
private static int size = 50;
Thread readThread;
private static double value =7000;
// A thread
static List<Integer> list = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<Integer>());
static JFrame jf = new JFrame("JAVA Dynamic graphics");
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. Set the width and height of the window
jf.setSize(600, 600);
jf.getContentPane().add(new GetData());
// 2. Set close window to close thread
jf.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// 3. Visible Setting
jf.setVisible(true);
// Open thread
}
public GetData() {
portList = CommPortIdentifier.getPortIdentifiers();
while (portList.hasMoreElements()) {
portId = (CommPortIdentifier) portList.nextElement();
if (portId.getPortType() == CommPortIdentifier.PORT_SERIAL
&& portId.getName().equals("COM3")) {
System.out.println("Discovery port:" + portId.getName());
try {
serialPort = (SerialPort) portId.open(DEMONAME, 2000);
// Get input stream
inputStream = serialPort.getInputStream();
// Set serial monitoring
serialPort.addEventListener(this);
// Set enable listening
serialPort.notifyOnDataAvailable(true);
// Set baud rate, data bit, stop bit and check bit
serialPort.setSerialPortParams(115200, SerialPort.DATABITS_8,
SerialPort.STOPBITS_1, SerialPort.PARITY_NONE);
} catch (TooManyListenersException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (UnsupportedCommOperationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (PortInUseException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/**
* Monitor function
*
* @param serialPortEvent
*/
@Override
public void serialEvent(SerialPortEvent serialPortEvent) {
if (serialPortEvent.getEventType() == SerialPortEvent.DATA_AVAILABLE) {
readComm();
}
}
/**
* Read serial port information
*/
private void readComm() {
byte[] readBuffer = new byte[2];
try {
inputStream.read(readBuffer);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (byte b : readBuffer) {
String a = Tools.byteToStr(b);
if (a.equals("00") || a == "00") {
} else {
sb.append(a);
}
}
// Add to thread collection
if (list.size() > size) {
list.remove(0);// Remove first data
}
// 2.1.2 put the number in the set
Plot p = Tools.add(sb.toString());
//System.out.println("x:" + p.getX());
list.add(p.getX());
System.out.println("size:" + list.size());
repaint();
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (IOException | InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void close() {
serialPort.close();
}
// 3 draw it
@Override
public void paintComponent(Graphics g) {
super.paintComponent(g);
// Ready to draw
Graphics2D g2d = (Graphics2D) g;
// Set the quality of drawn lines
g2d.setRenderingHint(RenderingHints.KEY_ANTIALIASING,
RenderingHints.VALUE_ANTIALIAS_ON);
// Set width height
// Set width height
int len = list.size();
int x =getWidth()/size;
double y =getHeight()/value;
System.out.println("height"+y);
System.out.println("len:" + len);
// Start looping through data
if (len > 2) {
for (int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
int x1=x * (size - len + i);
int y1=(int) (y * list.get(i));
int x2=x* (size - len + i + 1);
int y2=(int) (y * list.get(i + 1));
g2d.drawLine(x1, y1,x2,y2);
//System.out.println("value:"+list.get(i));
System.out.println("x1:"+x1+"y1:"+y1+"x1:"+x2+"y2:"+y2);
}
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Tools.java, a class for data processing
package cn.com.com;
import java.math.BigInteger;
public class Tools{
static int x=66666;
static int y=66666;
static int z=66666;
static boolean flag=false;
//1. Convert hexadecimal to decimal (if it is a negative number, find its complement)
public static int toTen(String a){
//Judge whether the first two digits are fd
String start= new BigInteger(a, 16).toString(10);
int i=Integer.parseInt(start);
int j=65535;
String x=a.substring(0, 1);
if("f".equals(x)||"8".equals(x)||"9".equals(x)||"a".equals(x)||"b".equals(x)||"c".equals(x)||"d".equals(x)||"e".equals(x)){
i=j-i;
}
return i;
}
//2. Processing data, x,y,x axis
public static Plot add(String str){
Plot p=null;
//1. Whether the string contains 5aa5 is handled if it is included or not.
if(str.indexOf("5aa5")!=-1){
x=y=z=66666;
flag=true;
}
//2. Process the data
if(str=="5aa5"||str.endsWith("5aa5")){
//Not deal with
}else{
int a=toTen(str);
if(x==66666){
x=a;
}else{
if(y==66666){
y=a;
}else{
z=a;
if(flag){
p=new Plot(x, y, z);
//empty
x=y=z=66666;
}
}
}
}
return p;
}
//3. byte type to String type
public static String byteToStr(byte b){
String a = "";
if (b < 0) {
// The range of byte s is - 128 to + 127
int i = 128 + (int) b + 127 + 1;
// Convert to hex
a = Integer.toHexString(i);
} else {
a = Integer.toHexString(b);
}
if (a.length() == 1) {
a = "0" + a;
}
return a;
}
}
It took 7 days. Because of my impatience, it took a long time to finish the 2-3 day question.