Day11—API—Object
API
summary
Application Programming Interface
Interface oriented programming - interface documentation
API development manual
On the official website
Object
summary
-
Package: Java lang ; Default auto guided package
-
Class Object
-
Class Object is the root class of the class hierarchy
-
Each class uses Object as the superclass (Object is the top-level parent of all classes)
-
Each class inherits the Object class
Construction method
Object() - parameterless construction
method
Clone
❤protected Object clone()
copy object
-
protected can only be used in this class, the same package class and subclasses
-
You can override the clone method class in OBject through subclasses to solve the problem of permission modifiers
-
Clonable interface: mark the interface (there is no abstract method in the interface)
If it is not implemented, an exception will be thrown, CloneNotSupportedException
-
The return value type is Object, which reflects the upward modeling
-
Superficial replication deep replication
code
Teacher teacher1 =newTeacher("Teacher 1",18);
Teacher teacher2 =newTeacher("Teacher 2",18);
Student student1 =newStudent("gakki",18,100, teacher1);
Student student2 =newStudent("Yuna Ito ",19,100, teacher2);
Student[] students ={student1,student2};
//First output the name of the teacher of the original array object
System.out.println(students[0].getTeacher().getName());
Student[] clone = students.clone();
//Modify reference
clone[0].getTeacher().setName("Modified");
System.out.println(clone[0].getTeacher().getName());
//Check whether the address has been modified
System.out.println(students[0].getTeacher().getName());
System.out.println("students: "+students);
System.out.println("clone: "+clone);
System.out.println("____________________________________________________________________________");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(students));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(clone));
System.out.println("____________________________________________________________________________");
System.out.println(students[0].getTeacher()+" "+students[1].getTeacher());
System.out.println(clone[0].getTeacher()+" "+clone[1].getTeacher());
Shallow replication
Deep replication
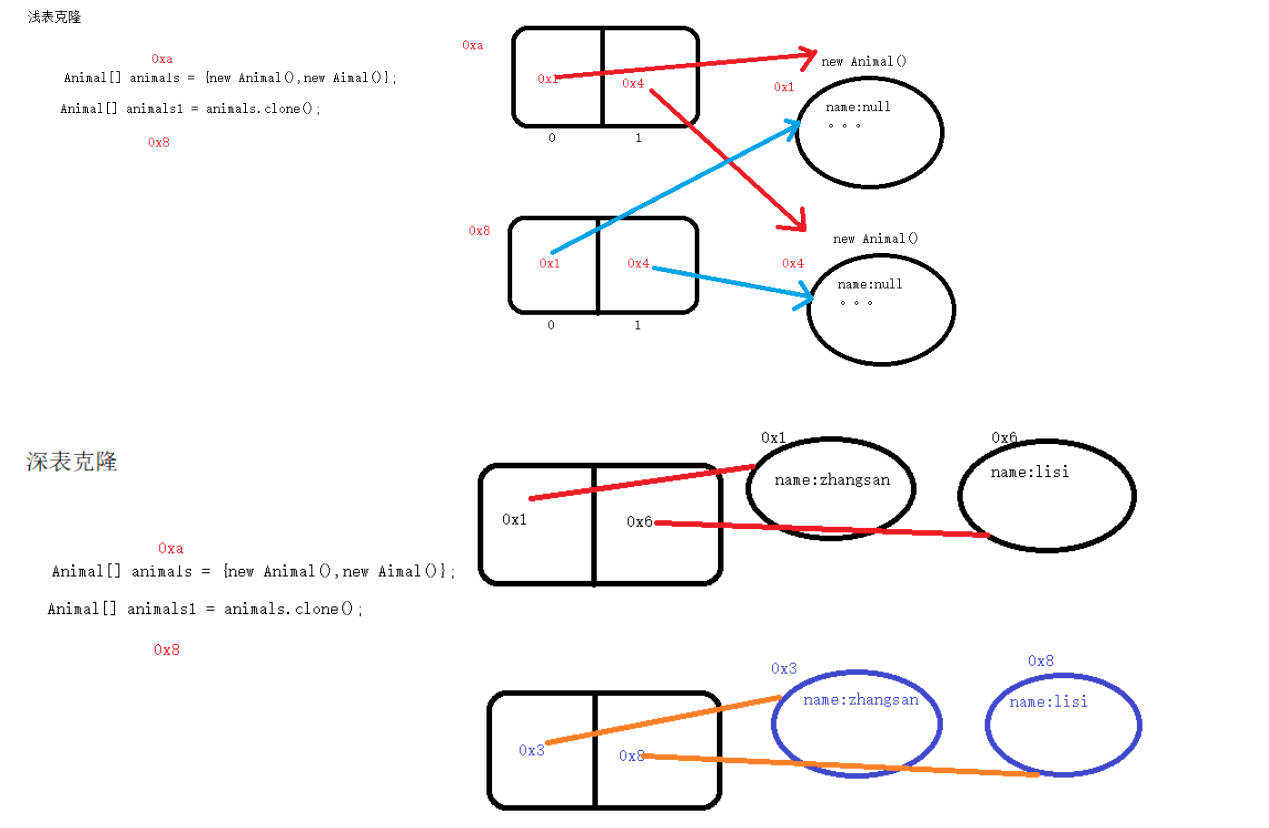
-
protected void finalize() - this method is called by the garbage collector and cannot recycle objects; Notify the garbage collector that the garbage is generated by garbage, but the collection time is uncertain
-
public final Class<?> GetClass () - returns the runtime class of this OBject
-
int hashCode() - returns the hash code value of the object
Summary: different objects have different hash code values. If the hash code values are the same, the same object should be executed
toString
- ❤ String toString -- returns the string representation of the queue
Object of toString Source code
public String toString() {
return getClass().getName() + "@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode());
}
//java.lang.Object@28d93b30
//Object toString source code
//The print result is the same as that of Object
System.out.println(new Student());
//println source code
public void println(Object x) {
String s = String.valueOf(x);
synchronized (this) {
print(s);
newLine();
}
}
//String.valueOf source code
public static String valueOf(Object obj) {
return (obj == null) ? "null" : obj.toString();
}
use
The direct output Object calls the toString method of the Object, and most classes inherit the toString method from Object. The default is to print the address value; If you want to output the string spliced by the attributes of the Object, you can override the toString method; When the Object is output again, the toString method after subclass rewriting is called;
toString method can be generated directly through IDE
euqals
- ❤ boolean equals(Object obj) - compares whether the current object and the parameter object are equal
equals()Source code
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return (this == obj);
}
Conclusion: the equals method in Object is also used to compare address values
The ratio of two variables is called equal
- ==
Basic data type: compare whether two data values are equal
Reference data type: compare whether the address values of two variables are equal
- Override the equals method
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
//1. Judge whether it is the same object
if (this == o) return true;
//2. Judge whether the parameter is null and whether the two are of the same type
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
//3. Convert parameter type to current type
Student student = (Student) o;
//4. Compare the specific attributes of objects in turn
if (age != student.age) return false;
if (score != student.score) return false;
if (!name.equals(student.name)) return false;
returnteacher.equals(student.teacher);
}
//It is best to override the hasCode method
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int result = name.hashCode();
result = 31 * result + age;
result = 31 * result + score;
result = 31 * result + teacher.hashCode();
return result;
}