Tip: after the article is written, the directory can be generated automatically. Please refer to the help document on the right for how to generate it
1, Array definition?
Declare before use
Data type [] array name = new data type [length]; String[] arr3 = new String[5];
Data type array name [] = new data type [length]; String arr[] = new String[5];
Direct initialization
String[] arrs = {"1","2","3"};
String[] sarr = new String[]{"a","b"};
2, array traversal
Flow traversal
Encapsulate the array into a stream for operation, and all operations are the same as those of the list
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] arrs = {"1","2","3"};
Arrays.stream(arrs).forEach(System.out::println);
}
General traversal
There are three common traversal methods. The first is recommended,
If you need to use indexes, you can use the third method
If you want to reverse the order, use the third one
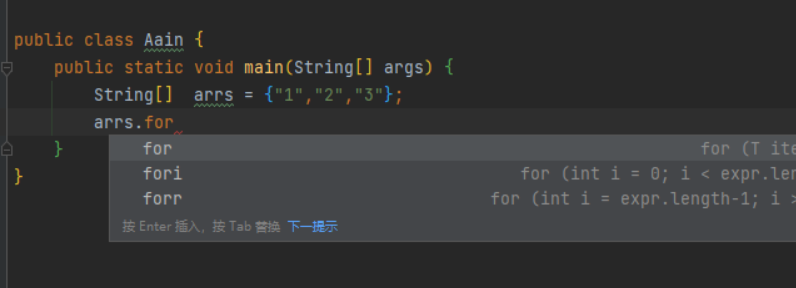
III Conversion between List and array
There is a great connection between list and array. The implementation forms of list include linked list and array. We often need to convert them in our development
1. Array to list
Convert to list using loop
Tools and methods
Code display:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] arrs = {"1","2","3"};
// Cyclic conversion
List<String> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
for (String arr : arrs) {
list1.add(arr);
}
// With the help of array tool class
List<String> list2 = Arrays.asList(arrs);
// With the help of collection tool class
List<String> list3 = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list2,arrs);
}
2. list to array
list built-in method toArray
Direct circulation Code display:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("1","2");
String[] arr1 = new String[list.size()];
// Loop traversal assignment
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
arr1[i] = list.get(i);
}
// Call the list method
String[] arr2 = (String[]) list.toArray();
}
4, Arrays tool class
toString()
Print array method. If this method is not called, the memory address is printed
stream()
Converting an array into a stream operation is not demonstrated
sort()
Sort the array. Note that this sort is the internal sort of the array. If there is no return value, the original array will be changed
setAll
To operate the elements in the array, you need to provide a function with different data types
String[] arrs = {"1","2","3"};
Arrays.setAll(arrs, e->e+"0");
for (String arr : arrs) {
System.out.println(arr);
}
binarySearch
You can see from the name that this is a binary search, and the specific algorithm is also very simple. If you can't do it yet, you can supplement it. If you know binary search, you should know that before calling this method, you should ensure that the array is orderly!
copyOf
The name is also very straightforward. Copying an array and expanding is to add some length restrictions or fill in data settings
equals
It doesn't seem to need explanation
deepEquals
Judge whether the depth of the two arrays is the same, that is, the array is nested several layers
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] arrs = {"1","2","3"};
String[][] arr2 = {{"1"},{"2"},{"3"}};
boolean b = Arrays.deepEquals(arr2, arrs);
System.out.println(b);
}
fill
If you know English, you basically know how to fill an array. Of course, you can also loop by yourself
hashCode
Calculate the hash code of the array
parallelPrefix
This interesting, parallel cumulative operation of the elements in the array. Just look at an example
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] sarr = new String[]{"a","b","c"};
Arrays.parallelPrefix(sarr, (sum,e1)->e1 + sum);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sarr));
}
See the execution results:
4. Possible problems
1. The index is out of bounds. The subscript index of the array starts from 0, and the last index is length -1. Be careful not to go out of bounds
2. The list created in the following way does not support adding
Because the ArrayList in Arrays does not implement the remove() and add() methods, an exception is thrown. So Arrays The List returned by aslist is an immutable length List. This List no longer has many features of the original List, so use Arrays with caution Aslist method.
String[] arr = {"1", "2", "3"};
List list = Arrays.asList(arr);
arr[1] = "4";
try {
list.add("5");
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
3. A little trick to loop the array
Use to remainder the length of the array
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] arr = {"a", "b", "c"};
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int length = arr.length;
while (j++ <10){
System.out.println(arr[i%length]);
i++;
}
}