Java foundation is the cornerstone of learning Java EE, big data and Android development
1. Keywords and reserved words
Definition and characteristics of keyword s
Definition: a string with special meaning given by the Java language for special purposes
Features: all letters in the keyword are lowercase
reserved word
The existing Java version has not been used, but later versions may be used as keywords
Such as const, goto
2. Identifier
identifier
The character sequence used by Java when naming various variables, methods, classes and other elements is called an identifier
Tip: any place where you can name yourself is called an identifier
For example: class name, variable name, method name, interface name
Naming rules for identifiers:
The following naming rules are not met, and the compilation cannot pass
- It consists of 26 English letters in case, 0-9_ Or $composition
- Cannot start with a number
- Keywords and reserved words cannot be used
- Java is strictly case sensitive and has no limit on length
- Cannot contain spaces
Naming conventions in Java
Package name: all letters are lowercase when composed of multiple words
Class name and interface name: when composed of multiple words, all words are capitalized
Variable name and method name: when composed of multiple words, the first word is lowercase, and the second word is capitalized
Constant name: all letters are capitalized, and multiple words are connected with underscores
Note: try to "see the name and know the meaning" when naming
3. Variables
Concept of variable
- A storage area in memory
- The data in this area can vary within the same data type range
- Variable is the most basic storage unit in the program, including variable type, variable name and stored value.
Role of variables
- Used to save data in memory
Use variable attention
- Each variable in Java must be declared before use
- Use the variable name to access the data of this area
- Scope of variable: the pair of {} in which it is defined
- The variable value is valid only if it is within its scope
- Variables with duplicate names cannot be defined within the same scope
Use of variables
Use format: data type variable name = variable value;
package day02;
public class Variable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Definition of variables
int age = 12;
// Use of variables
System.out.println(age);
int number;
number = 10;
System.out.println(number);
}
}
Type of variable
be careful:
- The Java integer constant defaults to int. when declaring a long variable, if the assigned value exceeds int, you need to add an 'l' or 'l' at the end
- Java floating point constant is double by default. When declaring float constant, you need to add 'f' and 'f'
Use of various data types
package day02;
public class Variable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Integer type: int, long
int a = 10;
System.out.println(a);
// When declaring a long type, add 'L' or 'L' after it
long b = 10000000l;
System.out.println(b);
// Floating point type: float, double
double c = 15.5;
System.out.println(c);
// When declaring a float type, add 'F' or 'F' after it
float d = 16.5f;
System.out.println(d);
// Character type: char
char e = 'a';
// char type can only be assigned one character
// char f = 'aa';
System.out.println(e);
// boolean type: boolean
// Boolean types have only two values: true and false
boolean g = true;
System.out.println(g);
}
}
Automatic conversion of basic data types
When the data type variable with small capacity and the data type variable with large capacity are operated, the result will be automatically converted to the data type with large capacity
byte,char,short->int->long->float->double
In particular, when byte, char and short are calculated, the result is int
Hadron conversion of basic data types
Reverse operation of automatic conversion
1. Strong conversion character () is required
2. Note: forced type conversion may result in precision loss (not rounding or truncation)
String type variable
1.String is a reference data type
2. When declaring a String type variable, use double quotation marks ""
3.String can operate with 8 basic data type variables, and the operation can only be connection operation:+
4. The operation result is String
package day02;
public class Variable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
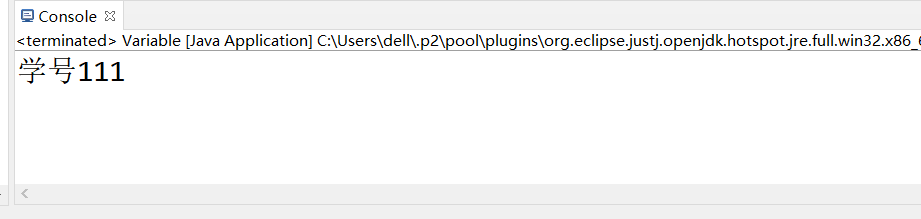
String a = "Student number";
int b = 111;
String c = a + b;
System.out.println(c);
}
}
Exercise 1
package day02;
public class Variable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
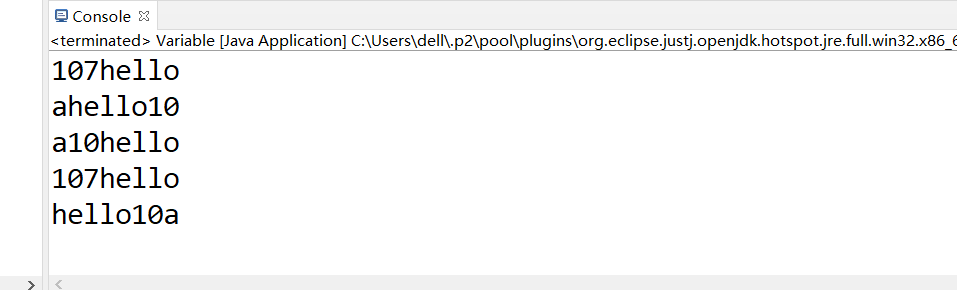
char c = 'a';
int num = 10;
String str = "hello";
System.out.println(c + num + str); // 107hello
System.out.println(c + str + num); // ahello10
System.out.println(c + (num + str)); // a10hello
System.out.println((c + num) + str); // 107hello
System.out.println(str + num + c); // hello10a
}
}
Exercise 2
Output '* *'
package day02;
public class Variable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
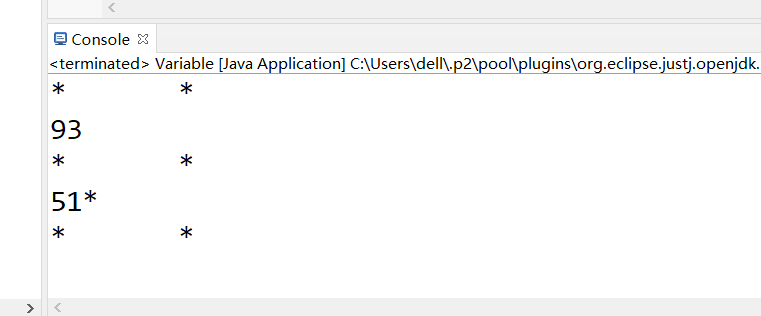
System.out.println("* *"); // * *
System.out.println('*' + '\t' + '*'); // 93
System.out.println('*' + "\t" + '*'); // * *
System.out.println('*' + '\t' + "*"); // 51*
System.out.println('*' + ('\t' + "*")); // * *
}
}
Conversion between base and base
There are 10 kinds of people in the world who know binary and don't know binary
All numbers exist in binary form at the bottom of the computer.
Binary integers have the following three forms
Positive number: three in one
Negative number:
- Original code: the highest bit is the symbol number
- Inverse code: except for the symbol code, the original code changes from 1 to 0 and 0 to 1
- Complement: complement + 1
At the bottom of the computer, they are stored in the form of complement (positive and negative numbers are the same)
There are specific binary conversion functions in the Java API
Daily test
- What are the naming rules for identifiers?
26 English letters, underscore (), dollar sign ($), 0-9 numbers, cannot start with a number - What are the naming conventions for identifiers?
Package name: word lowercase
Class name and interface name: big hump
Variable name and method name: small hump
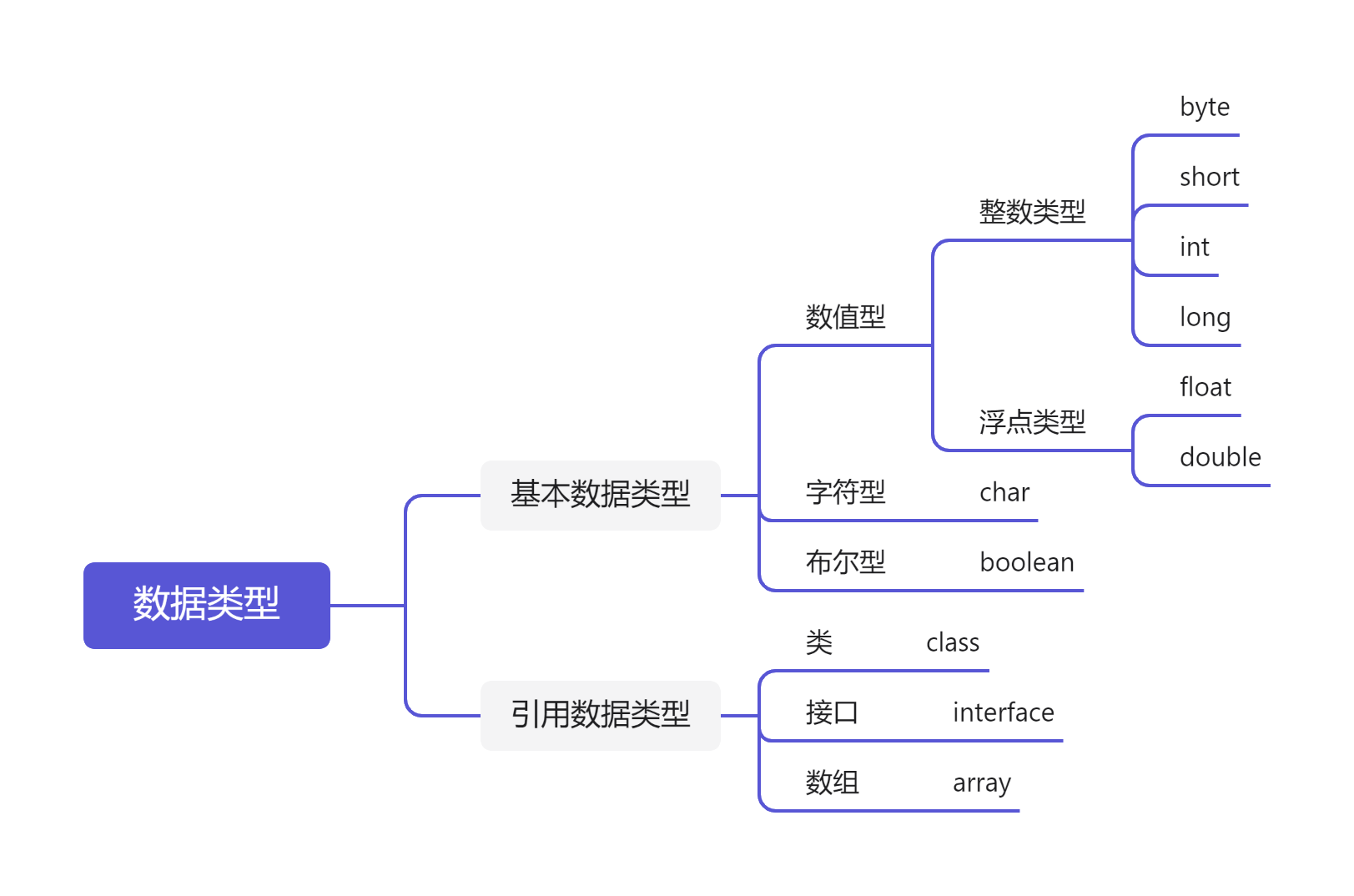
Constant name: word underscore connection - How are Java variables divided by data type? It also points out the 8 basic data types of Java and the size of their memory space.
Basic data type
Byte (1 byte), short (2 bytes), int (4 bytes), long (8 bytes)
char (1 character)
float (4 bytes), double (8 bytes)
boolean
Reference data type
Class, interface, array - Describes the operation rules for automatic type promotion between basic data type variables.
byte,short,char -> int -> long -> float -> double - Explain the use rules of forced conversion between basic data type variables and possible problems of strong conversion.
Large capacity - > small capacity
Strong conversion character: ()
Precision loss