1. Array overview
- Understanding of array: an array is a collection of multiple data of the same type arranged in a certain order and named with a name,
These data are uniformly managed by numbering. - Array related concepts:
- Array name
- element
- Corner mark, subscript, index
- Length of array: number of elements
- Array features:
- Arrays are ordered
- Array is a variable of reference data type. The element of an array can be either a basic data type or a reference data type
- Creating an array object opens up a whole contiguous space in memory
- Once the length of the array is determined, it cannot be modified.
- Classification of arrays:
① Illumination dimension: one-dimensional array, two-dimensional array...
② According to the type of array elements: array of basic data type elements and array of reference data type elements
2. One dimensional array
2.1 declaration and initialization
//The right way:
int num;//statement
num = 10;//initialization
int id = 1001;//Declaration + initialization
int[] ids;//statement
//1.1 static initialization: array initialization and array element assignment are performed simultaneously
ids = new int[]{1001,1002,1003,1004};
//1.2 dynamic initialization: array initialization and array element assignment are performed separately
String[] names = new String[5];
int[] arr4 = {1,2,3,4,5};//Type inference
//Wrong way:
// int[] arr1 = new int[];
// int[5] arr2 = new int[5];
// int[] arr3 = new int[3]{1,2,3};
2.2 reference of one-dimensional array elements: called by corner markers.
//The subscript (or index) of the array starts from 0 and ends with the length of the array - 1. names[0] = "Wang Ming"; names[1] = "Wang He"; names[2] = "placed under house arrest"; names[3] = "Sun Julong"; names[4] = "Wang Hongzhi";//charAt(0)
2.3 array attribute: length
System.out.println(names.length);//5 System.out.println(ids.length);
explain:
Once the array is initialized, its length is determined. arr.length
Once the array length is determined, it cannot be modified.
2.4 traversal of one-dimensional array
for(int i = 0;i < names.length;i++){
System.out.println(names[i]);
}
2.5 default initialization value of one-dimensional array elements
- Array element is an integer: 0
- Array elements are floating point: 0.0
- Array elements are char type: 0 or '\ u0000', not '0'
- Array elements are boolean: false
- Array element is a reference data type: null
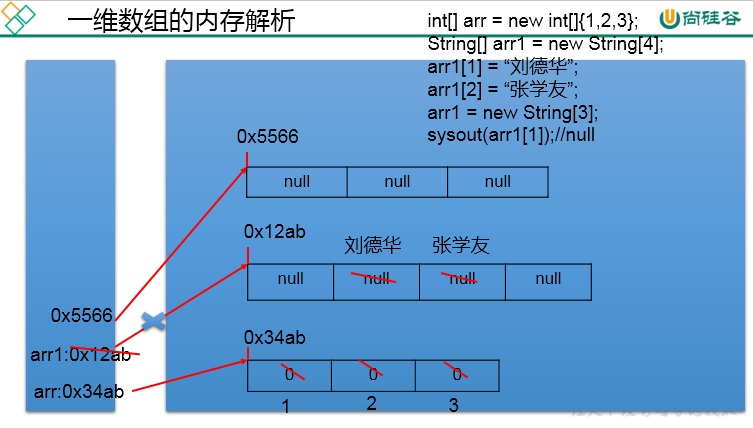
2.6 memory parsing of one-dimensional array
3. Two dimensional array
3.1 how to understand two-dimensional array?
Array is a reference data type
The elements of an array can also be reference data types
If the elements of a one-dimensional array a are of one-dimensional array type, the array A is called a two-dimensional array.
3.2 declaration and initialization of two-dimensional array
//The right way:
int[] arr = new int[]{1,2,3};//One dimensional array
//initiate static
int[][] arr1 = new int[][]{{1,2,3},{4,5},{6,7,8}};
//Dynamic initialization 1
String[][] arr2 = new String[3][2];
//Dynamic initialization 2
String[][] arr3 = new String[3][];
//It is also the correct way to write:
int[] arr4[] = new int[][]{{1,2,3},{4,5,9,10},{6,7,8}};
int[] arr5[] = {{1,2,3},{4,5},{6,7,8}};//Type inference
//Wrong way:
// String[][] arr4 = new String[][4];
// String[4][3] arr5 = new String[][];
// int[][] arr6 = new int[4][3]{{1,2,3},{4,5},{6,7,8}};
3.3 how to call 2D array elements:
System.out.println(arr1[0][1]);//2 System.out.println(arr2[1][1]);//null arr3[1] = new String[4]; System.out.println(arr3[1][0]); System.out.println(arr3[0]);//
3.4 properties of two-dimensional array:
System.out.println(arr4.length);//3 System.out.println(arr4[0].length);//3 System.out.println(arr4[1].length);//4
3.5 traversing two-dimensional array elements
for(int i = 0;i < arr4.length;i++){
for(int j = 0;j < arr4[i].length;j++){
System.out.print(arr4[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
3.6 default initialization value of two-dimensional array elements
Regulation: the two-dimensional array is divided into the elements of the outer array and the elements of the inner array
int[][] arr = new int[4][3];
Outer elements: arr[0],arr[1], etc
Inner elements: arr[0][0],arr[1][2], etc
Default initialization value for array elements
For initialization method 1: for example: int[][] arr = new int[4][3];
The initialization value of the outer element is: address value
The initialization value of the inner element is: the same as that of the one-dimensional array
For initialization mode 2: for example: int[][] arr = new int[4] [];
The initialization value of the outer element is null
The initialization value of the inner element is: it cannot be called, otherwise an error will be reported.
3.7 memory structure of two-dimensional array

4. Practice
- Write two ways to initialize a one-dimensional array
int[] arr = new int[5];// dynamic initialization
String[] arr1 = new String[]{“Tom”,“Jerry”,“Jim”};// initiate static
Once the array is initialized, its length is determined. arr.length
Once the array length is determined, it cannot be modified.
- Write out two ways to initialize a two-dimensional array
int[][] arr = new int[4][3];// Dynamic initialization 1
int[][] arr1 = new int[4][];// Dynamic initialization 2
- How to traverse the following two-dimensional array
int[] arr = new int[][]{{1,2,3},{4,5},{6,7,8}};
int[] arr = new int[][]{{1,2,3},{4,5},{6,7,8}};
for(int i = 0;i < arr.length;i++){
for(int j = 0;j < arr[i].length;j++){
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
- What are the default initialization values for different types of one-dimensional array elements
Integer: 0
Floating point: 0.0
char:0
boolean :false
Reference type: null
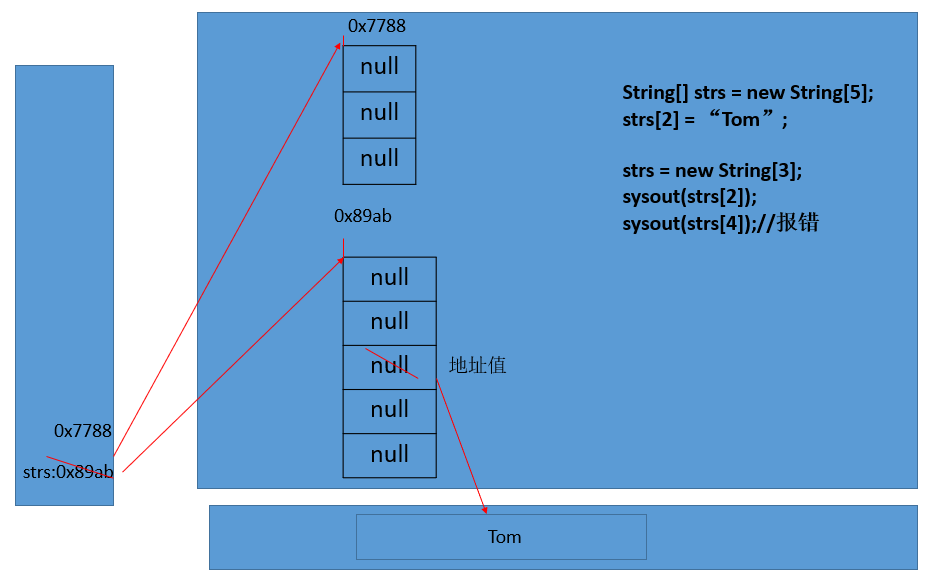
- Memory parsing of one-dimensional array:
String[] strs = new String[5];
strs[2] = "Tom";
strs = new String[3];