Map
Overview and use of Map collections
Overview of Map Collections
- Interface Map < K, V > K: Key type; V:Type of value
- Map keys to objects of value; Cannot contain duplicate keys; Each key can be mapped to at most one value
- Examples: student number and name
001 Small White
002 Small Black
003 Small Red
Objects that create a Map collection
- Polymorphic modes
- Specific implementation class HashMap
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/*
Map Overview of collections
- Interface Map<K,V> K:Type of key; V:Type of value
- Map keys to objects of value; Cannot contain duplicate keys; Each key can be mapped to at most one value
- Examples: student number and name
001 Small White
002 Little Black
003 Little Red
Objects that create a Map collection
- Polymorphic modes
- Specific implementation class HashMap
*/
public class MapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create Collection Object
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();//HashMap guarantees key uniqueness
//Add method: V put(K key,V value) associates the specified value with the specified key in the map
map.put("001", "Small White");
map.put("002", "Little Black");
map.put("003", "Little Red");
map.put("003", "Small Green");//When the key repeats, the original value is substituted for the key adjustment.
//Output Collection Object
System.out.println(map);
}
}
Run result:
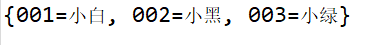
Basic Map Collection Functions
| Method Name | Explain |
|---|---|
| V put(K key,V value) | Add Elements |
| V remove(Objedt key) | Delete key-value pair elements based on keys |
| void clear() | Remove all key-value pair elements |
| boolean containsKey(Object key) | Determines whether the collection contains the specified key |
| boolean containsValue(Object value) | Determines whether a collection contains a specified value |
| boolean isEmpty() | Determine if the set is empty |
| int size() | The length of the set, that is, the number of key-value pairs in the set |
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class MapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create Collection Object
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();//HashMap guarantees key uniqueness
//Add method: V put(K key,V value) associates the specified value with the specified key in the map
map.put("Little Black", "Small White");
map.put("Small Green", "Little Red");
map.put("Blue", "Small Purple");
//V remove(Objedt key) Deletes key-value pair elements based on a key
System.out.println(map.remove("Blue"));//Return to Little Purple
System.out.println(map.remove("Xiaohuang"));//Return null
//void clear() removes all key-value pair elements
map.clear();//{}
//boolean containsKey(Object key) determines whether a collection contains the specified key
System.out.println(map.containsKey("Little Black"));//true
System.out.println(map.containsKey("Small White"));//false
//boolean containsValue(Object value) determines whether a collection contains a specified value
System.out.println(map.containsValue("Little Red"));//true
System.out.println(map.containsValue("Small Green"));//false
//boolean isEmpty() to determine if the collection is empty
System.out.println(map.isEmpty());//false
//The length of the int size() set, that is, the number of key-value pairs in the set
System.out.println(map.size());//3
//Output Collection Object
System.out.println(map);
}
}
Capturing Map Collections
| Method Name | Explain |
|---|---|
| V get(Object key) | Get value from key |
| Set keySet() | Get a collection of all keys |
| Collection values() | Get a collection of all values |
| Set<Map.Entry<K,V>>entrySet() | Gets a collection of all key-value pair objects |
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
/*
Map Collection acquisition capabilities
V get(Object key) Get value from key
Set<K> keySet()Get a collection of all keys
Collection<V> values()Get a collection of all values
*/
public class MapDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create Collection Object
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
//Add Elements
map.put("Little Black", "Small White");
map.put("Small Green", "Little Red");
map.put("Blue", "Small Purple");
//V get(Object key) Gets a value based on a key
// System.out.println(map.get("little black");// Small White
// System.out.println(map.get("small");// null
//Set<K> keySet() Gets the collection of all keys
// System. Out. Println (map.keySet();// [Small blue, small black, small green]
//Traversal Key Collection
Set<String> ks = map.keySet();
for (String s : ks) {
System.out.println(s);
}
//Collection<V> values() Gets a collection of all values
// System. Out. Println (map.values ();// [Small purple, small white, small red]
//Traversal value set
Collection<String> v = map.values();
for (String s : v) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
Run result:

Traversal of Map Collections
- Mode 1:
Gets a collection of all keys, implemented using the KeySet() method
Walk through a collection of keys, get each key, and implement with enhanced for
Find values based on keys, using get(Object key) method
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
/*
Map Collection acquisition capabilities
V get(Object key) Get value from key
Set<K> keySet()Get a collection of all keys
Collection<V> values()Get a collection of all values
*/
public class MapDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create Collection Object
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
//Add Elements
map.put("Little Black", "Small White");
map.put("Small Green", "Little Red");
map.put("Blue", "Small Purple");
//Set<K> keySet() Gets the collection of all keys
//Traversal Key Collection
Set<String> ks = map.keySet();
for (String k : ks) {
String v = map.get(k);
System.out.println(k + "," + v);
}
}
}
Run result:

- Mode 2
Get a collection of all key-value pairs of objects using Set<Map. Entry<K, V> entrySet()
Traverse through the set of key-value pair objects to get each key-value pair object, and use the enhanced for implementation to get each Map.Entry
Get keys and values from key-value pair objects, keys from **getKey(), and values from getValue()**
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Set;
/*
Map Collection acquisition capabilities
V get(Object key) Get value from key
Set<K> keySet()Get a collection of all keys
Collection<V> values()Get a collection of all values
*/
/*
Mode 2
Get a collection of all key-value pairs of objects using **Set<Map. Entry<K, V>entrySet()**
Traverse through the collection of key-value pair objects to get each key-value pair object, and use the enhanced for implementation to get each **Map.Entry**
Get keys and values from key-value pair objects, keys from **getKey()**, and values from **getValue()**
*/
public class MapDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create Collection Object
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
//Add Elements
map.put("Little Black", "Small White");
map.put("Small Green", "Little Red");
map.put("Blue", "Small Purple");
//Gets a collection of all key-value pair objects
Set<Entry<String, String>> es = map.entrySet();
//Traverse through the collection of key-value pair objects to get each key-value pair object
for (Entry<String, String> me : es) {
//Get keys and values from key-value pair objects
String key = me.getKey();
String value = me.getValue();
System.out.println(key + "," + value);
}
}
}
Run result:

Case study: HashMap collection stores student objects and traverses them
Requirements: Create a HashMap collection with a String key and a Student value. Store three key-value pair elements and iterate through them
//Define Student Classes
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Student() {
super();
}
}
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Set;
/*
Case study: HashMap collection stores student objects and traverses them
Requirements: Create a HashMap collection with a String key and a Student value.
Store three key-value pair elements and iterate through them
*/
public class HashMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create Collection Object
Map<String, Student> map = new HashMap<String, Student>();
//Create Student Object
Student s1 = new Student("Small White", 12);
Student s2 = new Student("Little Black", 15);
Student s3 = new Student("Little Red", 13);
//Add element to collection
map.put("001", s1);
map.put("002", s2);
map.put("003", s3);
//Traverse 1: Key Find Value
Set<String> keySet = map.keySet();
for (String k : keySet) {
Student v = map.get(k);
System.out.println(k + "," + v.getName() + "," + v.getAge());
}
System.out.println("--------");
//Traversal two: key-value pairs to find keys and values
Set<Entry<String, Student>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
for (Entry<String, Student> e : entrySet) {
String k = e.getKey();
Student v = e.getValue();
System.out.println(k + "," + v.getName() + "," + v.getAge());
}
}
}
Run result:

Case: HashMap collection stores student objects and traverses (2)
Requirements: Create a HashMap collection with a String key and a Student value. Store three key-value pair elements and iterate through them
Requirements: Keys are guaranteed to be unique. If the member variables of the student object have the same values, we will consider them the same object.
import java.util.Objects;
//Define Student Classes
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Student() {
super();
}
//Override two methods
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(age, name);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Student other = (Student) obj;
return age == other.age && Objects.equals(name, other.name);
}
}
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Set;
/*
Case study: HashMap collection stores student objects and traverses them
Requirements: Create a HashMap collection with a String key and a Student value.
Store three key-value pair elements and iterate through them
Requirements: Keys are guaranteed to be unique. If the member variables of the student object have the same values, we will consider them the same object.
*/
public class HashMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create Collection Object
HashMap<Student, String> map = new HashMap<Student, String>();
//Create Student Object
Student s1 = new Student("Small White", 12);
Student s2 = new Student("Little Black", 15);
Student s3 = new Student("Little Red", 13);
Student s4 = new Student("Little Red", 13);
//Add element to collection
map.put(s1, "Beijing");
map.put(s2, "Nanjing");
map.put(s3, "Shenzhen");
map.put(s4, "Hunan");//Member variables have the same value, value overrides the value above
//Traverse 1: Key Find Value
Set<Student> keySet = map.keySet();
for (Student k : keySet) {
String v = map.get(k);
System.out.println(k.getName() + "," + k.getAge() + v);
}
}
}
Run result:

Case: An ArrayList collection stores HashMap elements and traverses them (collection nesting)
Requirement: Create an ArrayList collection that stores three elements, each HashMap, each HashMap key and value String, and traverse
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Set;
/*
Case: The ArrayList collection stores HashMap elements and traverses them
Requirement: Create an ArrayList collection that stores three elements, each HashMap.
Each HashMap key and value is a String and traverses through it
*/
public class ArrayListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create ArrayList Collection Object
ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>> array = new ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>>();
//Create a HashMap collection object, add key-value pair elements
HashMap<String, String> hm1 = new HashMap<String, String>();
hm1.put("Small White", "Big White");
hm1.put("Little Black", "Big Black");
array.add(hm1);
HashMap<String, String> hm2 = new HashMap<String, String>();
hm2.put("Little Red", "Bright red");
hm2.put("Blue", "Big Blue");
array.add(hm2);
HashMap<String, String> hm3 = new HashMap<String, String>();
hm3.put("Small Green", "Big Green");
hm3.put("Small Purple", "Purple");
array.add(hm3);
//Traversing through the ArrayList collection
for (HashMap<String, String> hm : array) {
//Traversing HashMap Collection
Set<String> keySet = hm.keySet();
for (String k : keySet) {
String v = hm.get(k);
System.out.println(k + "," + v);
}
}
}
}
Run result:

Case study: HashMap collections store ArrayList elements and traverse (collection nesting)
Requirement: Create a HashMap collection that stores three elements, each key-value pair having a String key for the element, the value being an ArrayList, and each ArrayList element being a String and traversed
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Set;
/*
Case study: HashMap collections store ArrayList elements and traverse (collection nesting)
Requirement: Create a HashMap collection that stores three elements, each with a String key for the element and an ArrayList value.
Each ArrayList element is a String and traverses through it
*/
public class HashMapDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create HashMap Collection Object
HashMap<String, ArrayList<String>> hm = new HashMap<String, ArrayList<String>>();
//Create an ArrayList collection object, add elements
ArrayList<String> a1 = new ArrayList<String>();
a1.add("Small White");
a1.add("Big White");
hm.put("001", a1);
ArrayList<String> a2 = new ArrayList<String>();
a2.add("Little Black");
a2.add("Big Black");
hm.put("002", a2);
ArrayList<String> a3 = new ArrayList<String>();
a3.add("Little Red");
a3.add("Bright red");
hm.put("003", a3);
//Traversing HashMap Collection
Set<String> keySet = hm.keySet();
for (String k : keySet) {
System.out.println(k);
ArrayList<String> v = hm.get(k);
//Traversing through the ArrayList collection
for (String s : v) {
System.out.println(" " + s);
}
}
}
}
Run result:

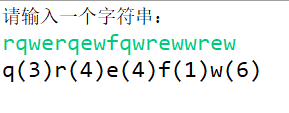
Case: Count the number of occurrences of each character in a string
Requirements: Keyboard enters a string and requires statistics on the number of occurrences of each string in the string
Example: Keyboard input:'a a B a B C a B C D a B C D E'output in console:'a(5)b(4)c(3)d(2)e(1)'
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Set;
/*
Case: Count the number of occurrences of each character in a string
Requirements: Keyboard enters a string and requires statistics on the number of occurrences of each string in the string
Example: Keyboard entry:'aababcabcdabcde'
Output in console:'a(5)b(4)c(3)d(2)e(1)'
The number of times a character corresponds to a character, which can be stored through the HashMap collection.
The key is a Character and the value is the number of characters (Integer)
*/
public class HashMapDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please enter a string:");
String line = sc.nextLine();
//Create HashMap Collection Object
//The key is a Character and the value is the number of characters (Integer)
HashMap<Character, Integer> hm = new HashMap<Character, Integer>();
// TreeMap<Character, Integer> hm=new TreeMap<Character, Integer>();// Natural sorting of keys (characters)
//Traversal string
for (int i = 0; i < line.length(); i++) {
char key = line.charAt(i);
//Character as key, find corresponding in HashMap, return value null, value 1, return value is not null, value + 1
Integer value = hm.get(key);
if (null == value) {
hm.put(key, 1);
} else {
value++;
hm.put(key, value);
}
}
//Traverse the HashMap collection and stitch as required
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();//For stitching
Set<Character> keySet = hm.keySet();
for (Character k : keySet) {
Integer v = hm.get(k);
sb.append(k).append("(").append(v).append(")");
}
String string = sb.toString();//Convert to string
System.out.println(string);//Output Results
}
}
Run result: