Important:
String buffer security has an internal security lock, which is the secure version of String builder
What is the difference between String and StringBuilder and StringBuffer?
Under multithreading, buffer is safer than builder and faster than String
Single thread speed is the fastest, and String builder is the fastest
Input and output
Calculator
import java.util.*;
public class aa{
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("Welcome to the calculator, please select the calculation type");
System.out.println("1.Add 2.Subtraction 3.Multiplication 4.Division, please enter a numeric type");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int flag = scanner.nextInt();
switch(flag){
case 1:
System.out.println("You have chosen addition");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("You have selected subtraction");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("You have chosen multiplication");
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("You have chosen division");
default:
System.out.println("Calculation type error");
return;
}
System.out.println("Please enter two numbers to calculate");
Scanner scanner1 = new Scanner(System.in)
Scanner scanner2 = new Scanner(System.in)
int x1 = scanner1.nextInt();
int x2 = scanner2.nextInt();
switch(flag){
case 1:
System.out.println("Calculation results: "+ (a+b));
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("Calculation results: "+ (a-b));
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("Calculation results: "+ (a*b));
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("Calculation results: "+ (a/b));
default:
System.out.println("Calculation type error");
return;
}
}
}
import java.util.*;
public class InputTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
//get first input
System.out.println("What is your name?");
String name = in.nextLine();
//get second input
System.out.println("How old are you?");
int age = in.nextInt();
//display output on console
System.out.println("Hello, " + name +".Next year,you will be" +(age+1));
}
}Format output
Output in a format
System.out.printf("#####%s#####%d#####%s#####"," hahaha ", 35," I'm good ");Is the type of number to string one-way number plus string or string? The type of string cannot be converted to number
Block scope
The block in which the variable is declared has no effect
File storage information shall be coded
Gets the path of the current file on disk
String dir = System.getProperty(user.dir);
Switch statement
The case tag can be:
- A constant expression of type char, byte, short, or int.
- Enumeration constants.
- Starting with Java SE 7, case tags can also be string literals.
import java.util.*;
public class Test6{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("How much money do you need to retire?");
double goal = in.nextDouble();
System.out.print("How much money will you contribute every year?");
double payment = in.nextDouble();
System.out.print("Interest rate in %:");
double interestRate = in.nextDouble();
double balance = 0;
int years = 0;
while(balance
balance += payment;
double interest = balance *interestRate / 100;
years++;
}
System.out.println("You can retire in"+years+"years.");
}
}Large value
If you want to calculate the exact value, use BigInteger for integer and BigDecimal for decimal
import java.util.*;
import java.math.*;
public class Test6{
public static void main(String[] args){
BigInteger aa = new BigInteger("2500000000000000000");
BigInteger bb = new BigInteger("1500000000000000000");
BigInteger cc = aa.add(bb);
BigInteger dd = aa.multiply(bb);
BigInteger ee = aa.subtract(bb);
BigInteger ff = aa.divide(bb);
System.out.println(cc);
System.out.println(dd);
System.out.println(ee);
System.out.println(ff);
}
}Chapter IV objects and classes
Everything runs in memory
The space occupied by a single process is a block
Different processes in memory occupy different areas and do not interfere with each other
The application space is actually an array
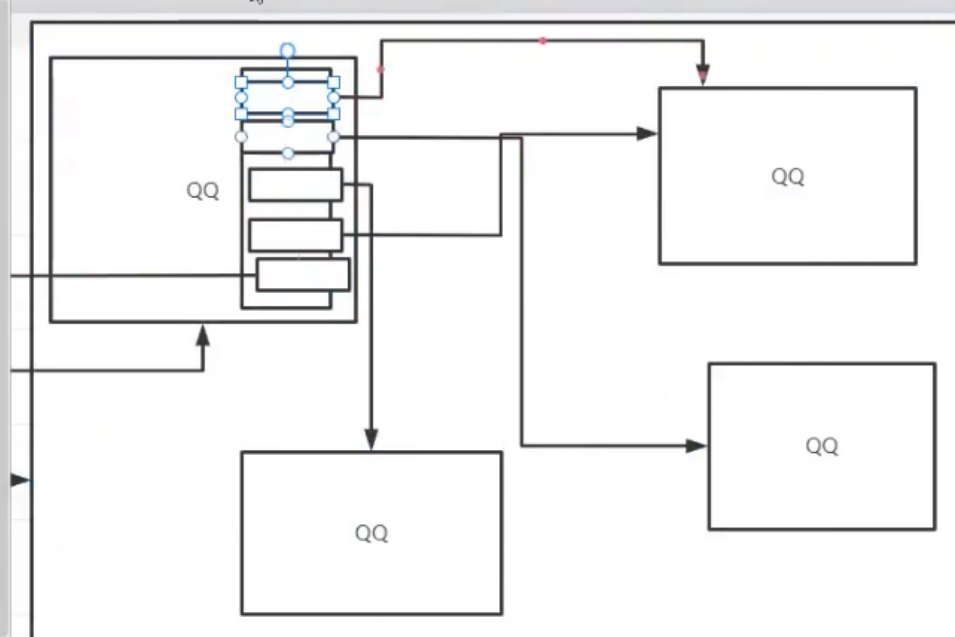
The program may not be physically in one area, and there is an area in each block to store various addresses
Links with other blocks
A space occupied by a single process is called a block, which is essentially a two-dimensional array
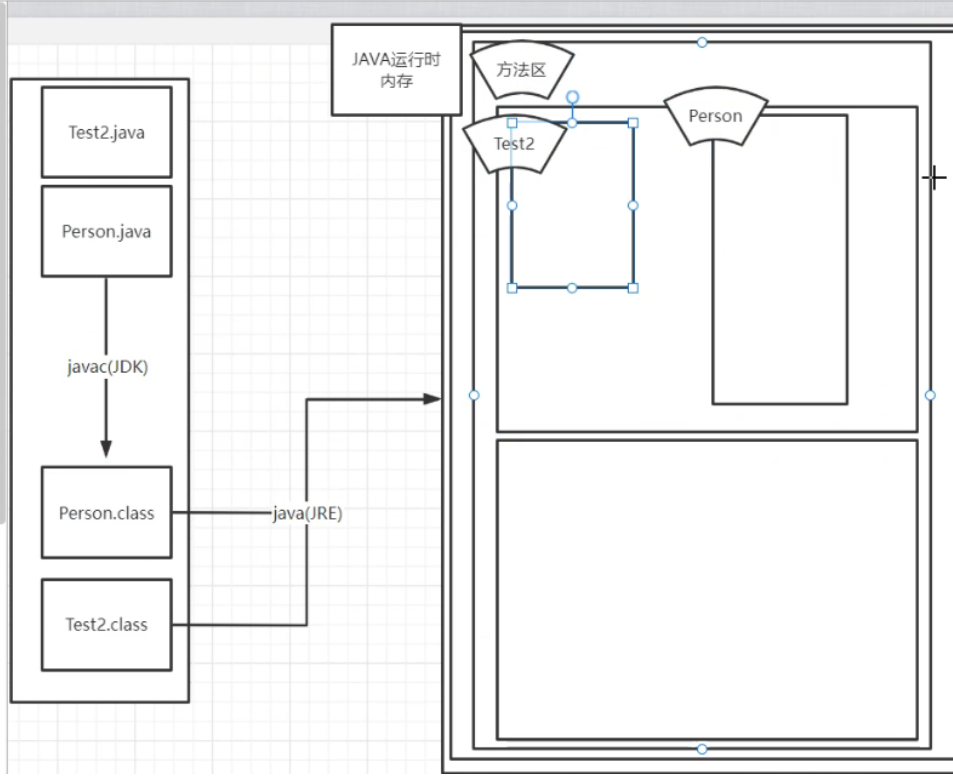
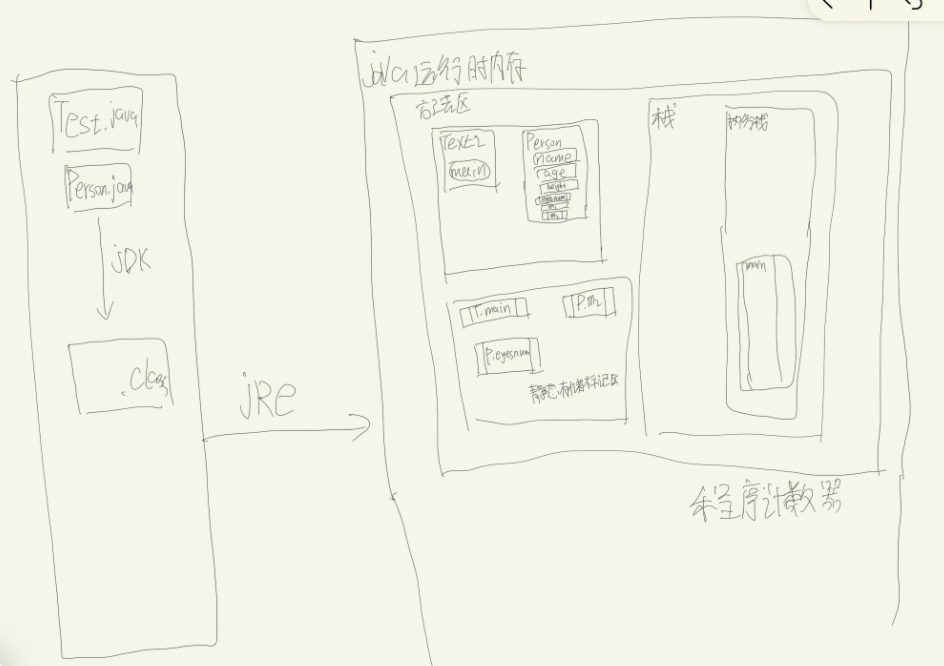
After the. class information enters the memory, first store the memory in the method area
There is a static area in the method area
Methods in the static area can be called directly, and have their own space when entering memory
Method executes a dependency stack application to the stack structure, applies for a sub stack copy, sends it to form a sub stack, and starts execution
Stack
- Control method execution sequence
- Domain of variable
Method executes a dependency stack application to the stack structure, applies for a sub stack copy, sends it to form a sub stack, and starts execution
During stack execution, a sub stack will be applied for in the large stack, which is the carrier of method execution
Copy the main method into the sub stack. If it is executed directly in the original place, there will be interference when multiple processes use the main method
Method executes a dependency stack application to the stack structure, applies for a sub stack copy, sends it to form a sub stack, and starts execution
A sub stack is a first in first out stack in a data structure
Thread execution dependency stack
Program counter
Controls when to stack and when to stack
Each object has a copy of non static content in the class
With static only in the static storage tag area
Object oriented programming (OOP) for short
Class properties
- encapsulation
- inherit
- polymorphic
- abstract
Creating an instance of a class is the object that creates the class
An attribute is an instance domain
The variable must be in the stack and the object must be in the heap
Reference type = is reference address
Predefined Class
Java itself is called a predefined class
Java is passed by value (very important)
Reference passes the address of the stack, but in fact, it passes the address of the value in the heap
- Pass by value: copy the method parameter value to another variable, and then pass the copied object, which is called pass by value.
- Pass by reference: pass the alias or reference to the actual parameter to the method, which is called the reason for passing by reference.
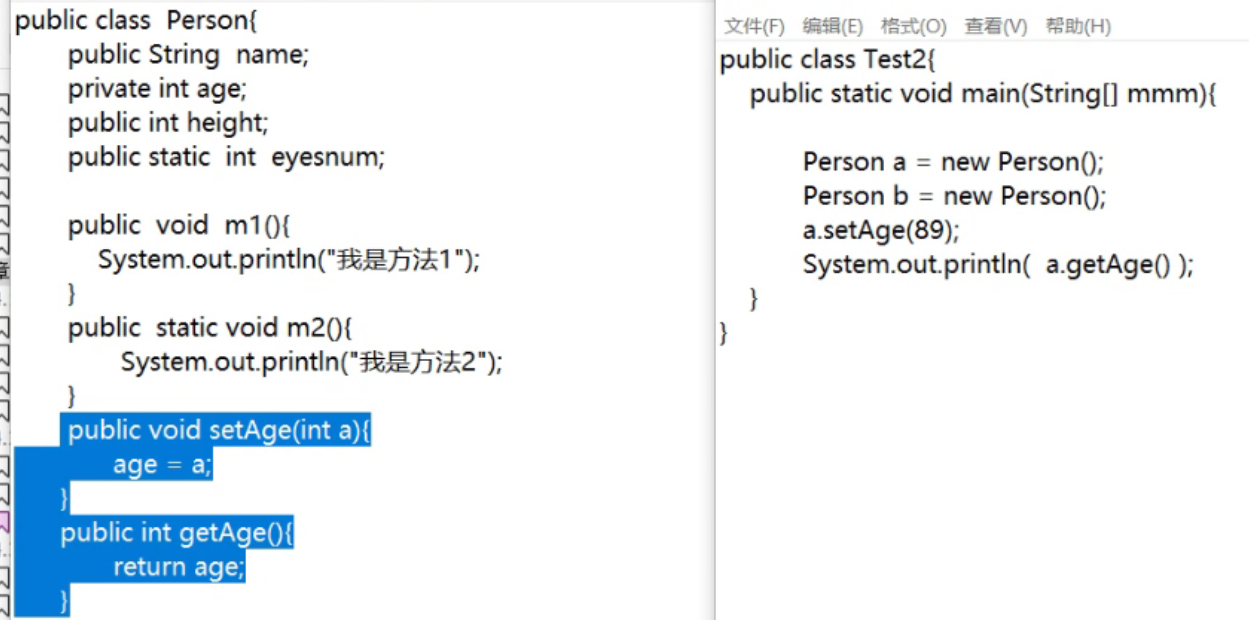
public void setAge(int a){ age = a;} Write changers to private
public void getAge(int a){ age = a;} Read accessor
Can control him to read and write
Multithreaded execution is actually a fast CPU switching. It does not necessarily execute first. The higher the priority, the greater the probability of being selected
The operating system itself has no thread pool
public class Test6{
public static void main(String[] mmm){
Thread t1 = new Thread(){
@Override
public void run(){
System.out.println("1");
}
};
Thread t2 = new Thread(){
@Override
public void run(){
System.out.println("2");
}
};
t1.start();
t2.start();
System.out.println("3");
}
}start: ready cannot be executed immediately, which will interrupt the CPU process and destroy other processes
Under multithreading, one thread modifies the data, and other threads may make errors and affect the reading results
The accessor must be coded to ensure security. If you use return directly, there is no security