9.1 hash table (hash) - Google questions
-
Let's take a look at the actual demand. A computer problem of google:
-
In one company, when a new employee comes to report, it is required to add the employee's information (id, gender, age, address...). When entering the employee's id, it is required to check
Find all the information of the employee
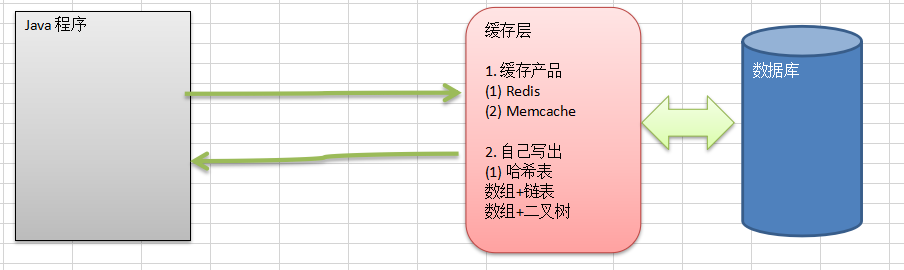
- Requirements: do not use the database and try to save memory. The faster the better = > hash table (hash)
9.2 basic introduction of hash table
Hash table (also known as hash table) is a data structure that is accessed directly according to the key value. That is, it works
The key value is mapped to a position in the table to access the record, so as to speed up the search. This mapping function is called a hash function and stores an array of records
It's called a hash table.
9.3 an online question from Google:
In one company, when a new employee comes to report, it is required to add the employee's information (id, gender, age, name, address...). When entering the employee's id,
It is required to find all the information of the employee
requirement:
-
If you don't use the database, the faster the better = > hash table (hash)
-
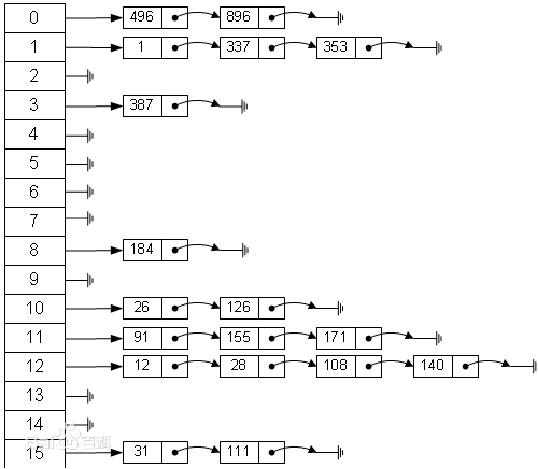
When adding, ensure that the id is inserted from low to high [after class thinking: if the id is not inserted from low to high, but each linked list is still required to be inserted from low to high
Gao, how to solve it?]
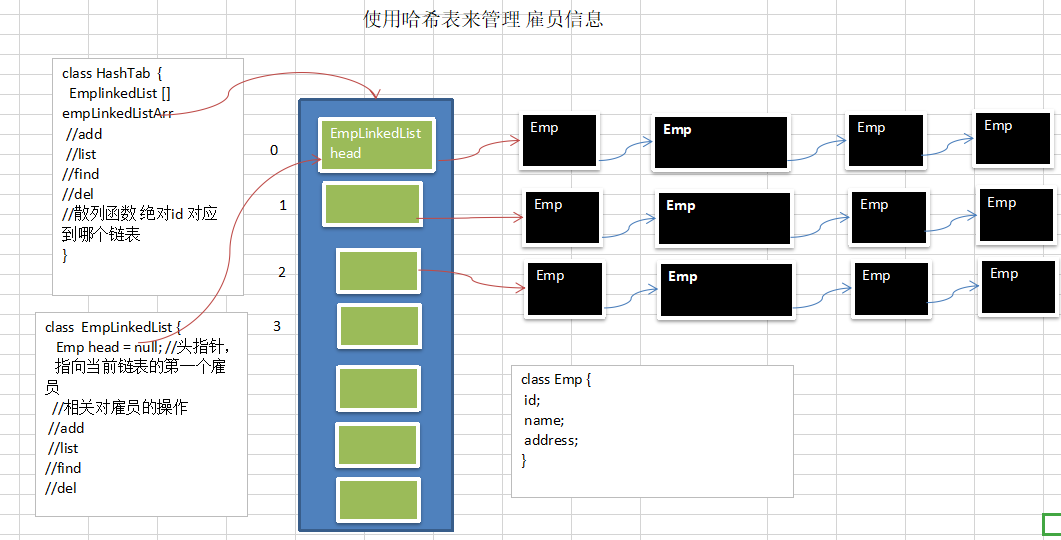
- Use the linked list to realize the hash table. The linked list does not have a header [that is, the first node of the linked list stores employee information]
4) Analyze the idea and draw a schematic diagram
5) Code implementation
package hashtab;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class HashTabDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create hash table
HashTab hashTab = new HashTab(7);
//Write a simple menu
String key = "";
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
System.out.println("add: Add employee");
System.out.println("list: Show employees");
System.out.println("find: Find employees");
System.out.println("dele: Find employees");
System.out.println("exit: Exit the system");
key = scanner.next();
switch (key) {
case "add":
System.out.println("input id");
int id = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter name");
String name = scanner.next();
//Create employee
Emp emp = new Emp(id, name);
hashTab.add(emp);
break;
case "list":
hashTab.list();
break;
case "find":
System.out.println("Please enter the to find id");
id = scanner.nextInt();
hashTab.findEmpById(id);
break;
// case"dele":
// System.out.println("please enter the id to delete");
// id = scanner.nextInt();
// hashTab.delEmpById(id);
// break;
case "exit":
scanner.close();
System.exit(0);
default:
break;
}
}
}
}
//Create HashTab to manage multiple linked lists
class HashTab {
private EmpLinkedList[] empLinkedListArray;
private int size; //Indicates how many linked lists there are
//constructor
public HashTab(int size) {
this.size = size;
//Initialize empLinkedListArray
empLinkedListArray = new EmpLinkedList[size];
//? Leave a hole. Don't initialize each linked list separately at this time
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
empLinkedListArray[i] = new EmpLinkedList();
}
}
//Add employee
public void add(Emp emp) {
//According to the employee's id, get the linked list to which the employee should be added
int empLinkedListNO = hashFun(emp.id);
//Add emp to the corresponding linked list
empLinkedListArray[empLinkedListNO].add(emp);
}
//Traverse all linked lists and hashtab
public void list() {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
empLinkedListArray[i].list(i);
}
}
//Find the employee based on the entered id
public void findEmpById(int id) {
//Use the hash function to determine which linked list to look up
int empLinkedListNO = hashFun(id);
Emp emp = empLinkedListArray[empLinkedListNO].findEmpById(id);
if (emp != null) {//find
System.out.printf("In the first%d Employee found in linked list id = %d\n", (empLinkedListNO + 1), id);
} else {
System.out.println("The employee was not found in the hash table~");
}
}
// //Delete the employee according to the entered id
// public void delEmpById(int id){
// //Use the hash function to determine which linked list to look up
// int empLinkedListNO = hashFun(id);
// Emp emp =empLinkedListArray[empLinkedListNO].delEmpByID(id);
// If (EMP! = null) {/ / found
// System.out.println("hash table after deletion is");
// empLinkedListArray[empLinkedListNO].list();
// } else {
// System.out.println("the employee ~" was not found in the hash table);
// }
// }
//Write hash function, using a simple modular method
public int hashFun(int id) {
return id % size;
}
}
//Represents an employee
class Emp {
public int id;
public String name;
public Emp next; //next defaults to null
public Emp last;
public Emp(int id, String name) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
}
//Create an EmpLinkedList to represent a linked list
class EmpLinkedList {
//The header pointer executes the first Emp, so the head of our linked list directly points to the first Emp
private Emp head; //Default null
//Add employee to linked list
//explain
//1. Suppose that when an employee is added, the id is self increasing, that is, the id allocation is always from small to large
// Therefore, we can add the employee directly to the end of this linked list
public void add(Emp emp) {
//If you are adding the first employee
if (head == null) {
head = emp;
return;
}
//If not the first employee, an auxiliary pointer is used to help locate the last employee
Emp curEmp = head;
while (true) {
if (curEmp.next == null) {//Description to the end of the linked list
break;
}
curEmp = curEmp.next; //Move back
}
//When exiting, add emp directly to the linked list
curEmp.next = emp;
}
//Employee information traversing the linked list
public void list(int no) {
if (head == null) { //Description: the linked list is empty
System.out.println("The first" + (no + 1) + " The linked list is empty");
return;
}
System.out.print("The first" + (no + 1) + " The information of the linked list is");
Emp curEmp = head; //Auxiliary pointer
while (true) {
System.out.printf(" => id=%d name=%s\t", curEmp.id, curEmp.name);
if (curEmp.next == null) {//It indicates that curEmp is the last node
break;
}
curEmp = curEmp.next; //Move back, traverse
}
System.out.println();
}
//Find employees by id
//If found, return Emp; if not found, return null
public Emp findEmpById(int id) {
//Determine whether the linked list is empty
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("The linked list is empty");
return null;
}
//Auxiliary pointer
Emp curEmp = head;
while (true) {
if (curEmp.id == id) {//find
break;//At this time, curEmp points to the employee to be found
}
//sign out
if (curEmp.next == null) {//Description: the employee cannot be found by traversing the current linked list
curEmp = null;
break;
}
curEmp = curEmp.next;//in the future
}
return curEmp;
}
//Delete employee by id
//If found, delete and return the new linked list. If not found, return null
public Emp delEmpByID(int id) {
//Determine whether the linked list is empty
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("The linked list is empty");
return null;
}
Emp curEmp = head;
while (true) {
if(curEmp.id ==id){
curEmp = null;
System.out.println("Deleted");
break;
}
curEmp = curEmp.next;
if (curEmp.next == null) {//Description: the employee cannot be found by traversing the current linked list
System.out.println("The employee cannot be found");
break;
}
}
return curEmp;
}
}
6) Operation results
add: Add employee list: Show employees find: Find employees dele: Find employees exit: Exit the system add input id 1 Enter name Tom add: Add employee list: Show employees find: Find employees dele: Find employees exit: Exit the system add input id 2 Enter name Zack add: Add employee list: Show employees find: Find employees dele: Find employees exit: Exit the system add input id 456 Enter name Littie add: Add employee list: Show employees find: Find employees dele: Find employees exit: Exit the system find Please enter the to find id 2 Find the employee in the third linked list id = 2 add: Add employee list: Show employees find: Find employees dele: Find employees exit: Exit the system find Please enter the to find id 3 The linked list is empty The employee was not found in the hash table~ add: Add employee list: Show employees find: Find employees dele: Find employees exit: Exit the system list The first linked list is empty The information of the second linked list is => id=1 name=Tom => id=456 name=Littie The information of the third linked list is => id=2 name=Zack The 4th linked list is empty The 5th linked list is empty The 6th linked list is empty The 7th linked list is empty add: Add employee list: Show employees find: Find employees dele: Find employees exit: Exit the system dele Please enter the to delete id 2 Deleted The hash table after deletion is null add: Add employee list: Show employees find: Find employees dele: Find employees exit: Exit the system
Supplement to knowledge points:
1.The function of static keyword in Java
2.The function of void keyword in java
3.Usage of void method return in java
4.[public static void main(String]args) meaning
5.The function of constructor in java
6.Common methods and usage of Java Scanner class (very detailed)
Such as next .nextInt .close
[learning notes]
java data structure Chapter 1 - Introduction to content framework
java data structure Chapter 2 - overview of data structure and algorithm
java data structure Chapter 3 - sparse arrays and queues
java data structure Chapter 4 - linked list (single linked list)
java data structure Chapter 4 - linked list (two-way linked list)
java data structure Chapter 5 - stack
java data structure Chapter 6 - recursion
java data structure Chapter 7 - sorting algorithm 01
Chapter 7 - java sorting algorithm bubble structure
java data structure Chapter 7 - sorting algorithm 03 - selective sorting
java data structure Chapter 7 - sorting algorithm 04 - insert sorting
java data structure Chapter 7 - sorting algorithm 05 - Hill sorting
java data structure Chapter 7 - sorting algorithm 06 - quick sorting
java data structure Chapter 7 - sorting algorithm 07 - merge sorting
java data structure Chapter 7 - sorting algorithm 08 - cardinal sorting
java data structure Chapter 7 - sorting algorithm 09 - summary and comparison of common sorting algorithms!
java data structure Chapter 8 - Search Algorithm
Continuous update