1, You don't know hash tables
1. What is a hash table?
- We already know a data item, keyword mapping storage location.
- In fact, our search process is to compare and constantly compare keywords, so that we can find the storage location.
- Now you should find that they are like functions, X = keyword and Y = storage location.
- The difficulty of hash table is to find the mapping relationship: f(x) = y
- Call the function: hash function.
- The table established according to this idea is a hash table.
- The advantage of hash table is that it does not need to be compared continuously, but can be found directly, just once.
- Bold is the key
2. Conflict
- The mathematical definition of a function has one thing: one X is not allowed to correspond to multiple Y.
- The hash function is also a function, so there is one case left: multiple X corresponds to a Y.
- Therefore, the conflict to be solved by hash table: different keywords may get the same storage address.
- Mistakes can be resolved, but conflicts cannot be completely avoided. We usually need to set up a method to deal with conflicts.
3. Key terms
- Hash table: a table formed by a keyword corresponding to a storage location.
- Storage location = hash address = hash address
- Function relation = mapping relation = correspondence relation = hash construction = hash
- H(x) = y
2, You already know the hash table
(1) Construction method of hash function
-Objective: to construct a hash function.
-Good hash function: the keyword gets a "random address" through the hash function, so that the hash addresses of a group of keywords are evenly distributed in the whole address interval, so as to reduce conflicts.
1. Direct addressing method
H ( k e y ) = k e y or H ( k e y ) = a ∗ k e y + b H(key) = key or H(key) = a*key + b H(key)=key or H(key)=a * key+b
2. Digital analysis
too spirit live Yes , know Avenue have this species square method Just that 's ok Yes It's too flexible. Just know this method It's too flexible. Just know this method
3. Square middle method - important
take
shut
key
word
flat
square
after
of
in
between
Several
position
by
Ha
Hope
land
site
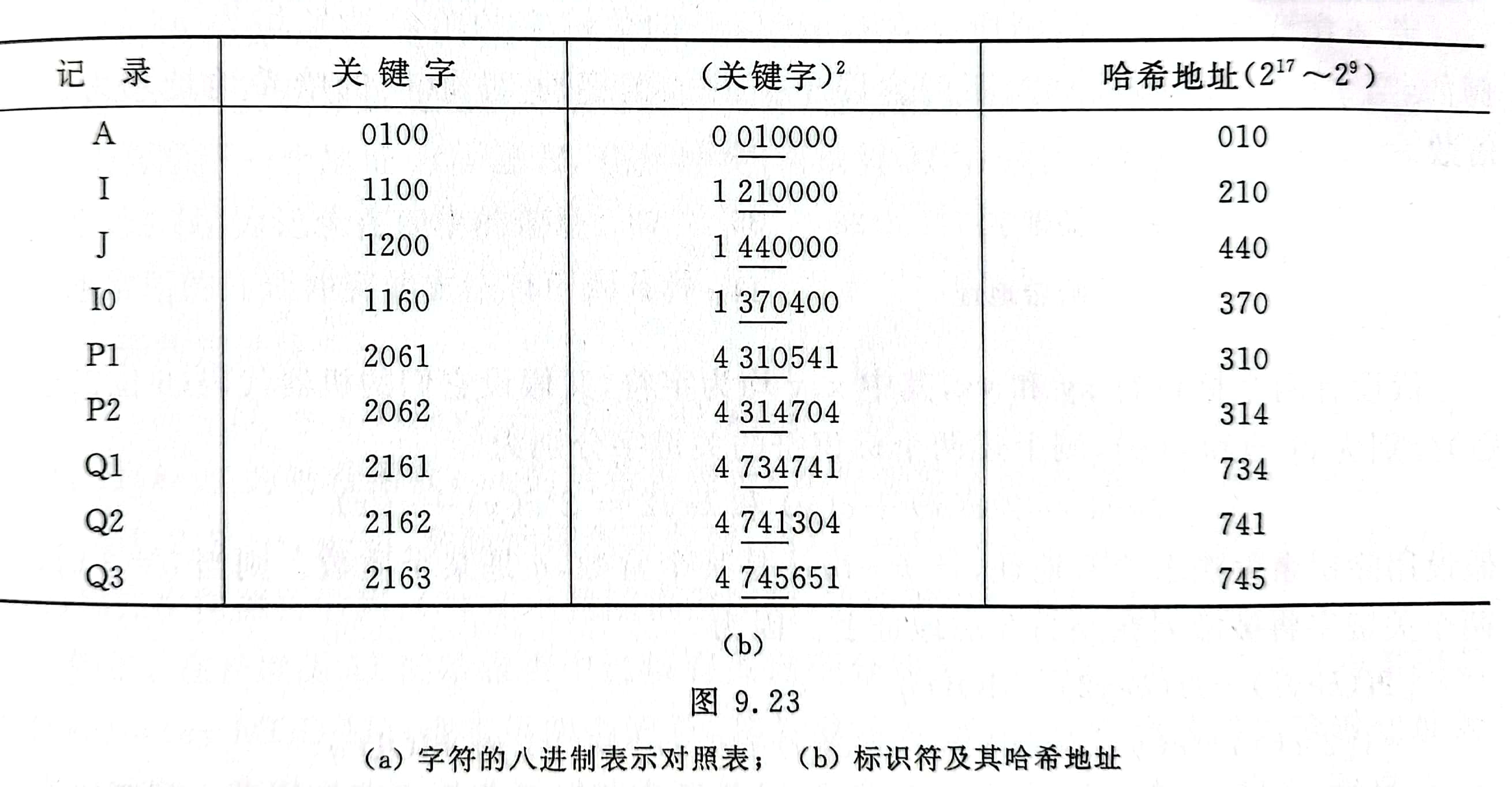
Take the middle digits after the square of the keyword as the hash address
Take the middle digits after the square of the keyword as the hash address
- For example:
4. Folding method
take shut key word branch cut become mutually with of Several Department branch ( most after one Department branch of position number can with no with ) , however after take this Several Department branch Fold plus and ( Shed go enter position ) do by Ha Hope land site Divide the keyword into the same parts (the digits of the last part can be different), and then take the superposition and (round off the carry) of these parts as the hash address Divide the keyword into the same parts (the digits of the last part can be different), and then take the superposition and (round off the carry) of these parts as the hash address
- Folding hair is suitable for a large number of keywords, and the numbers on each bit are roughly evenly distributed.
- For example:

5. Division and remainder method - important
H
(
k
e
y
)
=
k
e
y
M
O
D
p
,
p
<
=
m
H(key) = key MOD p, p <= m
H(key)=keyMODp,p<=m
m
by
Ha
Hope
surface
of
surface
long
m is the table length of the hash table
m is the table length of the hash table
- It can be used with other methods.
- The choice of p is very important.
(2) . methods of handling conflicts
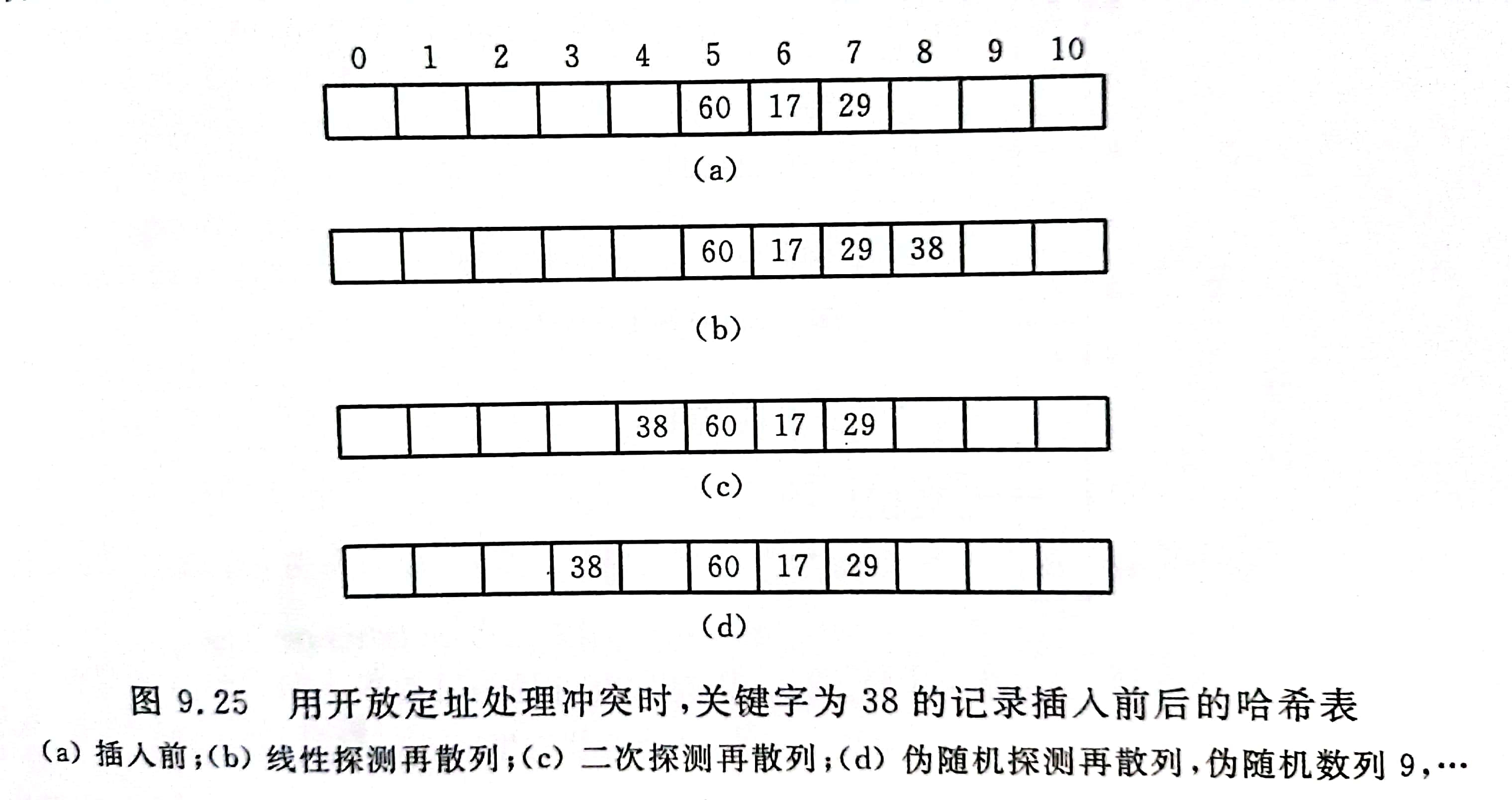
1. Open addressing - important
H i = ( H ( k e y ) + d i ) M O D m Hi = (H(key) + di) MOD m Hi=(H(key)+di)MODm
- H(key) is a hash function.
- m is the length of the hash table.
- di is an incremental sequence.
- The formula di = 1, 2, 3,..., m-1 is called linear detection re hashing.
- The formula di = 1^2, -1^2, 2^2, -2^2,..., K ^ 2, - K ^ 2 (k < = m / 2) is called quadratic detection hashing.
- The formula di = pseudo-random sequence is called random detection re hashing.
- For example:
2. In hash method
3. Chain address method
4. Establish a public overflow area
3, Hash table lookup code
(1) Data structure of hash table
// Storage structure of open addressing hash table
int hashsize[] = {997, ... }; // Hash table capacity increment table, an appropriate prime sequence
typedef struct {
ElemType * elem; // Dynamically allocate arrays
int count; // Number of current elements
int sizeindex; // hashsize[sizeindex] is the current capacity
}HashTable;
(2) Java code of hash table
- Construction of hash table:
/**
* Divide and remainder method to construct hash table
*
* @param keys
* @param values
* @param hashTableLength Hash table, table length, prime
*/
public Search(int[] keys, String[] values, int hashTableLength) {
length = hashTableLength;
searchTable = new DataItem[length];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
searchTable[i] = null;
}
int tempPosition;
for (int i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
tempPosition = keys[i] % hashTableLength;
while (searchTable[tempPosition] != null) {
tempPosition = (tempPosition + 1) % hashTableLength;
System.out.println("conflict, Move keywords forward" + keys[i]);
}
searchTable[tempPosition] = new DataItem(keys[i], values[i]);
}
}
- Hash lookup:
/**
* hash search
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
public String hashSearch(int key) {
int tempPosition = key % length;
while (searchTable[tempPosition] != null) {
if (searchTable[tempPosition].key == key) {
return searchTable[tempPosition].value;
}
tempPosition = (tempPosition + 1) % length;
}
return null;
} // hashSearch
- Test function:
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] key = { 1, 3, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10 };
String[] values = { "if", "then", "else", "switch", "case", "for", "while" };
Search search = new Search(key, values, 13);
System.out.println(search.toString());
System.out.println("Search result of 10 is: " + search.hashSearch(10));
}
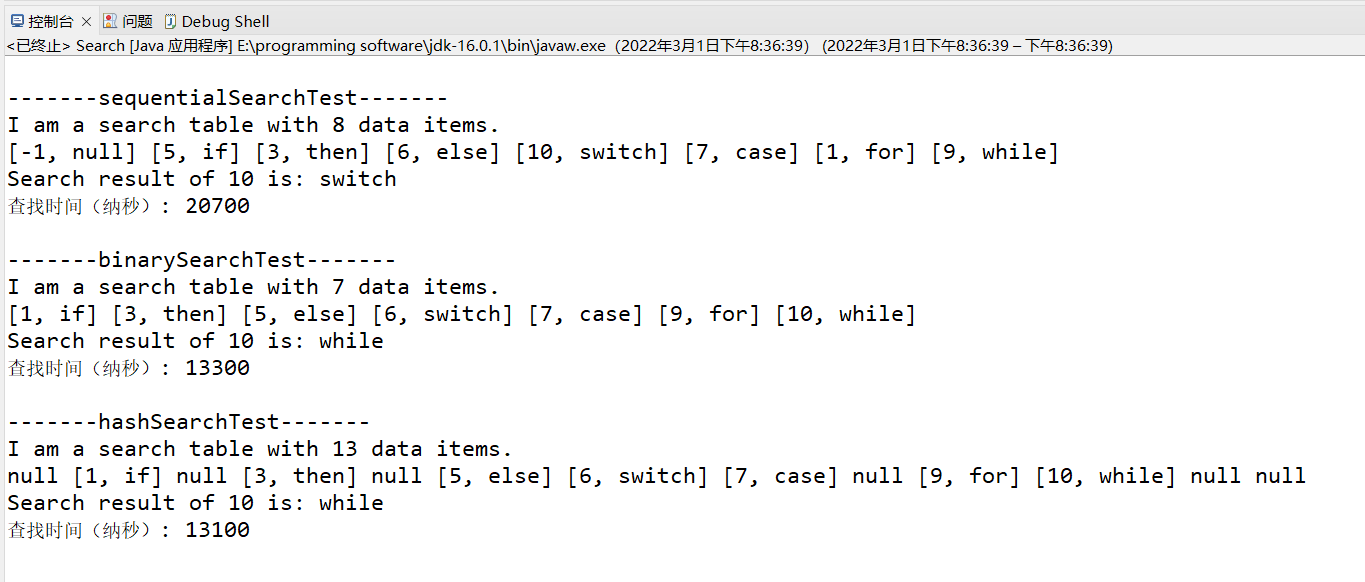
(3) . output sample
- Source code of Search class:
package search;
public class Search {
/** Lookup table */
DataItem[] searchTable;
/** Table length */
int length;
class DataItem {
/** Keyword domain */
int key;
/** Other domains */
String value;
DataItem(int key, String value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
public String toString() {
return "[" + key + ", " + value + "]";
}
} // data item
/**
* Construct lookup table
*
* @param keys
* @param values
*/
public Search(int[] keys, String[] values) {
// TODO
if (keys.length != values.length) {
throw new RuntimeException("Key does not correspond to value!");
}
length = keys.length;
searchTable = new DataItem[length];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
searchTable[i] = new DataItem(keys[i], values[i]);
}
} // structure
/**
* Divide and remainder method to construct hash table
*
* @param keys
* @param values
* @param hashTableLength Hash table, table length, prime
*/
public Search(int[] keys, String[] values, int hashTableLength) {
length = hashTableLength;
searchTable = new DataItem[length];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
searchTable[i] = null;
}
int tempPosition;
for (int i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
tempPosition = keys[i] % hashTableLength;
while (searchTable[tempPosition] != null) {
tempPosition = (tempPosition + 1) % hashTableLength;
System.out.println("conflict, Move keywords forward" + keys[i]);
}
searchTable[tempPosition] = new DataItem(keys[i], values[i]);
}
}
/**
* Print lookup table
*/
public String toString() {
String resultString = "I am a search table with " + length + " data items.\r\n";
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
resultString += searchTable[i] + " ";
}
return resultString;
}// toString
/**
* Sequential search
*
* @param key
* @return key Corresponding value
*/
public String sequentialSearch(int key) {
// TODO
searchTable[0].key = key; // "Sentry"
int i;
for (i = length - 1; searchTable[i].key != key; i--)
;
return searchTable[i].value;
} // sequentialSearch
/**
* Half search
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
public String binarySearch(int key) {
// TODO
int low = 0;
int high = length - 1;
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
while (low <= high) {
mid = (low + high) / 2;
if (searchTable[mid].key == key) {
return searchTable[mid].value;
} else if (searchTable[mid].key < key) {
low = mid + 1;
} else {
high = mid - 1;
}
} // Of while
return null;
}// binarySearch
/**
* hash search
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
public String hashSearch(int key) {
int tempPosition = key % length;
while (searchTable[tempPosition] != null) {
if (searchTable[tempPosition].key == key) {
return searchTable[tempPosition].value;
}
tempPosition = (tempPosition + 1) % length;
}
return null;
} // hashSearch
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO
System.out.println("\r\n-------sequentialSearchTest-------");
// 1 declaration
int[] keys1 = { -1, 5, 3, 6, 10, 7, 1, 9 };
String[] values1 = { "null", "if", "then", "else", "switch", "case", "for", "while" };
// Object 2
Search search1 = new Search(keys1, values1);
// 3 printing
System.out.println(search1.toString());
// 4 test
long startTime1 = System.nanoTime(); // Get start time
System.out.println("Search result of 10 is: " + search1.sequentialSearch(10));
long endTime1 = System.nanoTime(); // Get end time
System.out.println("Find time (nanoseconds): " + (endTime1 - startTime1));
System.out.println("\r\n-------binarySearchTest-------");
// 1 declaration
int[] keys2 = { 1, 3, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10 };
String[] values2 = { "if", "then", "else", "switch", "case", "for", "while" };
// 2 object
Search search2 = new Search(keys2, values2);
// 3 printing
System.out.println(search2.toString());
// 4 test
long startTime2 = System.nanoTime(); // Get start time
System.out.println("Search result of 10 is: " + search2.binarySearch(10));
long end2Time2 = System.nanoTime(); // Get end time
System.out.println("Find time (nanoseconds): " + (end2Time2 - startTime2));
System.out.println("\r\n-------hashSearchTest-------");
// 1 declaration
int[] key3 = { 1, 3, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10 };
String[] values3 = { "if", "then", "else", "switch", "case", "for", "while" };
// 2 object
Search search3 = new Search(key3, values3, 13);
// 3 printing
System.out.println(search3.toString());
// 4 test
long startTime3 = System.nanoTime(); // Get start time
System.out.println("Search result of 10 is: " + search3.hashSearch(10));
long endTime3 = System.nanoTime(); // Get end time
System.out.println("Find time (nanoseconds): " + (endTime3 - startTime3));
}
} // Search
- Output: