1. Write a Book class that has at least two properties, name and price.This class implements the Comparable interface by specifying that the size relationship between two Book class instances is the size relationship of the price attribute of the two Book class instances in the compareTo() method of the interface.In the main function, select the appropriate collection type to store several objects of the Book class, create a new Book class object, and check which objects in the collection are equal.The results of the query are as follows: 
package generic paradigm;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Book implements Comparable{
String name;
float price;
public Book(String name,float price){
this.name=name;
this.price=price;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
List<Book> list=new ArrayList<Book>();
Book b1=new Book("Java Basic Tutorials",28.0f);
Book b2=new Book("Database Technology",29.0f);
Book b3=new Book("C++Basic Tutorials",27.3f);
list.add(b1);
list.add(b2);
list.add(b3);
Book b4=new Book("<Pattern Recognition",29.0f);
System.out.println("New book:"+b4.name+"With the following books:");
for (int i = 0;i< list.size();i++){
Book book =(Book)list.get(i);
int index=book.compareTo(b4);
if(index==0){
System.out.println(book.name);
}
}
System.out.println("The prices are the same,"+"Specific prices are:"+b4.price+"element");
}
public int compareTo(Object obj) {
Book b=(Book)obj;
if(b.price>this.price)
{
return 1;
}
else if(b.price<this.price)
{
return -1;
}
else
return 0;
}
}Result Screenshot: 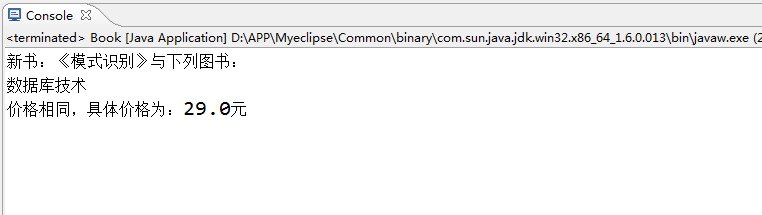
2. Write an application where users enter names and scores of students from two text boxes. The program displays the names and scores of these students in a text area sorted by their grades.
The program runs as follows: 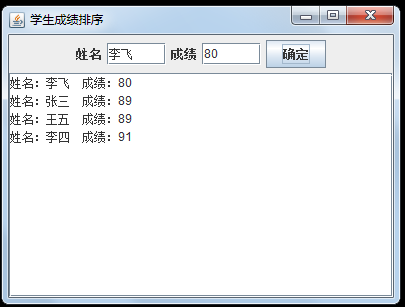
package generic paradigm;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JTextArea;
import javax.swing.JTextField;
public class Grade extends JFrame {
JLabel lName,lScore; //Name and Achievement Label
JTextField tName,tScore; //Text Box
JTextArea taShow; //Text area for display
JButton button;
JPanel pan;
Map<String,String> sMap,rMap;
//Principal function
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Grade();
}
//Construction method
public Grade() {
init();
click();
}
//Initialization Method
public void init() {
lName=new JLabel("Full name"); //instantiation
lScore=new JLabel("achievement");
tName=new JTextField(10);
tScore=new JTextField(10);
button=new JButton("Determine");
pan=new JPanel();
taShow=new JTextArea();
pan.add(lName); //Control Combination
pan.add(tName);
pan.add(lScore);
pan.add(tScore);
pan.add(button);
add(pan,BorderLayout.NORTH); //Set Location
add(taShow, BorderLayout.CENTER);
setTitle("Statistics Student Name and Score"); //Set window basic properties
setSize(400, 300);
setVisible(true);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE);
validate();
sMap=new HashMap<String,String>(); //Non-window property initialization
}
//Make sure the button is clicked
private void click() {
button.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
save();
showMap();
}
});
}
//Save method invoked by clicking a button
private void save() {
sMap.put(tName.getText(),tScore.getText());
rMap = sortMapByValue(sMap); //Sort by Value
tName.setText(""); //Text box content empty
tScore.setText("");
}
//Sort by Value
public static Map<String, String> sortMapByValue(Map<String, String> map) {
if (map == null || map.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
Map<String, String> sortedMap = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>();
//Save the element in a List of type entry
List<Map.Entry<String, String>> entryList = new ArrayList<Map.Entry<String, String>>(map.entrySet());
Collections.sort(entryList, new MapValueComparator());
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> iter = entryList.iterator();
Map.Entry<String, String> tmpEntry = null;
while (iter.hasNext()) {
tmpEntry = iter.next();
sortedMap.put(tmpEntry.getKey(), tmpEntry.getValue()); //Traverse elements from a List to save them in a map
}
return sortedMap;
}
//Print List
private void showMap() {
taShow.setText("");
for(Map.Entry<String,String> entry:rMap.entrySet()) {
taShow.append("Full name:"+entry.getKey()+" Results:"+entry.getValue()+"\n");
}
}
}
//Comparator Class
class MapValueComparator implements Comparator<Map.Entry<String, String>> {
public int compare(Entry<String, String> s1, Entry<String, String> s2) {
return s1.getValue().compareTo(s2.getValue());
}
} Result Screenshot: