This article is not intended to systematically introduce Java's I / O flow mechanism, only for personal notes
As a java small dish, every time I search other people's Java reading and writing files on the Internet, I always feel confused. Why do I have to declare so many classes and rules? They are totally divided into two categories, so I have a little understanding with questions;
In Java, there are two types of I / O mode classes: InputStream & OutputStream and Reader & writer. In addition, there is a class that processes files and folders;
The input and output stream class of Java adopts the decorator mode, and many other classes are derived from the above five classes. Here is a picture found on the Internet. Let's feel it
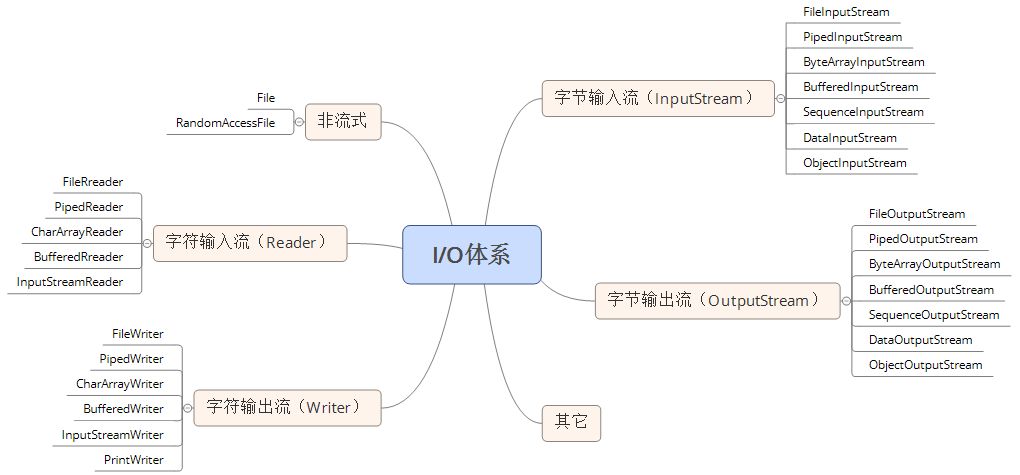
Java supports many types of input sources and output terminals, but I'm not going to expand here. I just want to talk about the reading and output of files. As we all know, computer access to external devices is very time-consuming, while access to buffer is very fast. Therefore, in order to improve the efficiency of reading and writing files, in addition to the necessary read-write mechanism between the program and the stream node, buffer mechanism should also be added.
Specific examples are as follows:
package com.practise.test; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.OutputStreamWriter; import java.io.BufferedWriter; //All with Stream The classes at the end are byte oriented FileInputStream/FileOutputStream //with Reader/Writer The class at the end is character oriented //with File The first class is external storage oriented //with Buffered The first class is buffer oriented public class ReadAndWrite { public static void main (String[] args) { String path = "D:\\Coding\\Java\\TestJava\\testdata\\"; try { File inFile = new File(path + "in.txt"); File outFile = new File(path + "out.txt"); InputStreamReader inSr = new InputStreamReader( new FileInputStream(inFile)); BufferedReader inBr = new BufferedReader(inSr); OutputStreamWriter outSw = new OutputStreamWriter( new FileOutputStream(outFile)); BufferedWriter outBw = new BufferedWriter(outSw); String line = ""; while ((line = inBr.readLine()) != null) { outBw.write(line + "\r\n"); } outBw.close(); outSw.close(); inBr.close(); inSr.close(); } catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }