Gateway gateway
The core of the Spring Cloud Gateway component is a series of filters that can forward (route) requests sent by clients to corresponding services.
Supplementary notes & benefits
- Gateway replaces a solution from Netflix Zuul
- Hide the IP / port information of the service
- Provide a unified API route management method (url management)
- Gateway core functions: filtering / routing / assertion
- Gateway is also a micro service and needs to register with Eureka
Core functions
- Route: route information consists of ID, target URL, a group of assertions and a group of filters (generally, route matching will be judged through assertions)
- Predicate: define any information in the matching HTTP (such as request header / parameters, etc...)
- Filter: some business processing can be performed on the request / response
Workflow
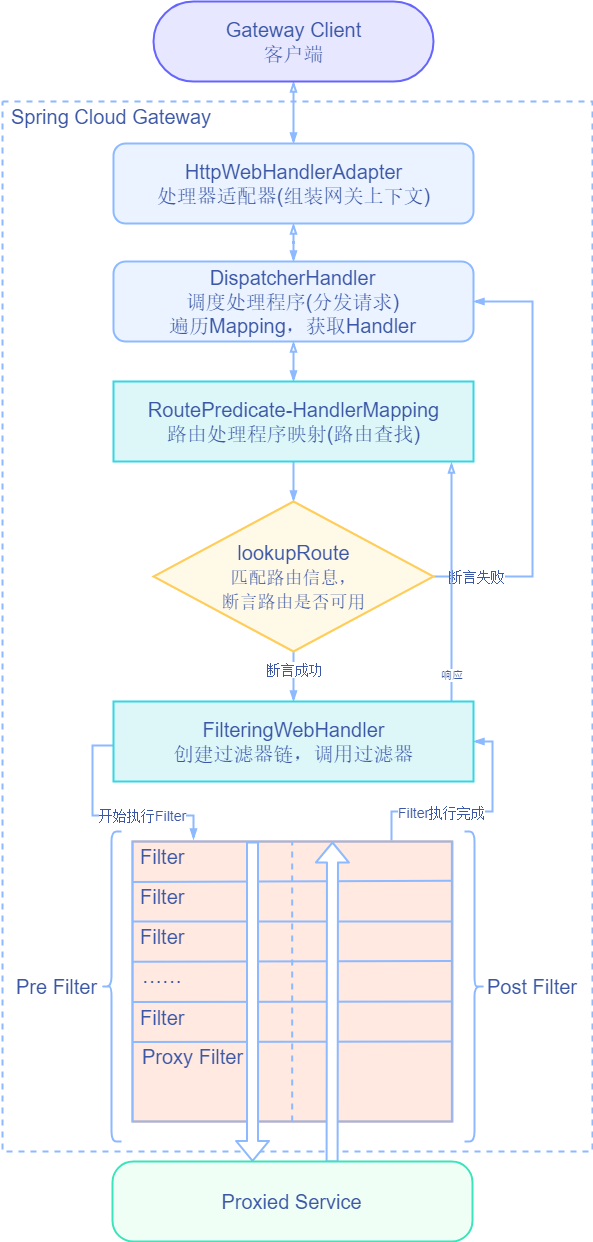
explain:
-
The client sends a request. If the request matches the route defined by the gateway program, the request will be sent to the micro service of the gateway for processing. At this time, the processing runs a specific request filter chain
-
The reason why the dotted line of the filter is separated: the request / response logic of the proxy request will be executed (all pre filter logic will be executed first, and then the proxy request; after the proxy request is completed, the post filter logic will be executed to respond)
Example
Code in 01Spring Cloud Edit based on
-
Create a new Maven project (no skeleton)
The project name I created is gateway -
gateway dependency configuration pom.xml
<!-- gateway --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- eureka --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId> </dependency> -
gateway startup class
@SpringBootApplication @EnableDiscoveryClient // Eureka client public class GatewayApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(GatewayApplication.class, args); } } -
gateway configuration application.yml
server : port : 10010 spring : application : name : api-gateway cloud : gateway : routes : # Routing id (optional) - id : user-service-route # Address of proxy service # uri: http://localhost:9091 # mode 1 fixed agent uri : lb://User service # mode 2 dynamic agent # Route assertions, mapping paths that can be configured predicates: - Path=/user/** eureka : client : service-url : defaultZone : http://localhost:10086/eureka instance : # Give priority to ip, not host prefer-ip-address : truebe careful:
- The path to fill in the route assertion cannot contain spaces - Path=/user/**
explain:
- Proxy path http://localhost:10010/user/1 ==> http://localhost:9091/user/1
- Proxy routing can be written in two ways, but generally it will not die. Therefore, the second method is applied
- When the protocol used for uri in routing configuration is lb, gateway will use LoadBalancerClient to parse user service into actual IP and port through eureka, and perform ribbon load balancing
-
test
- Open Eureka, server and gateway services in turn
- visit http://localhost:10010/user/1 (the returned data represents success)
filter
It can be seen from the above workflow that the Gateway's routing filter allows you to modify the HTTP of incoming requests / responses, which only works on specific routes
Filter life cycle
There are two kinds of Filter for Spring Cloud Gateway: pre (before invoking the request is executed), post (after the request is executed), and the above workflow can be seen.
Usage scenario
- Request authentication: before the filter chain calls the filter() method, if no permission is found, Null is returned
- Exception handling: after the filter chain calls the filter() method, the exception is recorded and returned
- Statistics of service call duration: before and after the filter chain call to the filter() method, statistics are made according to the duration
Common filter factory
There are many built-in filter factories in the Gateway. We only need to understand the commonly used filters
| Filter factory name | explain |
|---|---|
| AddRequestHeader | Add a header to the matching request |
| RemoveRequestHeader | Remove the header (request header) from the request on the match |
| AddRequestParameter | Add parameters to the request route on the match |
| SetStatus | Set the response code of the HTTP request |
| AddResponseHeader | Add a header (response header) to the response returned from the gateway |
| StripPrefix | Remove the prefix from the request path on the match |
| PrefixPath | Prefix request paths on matching |
More detailed reference Official website link
Filter example
AddRequestHeader add request header
For requests that match the rules successfully, the X-Request-Foo:bar request header will be added and passed to the back-end service
spring :
application :
name : api-gateway
cloud :
gateway :
routes :
- id : user-service-route
uri : lb://user-service
predicates:
- Path=/user/**
filters:
# Parameters: request header, value
- AddRequestHeader=X-Request-Foo,Bar
Removerequeheader remove request header
The Header can be removed before the request is forwarded to the back-end service
spring :
application :
name : api-gateway
cloud :
gateway :
routes :
- id : user-service-route
uri : lb://user-service
predicates:
- Path=/user/**
filters:
# Parameter: remove request header X-Request-Foo
- RemoveRequestHeader=X-Request-Foo
AddRequestParameter request to add a parameter
The MyName=Sans parameter will be attached to the request that matches the rule successfully
spring :
application :
name : api-gateway
cloud :
gateway :
routes :
- id : user-service-route
uri : lb://user-service
predicates:
- Path=/user/**
filters:
# Parameters: name, value (similar to K, V)
- AddRequestParameter=MyName,Sans
SetStatus response return code
Used to set the response code of HTTP request; supports integer / enumeration (org.springframework.http.HttpStatus class to view enumeration)
spring :
application :
name : api-gateway
cloud :
gateway :
routes :
- id : user-service-route
uri : lb://user-service
predicates:
- Path=/user/**
filters:
- SetStatus=401
AddResponseHeader add response header
Add response header to gateway response
spring :
application :
name : api-gateway
cloud :
gateway :
default-filters:
- AddResponseHeader=X-Request-Foo,Bar
StripPrefix removes the routing prefix
Remove the prefix of the request address and use it as the proxy address
spring :
application :
name : api-gateway
cloud :
gateway :
routes :
# Routing id (optional)
- id : user-service-route
# Address of proxy service
# uri: http://localhost:9091 # mode 1
uri : lb://User service # mode 2
# Route assertions, mapping paths that can be configured
predicates:
- Path=/api/user/**
filters:
- StripPrefix=1
···
For example: http://localhost:10010/api/user/1 ==> http://localhost:9091/user/1 (remove / api)
PrefixPath add route prefix
Add a prefix to the request address and use it as the proxy address
spring :
application :
name : api-gateway
cloud :
gateway :
routes :
# Routing id (optional)
- id : user-service-route
# Address of proxy service
# uri: http://localhost:9091 # mode 1
uri : lb://User service # mode 2
# Route assertions, mapping paths that can be configured
predicates:
- Path=/**
filters:
- PrefixPath=/user
···
For example: http://localhost:10010/1 ==> http://localhost:9091/user/1 (add / user)
The test can test and check the attribute changes in the following custom filter factory
Custom local filter
The Spring Cloud Gateway filter factory edits / validates requests during the process of request delivery. (application scenarios generally include authentication, selecting micro services specified in the cluster, etc
Example
explain:
- The custom filter factory needs to inherit the AbstractGatewayFilterFactory class, override the apply() method, and the filter class name is suffixed with GatewayFilterFactory
- Test request parameters are displayed on the console
-
Create a custom local filter (MyParamGatewayFilterFactory I created)
package com.sans.gateway.filter; import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.GatewayFilter; import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.factory.AbstractGatewayFilterFactory; import org.springframework.http.server.reactive.ServerHttpRequest; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; @Component public class MyParamGatewayFilterFactory extends AbstractGatewayFilterFactory<MyParamGatewayFilterFactory.Config> { /**Constructor*/ public MyParamGatewayFilterFactory() { super(Config.class); } /** initialization * Read the parameters in the configuration file and assign them to the configuration class * */ @Override public List<String> shortcutFieldOrder() { //One parameter return Arrays.asList("params"); } /**Filter logic*/ @Override public GatewayFilter apply(Config config) { // Instantiate GatewayFilter.filter() // exchange - Request properties // chain - provides a way to delegate to the next filter return (exchange , chain) -> { // Front ServerHttpRequest request = exchange.getRequest(); // Execute if the route contains the name parameter if (request.getQueryParams().containsKey(config.params)) { request.getQueryParams().get(config.params).forEach((v)->{ System.out.printf("Local filter => %s = %s\n",config.params,v); }); } /**Read parameters of filter configuration (stored as objects)*/ public static class Config { // Corresponds to the filter parameters configured in the application.yml configuration file private String params; public String getParams() { return params; } public void setParams(String params) { this.params = params; } } } -
Configure application.yml to add custom filters
spring : cloud : gateway : routes : # Routing id (optional) - id : user-service-route # Address of proxy service # uri: http://localhost:9091 # mode 1 uri : lb://User service # mode 2 # Route assertions, mapping paths that can be configured predicates: - Path=/user/** filters: # Add custom filter - MyParam=nameexplain:
- The GatewayFilterFactory suffix can be omitted in the configuration
- The above corresponding parameter is the List of the specified number of parameters returned by the shortcutFieldOrder() method (I specified above that the List of params is returned)
-
test
- Open Eureka, server and gateway services in turn
- visit http://localhost:10010/user/1?name=Sans
After accessing, the console will print. If the parameter name does not match, it will not print
Custom global filter
Global filter works on all routes without other configuration!!! Generally, it is used for unified permission verification, security verification and other functions
Example
explain:
- The global filter needs to implement the GlobalFilter interface
- The filter order needs to implement the value specified by the Ordered interface (the smaller the value, the faster)
- Test whether the request is authorized. Judge whether the request header of token is included
-
Create a custom global filter (MyGlobalFilter I created)
package com.sans.gateway.filter; import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils; import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.GatewayFilterChain; import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.GlobalFilter; import org.springframework.core.Ordered; import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import org.springframework.web.server.ServerWebExchange; import reactor.core.publisher.Mono; @Component public class MyGlobalFilter implements GlobalFilter, Ordered { @Override public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange , GatewayFilterChain chain) { System.out.println("=================Global filter MyGlobalFilter================="); String token = exchange.getRequest().getHeaders().getFirst("token"); if (StringUtils.isBlank(token)) { // Set the response status code to unauthorized 401 exchange.getResponse().setStatusCode(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED); return exchange.getResponse().setComplete(); } return chain.filter(exchange); } /**Set filter priority*/ @Override public int getOrder() { return 1; } } -
Test (because the request header needs to be added to the request)
- Open Eureka, server and gateway services in turn
- Through the following IDEA built-in HTTP test, there are examples below
Note: data will be returned if the request succeeds; 401 (unauthorized) will be returned if the request fails
IDEA built in HTTP debugging
-
Create a test HTTP request draft file
-
Set request url test
There are functions such as example viewing and usage
Cross domain configuration
Cross domain: when any one of the protocol / domain name / port requesting the URL is different from the current page URL, it is called cross domain
| Current URL | Requested URL | Cross domain | reason | compare |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| http://www.test.com/ | http://www.test.com/index.html | N | - | - |
| http://www.test.com/ | https://www.test.com/index.html | Y | Different agreement | http/https |
| http://www.test.com/ | http://www.baidu.com/ | Y | The primary domain name is different | test/baidu |
| http://www.test.com/ | http://blog.test.com/ | Y | Subdomain name is different | www/blog |
| http://www.test.com:8080/ | http://www.test.com:7001/ | Y | Different port numbers | 8080/7001 |
This cross domain problem can be configured in the Gateway gateway server. The configuration is as follows:
spring :
application :
name : api-gateway
cloud :
gateway :
globalcors :
cors-configurations :
# Represents the addresses on all access gateway servers
'[/**]' :
# Allow access to the specified server address
# allowedOrigins : * # *Access is supported on behalf of all
allowedOrigins :
- "http://demo.sans.top"
allowedMethods :
- GET
The above configuration allows from http://demo.sans.top GET service data from GET request
Official details: CORS Configuration (spring.io)
Load balancing & fuses
The Gateway integrates Ribbon and Hystrix by default (the same is true for the configuration policy). If there are other policy configurations, click the link to learn about the relevant configurations
Difference between Gateway and Feign
| Gateway | Feign | |
|---|---|---|
| Interface entry | Unified service entrance | Single microservice portal |
| Interface security | Interface concealment application | Interface exposure application |
| Routing processing | Can handle | Inherent. Cannot handle |
| Application scenario | Permission check and flow control | Internal invocation of microservices is more convenient |