Tools:
eclipse jdk 1.8 oracle 11g ojdbc6.jar(Database driver package)
Six steps of JDBC:
Here we follow these six steps of jdbc:
Registration driven Get connection Get execution sql statement object Execute sql statement Process result set close resource
URL: Uniform Resource Locator
oracle URL: jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:DataBaseName
jdbc:oracle:thin:@127.0.0.1:1521:DataBaseName
MySQL URL: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/DataBaseName
thin: small drive, drive mode
@localhost native ip address 127.0.0.1
DataBaseName: the name of the database
CMD - > ipconfig: ip address query
URI: Uniform Resource Identifier
URN: identifies a resource with the name of a specific namespace
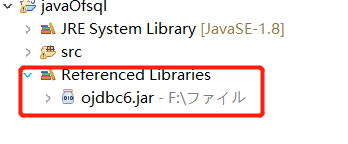
Import ojdbc6.jar
Right click new project - > build path - > configure build path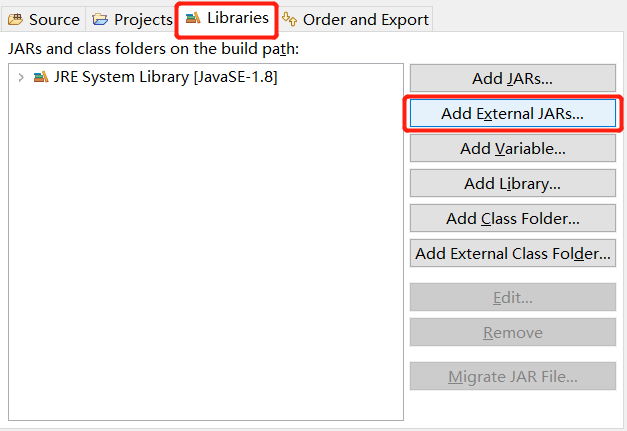
TestClass:
package javaOfsql;
import oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* Created by 10412 on 2016/12/27.
* JDBC Six steps of
* JAVA Three ways to connect to Oracle
*/
public class JdbcTest
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connect = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
//Step 1: register driver
//The first way: class loading (common)
//Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver");
//The second way: using the Driver object
Driver driver = new OracleDriver();
DriverManager.deregisterDriver(driver);
//The third way: to use system parameters, you need to configure program arguments in idea as the following parameters
//-Djdbc.drivers = oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver
//Step 2: get the connection
//The first way: using DriverManager (commonly used)
//connect = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:XE", "your oracle database user name", "user name password");
connect = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:oracle:thin:@127.0.0.1:1521:orcl", "scott", "tiger");
//The second way: use Driver directly
// Properties pro = new Properties();
// pro.put("user", "scott");
// pro.put("password", "tiger");
// connect = driver.connect("jdbc:oracle:thin:@127.0.0.1:1521:XE", pro);
//Test whether the connect is correct or not
System.out.println(connect);
System.out.println("Link success");
//Step 3: get the executed sql statement object
//The first way: statement
statement = connect.createStatement();
//The second way: PreStatement
//PreparedStatement preState = connect.prepareStatement("select * from student");
//Step 4: execute sql statement
//The first way:
resultSet = statement.executeQuery("select * from student");
//The second way:
// preState.setInt(1, 2);//1 refers to the first? , 2 means the first? values value
//resultSet = preState.executeQuery(); / / execute query statement
//Query any statement. If there is a result set, it returns true. If there is no result set, it returns false. Note that if you insert a piece of data, you can insert a piece of data successfully though there is no result set and it returns false
// boolean execute = preState.execute();
// System.out.println(execute);
//Step 5: process result set
while (resultSet.next())
{
int id = resultSet.getInt("SNO");
String name = resultSet.getString("SNAME");
String sex = resultSet.getString("SSEX");
System.out.println(id+" "+name+" "+sex); //Printout result set
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//Step 6: close resources
try {
if (resultSet!=null) resultSet.close();
if (statement!=null) statement.close();
if (connect!=null) connect.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
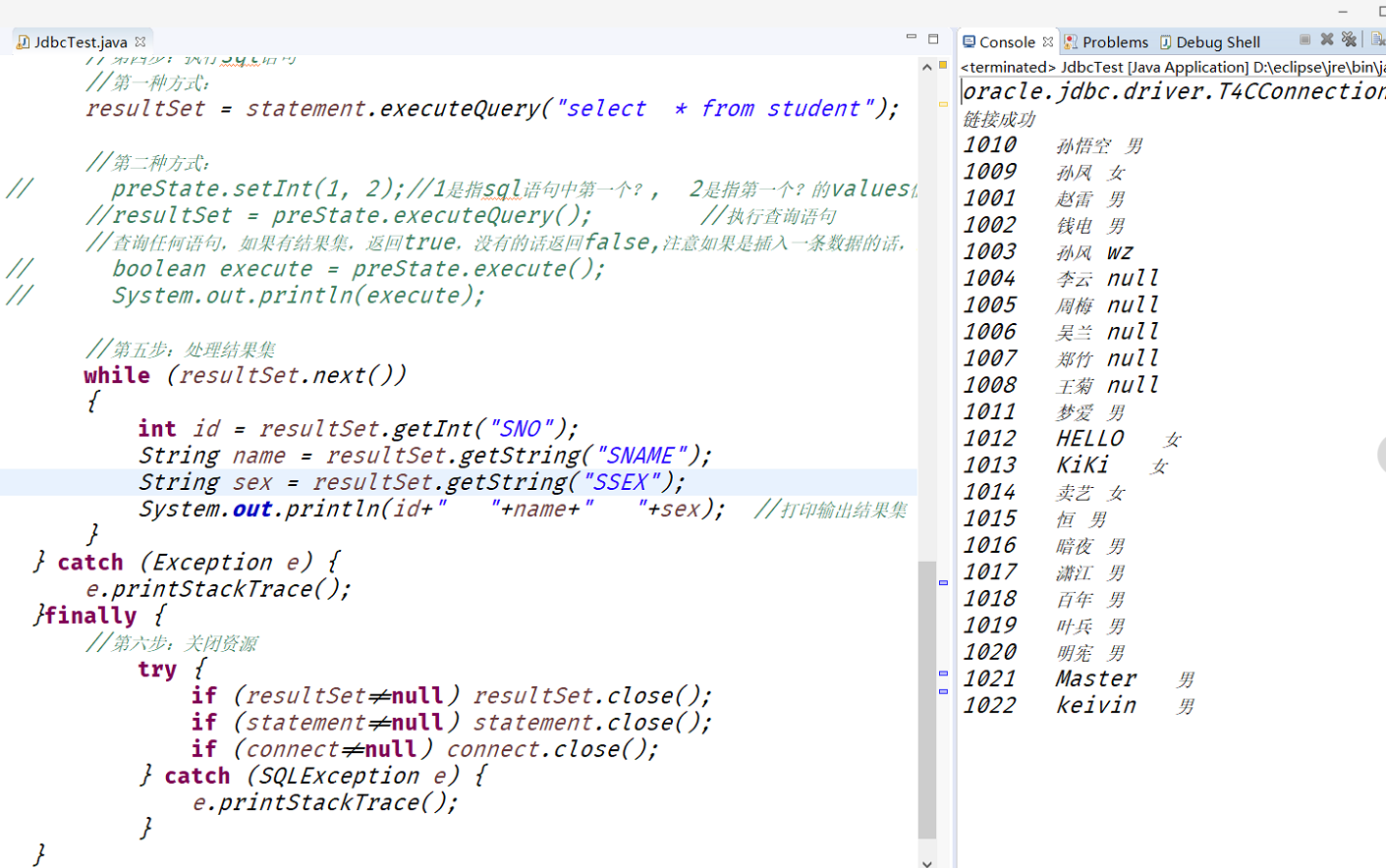
result:
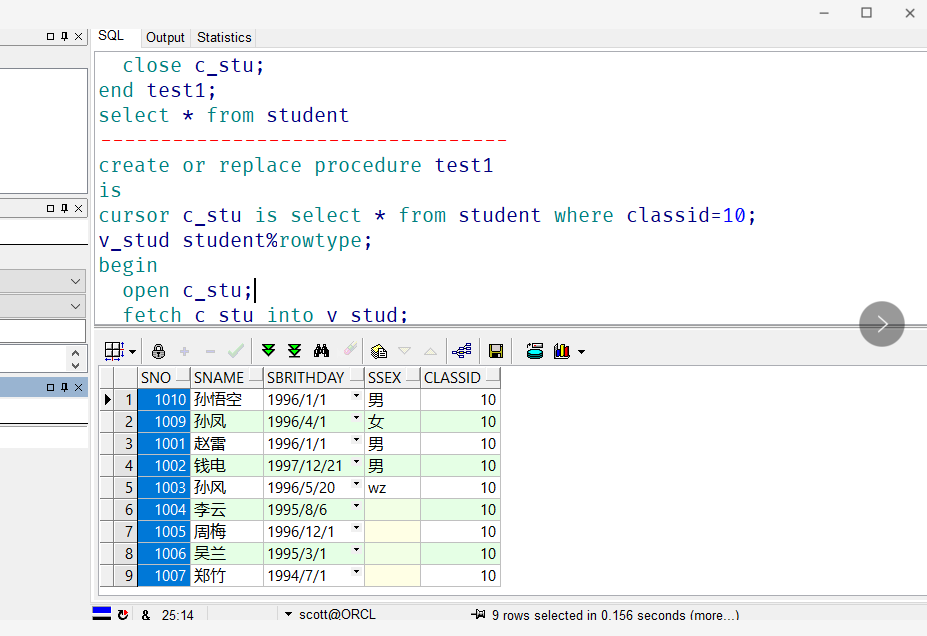
//student table created in DataBase: