1.SpringBoot auto configuration - Condition-1
Condition is spring 4 The conditional configuration interface introduced after 0 can conditionally load the corresponding beans by implementing the condition interface
@Conditional should be used with the implementation class of Condition (ClassCondition)
-
ClassCondition
public class ClassCondition implements Condition {
/**
*
* @param context Context object. Used to obtain environment, IOC container and ClassLoader object
* @param metadata Annotation meta object. It can be used to get the attribute value of annotation definition
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
//1. Requirement: create Bean after importing Jedis coordinates
//Idea: judge redis clients. jedis. Jedis. Class file exists
boolean flag = true;
try {
Class<?> cls = Class.forName("redis.clients.jedis.Jedis");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
flag = false;
}
return flag;
}
}UserConfig
@Configuration
public class UserConfig {
@Bean
@Conditional(ClassCondition.class)
public User user(){
return new User();
}
}test
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootConditionApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Start the application of SpringBoot and return to the IOC container of Spring
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(SpringbootConditionApplication.class, args);
Object user = context.getBean("user");
System.out.println(user);
}
}2.SpringBoot auto configuration - Condition-2
Requirement: define the judgment of class as dynamic. Determine which bytecode file exists, which can be specified dynamically.
Custom condition annotation class
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Conditional;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Conditional(ClassCondition.class)
public @interface ConditionOnClass {
String[] value();
}Note: here @ ConditionOnClass is a custom annotation
@Configuration
public class UserConfig {
@Bean
//@Conditional(ClassCondition.class)
@ConditionOnClass("com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON")
public User user(){
return new User();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "itcast",havingValue = "itheima")
public User user2(){
return new User();
}
}Test User object creation
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootConditionApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Start the application of SpringBoot and return to the IOC container of Spring
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(SpringbootConditionApplication.class, args);
Object user = context.getBean("user");
System.out.println(user);
}
}View conditional annotation source code
Common condition annotations provided by SpringBoot:
ConditionalOnProperty: the Bean is initialized by judging whether there are corresponding properties and values in the configuration file
ConditionalOnClass: judge whether there is a corresponding bytecode file in the environment before initializing the Bean
ConditionalOnMissingBean: initialize a Bean only after judging that there is no corresponding Bean in the environment
3. SpringBoot auto configuration - switch the built-in web server
View inheritance diagram
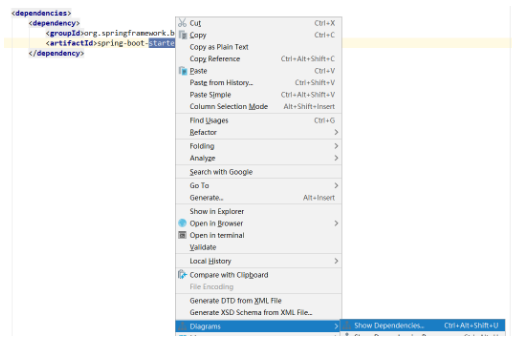
Exclude Tomcat
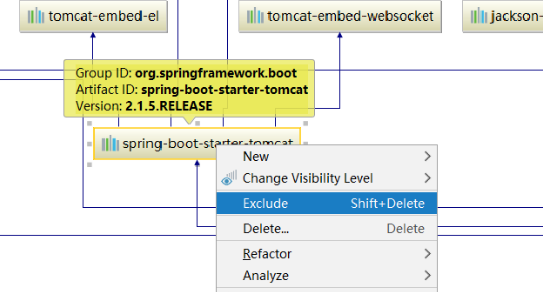
Exclusion dependency effect in pom file
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<!--exclude tomcat rely on-->
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!--introduce jetty Dependence of-->
<dependency>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jetty</artifactId>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
</dependency>4.SpringBoot auto configuration - Enable annotation principle
SpringBoot cannot directly obtain beans defined in other projects
Demo code:
Springboot enable project
/**
* @ComponentScan Scanning range: the package and its sub packages of the current boot class
*
* com.itheima.springbootenable
* com.itheima.config
* //1.Use @ ComponentScan to scan com itheima. Config package
* //2.You can use the @ Import annotation to load classes. These classes will be created by Spring and put into the IOC container
* //3.The Import annotation can be encapsulated.
*/
//@ComponentScan("com.itheima.config")
//@Import(UserConfig.class)
@EnableUser
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootEnableApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(SpringbootEnableApplication.class, args);
//Get Bean
Object user = context.getBean("user");
System.out.println(user);
}
}Spring boot enable other is introduced into pom
<dependency>
<groupId>com.itheima</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot-enable-other</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>Springboot enable other project
UserConfig
@Configuration
public class UserConfig {
@Bean
public User user() {
return new User();
}
}EnableUser annotation class
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(UserConfig.class)
public @interface EnableUser {}Reason: @ ComponentScan scanning range: the package and its sub packages of the current boot class
* * three solutions:**
1. Use @ ComponentScan to scan mytest Config package
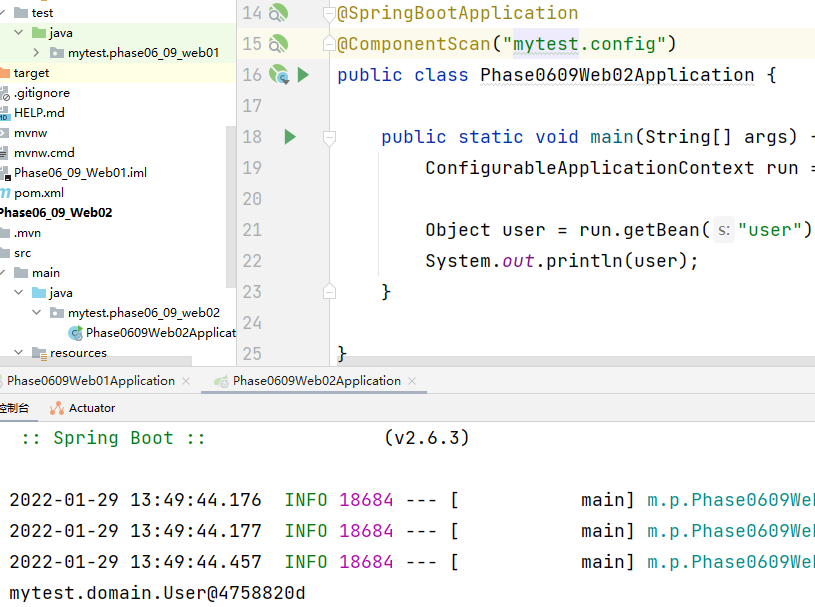
2. You can use the @ Import annotation to load classes. These classes will be created by Spring and put into the IOC container
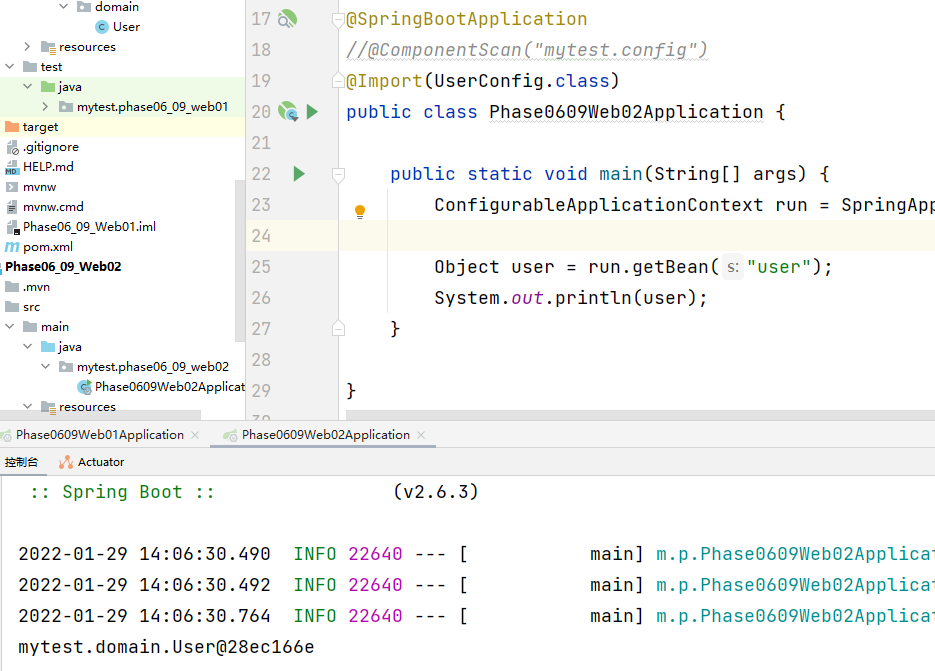
3. The Import annotation can be encapsulated.
@SpringBootApplication
//@ComponentScan("mytest.config")
//@Import(UserConfig.class)
@EnableUser
public class Phase0609Web02Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(Phase0609Web02Application.class, args);
Object user = run.getBean("user");
System.out.println(user);
}
}import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(UserConfig.class)
public @interface EnableUser {
}
* * key point: the underlying principle of Enable annotation is to use @ Import annotation to realize dynamic loading of beans**
5.SpringBoot auto configuration - @ Import details
@The bottom layer of Enable * depends on the @ Import annotation to Import some classes. The classes imported with @ Import will be loaded into the IOC container by Spring. While @ Import provides 4 usage:
① Import Bean
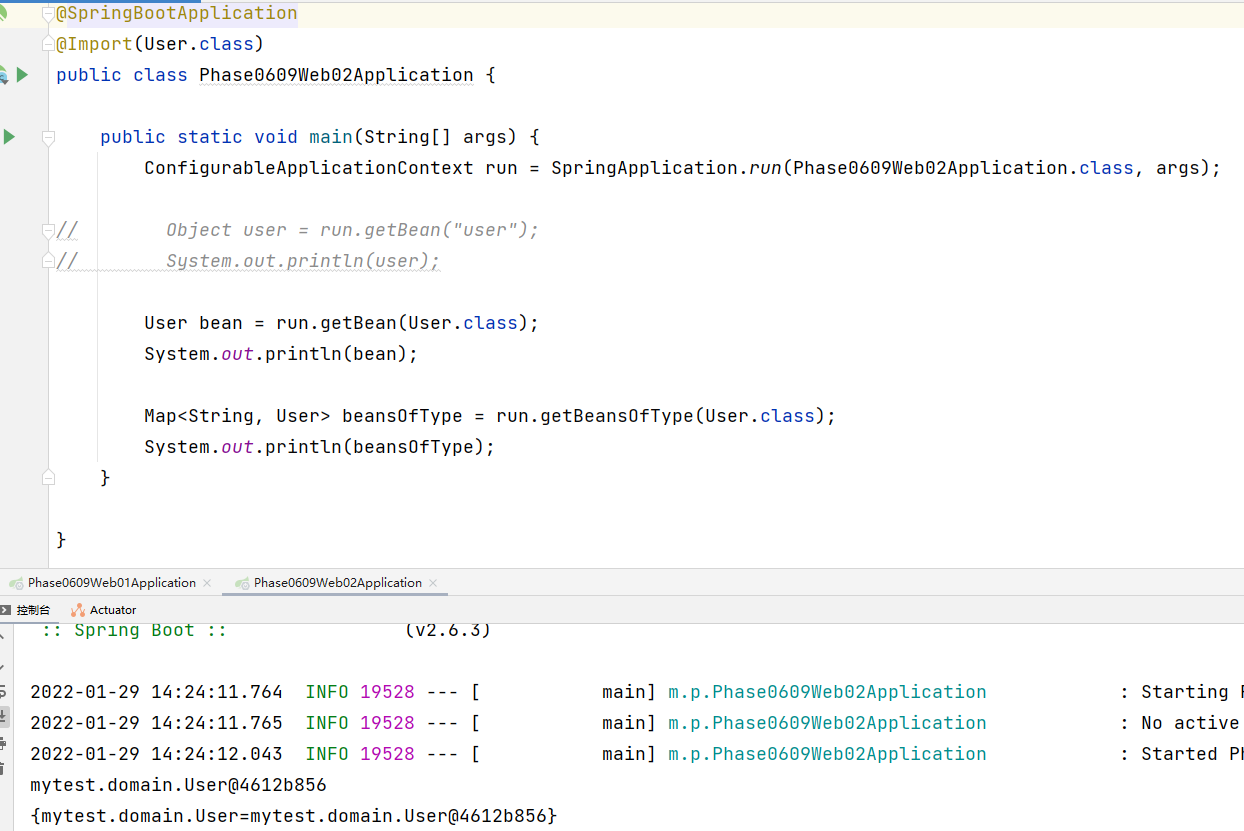
② Import configuration class
UserConfig.class
public class UserConfig {
@Bean
public User user(){
return new User();
}
@Bean
public Role role(){
return new Role();
}
}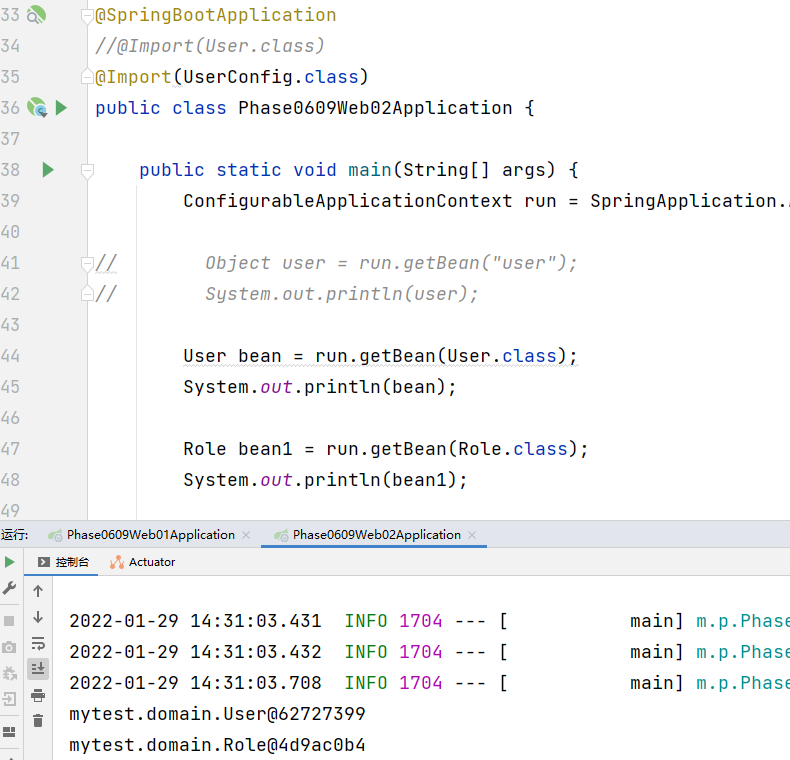
③ Import the ImportSelector implementation class. Generally used to load classes in configuration files
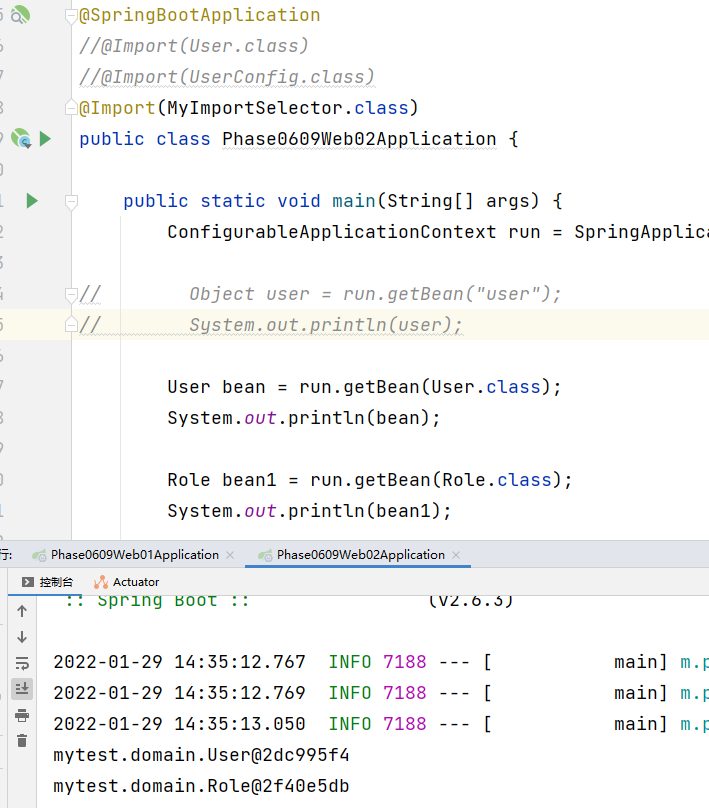
MyImportSelector
public class MyImportSelector implements ImportSelector {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
return new String[]{"com.itheima.domain.User", "com.itheima.domain.Role"};
}
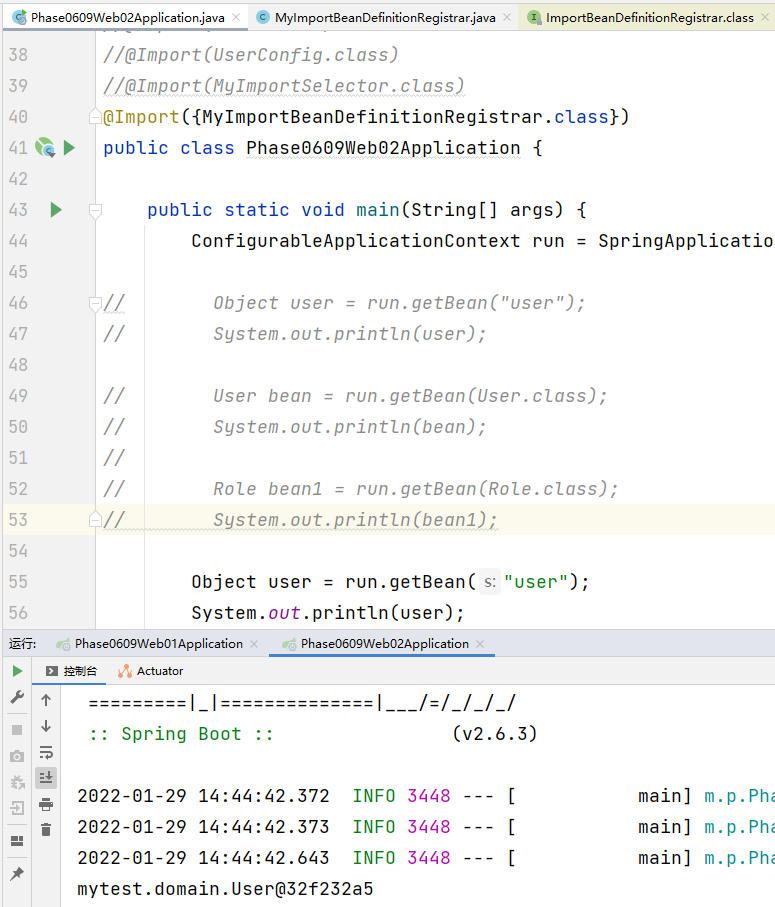
}④ Import the ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar implementation class.
Import the ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar implementation class@ Import({MyImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class})
public class MyImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = BeanDefinitionBuilder.rootBeanDefinition(User.class).getBeanDefinition();
registry.registerBeanDefinition("user", beanDefinition);
}
}
6.SpringBoot autoconfiguration - EnableAutoConfiguration annotation
-The @ EnableAutoConfiguration annotation uses @ Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.**class * *) internally to load configuration classes.
-Location of configuration file: meta-inf / spring Factories, a large number of configuration classes are defined in the configuration file. When the SpringBoot application starts, these configuration classes will be automatically loaded to initialize the Bean
-Not all beans will be initialized. Use Condition in the configuration class to load beans that meet the conditions
7.SpringBoot auto configuration - Custom Starter step analysis
Requirement: customize redis starter. When importing redis coordinates, SpringBoot is required to automatically create Jedis beans.
Steps:
① Create redis spring boot autoconfigure module
② Create the redis spring boot starter module, which depends on the redis spring boot autoconfigure module
③ Initialize Jedis Bean in redis spring boot autoconfigure module. And define meta-inf / spring Factories file
④ Introduce a custom redis starter dependency into the test module to test and obtain Jedis beans and operate redis.
8.SpringBoot auto configuration - Custom starter implementation - 1
1. Create redis spring boot starter project
Redis spring boot autoconfigure is introduced into pom file
<!--introduce configure-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.itheima</groupId>
<artifactId>redis-spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>2. Create redis spring boot autoconfigure configuration project
Create RedisProperties profile parameter binding class
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "redis")
public class RedisProperties {
private String host = "localhost";
private int port = 6379;
public String getHost() {
return host;
}
public void setHost(String host) {
this.host = host;
}
public int getPort() {
return port;
}
public void setPort(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
}Create RedisAutoConfiguration autoconfiguration class
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(RedisProperties.class)
public class RedisAutoConfiguration {
/**
* Beans that provide Jedis
*/
@Bean
public Jedis jedis(RedisProperties redisProperties) {
return new Jedis(redisProperties.getHost(), redisProperties.getPort());
}
}Create a META-INF folder under the resource directory and create spring factories
Note: "\" is used for line feed
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.itheima.redis.config.RedisAutoConfiguration
3. Introduce a customized redis starter in the springboot enable project
<!--Custom redis of starter-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.itheima</groupId>
<artifactId>redis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>Test in the SpringbootEnableApplication startup class
Jedis jedis = context.getBean(Jedis.class);
System.out.println(jedis);9.SpringBoot auto configuration - Custom starter implementation - 2
Test the application in the springboot enable project Configuration parameters in properties
redis.port=6666
Using annotations to complete conditional loading configuration classes
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(RedisProperties.class)
@ConditionalOnClass(Jedis.class)
public class RedisAutoConfiguration {
/**
* Beans that provide Jedis
*/
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "jedis")
public Jedis jedis(RedisProperties redisProperties) {
System.out.println("RedisAutoConfiguration....");
return new Jedis(redisProperties.getHost(), redisProperties.getPort());
}
}10.SprigBoot event listening
The event listening mechanism in Java defines the following roles:
① Event: event, inheriting Java util. Object of eventobject class
② Event Source: Source, arbitrary Object
③ Listener: listener, which implements Java util. Object of EventListener interface
SpringBoot will call back several listeners when the project starts. We can implement these listener interfaces to complete some operations when the project starts.
-
ApplicationContextInitializer,
-
SpringApplicationRunListener,
-
CommandLineRunner,
-
ApplicationRunner
Start time of custom listener: both MyApplicationRunner and MyCommandLineRunner are executed after the project is started, and can be used by putting @ Component into the container
MyApplicationRunner
/**
* Execute the run method when the project starts.
*/
@Component
public class MyApplicationRunner implements ApplicationRunner {
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("ApplicationRunner...run");
System.out.println(Arrays.asList(args.getSourceArgs()));
}
} MyCommandLineRunner
@Component
public class MyCommandLineRunner implements CommandLineRunner {
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("CommandLineRunner...run");
System.out.println(Arrays.asList(args));
}
}
To use MyApplicationContextInitializer, add meta-inf / spring.exe under the resource folder factories
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=mytest.phase06_11_listener.listener.MyApplicationContextInitializer
@Component
public class MyApplicationContextInitializer implements ApplicationContextInitializer {
@Override
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
System.out.println("ApplicationContextInitializer....initialize");
}
} 
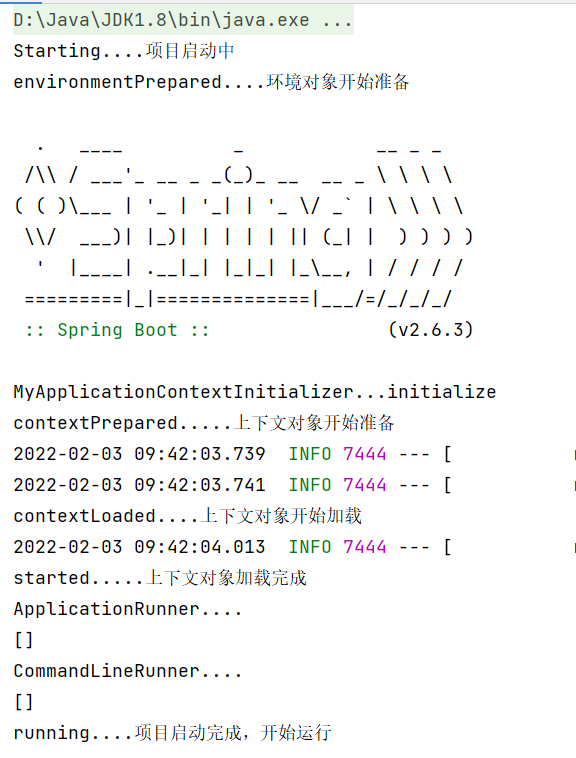
To use MySpringApplicationRunListener, add a constructor
public class MySpringApplicationRunListener implements SpringApplicationRunListener {
public MySpringApplicationRunListener(SpringApplication application, String[] args) {
}
@Override
public void starting() {
System.out.println("starting...Project startup");
}
@Override
public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
System.out.println("environmentPrepared...Environment object preparation");
}
@Override
public void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
System.out.println("contextPrepared...Context object ready");
}
@Override
public void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
System.out.println("contextLoaded...The context object starts loading");
}
@Override
public void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
System.out.println("started...Context object loading completed");
}
@Override
public void running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
System.out.println("running...The project is started and started");
}
@Override
public void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) {
System.out.println("failed...Project startup failed");
}
}
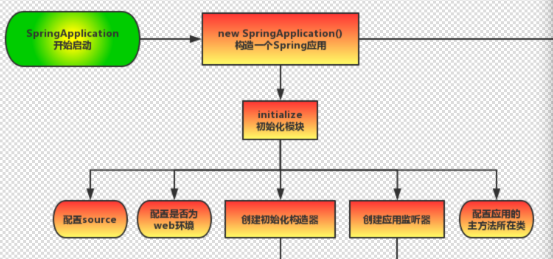
11.SpringBoot process analysis - initialization
-
Configure startup boot class (judge whether there is a startup main class)
-
Determine whether it is a Web environment
-
Get initialization class and listener class
12.SpringBoot process analysis Run
-
Start timer
-
Execution listener
-
Prepare the environment
-
Print banner: you can paste custom banner under resource
-
Create context
refreshContext(context);
The Bean is not really created until the refreshContext method is executed
13.SpringBoot monitoring - basic usage of actuator
① Import dependent coordinates
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId> </dependency>
② Visit http://localhost:8080/acruator
{
"_links":{
"self":{
"href":"http://localhost:8080/actuator",
"templated":false
},
"health":{
"href":"http://localhost:8080/actuator/health",
"templated":false
},
"health-component-instance":{
"href":"http://localhost:8080/actuator/health/{component}/{instance}",
"templated":true
},
"health-component":{
"href":"http://localhost:8080/actuator/health/{component}",
"templated":true
},
"info":{
"href":"http://localhost:8080/actuator/info",
"templated":false
}
}
}http://localhost:8080/actuator/info
In application Configuration in properties
info.name=lucy
info.age=99
http://localhost:8080/actuator/health
Turn on health check details
management.endpoint.health.show-details=always
{
"status":"UP",
"details":{
"diskSpace":{
"status":"UP",
"details":{
"total":159579508736,
"free":13558104064,
"threshold":10485760
}
},
"redis":{
"status":"UP",
"details":{
"version":"2.4.5"
}
}
}
}14.SpringBoot monitoring - actuato enable all andpoint s
Enable all endpoint s
In application Configuration in properties
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
Return results of opening all endpoint s:
{
"_links":{
"self":{
"href":"http://localhost:8080/actuator",
"templated":false
},
"auditevents":{
"href":"http://localhost:8080/actuator/auditevents",
"templated":false
},
"beans":{
"href":"http://localhost:8080/actuator/beans",
"templated":false
},
"caches-cache":{
"href":"http://localhost:8080/actuator/caches/{cache}",
"templated":true
},
"caches":{
"href":"http://localhost:8080/actuator/caches",
"templated":false
},
"health-component-instance":{
"href":"http://localhost:8080/actuator/health/{component}/{instance}",
"templated":true
},
"health":{
"href":"http://localhost:8080/actuator/health",
"templated":false
},
"health-component":{
"href":"http://localhost:8080/actuator/health/{component}",
"templated":true
},
"conditions":{
"href":"http://localhost:8080/actuator/conditions",
"templated":false
},
"configprops":{
"href":"http://localhost:8080/actuator/configprops",
"templated":false
},
"env":{
"href":"http://localhost:8080/actuator/env",
"templated":false
},
"env-toMatch":{
"href":"http://localhost:8080/actuator/env/{toMatch}",
"templated":true
},
"info":{
"href":"http://localhost:8080/actuator/info",
"templated":false
},
"loggers":{
"href":"http://localhost:8080/actuator/loggers",
"templated":false
},
"loggers-name":{
"href":"http://localhost:8080/actuator/loggers/{name}",
"templated":true
},
"heapdump":{
"href":"http://localhost:8080/actuator/heapdump",
"templated":false
},
"threaddump":{
"href":"http://localhost:8080/actuator/threaddump",
"templated":false
},
"metrics-requiredMetricName":{
"href":"http://localhost:8080/actuator/metrics/{requiredMetricName}",
"templated":true
},
"metrics":{
"href":"http://localhost:8080/actuator/metrics",
"templated":false
},
"scheduledtasks":{
"href":"http://localhost:8080/actuator/scheduledtasks",
"templated":false
},
"httptrace":{
"href":"http://localhost:8080/actuator/httptrace",
"templated":false
},
"mappings":{
"href":"http://localhost:8080/actuator/mappings",
"templated":false
}
}
}15.SpringBoot monitoring - use of the graphical interface of SpringBoot admin
SpringBoot Admin has two roles, client and server.
The following are the steps to create a server and client project:
admin-server:
① Create admin server module
② Import dependent coordinates admin starter server
<dependency>
<groupId>de.codecentric</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-admin-starter-server</artifactId>
</dependency>③ Enable monitoring function @ EnableAdminServer on boot class
@EnableAdminServer
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootAdminServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootAdminServerApplication.class, args);
}
}admin-client:
① Create admin client module
② Import dependent coordinates admin starter client
<dependency>
<groupId>de.codecentric</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-admin-starter-client</artifactId>
</dependency>③ Configuration related information: server address, etc
# Execute admin Server address spring.boot.admin.client.url=http://localhost:9000 management.endpoint.health.show-details=always management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
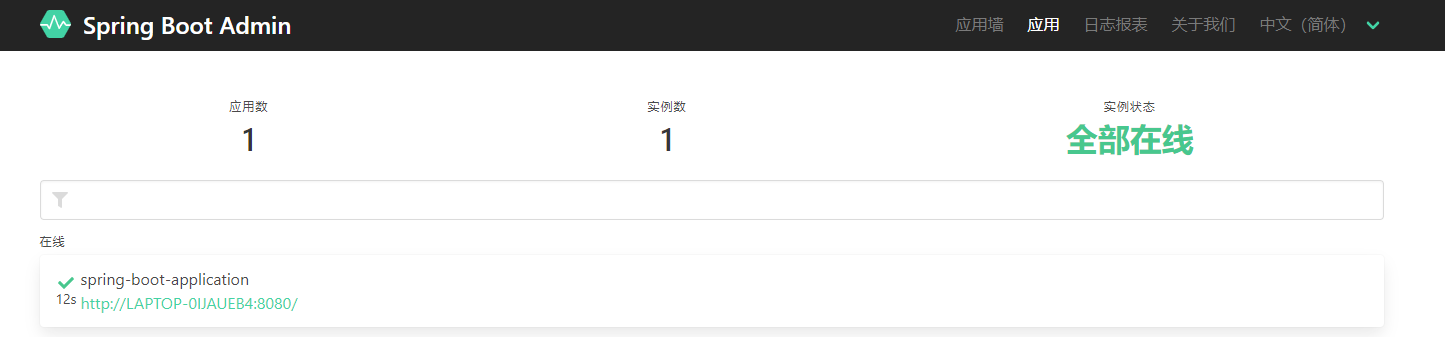
④ Start the server and client services and access the server
16. SpringBoot deployment
After the SpringBoot project is developed, it supports two ways to deploy to the server:
① jar package (official recommendation)
② war package
Change the packaging method in pom file to war
Modify startup class
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.builder.SpringApplicationBuilder;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.support.SpringBootServletInitializer;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootDeployApplication extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootDeployApplication.class, args);
}
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder builder) {
return builder.sources(SpringbootDeployApplication.class);
}
}Specifies the name of the package
<build>
<finalName>springboot</finalName>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Some of the contents exist in books, classes and online records. If they are the same, it is pure coincidence