What is the method
A method is a set of code that organizes code blocks with separate functions into a whole and has special functions.
Be careful:
- The method must be created before it can be used, and the process becomes the definition of the method
- The method is not created to run directly and needs to be used manually before execution. This process is called method invocation
Definition and invocation of methods
1. Method Definition
- Format:
public static void Method Name(){
//Method Body
}
2. Method calls:
- Format:
Method Name();
Note: Method must be defined before calling, otherwise the program will error
For example:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Call to method
isEvenNumber();
}
The results are: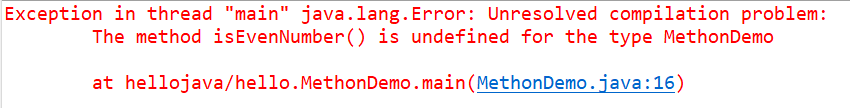
Example:
// Requirements: Define a method in which a variable is defined to determine if the number is even
public static void isEvenNumber() {
int number = 10;
// Determine if it is even
if (number % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println(true);
} else {
System.out.println(false);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Call to method
isEvenNumber();
}
- Method Exercise
Requirement: Design a larger number for printing two numbers
int a = 10;// Define two variables
int b = 20;
if (a > b) {// Branch statements handle variable size relationships
System.out.println(a);
} else {
System.out.println(b);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
getMax();
}
Definition and invocation of methods with parameters
1. Method definition with parameters
Format:
public static void Method Name(Data type variable name){//Single parameter
//Method Body
}
public static void Method Name(Data type variable name 1, data type variable name 2,......){//Multiple parameters
//Method Body
}
Example:
public static void isEvenNumber(int number){//Single parameter
//Method Body
}
public static void getMax(int number1,int number2,......){//Multiple parameters
//Method Body
}
Be careful:
- When a method is defined, neither the data type nor the variable name in the parameter can be missing, and any program that is missing will fail
- When defining a method, commas (,) are used to separate multiple parameters
2. Method calls with parameters
Format:
Method Name(Variable Name/constant value);//Single parameter Method Name(Variable Name 1/Constant value 1, variable name 2/Constant value 2,......);//Multiple parameters
Example:
isEvenNumber(5);//Single parameter getMax(5,6);//Multiple parameters
Be careful:
- When a method is called, the number and type of parameters must match the settings in the method definition or the program will fail
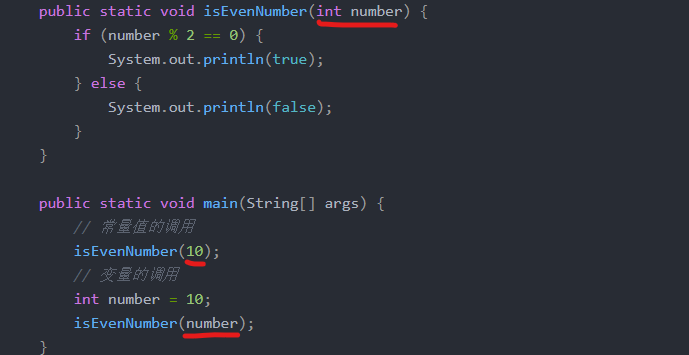
Examples include:
public static void isEvenNumber(int number) {
if (number % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println(true);
} else {
System.out.println(false);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Invocation of Constant Value
isEvenNumber(10);
// Call of variable
int number = 10;
isEvenNumber(number);
}
Run result:

3. Formal and actual parameters
Parameter: The parameter in the method definition, which is equivalent to the variable definition format, for example, int number
Arguments: Parameters in a method call, equivalent to using variables or constants, for example: 10,number
Example:
//Design a method to print a larger number of two numbers from the method parameters
public static void getMax(int a,int b) {//Define a method
if (a > b) {// Branch statements handle variable size relationships
System.out.println(a);
} else {
System.out.println(b);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Direct Transfer Constant
//When calling a method, you can give just a few, any type you want, any type you want
//getMax(30);
//getMax(10.0,20.0);
getMax(10,20);
//Define variables, pass
int a=10;
int b=20;
getMax(a,b);
}
Run result:
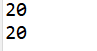
Definition and invocation of methods with return values
1. Method definition with return value
Format:
public static Data type method name(parameter){
return Data;
}
Example 1:
public static boolean isEvenNummber(int number){
return true;
}
Example 2:
public static int getMax(int a,int b){
return 100;
}
Be careful:
- When defining a method, the return value after return matches the data type on the method definition, otherwise the program will fail
2. Method calls with return values
Format 1:
Method Name(parameter);
Example 1:
isEvenNumber(5);//Single parameter
Format 2:
Data type variable name=Method Name(parameter);
Example 2:
boolean flag=isEvenNumber(5);
Be careful:
- The return value of a method is usually received with a variable, otherwise it will be meaningless
Example:
Requirements: Defines a method that receives a parameter, determines whether the data is even, and returns true and false values
//Defines a method that receives a parameter, determines whether the data is even, and returns true and false values
public static boolean isEvenNumber(int number) {
if (number % 2 == 0) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. Method name (parameter);
System.out.println(isEvenNumber(10));
//2. Data type variable name = method name (parameter);
boolean flag=isEvenNumber(10);
System.out.println(flag);
}
Run result:

- Method Exercise with Return Value
Requirements: Design a method to get a larger value of two numbers from parameters
//Requirements: Design a method to get a larger value of two numbers from parameters
public static int getMax(int a,int b) {
if (a > b) {// Branch statements handle variable size relationships
return a;
} else {
return b;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result=getMax(10,20);
System.out.println(result);
// //2. Print results directly
// System.out.println(getMax(10,20));
Run result:

Notes on Methods
1. Method cannot nest definitions
//Correct code:
public static void methodOne() {
//Snippet 1
}
public static void methodTwo() {
//Code Snippet 2
}
//Error code:
public static void methodOne() {
//Snippet 1
public static void methodTwo() {
//Code Snippet 2
}
}
2. void means no return value, return can be omitted or written separately without data
//Correct code 1:
public static void methodOne() {
//Snippet 1
}
//Correct code 2:
public static void methodOne() {
//Snippet 1
return;
}
//Error code:
public static void methodOne() {
//Snippet 1
return 100;
}
General format for methods
Format:
public static Return value type method name(parameter){
Method Body;
return Data;
}
-
public static - modifier
-
Return Value Type - The data type of the data returned after the method operation is complete; If the method operation is complete and there is no data return, void is written here and return is not typically written in the body of the method
-
Method Name - Handle ID used when calling a method
-
Parameters - consisting of data types and variable names separated by commas
-
Method Body - Code Block to Complete Function
-
Return - If the method operation is complete, returned from the data, used to return the data to the caller
-
When defining the way, two clarities should be noted
Explicit return value type: Mainly clarify whether there is data return after the method operation is completed, and if not, write void; If so, write the corresponding data type
Explicit parameters: mainly clarify the type and number of parameters -
When calling a method
A method of type void, called directly
Non-void type method, variable is recommended for receiving calls