A little morning light lights up the noisy world

There are many collection classes (the storage capacity can be changed, providing a storage model with variable storage space). Today we introduce one: ArrayList

ArrayList
<
E
>
<E>
<E> : (resizable array implementation, followed by E is generic)
ArrayList < S t r i n g > <String> <String>, ArrayList < S t u d e n t > <Student> < student > (replace e with data type)
1: ArrayList construction method and addition method
Xiaoyedou first built a new project with the following structure:
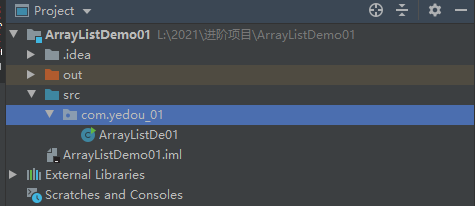
First, we create a collection with the following code:
ArrayList<String> array = new ArrayList<String>();
package com.yedou_01;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArrayListDe01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// public ArrayList(): create an empty collection object
// New features after jdk7, the first way to create a collection (Annotated)
// ArrayList<String> array = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> array = new ArrayList<String>();
// Output set
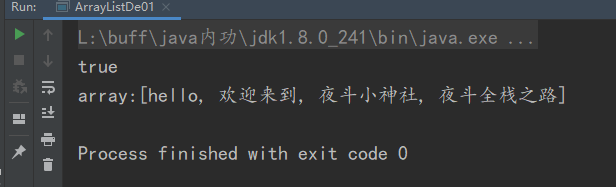
System.out.println("array:" + array);
}
}
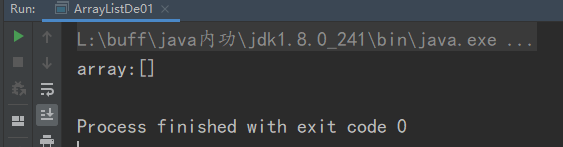
Printout set, as follows:
The code after adding three elements is as follows: array Add ("night fighting Shrine");
package com.yedou_01;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArrayListDe01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// public ArrayList(): create an empty collection object
// ArrayList<String> array = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> array = new ArrayList<String>();
// public boolean add(E, e): appends the specified element to the end
// Whether the printing is successful or not
System.out.println(array.add("hello"));
// Enter hello
array.add("Night fighting Shrine");
array.add("The road of the whole stack of night fighting");
// Output set
System.out.println("array:" + array);
}
}
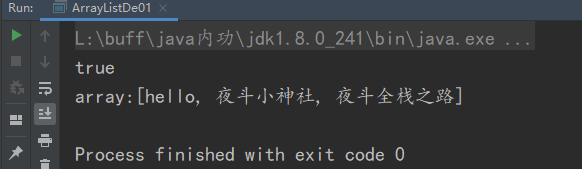
The results are as follows:
Insert the element at the specified position: array Add (1, "welcome to");
package com.yedou_01;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArrayListDe01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// public ArrayList(): create an empty collection object
// ArrayList<String> array = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> array = new ArrayList<String>();
// public boolean add(E, e): appends the specified element to the end
// Whether the print input is successful
System.out.println(array.add("hello"));
// Enter hello
array.add("Night fighting Shrine");
array.add("The road of the whole stack of night fighting");
// Insert element at specified position
array.add(1,"Welcome to");
// Output set
System.out.println("array:" + array);
}
}
However, this method has cross-border problems:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException: Index: 4, Size: 3
array.add(4,"Welcome to");
If it is written as above, because there are only three elements and the Size is less than index, there is an error report that exceeds the boundary!
2: Common methods of ArrayList collection
First, we create a collection ArrayList, as shown below:
package com.yedou_01;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArrayListDe02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String > array = new ArrayList<String >();
array.add("Welcome to");
array.add("Night bucket stack");
array.add("Road of");
System.out.println("array: " + array);
}
}
array: [welcome to the whole stack of night fighting, the road to the world]
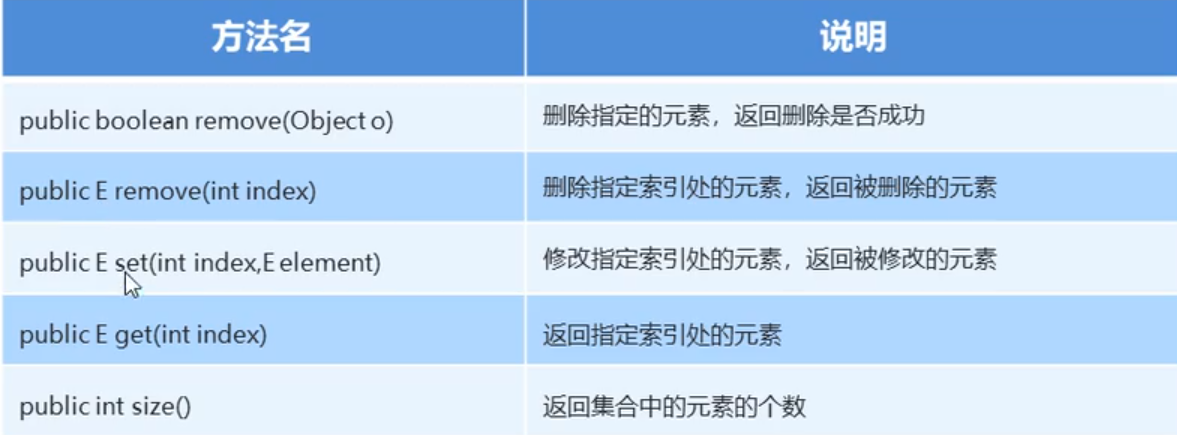
- Delete element: system out. Println (array. Remove ("welcome");
- According to index: system out. println(array.remove(0));
- Modify element: system out. Println (array. Set (0, "Hello!");
- Get element: system out. println(array.get(0));
- Number of sets: system out. println(array.size());
The whole code is as follows:
package com.yedou_01;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArrayListDe02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String > array = new ArrayList<String >();
array.add("Welcome to");
array.add("Night bucket stack");
array.add("Road of");
// Welcome to delete
// Displays whether the deletion was successful
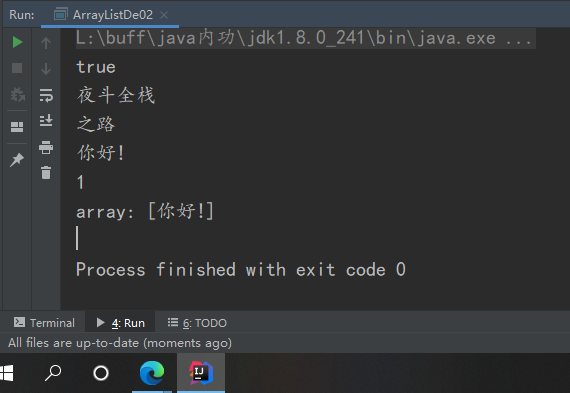
System.out.println(array.remove("Welcome to"));
// Delete by index
System.out.println(array.remove(0));
// Modify element value
System.out.println(array.set(0,"Hello!"));
// Returns the element at the specified index
System.out.println(array.get(0));
// Returns the number of sets
System.out.println(array.size());
// Print array
System.out.println("array: " + array);
}
}
3: ArrayList stores characters and traverses the collection
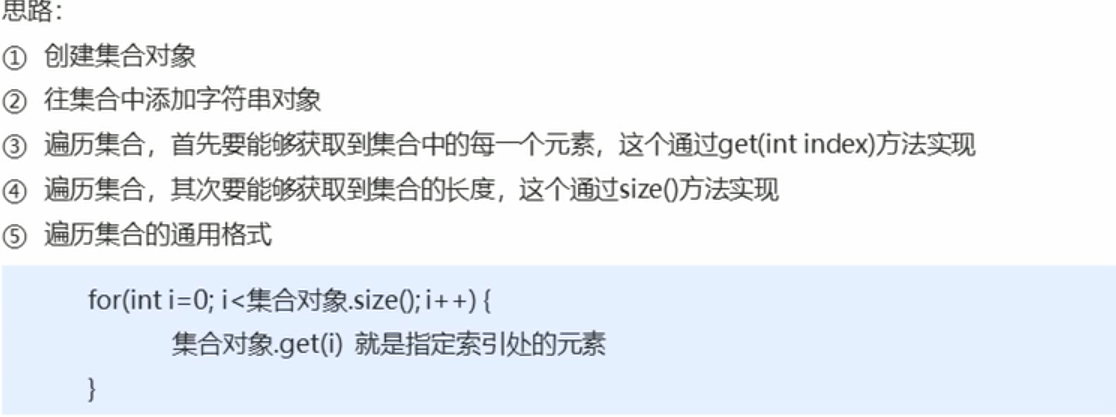
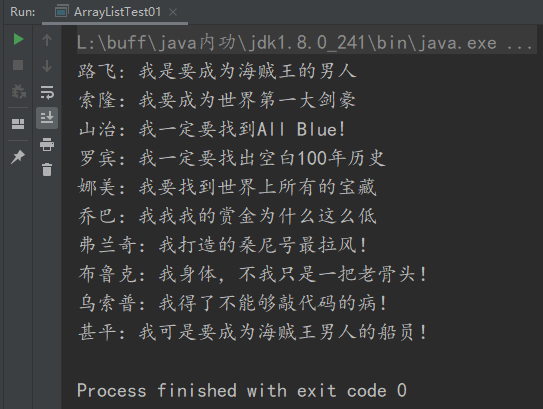
”I'm the man who wants to be the pirate king! "
We add the names and dreams of the straw hat party and print them out in a circle:
package com.yedou_02;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArrayListTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create object
ArrayList<String> array = new ArrayList<String>();
// Add object
array.add("Monkey D Luffy: I'm the man who wants to be the pirate king");
array.add("Sauron: I want to be the world's largest swordsman");
array.add("Yamaguchi: I must find it All Blue!");
array.add("Robin: I must find out the blank 100 year history");
array.add("Nami: I want to find all the treasures in the world");
array.add("Joba: why is my reward so low");
array.add("Frankie: the Sonny I built is the most popular!");
array.add("Brooke: my body, no, I'm just an old bone!");
array.add("Usop: I'm sick of not being able to knock code!");
array.add("I want to be a pirate king!");
// Traversal object
for(int i=0; i<array.size(); i++) {
// Get element
String s = array.get(i);
// Print element
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
4: Store the straw hat pirate king object and traverse it
1: Create a straw hat class HatPirateGroup (set,get shortcut (alt + insert))
package com.yedou_02;
/*
Straw hat
*/
public class HatPirateGroup {
private String name;
private String sentence;
// No reference
public HatPirateGroup(){}
// Have reference
public HatPirateGroup(String name, String sentence){
this.name = name;
this.sentence = sentence;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSentence() {
return sentence;
}
public void setSentence(String sentence) {
this.sentence = sentence;
}
}
2: Create a collection to store the members of the straw hat pirate and cycle through printing
package com.yedou_02;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArrayListTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create collection object
ArrayList<HatPirateGroup> array = new ArrayList<HatPirateGroup>();
// Create a pirate object
HatPirateGroup s1 = new HatPirateGroup("Monkey D Luffy:", "I'm the man who wants to be the pirate king");
HatPirateGroup s2 = new HatPirateGroup("Sauron:","I want to be the world's largest swordsman");
HatPirateGroup s3 = new HatPirateGroup("Yamaguchi:","I must find it All Blue!");
// Add a pirate to the grass hat Pirate Group
array.add(s1);
array.add(s2);
array.add(s3);
// Traversal set
for(int i=0; i<array.size(); i++){
HatPirateGroup s = array.get(i);
System.out.println(s.getName()+ s.getSentence());
}
}
}
5: Enter the straw hat pirate king object on the keyboard and traverse it
1: Create a straw hat class HatPirateGroup (set,get shortcut (alt + insert))
package com.yedou_02;
/*
Straw hat
*/
public class HatPirateGroup {
private String name;
private String sentence;
// No reference
public HatPirateGroup(){}
// Have reference
public HatPirateGroup(String name, String sentence){
this.name = name;
this.sentence = sentence;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSentence() {
return sentence;
}
public void setSentence(String sentence) {
this.sentence = sentence;
}
}
2: Enter the pirate information on the keyboard and call the method to add it to the collection
package com.yedou_03;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create collection object
ArrayList<HatPirateGroup> array = new ArrayList<HatPirateGroup>();
// Call method
addPirate(array);
addPirate(array);
addPirate(array);
// Traversal set
for(int i=0; i<array.size(); i++){
HatPirateGroup s = array.get(i);
System.out.println(s.getName() + s.getSentence());
}
}
public static void addPirate(ArrayList<HatPirateGroup> array){
/*
Methods: return value types and parameters
*/
// Keyboard input data
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the name of the pirate:");
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("Please enter a sentence:");
String sentence = sc.nextLine();
// Create a pirate object
HatPirateGroup s = new HatPirateGroup();
s.setName(name);
s.setSentence(sentence);
// Add a student object to the collection
array.add(s);
}
}
- On this planet, you are very important. Please cherish your precious~~~ Night fighting Shrine