Procedure requirements:
1. Randomly generate maze map
The maze map needs to be randomly generated in the game and Java util. Random class uses the random number generation method provided by random class to randomly generate obstacles, paths or rewards. Maze map is represented and stored by two-dimensional array.
2. Judge whether the player has successfully entered the level
According to whether the player's current position is located at the exit point of the map, judge whether the player has successfully broken through the pass. If successful, modify the game points according to the number of game steps.
3. Game main control module
The main control module of the game is a key if/else control module based on user input.
Enter "←↑↓→" to update the game interface and current position according to whether it can move, provided that the game is not over.
Enter W/S to increase / decrease the size of the maze accordingly; Enter "Y" to display the maze path, and enter "X" to refresh the maze;
If the game ends, exit the game main control module and output the winning or losing status of the player; Otherwise, the main control module will constantly modify the map status and update the player points according to the direction keys entered by the user.
catalogue
2. Astar class (A * algorithm)
Win or lose, output
Where: 1 represents obstacle, 0 represents access, 2 represents reward, and 8 represents current position.
By default, the maze is surrounded by obstacles. The entry point is located in the upper left corner of the map and the exit point is located in the lower right corner of the map.
The user inputs "awsd" characters on the console, representing the direction keys "←↑↓→"; Enter the "x" character to exit the game early.
Under a finite number of steps, judge
Household score.
Users are encouraged to complete the game with shorter paths and more rewards. Set the following integration principles:
At the end of the game, the points increase the difference between the limited step size of the game and the current step size of the game. If the limited step size is 30 and the player takes 20 steps to reach the end this time, the score will be increased by 10.
Program running results
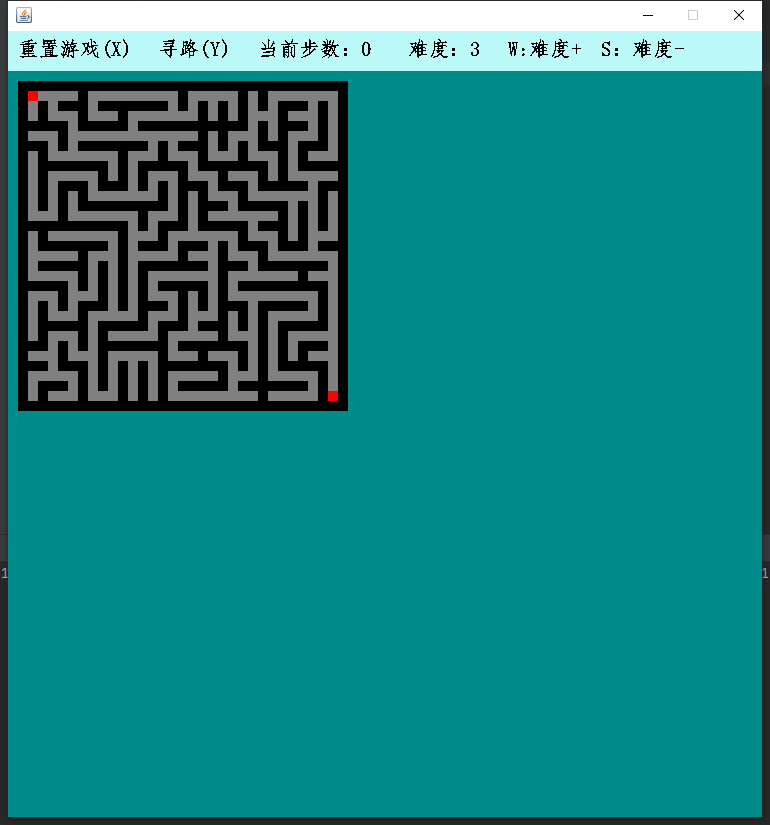
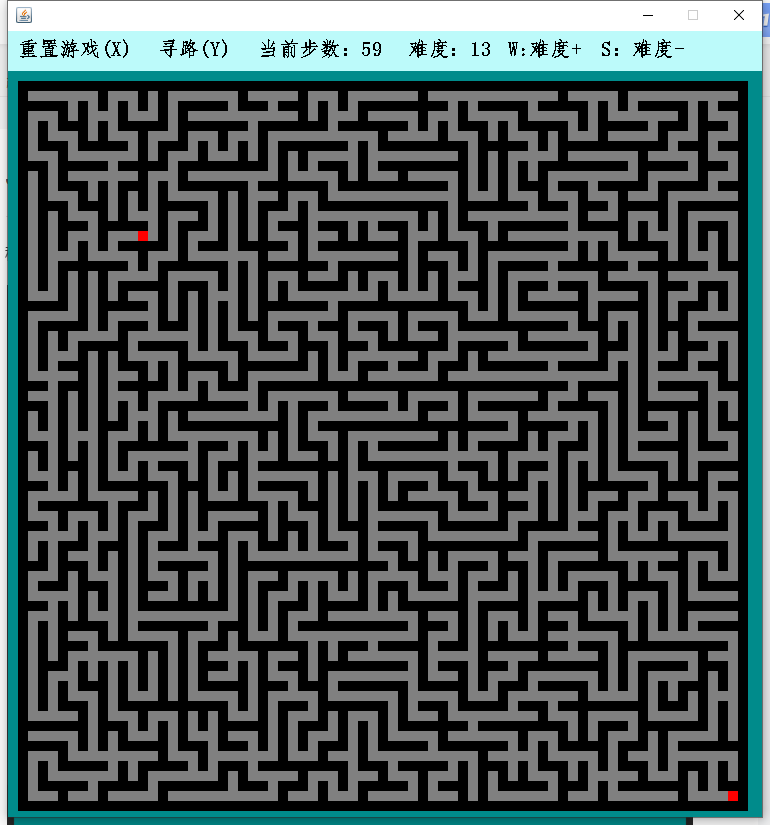
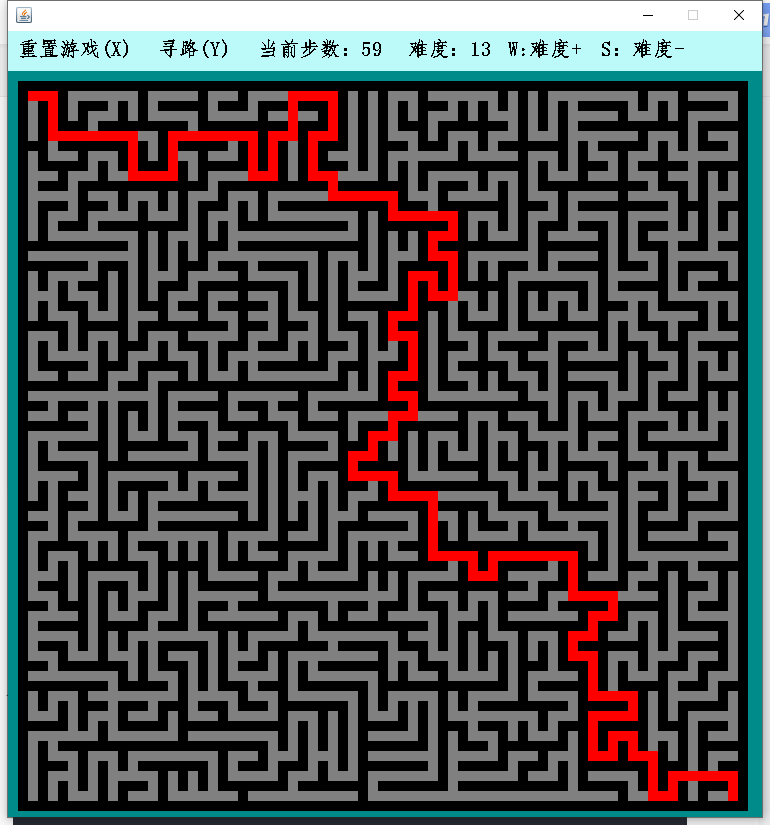
1. Maze class (Prim method)
package com.company;
import java.util.Random;
class Maze {
// Initialize a map. All roads are blocked by default
//The size of the resulting two-dimensional array is actually (2width + 1) * (2weight + 1)
private static int width;
private static int height;
public static int[][] map;// Array of mazes
private static int r;
private static int c;
Maze(int r0, int c0) {
width = r0;
height = c0;
r = 2 * width + 1;
c = 2 * height + 1;
map = new int[r][c];
}
public static int[][] Init() {
for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) // Set all cells as walls
for (int j = 0; j < c; j++)
map[i][j] = 0;// 0 is the wall and 1 is the road
// The middle grid is 1
for (int i = 0; i < width; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < height; j++)
map[2 * i + 1][2 * j + 1] = 1;// 0 is the wall and 1 is the road
// Prim algorithm
accLabPrime();
return map;
}
public static void accLabPrime() {
// ok stores the accessed queue, not stores the non accessed queue
int[] ok, not;
int sum = width * height;
int count = 0;// Record the number of visited points
ok = new int[sum];
not = new int[sum];
// Offset in each direction of width offset in each direction of height 0 left 1 right 3 up 2 down
int[] offR = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
int[] offC = {0, 0, 1, -1};
// The offset in four directions is left, right, up and down
int[] offS = {-1, 1, width, -width}; // Moving up and down is a line of change
// 0 in initialization ok means no access, and 0 in not means no access
for (int i = 0; i < sum; i++) {
ok[i] =0;
not[i] = 0;
}
// starting point
Random rd = new Random();
ok[0] = rd.nextInt(sum);// starting point
int pos = ok[0];
// First point deposit
not[pos] = 1;
while (count < sum) {
// Take out the current point
int x = pos % width;
int y = pos / width;// The coordinates of the point
int offpos = -1;
int w = 0;
// Try it in all four directions until you dig through
while (++w < 5) {
// Random access to the nearest point
int point = rd.nextInt(4); // 0-3
int repos;
int move_x, move_y;
// Calculate the moving direction
repos = pos + offS[point];// Subscript after move
move_x = x + offR[point];// Orientation after movement
move_y = y + offC[point];
if (move_y >= 0 && move_x >= 0 && move_x < width && move_y < height && repos >= 0 && repos < sum
&& not[repos] != 1) {
not[repos] = 1;// Mark the point as accessed
ok[++count] = repos;// ++count represents the number of accessed points, and repos represents the subscript of the point
pos = repos;// Take this point as the starting point
offpos = point;
// Place 1 in the middle of the adjacent grid
map[2 * x + 1 + offR[point]][2 * y + 1 + offC[point]] = 1;
break;
} else {
if (count == sum - 1)
return;
}
}
if (offpos < 0) {// There is no way to go around. Find a new starting point from the way you have walked
pos = ok[rd.nextInt(count + 1)];
}
}
}
}
2. Astar class (A * algorithm)
package com.company;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
class AStar {
public static int[][] NODES;//Define a maze cell array
public int STEP = 10;//Set the weight of each step to 10
private ArrayList<Node> openList = new ArrayList<Node>();//Maintain an open list
private ArrayList<Node> closeList = new ArrayList<Node>();//Maintain a closed list
AStar(int[][] map) {
NODES=map;//Initialize the Maze unit as the newly generated corresponding map, transfer the map generated in Maze class to NODES, and then find the path with A * algorithm on the basis of this map
Node startNode = new Node(1, 1);//starting point
Node endNode = new Node(map.length-2, map.length-2);//End
Node parent = findPath(startNode, endNode); //Parent node
ArrayList<Node> arrayList = new ArrayList<Node>();
while (parent != null) {
arrayList.add(new Node(parent.x, parent.y));
parent = parent.parent;
}
//Print a map with a path and view it in the console output
System.out.println("\n"+"Print map with path:");
for (int i = 0; i < NODES.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < NODES.length; j++) {
if (exists(arrayList, i, j)) {
NODES[i][j]=2;//Mark the grid in the closed list as 2. For the convenience of drawing the system pathfinding path on the interface later
}
System.out.print(NODES[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static int[][] ans(){
return NODES;
}
//Method for finding the node with the lowest F value in the open list
public Node findMinFNodeInOpneList() {
Node tempNode = openList.get(0);
for (Node node : openList) {
if (node.F < tempNode.F) {
tempNode = node;
}
}
return tempNode;
}
//The method of traversing the upper, lower, left and right neighbors of the current node,
public ArrayList<Node> findNeighborNodes(Node currentNode) {
ArrayList<Node> arrayList = new ArrayList<Node>();
// Only up, down, left and right, not diagonal
int topX = currentNode.x;
int topY = currentNode.y - 1;
if (canReach(topX, topY) && !exists(closeList, topX, topY)) {
arrayList.add(new Node(topX, topY));
}
int bottomX = currentNode.x;
int bottomY = currentNode.y + 1;
if (canReach(bottomX, bottomY) && !exists(closeList, bottomX, bottomY)) {
arrayList.add(new Node(bottomX, bottomY));
}
int leftX = currentNode.x - 1;
int leftY = currentNode.y;
if (canReach(leftX, leftY) && !exists(closeList, leftX, leftY)) {
arrayList.add(new Node(leftX, leftY));
}
int rightX = currentNode.x + 1;
int rightY = currentNode.y;
if (canReach(rightX, rightY) && !exists(closeList, rightX, rightY)) {
arrayList.add(new Node(rightX, rightY));
}
return arrayList;
}
//Judge whether the coordinates here are reachable. If they exceed the boundary or are walls, they are not reachable
public boolean canReach(int x, int y) {
if (x >=0 && x < NODES.length && y >=0 && y < NODES.length && NODES[x][y]==1) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
//A * routing process
public Node findPath(Node startNode, Node endNode) {
openList.add(startNode);// Add the starting point to the open list
while (openList.size() > 0) {
Node currentNode = findMinFNodeInOpneList();// Traverse the open list, find the node with the smallest F value, and take it as the node to be processed at present
openList.remove(currentNode);// Remove from open list
closeList.add(currentNode);// Move this node to the close list
ArrayList<Node> neighborNodes = findNeighborNodes(currentNode);
for (Node node : neighborNodes) {//Traverse four neighbors
if (exists(openList, node)) {
foundPoint(currentNode, node);
} else {
notFoundPoint(currentNode, endNode, node);
}
}
if (find(openList, endNode) != null) {
return find(openList, endNode);//Find the end and return
}
}
return find(openList, endNode);
}
//You can find the situation after the node in the list
private void foundPoint(Node tempStart, Node node) {
int G = calcG(tempStart, node);
if (G < node.G) {
node.parent = tempStart;
node.G = G;
node.calcF();
}
}
//The node cannot be found in the node
private void notFoundPoint(Node tempStart, Node end, Node node) {
node.parent = tempStart;
node.G = calcG(tempStart, node);
node.H = calcH(end, node);
node.calcF();
openList.add(node);
}
//Method of calculating G value
private int calcG(Node start, Node node) {
int G = STEP;
int parentG = node.parent != null ? node.parent.G : 0;
return G + parentG;
}
//Method of calculating H value
private int calcH(Node end, Node node) {
int step = Math.abs(node.x - end.x) + Math.abs(node.y - end.y);
return step * STEP;
}
//How to find the end point
public static Node find(List<Node> nodes, Node point) {
for (Node n : nodes)
if ((n.x == point.x) && (n.y == point.y)) {
return n;
}
return null;
}
//The following two are overloads of the exist method to determine whether the node is in the list under different parameters
public static boolean exists(List<Node> nodes, Node node) {
for (Node n : nodes) {
if ((n.x == node.x) && (n.y == node.y)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public static boolean exists(List<Node> nodes, int x, int y) {
for (Node n : nodes) {
if ((n.x == x) && (n.y == y)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//Node class, which defines the attributes of each node
public static class Node {
public Node(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public int x;
public int y;
public int F;
public int G;
public int H;
public void calcF() {
this.F = this.G + this.H;
}
public Node parent;
}
}3. MazePanel class:
The maze interface is generated by filling color to produce the maze, and the keyboard is used to monitor the movement
package com.company;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
class MazePanel extends JPanel implements KeyListener,ActionListener {
public final static int WALL = 0;//obstacle
public final static int ROAD = 1;//access
public static int width; //Map scale
public static int height;
public final static int current = 2; //Legend identifying the current location
public final static int MAXSTEPS = 200; //Maximum number of steps in the game
static int mx = 1; //Current position (curX,curY)
static int my = 1;
static int score = 0; //Game score and steps
static int steps = 0; // Number of steps
static int level = 3;//difficulty
static int[][] map; //Storage maze
private JButton ans = new JButton("Display path"); //Keys and keyboard mode are not realized. They are directly operated by the keyboard
private JButton remake = new JButton("Reset maze");
private JPanel jp = new JPanel();
private JButton hide = new JButton("Hide path");
private JButton exit = new JButton("Exit the game");
private JButton start = new JButton("Start the game");
public static int Difficult(int level) { //Game difficulty, initially 10, difficulty + 1, map + 5
int number = 10;
for (int i = 0; i < level; i++) {
number += 2;
}
return number;
}
public static void MapRandom() { //Random maze
width = Difficult(level);
height = Difficult(level);
Maze maze = new Maze(width, height); //Initialize maze
map = Maze.Init(); //Inheritance maze
map[1][1] = 2; //Set the entrance and exit of the labyrinth
mx = 1;
my = 1;
//map[map.length - 2][map.length - 2] = 2;
}
//Game interface initialization and design
public void paintComponent(Graphics g) {
super.paintComponent(g);
this.addKeyListener(this);
//count = Difficult(level);
g.setColor(new Color(0,139,139));//Add RGB background color
g.fillRect(0, 0, 760, 807);
//Date.location.paintIcon(this,g,0,50);
//g.setColor(new Color(224, 238, 238));
for (int i = 0; i < map.length; i++) { //Fill the color method to draw the wall and load of the maze
for (int j = 0; j < map.length; j++) {
if(i==map.length-2&&j==map.length-2){
g.setColor(Color.RED);
g.fillRect(10 * i + 10, 10 * j + 50, 10, 10);
}else if (map[i][j] == 0) {
g.setColor(Color.BLACK);
g.fillRect(10 * i + 10, 10 * j + 50, 10, 10);
} else if (map[i][j] == 1) {
g.setColor(Color.GRAY);
g.fillRect(10 * i + 10, 10 * j + 50, 10, 10);
} else if (map[i][j] == 2) {
g.setColor(Color.RED);
g.fillRect(10 * i + 10, 10 * j + 50, 10, 10);
}
}
g.setColor(new Color(188, 250, 250));
g.fillRect(0, 0, 1000, 40);
g.setColor(Color.BLACK);
g.setFont(new Font("Imitation Song Dynasty", Font.BOLD, 20));
g.drawString("Reset game(X)", 10, 25);
g.drawString("Pathfinding(Y)", 150, 25);
g.drawString("Current steps:" + steps, 250, 25);
g.drawString("Difficulty:"+level,400,25);
g.drawString("W:difficulty+ S: difficulty-",500,25);
if (MazePanel.isSuccess()) {
g.setFont(new Font("Song typeface", Font.BOLD, 50));
g.drawString("Congratulations on customs clearance", 500, 400);
}
}
}
//Return the path obtained by A * algorithm to map
public void ans() {
AStar aStart = new AStar(map);
map = AStar.ans();
}
public MazePanel() {
MapRandom();
this.setFocusable(true);
this.addKeyListener(this);
}
//Judge whether to get out of the maze
public static boolean isSuccess() {
//score += MazePanel.MAXSTEPS - steps;
return map.length - 2 == mx && map.length - 2 == my;
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
}
static int i=0;
@Override
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e) {
int key = e.getKeyCode();
int x = mx, y = my;
//Game movement mode and restrictions. The next step cannot be a wall and single monitoring. If i=0 is not added, there will be a bug
if(!isSuccess()&&steps<MAXSTEPS) {
if (key == KeyEvent.VK_LEFT && map[x - 1][y] != MazePanel.WALL&&i==0) {//Shift left
map[x - 1][y] = MazePanel.current; //Change the current position to the moved position
map[x][y] = 1;//Restore the original icon of the map
mx--;i++; //Change current position coordinates
steps++;
} else if (key == KeyEvent.VK_RIGHT&&map[x + 1][y] != MazePanel.WALL&&i==0) {
map[x + 1][y] = MazePanel.current; //Shift right
map[x][y] = 1;
mx++;i++;
steps++;
} else if (key == KeyEvent.VK_UP&&map[x][y - 1] != MazePanel.WALL&&i==0) {
map[x][y - 1] = MazePanel.current; //Move up
map[x][y] = 1;
my--;i++;
steps++;
} else if (key == KeyEvent.VK_DOWN&&map[x][y + 1] != MazePanel.WALL&&i==0) {
map[x][y + 1] = 2; //Move down
map[x][y] = 1;
my++;i++;
steps++;
}else if(key == KeyEvent.VK_Y&&i==0){ //Display path
ans();
}else if(key == KeyEvent.VK_X&&i==0){ //Reset maze
MapRandom();
}
else if(key==KeyEvent.VK_W&&i==0&&level<13){ //Increase maze difficulty
level++;i++;
MapRandom();
}else if(key==KeyEvent.VK_S&&i==0&&level>=3){ //Reduce maze difficulty
level--;i++;
MapRandom();
}
}
repaint(); //Refresh game interface
}
@Override
public void keyTyped(KeyEvent e) {
}
@Override
public void keyReleased(KeyEvent e) {
i=0; //Keyboard monitoring is limited. If it is not limited, it will move several grids at a time
}
}
4. Main class
package com.company;
import javax.swing.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame(); Generate window
frame.setSize(770,825); //Set window size
MazePanel maze = new MazePanel();
frame.add(maze); //Add game panel
frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null);//Center of display screen
frame.setResizable(false);//Fixed screen
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//Close command
frame.setVisible(true); //Window visualization
}
}