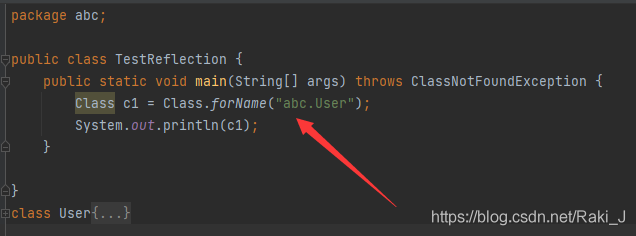
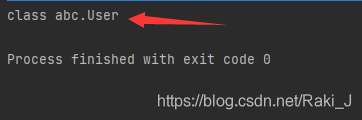
Yes, but I forgot all about it. I'm ready to be a migrant worker, so I'll learn it again from scratch
1. Install Java and IDEA
First go to the official website of oracle to download JDK8
Then install the JDK into the folder you want to put

Then start configuring environment variables
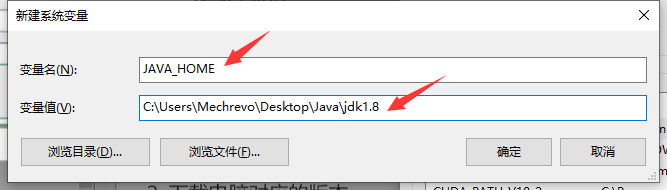
Add two paths to the path
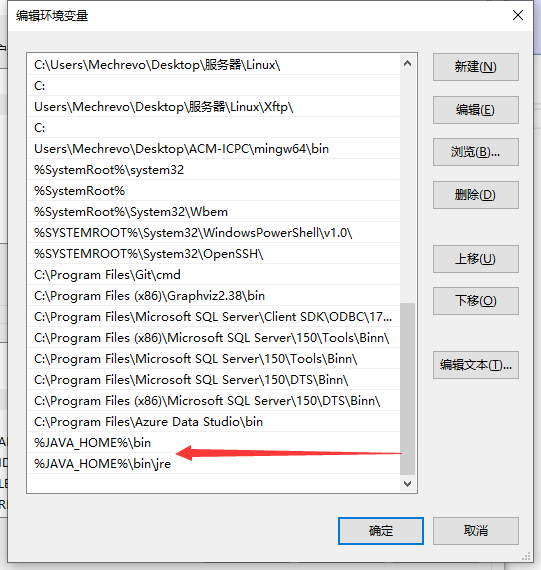
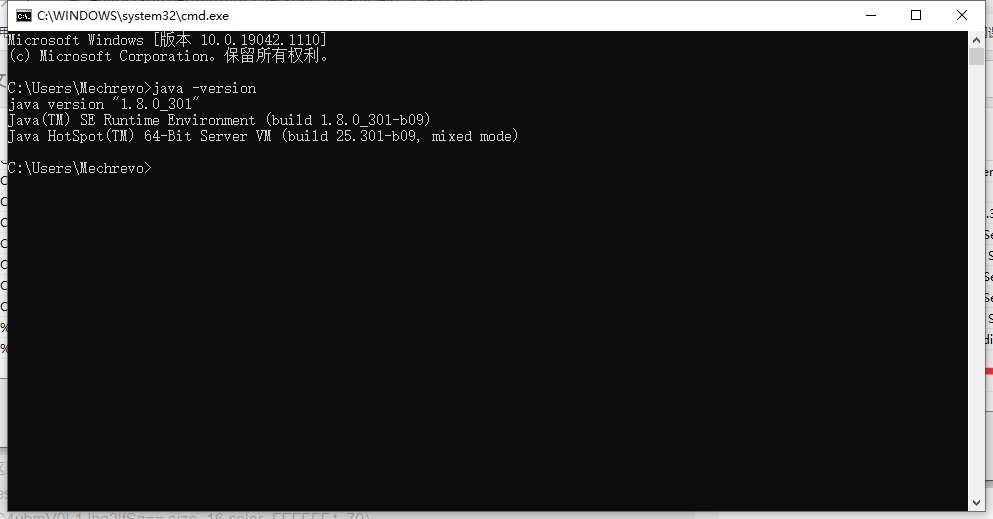
Then check whether our configuration is successful
Open cmd and you can see that the installation has been successful
This is the end of Java installation. Let's install IDEA
IDEA is a java ide of jb family. It's the best to use
Install it under the folder you want to find
Then the installation is complete
2. Advanced Java Tutorial
2.1 Java generics
Java generics is a new feature introduced in JDK 5. Generics provides a compile time type safety detection mechanism, which allows programmers to detect illegal types at compile time.
The essence of generics is parameterized type, that is, the data type operated on is specified as a parameter.
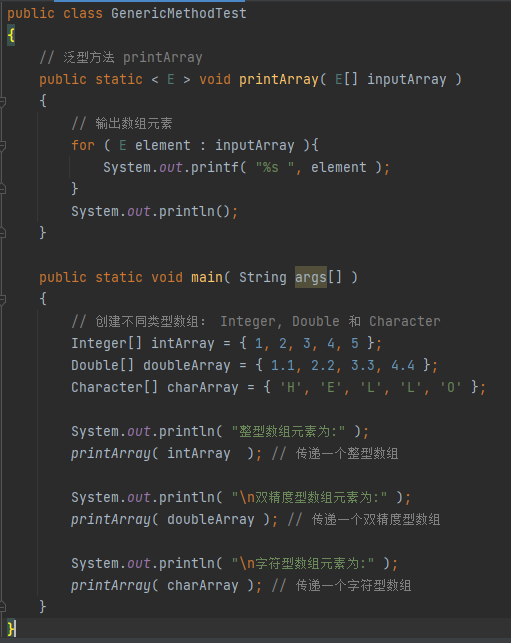
output

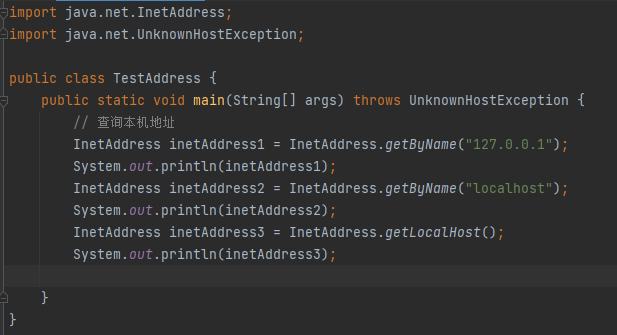
2.2 Java network programming
Port: refers to the process of a program on a computer program. Different processes have different port numbers, which are used to distinguish software
Be regulated 0 0 0 ~ 65535 65535 65535
Port classification:
- Public port 0 ~ 1023
- HTTP:80
- HTTPS:443
- FTP:21
- Telnet: 23
- Program registration port: 1024 ~ 49151, assign users or programs
- Tomcat: 8080
- MySQL: 3306
- oracle: 1521
- Dynamic, private: 49152 ~ 65535
netstat -ano #View all ports
2.3 multithreading
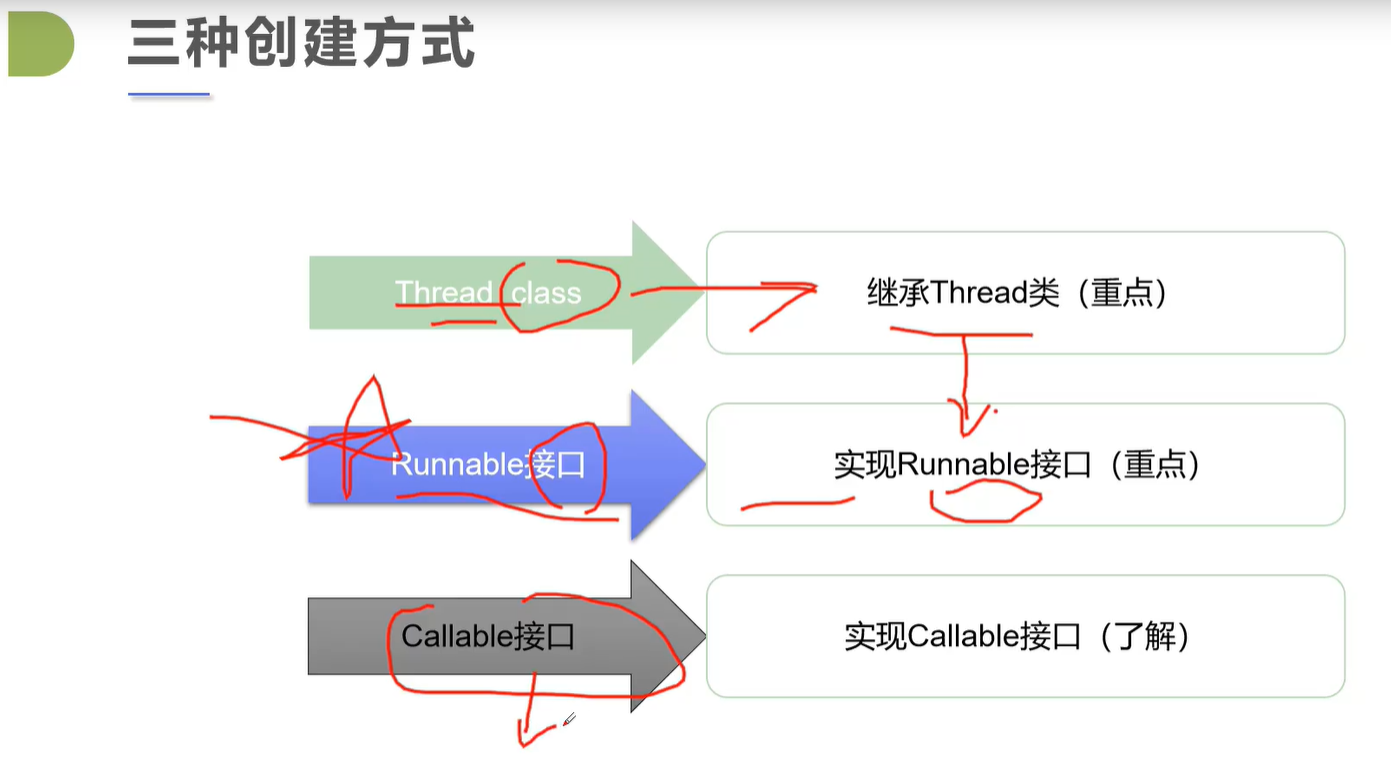
Inherit Thread class
public class TestThread1 extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
//run method thread body
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("I'm looking at the code");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//main thread
//create a thread object
TestThread1 testThread1 = new TestThread1();
//call start() method to start thread
testThread1.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("I'm learning multithreading -- " + i);
}
}
}
Implement Runnable interface
//way 2 to create a thread:implements runnable interface,override the run method
public class TestThread2 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
//run method thread body
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("I'm looking at the code");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//main thread
//create a thread object
TestThread2 testThread2 = new TestThread2();
Thread thread = new Thread();
new Thread(testThread2).start();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("I'm learning multithreading -- " + i);
}
}
}
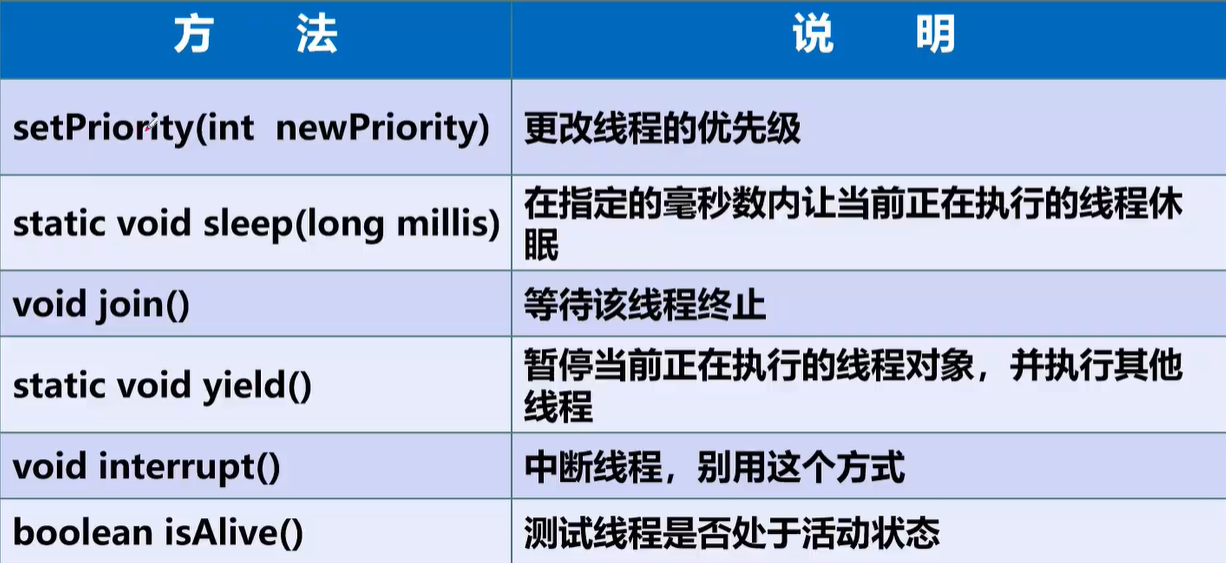
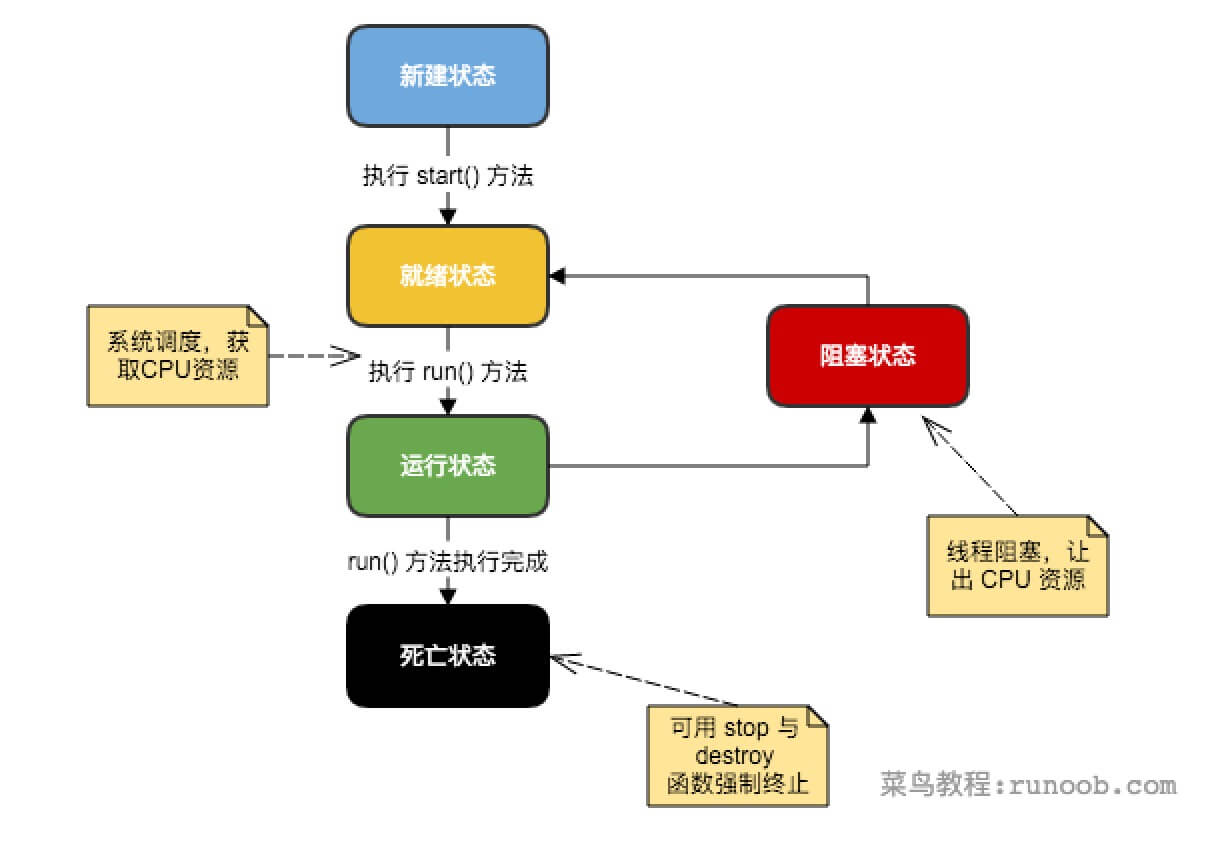
lambda expression of java
public class TestLambda {
// 3. Static internal class
static class Like2 implements Ilike{
@Override
public void lambda() {
System.out.println("i like lambda2");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ilike like = new Like();
like.lambda();
like = new Like2();
like.lambda();
// 4. Local internal class
class Like3 implements Ilike{
@Override
public void lambda() {
System.out.println("i like lambda3");
}
}
like = new Like3();
like.lambda();
// 5. Anonymous inner class
like = new Ilike() {
@Override
public void lambda() {
System.out.println("i like lambda4");
}
};
like.lambda();
// 6. Simplify with lambda
like = ()->{
System.out.println("i like lambda5");
};
like.lambda();
}
}
//1. Define a functional interface
interface Ilike{
void lambda();
}
// 2. Implementation class
class Like implements Ilike{
@Override
public void lambda() {
System.out.println("i like lambda");
}
}
Daemon, the virtual machine does not need to wait for the daemon to end
public class TestDaemon {
public static void main(String[] args) {
God god = new God();
You you = new You();
Thread thread = new Thread(god);
thread.setDaemon(true);
thread.start();
new Thread(you).start();
}
}
class God implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
System.out.println("God bless you");
}
}
}
class You implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 36500; i++) {
System.out.println("You live happily all your life");
}
System.out.println("=======goodbye world=========");
}
}
Thread synchronization mechanism:
Concurrency: the same object is operated by multiple threads at the same time
Unsafe thread
public class UnSafeBuyTicket {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BuyTicket station = new BuyTicket();
new Thread(station,"a").start();
new Thread(station,"b").start();
new Thread(station,"c").start();
}
}
class BuyTicket implements Runnable
{
private int ticketNums = 10;
boolean flag = true;
@Override
public void run() {
while (flag){
try {
buy();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private void buy() throws InterruptedException {
if(ticketNums <=0){
flag = false;
return;
}
Thread.sleep(100);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "Get" + ticketNums--);
}
}
Add a synchronized method in front of the method to turn the method into a synchronized method. The lock is this
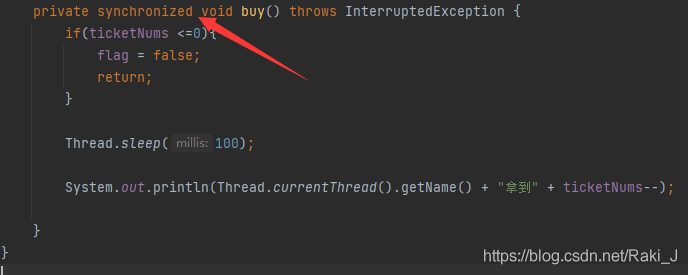
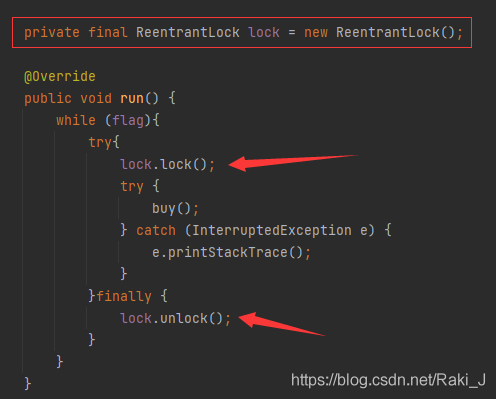
Locks can also be explicitly defined through the lock method

deadlock

Thread pool

2.4 notes
Annotations are used to check and constrain programs



2.5 reflection