Memory allocation in Java
When a Java program is running, it needs to allocate space in memory. In order to improve the efficiency of operation, the space is divided into different regions, because each region has a specific way of data processing and memory management.
- Stack store local variable
- The variables of local variables in method definition or method declaration are called local variables, which disappear immediately after use
- Heap to store new things
-
Each entity has a first address value
-
Data within each entity has a default value
byte,short,int,long 0 float,double 0.0 char '\u0000' boolean false Reference type: null
-
After use, it will be recycled when the garbage collector is idle.
-
- Class information, constants, static constants, etc. loaded by virtual machine in method area.
- Local method area (system related)
- Register (for CPU)
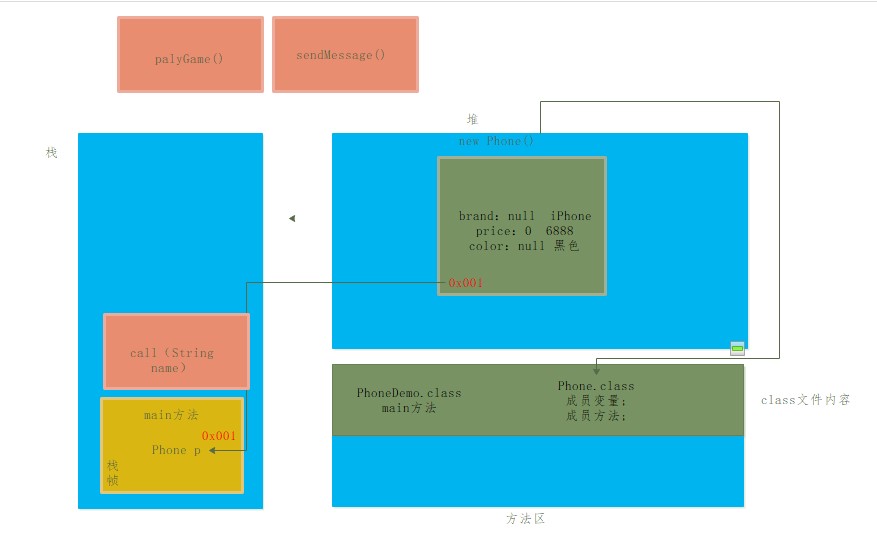
class Phone{
//brand
String brand;
//Price
int price;
//colour
String color;
//Phone
public void call(String name){
System.out.println("to"+name+"Phone");
}
//Send message
public void sendMessage(){
System.out.println("send message...");
}
//Play a game
public void playGame(){
System.out.println("Glory of Kings carry Medium.");
}
}
class PhoneDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
//Objects need to be created before use
//Class name object name = new class name ();
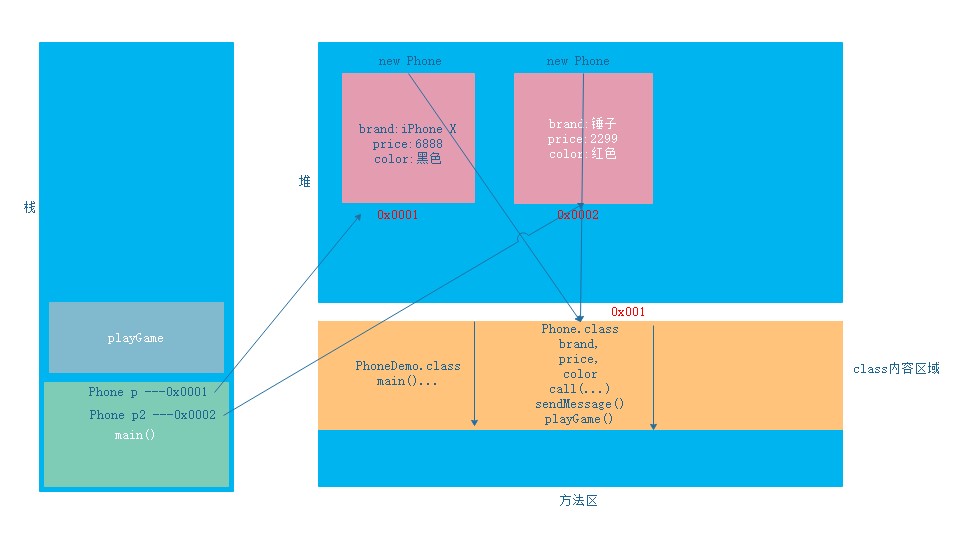
Phone p = new Phone();
System.out.println(p.brand+"==="+p.price+"==="+p.color);
//Assign a value to a member
p.brand = "iPhone X";
p.price = 6888;
p.color = "black";
System.out.println(p.brand+"==="+p.price+"==="+p.color);
//Calling method
p.call("Stay in the bell");
p.sendMessage();
p.playGame();
System.out.println("------------------------");
Phone p2 = new Phone();
System.out.println(p2.brand+"==="+p2.price+"==="+p2.color);
//Assign a value to a member
p2.brand = "Hammer";
p2.price = 2299;
p2.color = "Red";
System.out.println(p2.brand+"==="+p2.price+"==="+p2.color);
//Calling method
p2.call("Di Ali Gerba");
p2.sendMessage();
p2.playGame();
System.out.println("------------------------");
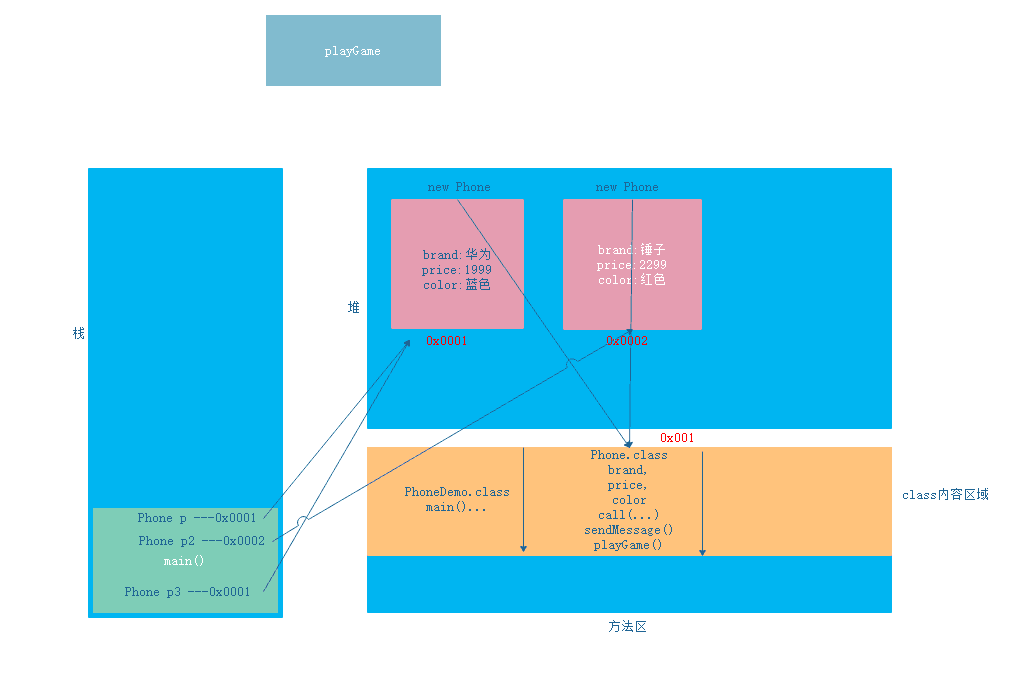
Phone p3 = p;
System.out.println(p3.brand+"==="+p3.price+"==="+p3.color);
//Assign a value to a member
p3.brand = "HUAWEI";
p3.price = 1999;
p3.color = "blue";
System.out.println(p3.brand+"==="+p3.price+"==="+p3.color);
System.out.println(p.brand+"==="+p.price+"==="+p.color);
}
}
Memory graph of an object
Memory map of two objects
Memory graph of three objects
Dumeng Zhong, all rights reserved, unless otherwise specified, are used by the original website BY-NC-SA The agreement is authorized. Please indicate JAVA basic course of Dumeng clock - object memory analysis!