JavaWeb - file upload and download
BiliBili frog course network [power node] JavaWeb eclipse learning video website
The article is only for sharing learning experience and reviewing. It is more effective to check the formal video website and official documents
| analysis | ascription | remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|
| mutipart/form-data | Multipart request / form data | File upload | enctype special request |
| getInputStream() | Get input stream | IO | |
| FileUpload | apache upload tool | File upload | apache upload tool |
| ServletFileUpload | Servlet file upload | File upload | |
| .isMultipartContent() | Is a multipart content request | File upload | |
| DiskFileItemFactory() | Disk file project factory | FileUpload | |
| ServletFileUpload() | Servlet file upload component | FileUpload | |
| .parseRequest() | Using tools to parse requests | Basic upload | |
| .isFormField() | Is a normal form byte | Basic upload | |
| .getInputStream() | Get input stream upload content | Basic upload | |
| .getRealPath | Get real path | Basic upload | |
| FileOutputStream | File output stream output | Basic upload | |
| setSizeThreshold | Set threshold size of temporary directory | Temporary directory | |
| setRepository | Set up temporary repository | Temporary directory | |
| .delete() | Temporary file deletion | Temporary directory | |
| .setHeaderEncoding("UTF-8") | Chinese name of solution file | Parameter name problem | |
| System.currentTimeMillis() | Current system time | Parameter name problem | |
| .setFileSizeMax | Upload file size | Parameter name problem | |
| .setSizeMax | Total size of all uploaded files | Parameter name problem | |
| Calendar.getInstance() | Get current system time | Parameter name problem | |
| Calendar.YEAR,.MONTH | Year, month | Parameter name problem | MONTH is calculated from 0 |
| Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH | day | Parameter name problem | |
| .mkdir() | Create directory | Parameter name problem | . mkdirs() multi level directory |
| new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMdd") | format date | Servlet Download | |
| format() | format date | Servlet Download | |
| setHeader | Header information | Servlet Download | |
| "content-disposition","attachment" | Downloaded header information | Servlet Download | |
| filename | Downloaded file name | Servlet Download |
File upload and download
1. File upload
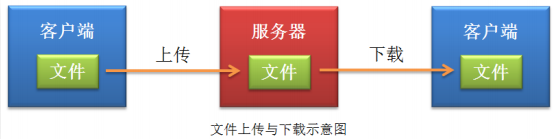
1.1 what is upload and download?
Data upload means that the client uploads data to the server. All requests sent by the client to the server belong to data upload. File upload is a special case of data upload, which means that the client uploads files to the server. Upload a copy of the file saved in the client to the server and save it to the server.
Data download refers to the process that the client obtains data from the server. File download is a special case of data download, which means that the client downloads files from the server, that is, the files originally saved in the server are downloaded to the client and saved in a copy. Usually, most of the requests we send to the server are file download requests. We download text, pictures, sound, video and other files from the server, and then the client browser parses these files before we can see these multimedia information.
However, the file download here refers to that after the file is downloaded from the server to the browser, the browser does not parse it directly, but saves it to the client in the form of an attachment.
The uploaded and downloaded files can be text files, pictures, sounds, videos and other types.
1.2 implementation of file upload
1.2. 1. Upload form requirements
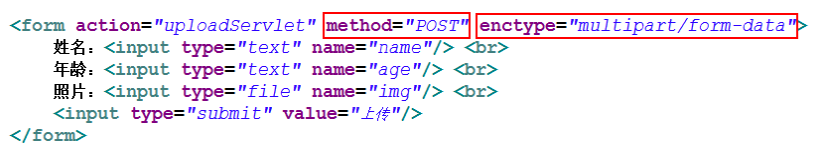
File upload requires the client form to submit a special request - multipart request, that is, a request containing multiple parts of data. Therefore, the encoding type of form data in the file upload form must be music / form data. That is, specify the enctype attribute value as "music / form data" for the < form / > tag. Enctype, that is, encoding type.
Because the size of the file uploaded by the client is uncertain, the HTTP protocol stipulates that the data uploaded by the file should be stored in the request body and cannot appear in the address bar of the URL, because the amount of data that can be stored in the address bar is too small. In other words, the form for file upload must submit a POST request instead of a GET request.
1.2. 2. Multipart / form data protocol
The encoding type of multipart / form data is a fixed format encoding scheme and a communication format specified in the HTTP request protocol. The coding scheme first tells the server that the request sent now is a multi part request from form data, and the request body contains multi part data.
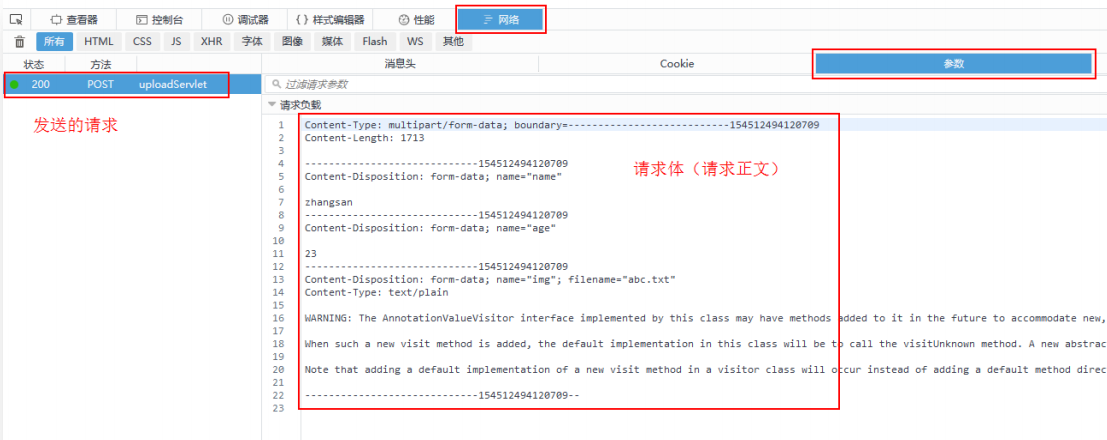
The specific format of the request can be viewed through the "network / parameters" of Firefox browser. Open the developer toolbar window of Firefox browser. When the request is sent, click the request, and then select "network / parameters" to see the text of the sent request. Note: do not use HttpWatch under IE to view the request body of file upload, because HttpWatch will intercept the next request and make the request unable to be sent successfully.
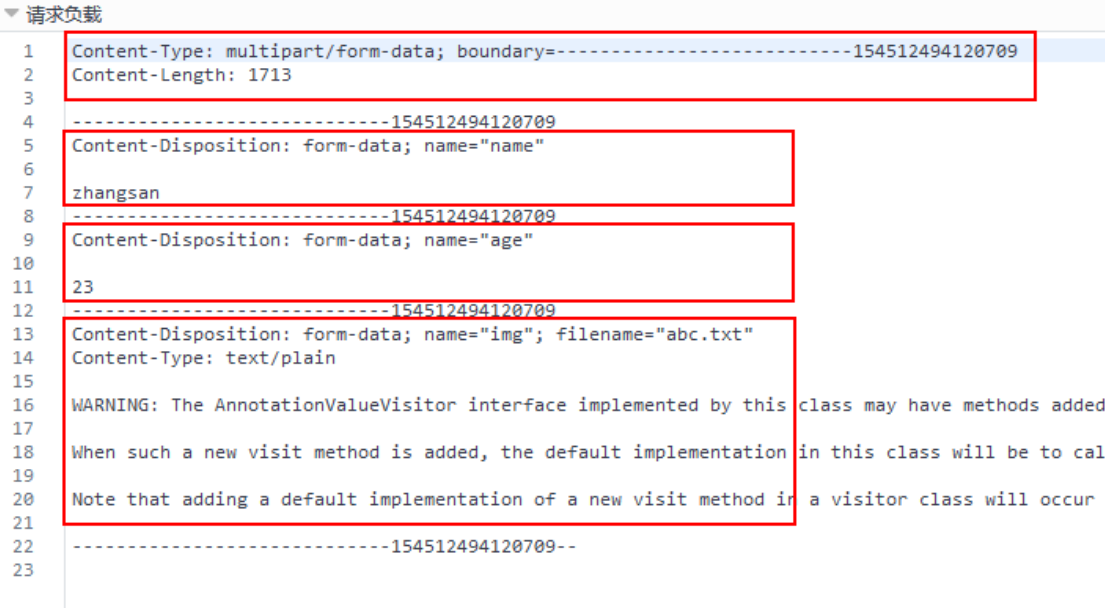
For this example, the form contains name, age, and the file img to be uploaded. The name value is zhangsan, the age value is 23, and the file img is a text file. The file name of the text file on the client is ABC txt.
According to the HTTP protocol, the request body of multipart / form data includes the following parts:
Request body header
It contains the content type of the request. Of course, it is fixed as multipart / form data. Multipart requests the separator boundary between parts, which is composed of several dashes and a random number. Content length of the request body.
Request body
The request body header, the request body, and the request body are separated by the separator specified above to separate the request body into multiple parts, that is, multipart. Each part is called an Item.
Each Item consists of three parts:
- Parameter information: the parameter information includes content disposition, and form data is form data; Parameter name; If the parameter is the file to be uploaded, it also includes the original name of the file filename, the MIME type of the file content type, and text/plain represents an ordinary text file.
- Separate blank lines: only one blank line is used to separate parameter information and parameter values.
- Parameter value: the value of the uploaded parameter. If the uploaded file is a text file, the normal text will be written here. If the uploaded file is a picture, video, audio, etc., its binary file will be uploaded. The following figure shows the parameter values of the uploaded image file.
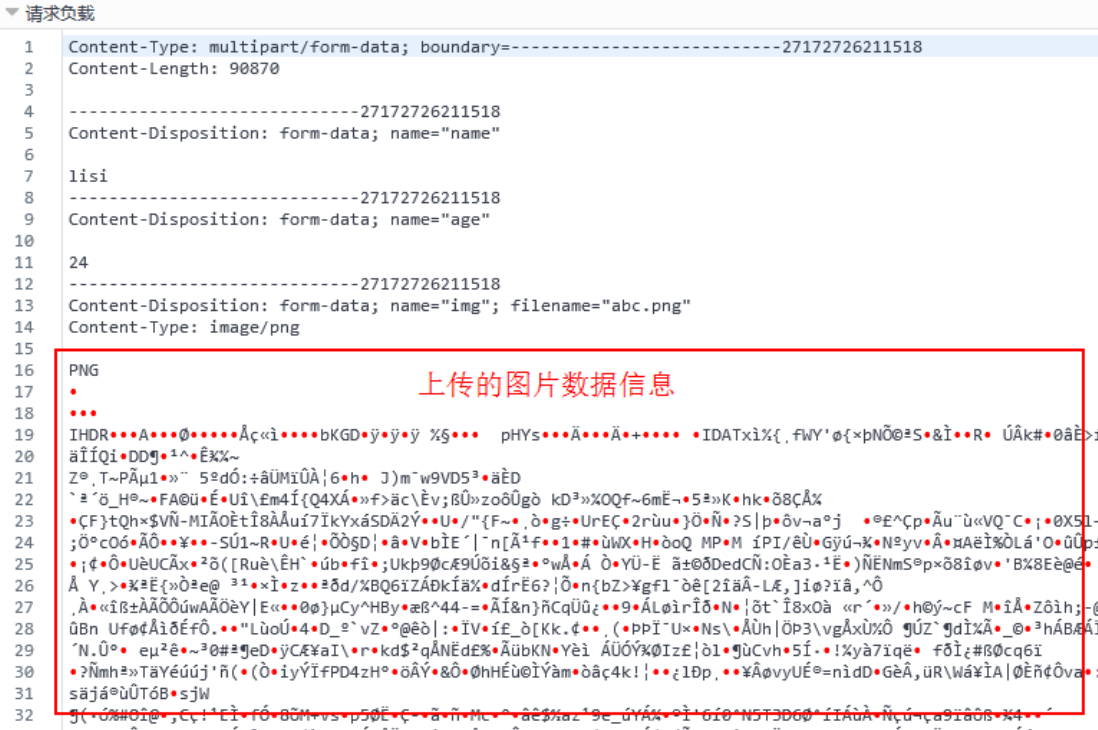
1.2. 3. The server receives and uploads files manually
The server can receive the uploaded file through the input stream. The input stream can be obtained through * * getInputStream() * * of HttpServletRequest.
After receiving, you can parse the data in the input stream and respond to the client. It is troublesome to manually complete the protocol analysis of multipart / form data, so it is not done manually here. Just receive it and display it on the console.
Define form page index jsp

Define UploadServlet
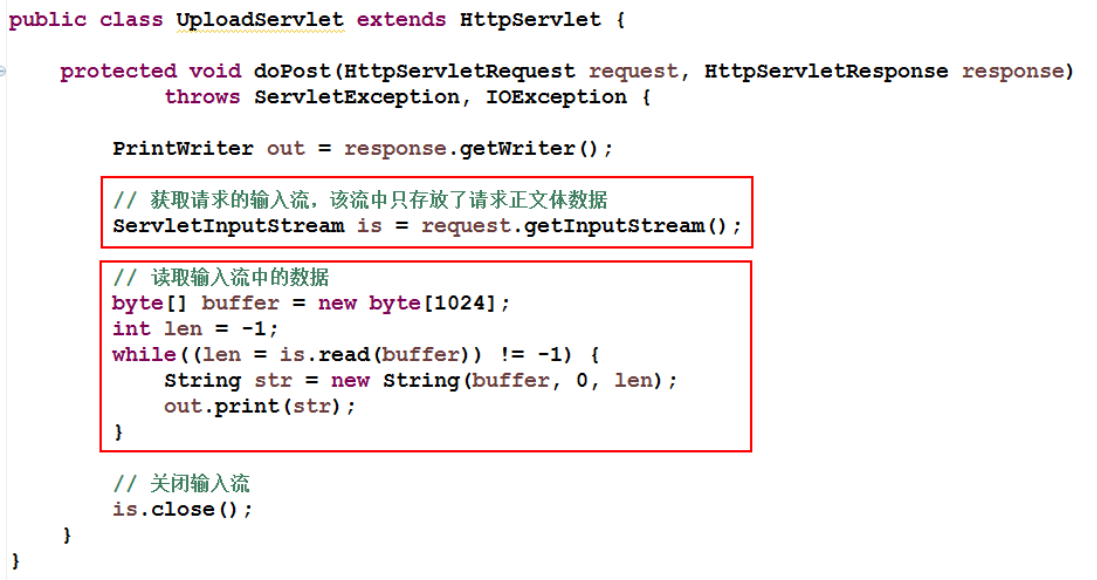
Register UploadServlet

1.2. 4. Upload using third-party tools
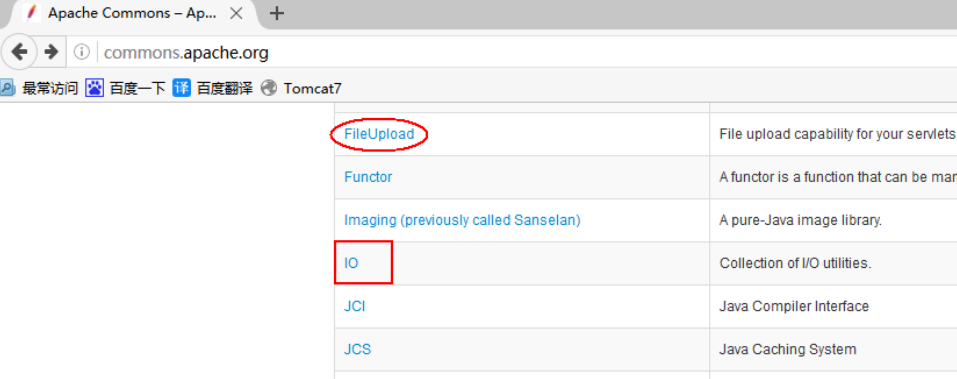
There are many third-party tools that can complete the upload function, but the more famous is Apache's FilterUpload tool. The tool can be downloaded from Apache's official website. Apache's official website is: http://apache.org .
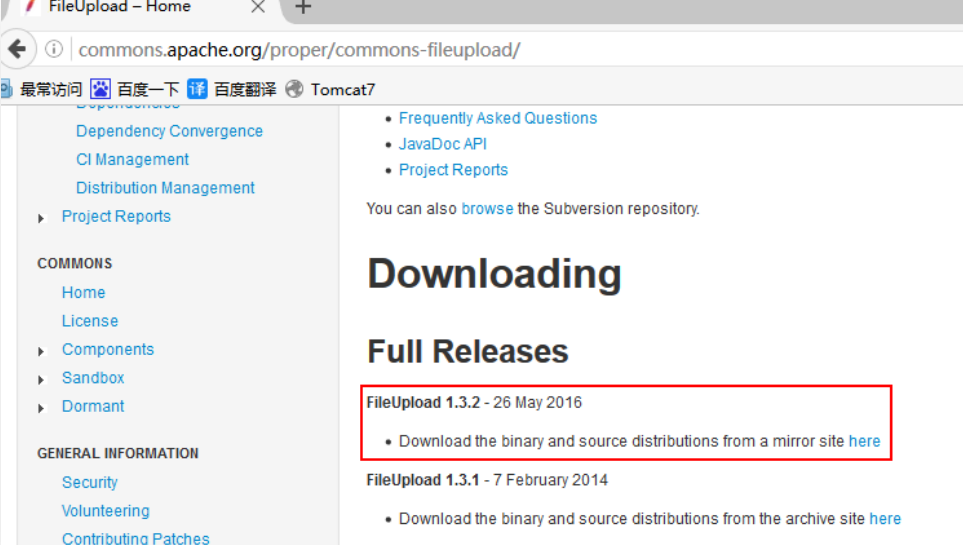
FileUpload tool download
The FileUpload tool is stored in Apache R's commons, so it needs to be downloaded under Commons.
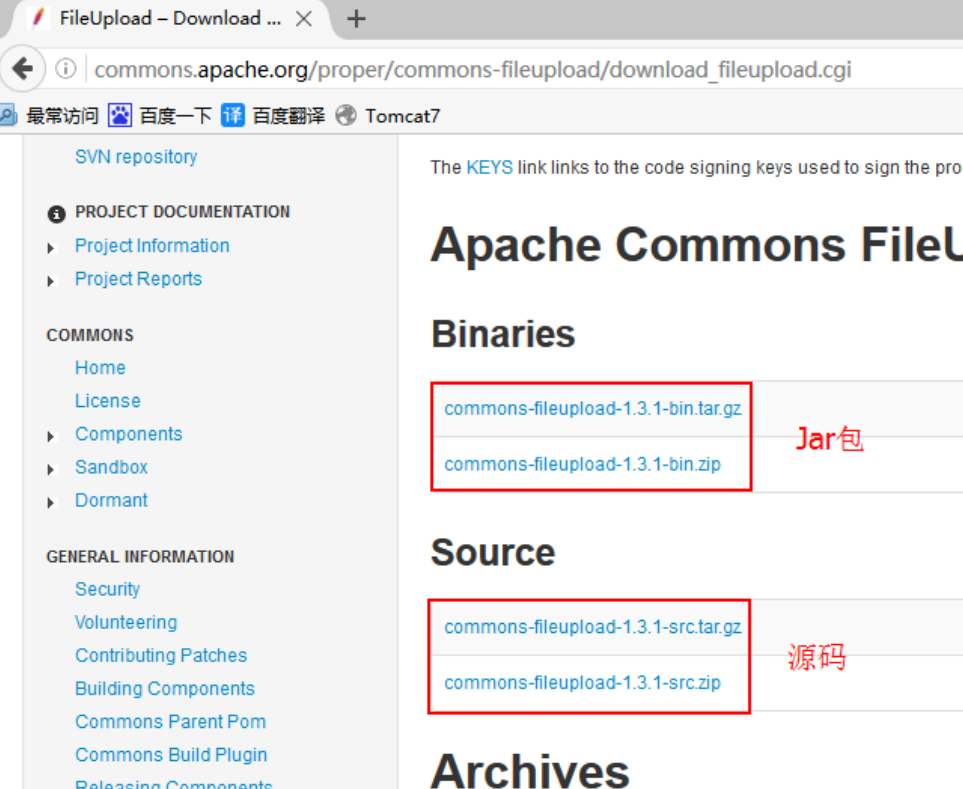
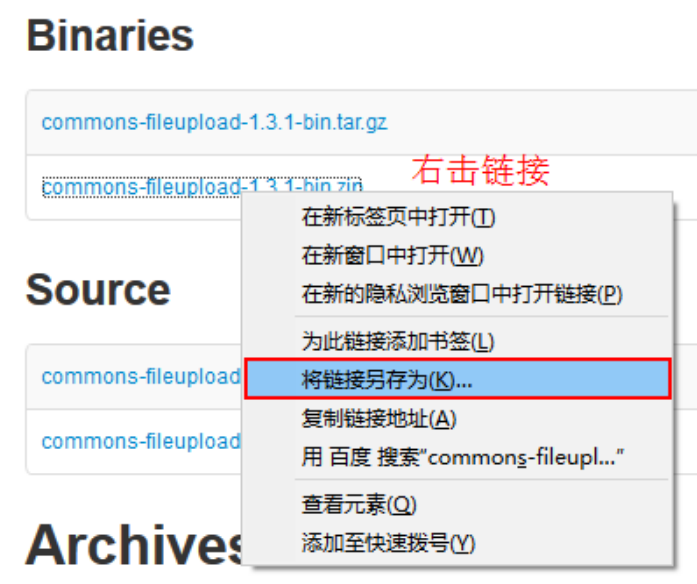
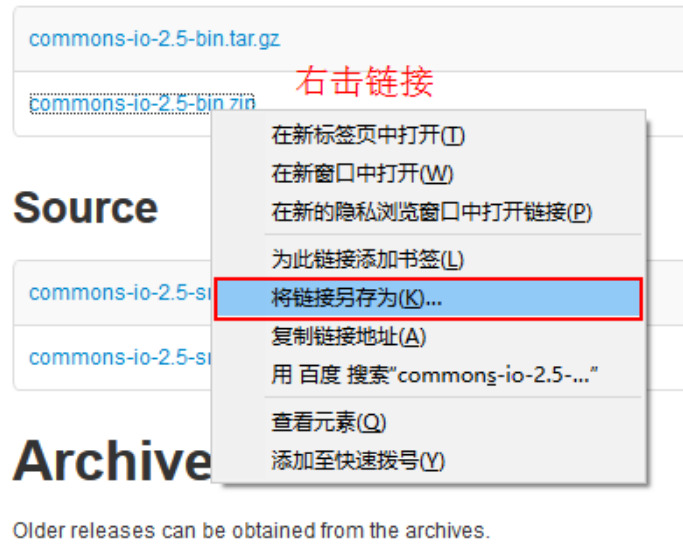
Right click the link and select Save Link as to download it.
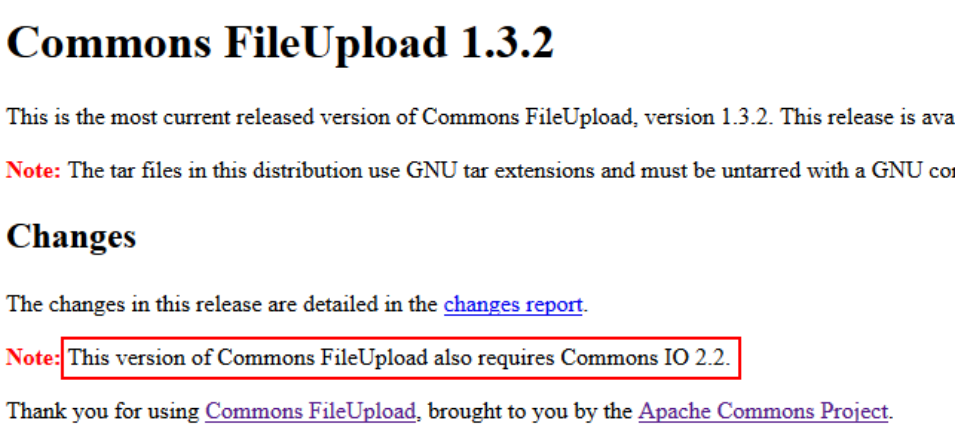
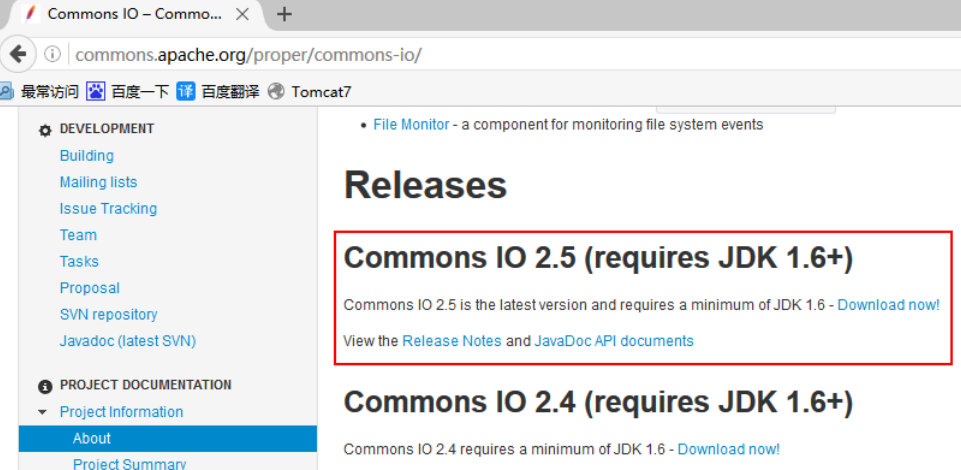
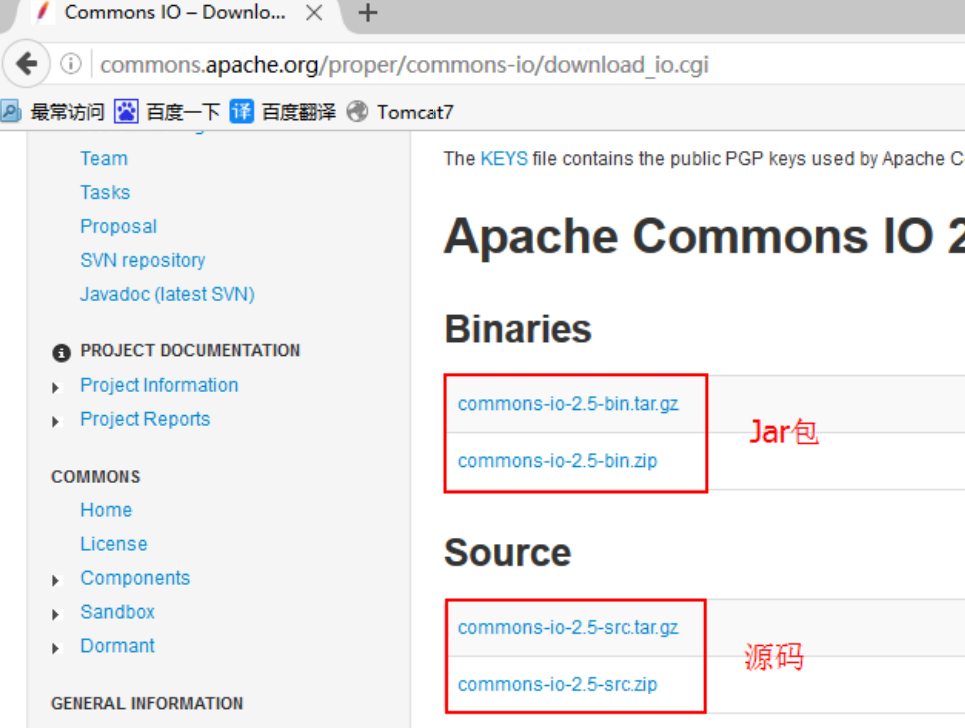
IO package download
Further tracking the Jar package information, you will see the following note: This version needs to rely on io2.0 under Apache Commons 2 bags.
Official Website User Wizard
Open the User guide of the file upload home page of the Apache official website, including an example of file upload using the FileUpload tool.
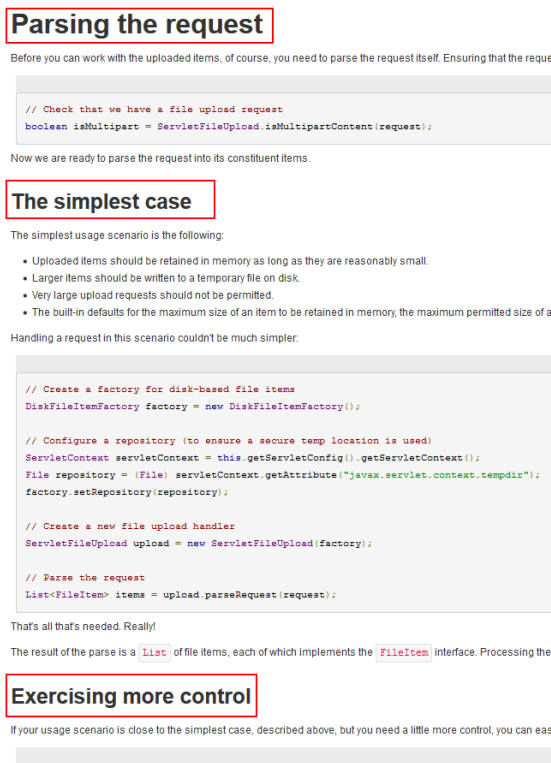
1. Code implementation - version 1 - Basic upload
This version completes the basic file upload function.
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.List;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.servlet.ServletFileUpload;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.FileItem;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.FileUploadException;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.disk.DiskFileItemFactory;
public class RegisterServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
//1. Judge whether the request is a multipart request
if (!ServletFileUpload.isMultipartContent(request)) {
throw new RuntimeException("The current request does not support file upload");
}
try {
//Create a FileItem factory
DiskFileItemFactory factory = new DiskFileItemFactory();
//Create file upload core component
ServletFileUpload upload = new ServletFileUpload(factory);
//Use the tool to parse the request and get all the item s
List<FileItem> items = upload.parseRequest(request);
//Traverse item
for (FileItem item : items) {
if (item.isFormField()) { //If item is a normal form item
String fieldName = item.getFieldName(); // Get form item name
String fieldValue = item.getString(); // Gets the value of the form item
System.out.println(fieldName + " = " + fieldValue);
}else { //If item is a file form item
String fileName = item.getName(); // Get the original name of the uploaded file
// Get the input stream, which contains the contents of the uploaded file
InputStream is = item.getInputStream();
// Gets the path where the file is saved on the server
String path = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/images");
// Create a target file to save the uploaded file in the future
File descFile = new File(path, fileName);
// Create file output stream
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(descFile);
// Writes data from the input stream to the output stream\
int len = -1;
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
while((len = is.read(buf)) != -1) {
os.write(buf, 0, len);
}
// Close flow
os.close();
is.close();
}
}
} catch (FileUploadException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2. Code implementation - version 2 - temporary directory
The file is uploaded to the server by the browser through the network, rather than directly sending all the requested data to the server through a network line.
Instead, these data are divided into many data packets, which are numbered respectively and finally sent to the same machine - server through different network lines.
These packets arrive at the server at different times according to different network lines. They do not necessarily arrive in the order of numbers, or they will not arrive in the order of numbers in most cases. Then, the server will create a temporary file in its temporary directory and splice these packets.
// Set the boundary value of using temporary file. If it is greater than this value, the uploaded file will be saved in the temporary file first. Otherwise, the uploaded file will be written directly to memory.
// Unit: bytes. This example sets the boundary value to 1M
factory.setSizeThreshold(1024 * 1024 * 1);
// Set temporary file
String tempPath = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/temp");
File temp = new File(tempPath);
factory.setRepository(temp);
By default, the temporary directory of Tomcat is the temp subdirectory of the Tomcat server installation directory. Of course, we can also change the default location of the temporary directory.
Apache's FileUpload supports setting the minimum threshold for creating temporary files, that is, temporary files will be created only if the uploaded file size exceeds this value. You can set the critical value in bytes through the setSizeThreshold() method of DiskFileItemFactory.
The temporary directory can be specified through the setRepository() method of DiskFileItemFactory.
Once the temporary files are used up, they can be deleted, otherwise they will occupy the hard disk space of the server. The delete() method of FileItem is used to delete temporary files.
It should be noted that temporary files cannot be deleted until the IO stream is closed.
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.List;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.servlet.ServletFileUpload;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.FileItem;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.FileUploadException;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.disk.DiskFileItemFactory;
public class RegisterServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
//1. Judge whether the request is a multipart request
if (!ServletFileUpload.isMultipartContent(request)) {
throw new RuntimeException("The current request does not support file upload");
}
try {
//Create a FileItem factory
DiskFileItemFactory factory = new DiskFileItemFactory();
// Set the boundary value of using temporary file. If it is greater than this value, the uploaded file will be saved in the temporary file first. Otherwise, the uploaded file will be written directly to memory.
// Unit: bytes. This example sets the boundary value to 1M
factory.setSizeThreshold(1024 * 1024 * 1);
// Set temporary file
String tempPath = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/temp");
File temp = new File(tempPath);
factory.setRepository(temp);
//Create file upload core component
ServletFileUpload upload = new ServletFileUpload(factory);
//Use the tool to parse the request and get all the item s
List<FileItem> items = upload.parseRequest(request);
//Traverse item
for (FileItem item : items) {
if (item.isFormField()) { //If item is a normal form item
String fieldName = item.getFieldName(); // Get form item name
String fieldValue = item.getString(); // Gets the value of the form item
System.out.println(fieldName + " = " + fieldValue);
}else { //If item is a file form item
String fileName = item.getName(); // Get the original name of the uploaded file
// Get the input stream, which contains the contents of the uploaded file
InputStream is = item.getInputStream();
// Gets the path where the file is saved on the server
String path = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/images");
// Create a target file to save the uploaded file in the future
File descFile = new File(path, fileName);
// Create file output stream
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(descFile);
// Writes data from the input stream to the output stream\
int len = -1;
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
while((len = is.read(buf)) != -1) {
os.write(buf, 0, len);
}
// Close flow
os.close();
is.close();
// Delete temporary file
item.delete();
}
}
} catch (FileUploadException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3. Code implementation - version 3 - parameter name problem
The current program has the following problems:
-
When the common parameters submitted by the user from the form contain Chinese characters, the problem of garbled code will occur.
-
When the file name of the uploaded file contains Chinese, the file name uploaded to the server will be garbled.
-
Different browsers upload different file names to the server, that is, the file names obtained by the getName() method of FileItem are different.
For example, the user uploaded D: \ ABC \ XXX. From the client JPG file, the file name uploaded by Firefox browser is XXX Jpg, and the file name uploaded by IE browser is D: \ ABC \ XXX jpg.
-
If different users submit files with the same file name, the files of subsequent users will not be uploaded.
Ideas to solve these problems:
(1) To solve the Chinese garbled code problem of common parameters, just use the parameter getString(String Encoding) method of FileItem to obtain the parameter name.
// Set the header character code of each item, which can solve the problem of Chinese garbled file names
upload.setHeaderEncoding("UTF-8");
(2) The Chinese garbled code of the upload file name needs to be solved by specifying the header code of the upload file request through the ServletFileUpload method setHeadEncoding(). However, it should be noted that this setting method will not change the encoding of the common parameter request header.
String fieldName = item.getFieldName(); // Get form item name
String fieldValue = item.getString("UTF-8"); // Gets the value of the form item
(3) In order to solve the problem that the file name sent by the browser to the server is different, you need to use the substring() method of String to intercept the file name. Because the file name must be after the last "\".
(4) For the upload of the same file name, you only need to make the file name saved on the server unique. For example, add a current system time System.currentTimeMillis() before the original file name.
String fileName = item.getName(); // Get the original name of the uploaded file //System.currentTimeMillis() system time + original file name fileName = System.currentTimeMillis() + fileName;
(7) Code implementation - version 4 - file size
The size of the uploaded file can be controlled through the setFileSizeMax() and setSizeMax() methods of ServletFileUpload. setFileSizeMax() is used to set the maximum value of a single file upload, and setSizeMax() is used to set the maximum value of a single upload. That is, if multiple files are uploaded at one time, the size boundary value of each file and the maximum value of all files.
// Set the maximum boundary value of a single uploaded file to 2M upload.setFileSizeMax(1024 * 1024 * 2); // Set the maximum sum of all files uploaded at one time to 5M (effective when uploading multiple files) upload.setSizeMax(1024 * 1024 * 5);
(8) Code implementation - version 5 - self built directory
Whether it is Windows system, Linux system or other systems, there is an upper limit on the number of files contained in its directory. Therefore, the uploaded files should be managed by directory. If there are not too many files, you can create another level of subdirectory in images according to yyyyMMdd date format. If there are many files, you can create multi-level subdirectories by year, month and day. In this way, it is easy to manage without exceeding the maximum number of files in the directory.
The following implements a first level subdirectory named in yyyyMMdd format.
// Gets the path where the file is saved on the server
String path = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/images");
// Get current system time
Date date = new Date();
// format date
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMdd");
String now = sdf.format(date);
//Day based primary directory
path = path + "/" + now;
// If directory does not exist, create it
File dirFile = new File(path);
if (!dirFile.exists()) {
//mkdir() create directory
dirFile.mkdir();
}
The following implementation is multi-level directory
// Gets the path where the file is saved on the server
String path = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/images");
// Get current system time
Calendar now = Calendar.getInstance();
// Get year, month and day
int year = now.get(Calendar.YEAR);
int month = now.get(Calendar.MONTH) + 1; //MONTH starts at 0, so + 1 is required
int day = now.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
path = path + "/" + year + "/" + month + "/" + day;
// If directory does not exist, create it
File dirFile = new File(path);
if (!dirFile.exists()) {
dirFile.mkdirs(); //Multi level directories use mkdirs
}
All codes
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.FileItem;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.FileUploadException;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.disk.DiskFileItemFactory;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.servlet.ServletFileUpload;
public class RegisterServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("Execute upload");
// Judge whether the request is a multipart request
if( !ServletFileUpload.isMultipartContent(request) ) {
throw new RuntimeException("The current request does not support file upload");
}
try {
// Create a FileItem factory
DiskFileItemFactory factory = new DiskFileItemFactory();
// Set the boundary value of using temporary file. If it is greater than this value, the uploaded file will be saved in the temporary file first. Otherwise, the uploaded file will be written directly to memory.
// Unit: bytes. This example sets the boundary value to 1M
factory.setSizeThreshold(1024 * 1024 * 1);
// Set temporary file
String tempPath = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/temp");
File temp = new File(tempPath);
factory.setRepository(temp);
// Create file upload core component
ServletFileUpload upload = new ServletFileUpload(factory);
// Set the header character code of each item, which can solve the problem of Chinese garbled file names
upload.setHeaderEncoding("UTF-8");
// Set the maximum boundary value of a single uploaded file to 2M
upload.setFileSizeMax(1024 * 1024 * 2);
// Set the maximum sum of all files uploaded at one time to 5M (effective when uploading multiple files)
upload.setSizeMax(1024 * 1024 * 5);
// Parse the request and get all the item s
List<FileItem> items = upload.parseRequest(request);
// Traverse items
for (FileItem item : items) {
if(item.isFormField()) { // If item is a normal form item
String fieldName = item.getFieldName(); // Get form item name
String fieldValue = item.getString("UTF-8"); // Gets the value of the form item
System.out.println(fieldName + " = " + fieldValue);
} else { // If item is a file form item
String fileName = item.getName(); // Get the original name of the uploaded file
fileName = System.currentTimeMillis() + fileName;
// Get the input stream, which contains the contents of the uploaded file
InputStream is = item.getInputStream();
// Gets the path where the file is saved on the server
String path = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/images");
// Get current system time
Calendar now = Calendar.getInstance();
// Get year, month and day
int year = now.get(Calendar.YEAR);
int month = now.get(Calendar.MONTH) + 1; //MONTH starts at 0, so + 1 is required
int day = now.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
path = path + "/" + year + "/" + month + "/" + day;
// If directory does not exist, create it
File dirFile = new File(path);
if (!dirFile.exists()) {
dirFile.mkdirs(); //Multi level directories use mkdirs
}
// Create a target file to save the uploaded file in the future
File descFile = new File(path, fileName);
// Create file output stream
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(descFile);
// Writes data from the input stream to the output stream
int len = -1;
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
while((len = is.read(buf)) != -1) {
os.write(buf, 0, len);
}
// Close flow
os.close();
is.close();
// Delete temporary file
item.delete();
}
}
} catch (FileUploadException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2. File download
2.1. Hyperlink Download
The so-called hyperlink download means that the downloaded resources appear as the link destination file of the hyperlink.
If the browser can parse the resource file, the file content will be displayed directly on the browser; If the browser does not support the parsing of the file, a save as dialog box will pop up and ask the user to save.
Disadvantages: if different browsers and plug-ins installed in the same browser are different, their ability to resolve resources will be different, and whether to pop up the Save As dialog box will be different. The decision is up to the browser.
Storage resources
Create a new directory resources under the WebRoot of the project to store various resource files.
Write link
In index Write the following hyperlink in the JSP page.
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Hyperlink file download -->
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/resources/aaa.jpg">aaa.jpg</a> <br>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/resources/bbb.jar">bbb.jar</a> <br>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/resources/ccc.zip">ccc.zip</a> <br>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/resources/ddd.pdf">ddd.pdf</a> <br>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/resources/eee.exe">eee.exe</a> <br>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/resources/fff.txt">fff.txt</a> <br>
</body>
</html>
2.2. Servlet Download
To make the downloaded file appear in the browser as an attachment, you need to set the value of the attribute content disposition of the response header to attachment, and you need to specify the file name displayed by the browser after downloading.
Response is required Setheader specifies that the value of content disposition is attachment; Filename = filename
2.2. 1. Implementation of download
Define index jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Hyperlink file download -->
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/downloadServlet">Sports car</a> <br>
</body>
</html>
Define DownloadServlet
package com.bjpowernode.servlets;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletOutputStream;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class DownloadServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String fileName = "Super run.jpg";
// Scatter: scatter according to the current character code
byte[] bytes = fileName.getBytes("UTF-8");
// Assembly: assemble according to the target character code
fileName = new String(bytes, "ISO8859-1");
// Modify the header attribute content disposition value of the response to attachment
response.setHeader("content-disposition", "attachment;filename=" + fileName);
// Gets the input stream of the connection server resource file
InputStream is = this.getServletContext().getResourceAsStream("/resources/aaa.jpg");
// Get output stream
ServletOutputStream os = response.getOutputStream();
// Writes data from the input stream to the output stream
int len = -1;
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
while((len = is.read(buf)) != -1) {
os.write(buf, 0, len);
}
// Close flow
os.close();
is.close();
}
}
Register DownloadServlet
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="2.5">
<display-name>08-download-1</display-name>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>index.htm</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.html</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.htm</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
<servlet>
<description></description>
<display-name>DownloadServlet</display-name>
<servlet-name>DownloadServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.bjpowernode.servlets.DownloadServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>DownloadServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/downloadServlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
2.2. 2. Solve the problem of garbled file names
-
Break up the currently received character encoding
-
Then assemble according to the target character code
-
Finally, it is rendered according to the code set by the browser
String fileName = "Super run.jpg";
// Scatter: scatter according to the current character code
byte[] bytes = fileName.getBytes("UTF-8");
// Assembly: assemble according to the target character code
fileName = new String(bytes, "ISO8859-1");
apache help document URL
http://commons.apache.org/proper/commons-fileupload/using.html