JDBC: Java DateBase Connectivity
Essence: JDBC is an official set of specifications, interfaces for connecting database operations. The code that actually runs is the code of the implementation class in the jar package provided by the database vendor.
Example:
1. Importing jar packages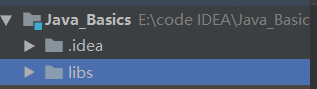
Create a folder named libs in an idea project and copy the downloaded jar into it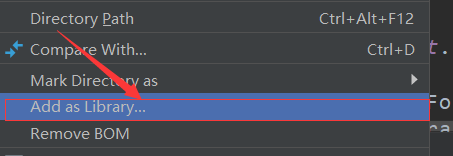
Right-click the folder and select Add As Library...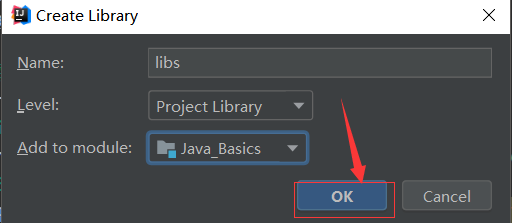
Click ok to complete the import of the jar package
Insert code slices here package JDBC_Database Connection;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class testJDBC {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. Importing jar packages
Connection conn = null;
Statement state = null;
try {
//2. Registration Driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//3. Get Connection of Connection Object
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test", "root", "root");
//4. Writing SQL Statements
String sql = "update user3 set name='zhangsan' where id=107";
//5. Get the execution object Statement
state = conn.createStatement();
//6. Execute the SQL statement and return the result
int row = state.executeUpdate(sql);
//7. Processing results
if (row > 0)
System.out.println("successful");
else
System.out.println("failed");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
//8. Releasing Resources
} finally {
if (state != null) {
try {
state.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}