1. Overview of Hibernate
Hibernate is a Open source of Object relational mapping Frame, it's right JDBC A very lightweight object encapsulation is carried out. It establishes the mapping relationship between POJO and database tables. It is a fully automatic orm framework. Hibernate can automatically generate and execute SQL statements, so that Java programmers can use object programming thinking to manipulate the database at will. Hibernate can be used in any situation where JDBC is used, not only in Java client programs, but also in Servlet/JSP Web applications. The most revolutionary thing is that hibernate can be used in EJB applications JavaEE Replace CMP in architecture, complete Data persistence The important task of.
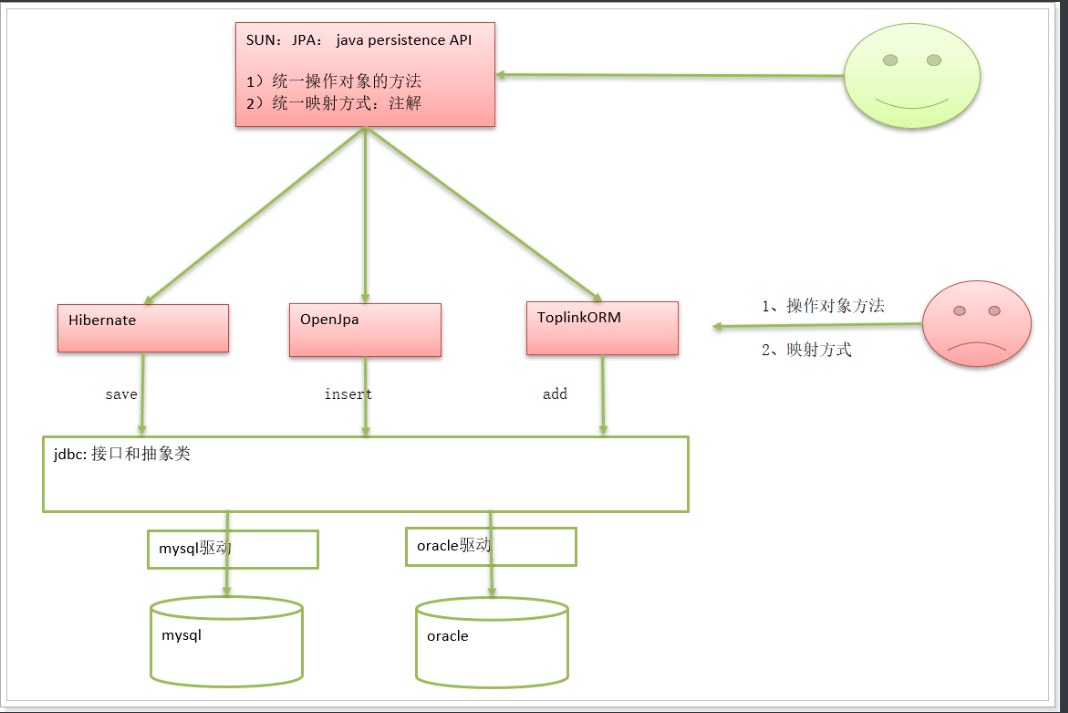
1. Introduction to JAP
1. Development preparation
/*Create customer table*/
CREATE TABLE cst_customer (
cust_id BIGINT(32) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'Customer number(Primary key)',
cust_name VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Customer name(corporate name)',
cust_source VARCHAR(32) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Customer information source',
cust_industry VARCHAR(32) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Customer industry',
cust_level VARCHAR(32) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Customer level',
cust_address VARCHAR(128) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Customer contact address',
cust_phone VARCHAR(64) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Customer contact number',
PRIMARY KEY (`cust_id`)
) ENGINE=INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
2. Add dependency
<!--Add dependency-->
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.hibernate.version>5.0.7.Final</project.hibernate.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- junit -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- hibernate yes jpa Support package for -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-entitymanager</artifactId>
<version>${project.hibernate.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- c3p0 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-c3p0</artifactId>
<version>${project.hibernate.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- log journal -->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Mysql and MariaDB -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.6</version>
</dependency>
<!--add to lombok-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.16</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
3. Prepare pojo
//Flag entity class
@Entity
//Mapping table
@Table(name = "cst_customer")
//Add get()set method
@Data
public class Customer implements Serializable {
@Id //Mark an attribute as a primary key
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) //Primary key generation side column
@Column(name = "cust_id") //Attribute names and table fields are mapped
private Long custId;
@Column(name = "cust_name")
private String custName;
@Column(name = "cust_source")
private String custSource;
@Column(name = "cust_Industry")
private String custIndustry;
@Column(name = "cust_level")
private String custIevel;
@Column(name = "cust_address")
private String custAddress;
@Column(name = "cust_phone")
private String custPhone;
}
4. Prepare configuration file
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<persistence xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence/persistence_2_0.xsd"
version="2.0">
<!-- Persistence unit
name: Persistence unit name
transaction-type: Transaction type
RESOURCE_LOCAL: Local transaction
JTA: Java Transaction API : Cross database transactions
-->
<persistence-unit name="myJpa" transaction-type="RESOURCE_LOCAL">
<!-- Designated provider -->
<provider>org.hibernate.jpa.HibernatePersistenceProvider</provider>
<!-- Configuration attribute: four elements of linked database, optional configuration, such as display sql sentence -->
<properties>
<property name="javax.persistence.jdbc.driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="javax.persistence.jdbc.url" value="jdbc:mysql://192.168.93.222:3306/day19?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8"/>
<property name="javax.persistence.jdbc.user" value="root"/>
<property name="javax.persistence.jdbc.password" value="root"/>
<!-- display sql sentence -->
<property name="hibernate.show_sql" value="true"/>
</properties>
</persistence-unit>
</persistence>
5 test
Core steps
* Steps: * 1,Load configuration file to create entity class manager factory * 2,Create entity class manager through factory * 3,Get transaction object * 4,Open transaction * 5,CRUD: Save customer entity * 6,Commit transaction * 7,Release resources
Test code
@Test
public void show(){
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setCustName("Xingjian, be good");
customer.setCustIevel("Eternal brick");
//Steps:
//1. Load configuration file to create entity class manager factory
EntityManagerFactory factory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("myJpa");
//2. Create entity class manager through factory
EntityManager entityManager = factory.createEntityManager();
//3. Get transaction object
EntityTransaction tx = entityManager.getTransaction();
//4. Open transaction
tx.begin();
//5. CRUD: save customer entity
entityManager.persist(customer);
//6. Commit transaction
tx.commit();
//7. Release resources
entityManager.close();
factory.close();
}
6.JPA summary
-
Create project and add dependency
-
Create entity classes and create databases
-
Mapping JPA
- @Entity class mapping
- @The mapping parameter name of Table(name = "cst_customer") indicates the table name
- @Id / / mark an attribute as a primary key
- @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) / / generate the side column of the primary key
- @Column(name = "cust_id") / / map the attribute name to the table field. The parameter name represents the database field
-
Configure the core file of JPA
- File name: persistence xml
- Table of contents: META-INF
-
Test save a user
- Loading configuration file to create entity class management co warehouse
- Create entity class manager through factory
- Get transaction object
- Open transaction object
- Start transaction
- CRUD: save user
- Commit transaction
- Release resources
3. Introduction to the core API of JPA
1. Persistence importance: General
Function: used to load configuration files and create entity class manager factory
Main methods:
createEntityManagerFactory("Persistence unit name")
2. EntityManagerFactory importance: relatively important
Role: used to create entity class manager Common methods: createEntityManager() close() Details: 1,This class is a heavyweight class: it maintains all fields CRUD of sql Statement, L2 cache 2,This class is thread safe. Thread safe concurrency will not occur in a multithreaded environment use: One web The project should have only one such object
3. EntityManager importance: very important
Function: the interaction with the database is completed by him, and the transaction object is also obtained by him Common methods: getTransaction() persist() close find getReference .... Details: 1,Since the factory has maintained more information, this class maintains less information, so it is a lightweight object 2,He is thread unsafe use: A thread has only one object, one request
4. Importance of EntityTransaction: just use it
Role: control transactions Common methods: begin commit rollback
4. Tool class for extracting JPA: JpaUtil
public class JpaUtil {
private static EntityManagerFactory myJpa;
/*
* Static loading
* */
static {
myJpa = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("myJpa");
}
/*
* Entity class manager
* */
public static EntityManager getEntityManager(){
return myJpa.createEntityManager();
}
/*
* close resource
* */
public static void close(EntityManager entityManager){
if (entityManager!=null){
entityManager.close();
}
}
}
5. CRUD of JPA
1. Add data
/*
* Add package
* */
@Test
public void show(){
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setCustName("Xingjian, be good");
customer.setCustIevel("VIP");
EntityManager entityManager = JpaUtil.getEntityManager();
// //3. Get transaction object
EntityTransaction tx = entityManager.getTransaction();
//4. Open transaction
tx.begin();
//5. CRUD: save customer entity
entityManager.persist(customer);
//6. Commit transaction
tx.commit();
//7. Release resources
JpaUtil.close(entityManager);
}
2. Delete data
/*
* Delete data
* */
@Test
public void delete(){
//Get entity class manager
EntityManager entityManager = JpaUtil.getEntityManager();
// Get transaction object
EntityTransaction tx = entityManager.getTransaction();
//Open transaction
tx.begin();
Customer customer1 = entityManager.find(Customer.class, 1L);
entityManager.remove(customer1);
// Commit transaction
tx.commit();
//
JpaUtil.close(entityManager);
}
3. Update data
/*
* Update data
* */
@Test
public void update(){
// Gets the manager of the entity class
EntityManager entityManager = JpaUtil.getEntityManager();
// Get transaction object
EntityTransaction tx= entityManager.getTransaction();
// Open transaction
tx.begin();
//Query before updating
Customer customer = entityManager.find(Customer.class, 2L);
customer.setCustName("Here we are, brother");
entityManager.persist(customer);
// Commit transaction
tx.commit();
JpaUtil.close(entityManager);
}
4. Query data
/*
* Query all data
* */
@Test
public void findList(){
EntityManager entityManager = JpaUtil.getEntityManager();
Query query = entityManager.createQuery("from Customer");
List<Customer> resultList = query.getResultList();
resultList.forEach(o-> System.out.println("o = " + o));
}
/*
* Query data by id
* */
@Test
public void findById(){
// Gets the manager of the entity class
EntityManager entityManager = JpaUtil.getEntityManager();
//Query information according to id
Customer customer = entityManager.find(Customer.class, 2L);
System.out.println("customer = " + customer);
}
6.JPQL query
1.JPQL queries all data
@Test
public void show(){
EntityManager entityManager = JpaUtil.getEntityManager();
String sql="from Customer";
Query query = entityManager.createQuery(sql);
List resultList = query.getResultList();
resultList.forEach(o -> System.out.println("o = " + o));
}
2.JPQL paging query
JPA paging analysis:
mysql: limit ? Query the previous n items
limit ? ,?
First parameter: start index = (current page - 1) * page size
Second parameter: page size
/*
* paging
* */
@Test
public void show1(){
EntityManager entityManager = JpaUtil.getEntityManager();
Query query = entityManager.createQuery("from Customer ");
// Set paging condition: page size
query.setFirstResult(1); //(2-1)*2
query.setMaxResults(2);
List resultList = query.getResultList();
resultList.forEach(p-> System.out.println("p = " + p));
}
3.JPQL condition query
/*
* Multi condition query
* */
@Test
public void show5(){
EntityManager entityManager = JpaUtil.getEntityManager();
//Create query criteria
Query query = entityManager.createQuery("from Customer where custName like ? and custIevel= ? ");
query.setParameter(1,"Xingjian%");
query.setParameter(2,"VIP");
List resultList = query.getResultList();
resultList.forEach(o-> System.out.println("o = " + o));
}
/*
* Fuzzy query
* */
@Test
public void show4(){
EntityManager entityManager = JpaUtil.getEntityManager();
//Create query criteria
Query query = entityManager.createQuery("from Customer where custName like ?");
// Assign values to placeholders
query.setParameter(1,"Xingjian%");
List resultList = query.getResultList();
resultList.forEach(p-> System.out.println("p = " + p));
}
/*
* Precise query
* */
@Test
public void show3(){
EntityManager entityManager = JpaUtil.getEntityManager();
//Create query criteria
Query query = entityManager.createQuery("from Customer where custName= ?");
query.setParameter(1,"Here we are, brother");
List resultList = query.getResultList();
resultList.forEach(p-> System.out.println("p = " + p));
}
4.JPQL query: sorting, statistical query
/*
* sort
* */
@Test
public void show6(){
EntityManager entityManager = JpaUtil.getEntityManager();
Query query = entityManager.createQuery("from Customer where custName like ? order by custId desc");
query.setParameter(1,"Xingjian%");
List resultList = query.getResultList();
resultList.forEach(o-> System.out.println("o = " + o));
}
/**
* Statistics query: one row, one column: one number
*/
@Test
public void test5() {
EntityManager em = JpaUtil.getEntityManager();
EntityTransaction tx = em.getTransaction();
tx.begin();
//Statistics
/**
* select count(*) Approximately equal to count (1) mysql5 After 7
* select count(id)
* select count(1)
*/
Query query = em.createQuery("select avg(custId) from Customer where custName like ?");
//Assign values to placeholders
query.setParameter(1, "Xingjian%");
//Get result set
List<Double> list = query.getResultList();
//iteration
for (Double l : list) {
System.out.println("============================="+l);
}
}
2. Getting started with springdatejpa
1. Introduction to JPA
1. Import dependency
<properties>
<spring.version>5.0.2.RELEASE</spring.version>
<hibernate.version>5.0.7.Final</hibernate.version>
<slf4j.version>1.6.6</slf4j.version>
<log4j.version>1.2.12</log4j.version>
<c3p0.version>0.9.1.2</c3p0.version>
<mysql.version>5.1.18</mysql.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- junit unit testing -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- spring beg -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.6.8</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-orm</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- spring end -->
<!-- hibernate beg -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
<version>${hibernate.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-entitymanager</artifactId>
<version>${hibernate.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId>
<version>5.2.1.Final</version>
</dependency>
<!-- hibernate end -->
<!-- c3p0 beg -->
<dependency>
<groupId>c3p0</groupId>
<artifactId>c3p0</artifactId>
<version>${c3p0.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- c3p0 end -->
<!-- log end -->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>${log4j.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>${slf4j.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
<version>${slf4j.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- log end -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>${mysql.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- SpringDataJpa Core package -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-data-jpa</artifactId>
<version>1.9.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- el beg use spring data jpa Must be introduced -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.el</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.el-api</artifactId>
<version>2.2.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.glassfish.web</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.el</artifactId>
<version>2.2.4</version>
</dependency>
<!-- el end -->
<!--add to lombok-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.20</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2. Preparation of documents
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:jpa="http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa" xmlns:task="http://www.springframework.org/schema/task"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa/spring-jpa.xsd">
<!-- SpringDataJpa to configure -->
<!-- 1,EntityManagerFactory hand spring Administration-->
<bean id="entityManagerFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean">
<!-- 1,Scan packages for entity classes -->
<property name="packagesToScan" value="com.xjggb.pojo"></property>
<!-- 2,Reference data source -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
<!-- 3,to configure jpa Provider of -->
<property name="persistenceProvider">
<bean class="org.hibernate.jpa.HibernatePersistenceProvider"></bean>
</property>
<!-- 4,jpa Provider's adapter-->
<property name="jpaVendorAdapter">
<bean class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.vendor.HibernateJpaVendorAdapter">
<property name="generateDdl" value="false" />
<property name="database" value="MYSQL" />
<property name="databasePlatform" value="org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect" />
<property name="showSql" value="true" />
</bean>
</property>
<!-- 5,JPA dialect:have access to jpa Advanced features of -->
<property name="jpaDialect">
<bean class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.vendor.HibernateJpaDialect"></bean>
</property>
<!-- 6,Give Way hibenrate Maintenance table structure -->
<property name="jpaProperties">
<props>
<!--
create: Every time, delete the table first and then create the table
update: If there are changes and the attributes and fields are inconsistent, update the table; If there is no table, the table is created
none: It's the same as no configuration. Do nothing
-->
<prop key="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">create</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 2,Configure data sources -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://192.168.93.222:3306/day19"></property>
<property name="user" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="root"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 3,Platform transaction manager -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager">
<property name="entityManagerFactory" ref="entityManagerFactory"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 4,SpringDataJpa Configuration of
base-package: Base package: dao Package where the interface is located
entity-manager-factory-ref: Reference entity class manager factory
transaction-manager-ref: Platform transaction manager
-->
<jpa:repositories base-package="com.xjggb.mapper" entity-manager-factory-ref="entityManagerFactory" transaction-manager-ref="transactionManager"></jpa:repositories>
<!-- 5,Turn on scanning of components-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.xjggb"></context:component-scan>
</beans>
be careful
<!-- 6,Give Way hibenrate Maintenance table structure -->
<property name="jpaProperties">
<props>
<!--
create: Each time, delete the table before creating it
update: If there are changes and the attributes and fields are inconsistent, update the table; If there is no table, the table is created
none: It's the same as no configuration. Do nothing
-->
<prop key="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">create</prop>
</props>
</property>
3. Write entity class
package com.xjggb.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Entity
@Table(name="cst_customer")
@Data
public class Customer implements Serializable {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name="cust_id")
private Long custId;
@Column(name="cust_name")
private String custName;
@Column(name="cust_source")
private String custSource;
@Column(name="cust_industry")
private String custIndustry;
@Column(name="cust_level")
private String custLevel;
@Column(name="cust_address")
private String custAddress;
@Column(name="cust_phone")
private String custPhone;
}
4. Write Mapper interface
public interface CustomerMapper extends JpaRepository<Customer,Long>, JpaSpecificationExecutor<Customer> {
}
5. Test
//Specify operation period
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
//Load profile
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class JpaTest {
@Autowired
private CustomerMapper customerMapper;
/*
* Query an object
* */
@Test
public void show(){
Customer one = customerMapper.findOne(2L);
System.out.println("one = " + one);
}
}
2.JPA -CRUD
//Specify operation period
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
//Load profile
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class JpaTest2 {
@Autowired
private CustomerMapper customerMapper;
/*
* Add object
* */
@Test
public void show(){
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setCustName("sweet stewed snow pear");
customer.setCustLevel("Strong mouth King");
customerMapper.save(customer);
}
/*
* Delete data
* */
@Test
public void show1(){
customerMapper.delete(4L);
}
/*
* Update data
* */
@Test
public void show3(){
//Query before updating
Customer one = customerMapper.findOne(2L);
one.setCustName("My name is Xingjian Guaiba");
System.out.println("one = " + one);
customerMapper.save(one);
}
/*
* Query all data
* */
@Test
public void show4(){
//Query all data
List<Customer> all = customerMapper.findAll();
all.forEach(p-> System.out.println("p = " + p));
}
}
Summary
- Create maven project
- Write the spring configuration file ApplicationContext XML file
- Write annotations for configuration class jpa
- Write mapper interface to inherit two interfaces 1 Jparepository < entity class, primary key type > 2 Jpaspecificationexecutor < entity class >
- Test CRUD
3. Interface method definition query
1. Two ways to query a
/*
* Two ways to query a
* */
@Test
@Transactional
public void show(){
// Customer one = customerMapper.findOne(3L);// Load now
Customer one = customerMapper.getOne(3L);
System.out.println("one = " + one); //
}
2. Paging query + Sorting Query
/*
* Paging query
* */
@Test
public void show2(){
/*
* Paging query
* Parameter I current page
* Parameter 2 page size
* Parameter 3 sorting object [optional]
* */
PageRequest pageRequest = new PageRequest(2,2);
//Execute paging query
Page<Customer> all = customerMapper.findAll(pageRequest);
System.out.println("Get total records " + all.getTotalElements());
System.out.println("PageCount " + all.getTotalPages());
List<Customer> content = all.getContent();
for (Customer customer : content) {
System.out.println("customer = " + customer);
}
}
/*
* Paging query + Sorting Query
* */
@Test
public void show2(){
// Collation flashback
Sort orders = new Sort(Sort.Direction.DESC,"custId");
/*
* Paging query
* Parameter I current page
* Parameter 2 page size
* Parameter 3 sort object
* */
PageRequest pageRequest = new PageRequest(2,2,orders);
//Execute paging query
Page<Customer> all = customerMapper.findAll(pageRequest);
System.out.println("Get total records " + all.getTotalElements());
System.out.println("PageCount " + all.getTotalPages());
List<Customer> content = all.getContent();
for (Customer customer : content) {
System.out.println("customer = " + customer);
}
}
3. Query statistics and judge whether the object exists
/*
* Statistics all\
* This is equivalent to the select count(*) from table
* */
@Test
public void show4(){
long count = customerMapper.count();
System.out.println("count = " + count);
}
/*
* Determine whether an object exists
* The presence is true and the absence is false
* Equivalent to select * from table where id =?
* */
@Test
public void show3(){
boolean exists = customerMapper.exists(4L);
System.out.println("equals = " + exists);
}
4.JPQL query operation
1. Mode 1 query operation
Master @ Query annotation
JPQL query rules:
1)stay dao Write methods in the interface 2)Use on method@Query(value="JPQL sentence") 3)The return value is determined by yourself. If it is a single object, you write a single object. If there are multiple objects, you use List
mapper code
/*
* Precise query
* */
@Query(value="from Customer where custName= ?")
Customer findJPQL1(String l);
/*
*Fuzzy query
* */
@Query(value="from Customer where custName like ?")
List<Customer> findListJPQL(String s);
/*
* Multi condition query
* By default: all of the method parameters are consistent with the index of the placeholder. If the data types are inconsistent, an error will be reported
* We can change the index manually: just add the index of the method parameter after the placeholder
* */
@Query(value="from Customer where custId =?2 or custName like ?1")
List<Customer> findJPQL3(String o ,Long id);
test
package com.xjggb.test;
import com.xjggb.mapper.CustomerMapper;
import com.xjggb.pojo.Customer;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import java.util.List;
//Specify operation period
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
//Load profile
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class JpaTest4 {
@Autowired
private CustomerMapper customerMapper;
/*
* Precise query
* */
@Test
public void show2(){
Customer customer = customerMapper.findJPQL1("sweet stewed snow pear");
System.out.println("customer = " + customer);
}
/*
* Fuzzy query
* */
@Test
public void show(){
List<Customer> listJPQL = customerMapper.findListJPQL("Xingjian%");
listJPQL.forEach(u-> System.out.println("u = " + u));
System.out.println();
}
/*
*Multi condition query
* */
@Test
public void show3(){
List<Customer> jpql3 = customerMapper.findJPQL3("Xingjian%", 3L);
jpql3.forEach(o-> System.out.println("o = " + o));
System.out.println();
}
}
2. Method 2: query and update
Objective: to master how to use JPQL to update objects
dao interface requirements:
1) jpql statement of update written in the value attribute of Query
2) You need to add a comment on the method of dao interface: @ Modifying
Test requirements:
1) Transaction required
2) In the testing phase, if spring testing is used, it will be rolled back automatically after successful execution. If you see the effect, you need to add comments: @ Rollback(false)
mapper code
/*
* update operation
* */
@Modifying //Mark as update operation
@Query(value="update Customer set custName=?2 where custId=?1")
void updateJPQL(Long id ,String nmae);
Test code
/*
* update operation
* */
@Test
//Since we are now using the spring test, after the test is successful, spring rolls back to us
//In the test phase, if you want to see the results, you need to add another annotation. Note that this annotation does not need to be added in non test code
//TransactionRequiredException: Executing an update/delete query transaction exception
@Transactional
@Rollback(false)
public void show4(){
customerMapper.updateJPQL(2L,"Lao Wang next door");
}
3. Method 3: sql query
sql query rules
1)stay dao Write methods in the interface 2)Use on method@Query(value="SQL sentence",nativeQuery=true)nativeQuery=true open sql Statement query 3)The return value is determined by yourself. If it is a single object, you write a single object. If there are multiple objects, you use List
mapper code
/**
* sql query
* nativeQuery=true Open sql query
*/
@Query(value="select * from cst_customer where cust_name like ?2 or cust_id = ?1",nativeQuery=true)
public List<Customer> findSQL(Long id, String name);
Test code
/*
* sql query
* */
@Test
public void show5(){
List<Customer> sql = customerMapper.findSQL(3L, "Xingjian%");
sql.forEach(o-> System.out.println("o = " + o));
}
4. Method 4: query according to method name rules
Method name rule of Dao interface:
1)with findBy start 2)Followed by the attribute condition of the query: the initial letter of the attribute name is capitalized 3)The attribute name is followed by the query rule: fuzzy[ Like],Accurate [irregular represents accurate query] 4)Multiple conditions to And , Or Splicing 5)Repeat the above steps, starting from 2
mapper interface
// Precise query
Customer findByCustName(String name);
// Fuzzy query
List<Customer> findByCustNameLike(String name);
// Multi condition query
List<Customer> findByCustNameOrCustId(String name , Long id);
test
/*
* Multi condition query
* */
@Test
public void show8(){
List<Customer> p = customerMapper.findByCustNameOrCustId("sweet stewed snow pear", 8L);
p.forEach(o-> System.out.println("o = " + o));
}
/*
* Precise query
* */
@Test
public void show7(){
Customer o = customerMapper.findByCustName("sweet stewed snow pear");
System.out.println("o = " + o);
}
/*
* Fuzzy query
* */
@Test
public void show6(){
List<Customer> byCustNameLike = customerMapper.findByCustNameLike("Xingjian%");
byCustNameLike.forEach(o->System.out.println("byCustNameLike = " + o));
}
Keywords for rule:
| Keyword | Method name example | JPQL | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| And | findByLastnameAndFirstname | ... where x.lastname = ?1 and x.firstname = ?2 | ||
| Or | findByLastnameOrFirstname | ... where x.lastname = ?1 or x.firstname = ?2 | ||
| Is,Equals | findByFirstnameIs, findByFirstnameEquals | ... where x.firstname = ?1 | ||
| Between | findByStartDateBetween | ... where x.startDate between ?1 and ?2 | ||
| LessThan | findByAgeLessThan | ... where x.age < ?1 | ||
| LessThanEqual | findByAgeLessThanEqual | ... where x.age ⇐ ?1 | ||
| GreaterThan | findByAgeGreaterThan | ... where x.age > ?1 | ||
| GreaterThanEqual | findByAgeGreaterThanEqual | ... where x.age >= ?1 | ||
| After | findByStartDateAfter | ... where x.startDate > ?1 | ||
| Before | findByStartDateBefore | ... where x.startDate < ?1 | ||
| IsNull | findByAgeIsNull | ... where x.age is null | ||
| IsNotNull,NotNull | findByAge(Is)NotNull | ... where x.age not null | ||
| Like | findByFirstnameLike | ... where x.firstname like ?1 | ||
| NotLike | findByFirstnameNotLike | ... where x.firstname not like ?1 | ||
| StartingWith | findByFirstnameStartingWith | ... where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound with appended %) | ||
| EndingWith | findByFirstnameEndingWith | ... where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound with prepended %) | ||
| Containing | findByFirstnameContaining | ... where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound wrapped in %) | ||
| OrderBy | findByAgeOrderByLastnameDesc | ... where x.age = ?1 order by x.lastname desc | ||
| Not | findByLastnameNot | ... where x.lastname <> ?1 | ||
| In | findByAgeIn(Collection ages) | ... where x.age in ?1 | ||
| NotIn | findByAgeNotIn(Collection age) | ... where x.age not in ?1 | ||
| TRUE | findByActiveTrue() | ... where x.active = true | ||
| FALSE | findByActiveFalse() | ... where x.active = false | ||
| IgnoreCase | findByFirstnameIgnoreCase | ... where UPPER(x.firstame) = UPPER(?1) |
3. Introduction to specification dynamic query
Introduction to jpaspecification executor interface: complete complex query and dynamic query
JpaSpecificationExecutor<T> {
T findOne(Specification<T> spec);
List<T> findAll(Specification<T> spec);
Page<T> findAll(Specification<T> spec, Pageable pageable);
List<T> findAll(Specification<T> spec, Sort sort);
long count(Specification<T> spec);
}
Specification: it is an interface. All dynamic splicing conditions are completed in the method of this interface
public interface Specification<T> {
Predicate toPredicate(Root<T> root, CriteriaQuery<?> query, CriteriaBuilder cb);
}
It has only one method: toPredicate, which has three parameters
The first: Root: to get the properties of the object
The second: CriteriaQuery: the top-level interface of query. It can complete custom query, which is generally not used
The third: CriteriaBuilder: dynamically build query conditions and use it
1.Specification query: accurate, fuzzy and multi condition query
//Specify operation period
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
//Load profile
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class JpaTest5 {
@Autowired
private CustomerMapper customerMapper;
/*
* Multi condition query
* */
@Test
public void show(){
Specification<Customer> spec = new Specification<Customer>() {
@Override
public Predicate toPredicate(Root<Customer> root, CriteriaQuery<?> criteriaQuery, CriteriaBuilder cd) {
// Get comparison properties
Path<String> custName = root.get("custName");
Path<Object> custLevel = root.get("custLevel");
// Build query criteria
Predicate like = cd.like(custName, "Xingjian%");
Predicate equal = cd.equal(custLevel, "VIP");
// Merge query criteria
Predicate or = cd.or(like, equal);
return or;
}
};
List<Customer> all = customerMapper.findAll(spec);
all.forEach(o-> System.out.println("o = " + o));
}
}
2.Specification query: paging and sorting query
/*
* Paging sort
* */
@Test
public void show2(){
// Equivalent to where
Specification<Customer> spec =null;
// sort
Sort orders = new Sort(Sort.Direction.DESC,"custId");
// paging
PageRequest pageRequest = new PageRequest(0, 2, orders);
Page<Customer> all = customerMapper.findAll(spec, pageRequest);
System.out.println("Get total records " + all.getTotalElements());
System.out.println("Get pages" + all.getTotalPages());
all.getContent().forEach(o-> System.out.println("o = " + o));
}
4. One to many mapping
1. One to many one-way saving
1. Step 1
One to many using the carry in method
Customer table : One customer can have multiple contacts Contact list : One contact can only belong to one company
2. Step 2
Find the main foreign key
Multi party [slave table]: foreign keys are in multiple parties
Primary table of one party: the value of the foreign key comes from the primary key of one party
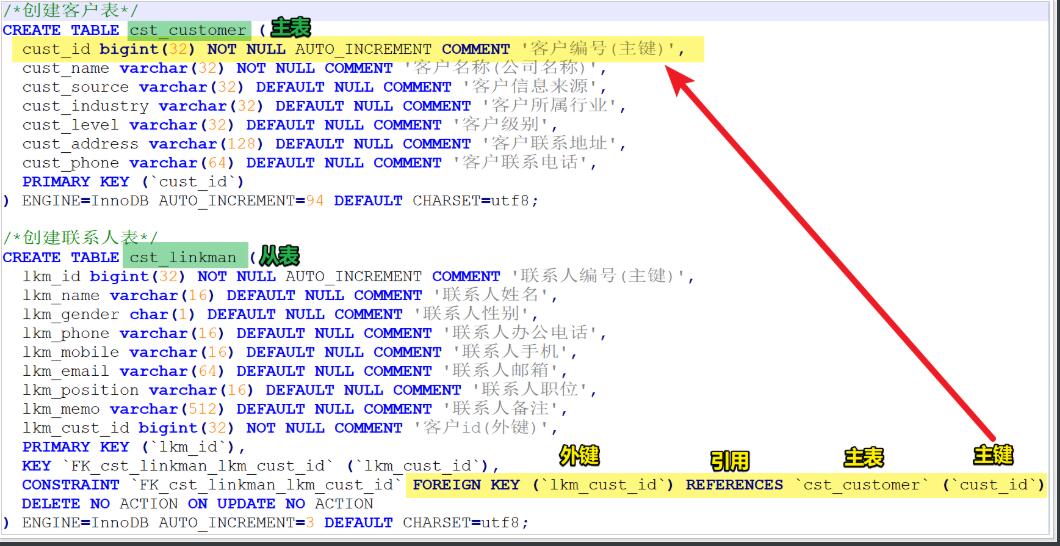
3. Step 3:
Describe their relationships in entity classes
Class to class relationships: Inheritance and inclusion
We use inclusion
Customer contains multiple contacts: List / Set
The contact contains a contact Customer
Customer entity class code
package com.xjggb.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
@Entity
@Table(name="cst_customer")
@Data
public class Customer implements Serializable {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name="cust_id")
private Long custId;
@Column(name="cust_name")
private String custName;
@Column(name="cust_source")
private String custSource;
@Column(name="cust_industry")
private String custIndustry;
@Column(name="cust_level")
private String custLevel;
@Column(name="cust_address")
private String custAddress;
@Column(name="cust_phone")
private String custPhone;
//Currently on one side
/**
* new :
* 1,If new finds the current method, the collection will also be instantiated
* 2,In order to solve the possible null pointer exception, new, we can specify the size of the new when new
*
* Not new:
* Containers are used to hold contact entities
* customer.getLinkman().add(new Linkman())
* Null pointer exception may occur
*
*/
// Configure one to many relationship annotations
//Configure one to many
@OneToMany(targetEntity = Linkman.class)
// Configure foreign key annotations
@JoinColumn(
// Foreign key name
name = "lkm_cust_id",
// Source of foreign key value: from the primary key of the primary table
referencedColumnName = "cust_id"
)
private Set<Linkman> linkmen=new HashSet<>(0);
}
Linkman contact entity class
package com.xjggb.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Entity
@Table(name = "cst_linkman")
@Data
public class Linkman implements Serializable {
@Id
@Column(name="lkm_id")
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long lkmId;
@Column(name="lkm_name")
private String lkmName;
@Column(name="lkm_gender")
private String lkmGender;
@Column(name="lkm_phone")
private String lkmPhone;
@Column(name="lkm_mobile")
private String lkmMobile;
@Column(name="lkm_email")
private String lkmEmail;
@Column(name="lkm_position")
private String lkmPosition;
@Column(name="lkm_memo")
private String lkmMemo;
//At present, there are many parties
// Relationship annotation many to one
@ManyToOne(targetEntity = Customer.class)
// Foreign key annotation
@JoinColumn(
// Foreign key name
name = "lkm_cust_id",
// Source of foreign key value: from the primary key of the main table
referencedColumnName = "cust_id"
)
private Customer customer;
}
4. Step 4
package com.xjggb.test;
import com.xjggb.mapper.CustomerMapper;
import com.xjggb.mapper.LinkmanMapper;
import com.xjggb.pojo.Customer;
import com.xjggb.pojo.Linkman;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.annotation.Rollback;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
//Specify operation period
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
//Load profile
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class JpaTest6 {
@Autowired
private CustomerMapper customerMapper;
@Autowired
private LinkmanMapper linkmanMapper;
/**
* One way save:
* One to many saving principle: save the data of the master table first, and then save the data of the slave table
*/
@Test
@Transactional
@Rollback(false)
public void show(){
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setCustName("Xingjian, be good");
Linkman linkman = new Linkman();
linkman.setLkmName("I'm Xingjian");
linkman.setLkmPosition("CEO");
//To have a value for a foreign key, you must configure the relationship:
//1. Let the customer maintain the relationship: the customer maintains the foreign key through the update statement
// customer.getLinkmen().add(linkman);
//2. Let the contact maintain foreign keys: the contact can maintain foreign keys through the insert statement [let the contact maintain foreign keys efficiently without the update statement]
linkman.setCustomer(customer);
//Save: save the data of the master table first, and then save the data of the slave table
// Save the data of the master table and save the number of slave tables
customerMapper.save(customer);
linkmanMapper.save(linkman);
}
}
2. One pair of two-way bao storage
analysis
If it is a two-way save, there will be two insert And one update Reason: the extra one update Statement, which is caused by the maintenance of foreign keys by customers solve: I don't want to see the extra one update Statement of Let customers do not maintain foreign keys delete@JoinColumn annotation
1. Customer entity
package com.xjggb.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* Entity class
* @author Johnny.Chen
*
*/
@Entity
@Table(name="cst_customer")
public class Customer implements Serializable{
@Id
@Column(name="cust_id")
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long custId;
@Column(name="cust_name")
private String custName;
@Column(name="cust_source")
private String custSource;
@Column(name="cust_level")
private String custLevel;
@Column(name="cust_industry")
private String custIndustry;
@Column(name="cust_phone")
private String custPhone;
@Column(name="cust_address")
private String custAddress;
//Currently on one side
/**
* new :
* 1,If new finds the current method, the collection will also be instantiated
* 2,In order to solve the possible null pointer exception, new, we can specify the size of the new when new
*
* Not new:
* Containers are used to hold contact entities
* customer.getLinkman().add(new Linkman())
* Null pointer exception may occur
*
*/
//Configure one to many relationship annotations
//Customer maintenance foreign key
/*//1,Relationship annotation: one to many
@OneToMany(targetEntity=Linkman.class)
//2,Foreign key annotation
@JoinColumn(
//Foreign key name
name="lkm_cust_id",
//Source of foreign key value: from the primary key of the primary table
referencedColumnName="cust_id"
)*/
//The customer does not maintain foreign keys
@OneToMany(mappedBy="customer")//mappedBy: the name of the attribute with @ JoinColumn annotation on the other side of the configuration
private Set<Linkman> linkmans = new HashSet<>(0);
/**
* obtain
* @return custId
*/
public Long getCustId() {
return custId;
}
/**
* set up
* @param custId
*/
public void setCustId(Long custId) {
this.custId = custId;
}
/**
* obtain
* @return custName
*/
public String getCustName() {
return custName;
}
/**
* set up
* @param custName
*/
public void setCustName(String custName) {
this.custName = custName;
}
/**
* obtain
* @return custSource
*/
public String getCustSource() {
return custSource;
}
/**
* set up
* @param custSource
*/
public void setCustSource(String custSource) {
this.custSource = custSource;
}
/**
* obtain
* @return custLevel
*/
public String getCustLevel() {
return custLevel;
}
/**
* set up
* @param custLevel
*/
public void setCustLevel(String custLevel) {
this.custLevel = custLevel;
}
/**
* obtain
* @return custIndustry
*/
public String getCustIndustry() {
return custIndustry;
}
/**
* set up
* @param custIndustry
*/
public void setCustIndustry(String custIndustry) {
this.custIndustry = custIndustry;
}
/**
* obtain
* @return custPhone
*/
public String getCustPhone() {
return custPhone;
}
/**
* set up
* @param custPhone
*/
public void setCustPhone(String custPhone) {
this.custPhone = custPhone;
}
/**
* obtain
* @return custAddress
*/
public String getCustAddress() {
return custAddress;
}
/**
* set up
* @param custAddress
*/
public void setCustAddress(String custAddress) {
this.custAddress = custAddress;
}
/**
* obtain
* @return linkmans
*/
public Set<Linkman> getLinkmans() {
return linkmans;
}
/**
* set up
* @param linkmans
*/
public void setLinkmans(Set<Linkman> linkmans) {
this.linkmans = linkmans;
}
}
2. Contact entity class
package com.xjggb.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* contacts
* @author Johnny.Chen
*
*/
@Entity
@Table(name="cst_linkman")
public class Linkman implements Serializable{
@Id
@Column(name="lkm_id")
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long lkmId;
@Column(name="lkm_name")
private String lkmName;
@Column(name="lkm_gender")
private String lkmGender;
@Column(name="lkm_phone")
private String lkmPhone;
@Column(name="lkm_mobile")
private String lkmMobile;
@Column(name="lkm_email")
private String lkmEmail;
@Column(name="lkm_position")
private String lkmPosition;
@Column(name="lkm_memo")
private String lkmMemo;
//At present, there are many parties
//1. Relationship annotation: many to one
@ManyToOne(targetEntity=Customer.class)
//2. Foreign key annotation
@JoinColumn(
//Foreign key name
name="lkm_cust_id",
//Source of foreign key value: from the primary key of the primary table
referencedColumnName="cust_id"
)
private Customer customer;
/**
* obtain
* @return lkmId
*/
public Long getLkmId() {
return lkmId;
}
/**
* set up
* @param lkmId
*/
public void setLkmId(Long lkmId) {
this.lkmId = lkmId;
}
/**
* obtain
* @return lkmName
*/
public String getLkmName() {
return lkmName;
}
/**
* set up
* @param lkmName
*/
public void setLkmName(String lkmName) {
this.lkmName = lkmName;
}
/**
* obtain
* @return lkmGender
*/
public String getLkmGender() {
return lkmGender;
}
/**
* set up
* @param lkmGender
*/
public void setLkmGender(String lkmGender) {
this.lkmGender = lkmGender;
}
/**
* obtain
* @return lkmPhone
*/
public String getLkmPhone() {
return lkmPhone;
}
/**
* set up
* @param lkmPhone
*/
public void setLkmPhone(String lkmPhone) {
this.lkmPhone = lkmPhone;
}
/**
* obtain
* @return lkmMobile
*/
public String getLkmMobile() {
return lkmMobile;
}
/**
* set up
* @param lkmMobile
*/
public void setLkmMobile(String lkmMobile) {
this.lkmMobile = lkmMobile;
}
/**
* obtain
* @return lkmEmail
*/
public String getLkmEmail() {
return lkmEmail;
}
/**
* set up
* @param lkmEmail
*/
public void setLkmEmail(String lkmEmail) {
this.lkmEmail = lkmEmail;
}
/**
* obtain
* @return lkmPosition
*/
public String getLkmPosition() {
return lkmPosition;
}
/**
* set up
* @param lkmPosition
*/
public void setLkmPosition(String lkmPosition) {
this.lkmPosition = lkmPosition;
}
/**
* obtain
* @return lkmMemo
*/
public String getLkmMemo() {
return lkmMemo;
}
/**
* set up
* @param lkmMemo
*/
public void setLkmMemo(String lkmMemo) {
this.lkmMemo = lkmMemo;
}
/**
* obtain
* @return customer
*/
public Customer getCustomer() {
return customer;
}
/**
* set up
* @param customer
*/
public void setCustomer(Customer customer) {
this.customer = customer;
}
}
3. Test
package com.xjggb.test;
import com.xjggb.mapper.CustomerMapper;
import com.xjggb.mapper.LinkmanMapper;
import com.xjggb.pojo.Customer;
import com.xjggb.pojo.Linkman;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.annotation.Rollback;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
//Specify operation period
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
//Load profile
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class JpaTest6 {
@Autowired
private CustomerMapper customerMapper;
@Autowired
private LinkmanMapper linkmanMapper;
/*
* Bidirectional binding
* */
/**
* Bidirectional save:
* One to many saving principle: save the data of the master table first, and then save the data of the slave table
*
* You know me, and I know you
*/
@Test
//To resolve the exception: join the transaction first
@Transactional
//Because during the test phase, spring rolls back
@Rollback(false)
public void test() {
Customer c = new Customer();
c.setCustName("Akagi tempered glass company");
Linkman l = new Linkman();
l.setLkmName("Qingzi");
l.setLkmPosition("CEO");
//To have a value for a foreign key, you must configure the relationship: bidirectional
c.getLinkmans().add(l);
l.setCustomer(c);
//Save: save the data of the master table first, and then save the data of the slave table
customerMapper.save(c);
linkmanMapper.save(l);
}
}
3. One to many deletion
1) No data reference from the table: delete casually
2) There are slave table data
a. Under the default [maintain foreign keys by both parties], it will set the foreign key field to null, and then delete the main table data. If there is a non NULL constraint on the foreign key field in the table structure of the database, an error will be reported by default.
b. If it is configured to give up the right to maintain the association relationship, it cannot be deleted (it has nothing to do with whether the foreign key field is allowed to be null), because it will not update the foreign key field of the slave table at all.
c. If you also want to delete, use cascading to delete references
- Configure where you operate [we delete the customer, so configure it on the customer side and cascade it in the relationship annotation]
- Use with caution
1. Entity class configuration
package com.xjggb.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* Entity class
* @author Johnny.Chen
*
*/
@Entity
@Table(name="cst_customer")
public class Customer implements Serializable{
@Id
@Column(name="cust_id")
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long custId;
@Column(name="cust_name")
private String custName;
@Column(name="cust_source")
private String custSource;
@Column(name="cust_level")
private String custLevel;
@Column(name="cust_industry")
private String custIndustry;
@Column(name="cust_phone")
private String custPhone;
@Column(name="cust_address")
private String custAddress;
//Currently on one side
/**
* new :
* 1,If new finds the current method, the collection will also be instantiated
* 2,In order to solve the possible null pointer exception, new, we can specify the size of the new when new
*
* Not new:
* Containers are used to hold contact entities
* customer.getLinkman().add(new Linkman())
* Null pointer exception may occur
*
*/
//Configure one to many relationship annotations
//Customer maintenance foreign key
/*//1,Relationship annotation: one to many
@OneToMany(targetEntity=Linkman.class)
//2,Foreign key annotation
@JoinColumn(
//Foreign key name
name="lkm_cust_id",
//Source of foreign key value: from the primary key of the primary table
referencedColumnName="cust_id"
)*/
//The customer does not maintain foreign keys
@OneToMany(
mappedBy="customer",//mappedBy: the name of the attribute with @ JoinColumn annotation on the other side of the configuration
cascade = CascadeType.ALL//Cascade save update delete
)
private Set<Linkman> linkmans = new HashSet<>(0);
/**
* obtain
* @return custId
*/
public Long getCustId() {
return custId;
}
/**
* set up
* @param custId
*/
public void setCustId(Long custId) {
this.custId = custId;
}
/**
* obtain
* @return custName
*/
public String getCustName() {
return custName;
}
/**
* set up
* @param custName
*/
public void setCustName(String custName) {
this.custName = custName;
}
/**
* obtain
* @return custSource
*/
public String getCustSource() {
return custSource;
}
/**
* set up
* @param custSource
*/
public void setCustSource(String custSource) {
this.custSource = custSource;
}
/**
* obtain
* @return custLevel
*/
public String getCustLevel() {
return custLevel;
}
/**
* set up
* @param custLevel
*/
public void setCustLevel(String custLevel) {
this.custLevel = custLevel;
}
/**
* obtain
* @return custIndustry
*/
public String getCustIndustry() {
return custIndustry;
}
/**
* set up
* @param custIndustry
*/
public void setCustIndustry(String custIndustry) {
this.custIndustry = custIndustry;
}
/**
* obtain
* @return custPhone
*/
public String getCustPhone() {
return custPhone;
}
/**
* set up
* @param custPhone
*/
public void setCustPhone(String custPhone) {
this.custPhone = custPhone;
}
/**
* obtain
* @return custAddress
*/
public String getCustAddress() {
return custAddress;
}
/**
* set up
* @param custAddress
*/
public void setCustAddress(String custAddress) {
this.custAddress = custAddress;
}
/**
* obtain
* @return linkmans
*/
public Set<Linkman> getLinkmans() {
return linkmans;
}
/**
* set up
* @param linkmans
*/
public void setLinkmans(Set<Linkman> linkmans) {
this.linkmans = linkmans;
}
public String toString() {
return "Customer{custId = " + custId + ", custName = " + custName + ", custSource = " + custSource + ", custLevel = " + custLevel + ", custIndustry = " + custIndustry + ", custPhone = " + custPhone + ", custAddress = " + custAddress + ", linkmans = " + linkmans + "}";
}
}
2. Test
package com.xjggb.test;
import com.xjggb.mapper.CustomerMapper;
import com.xjggb.pojo.Customer;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.annotation.Rollback;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
//Specify operation period
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
//Load profile
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class JpaTest7 {
@Autowired
private CustomerMapper customerMapper;
@Test
@Transactional
@Rollback(false)
public void show(){
//a. Under the default [maintain foreign keys by both parties], it will set the foreign key field to null, and then delete the main table data. If there is a non NULL constraint on the foreign key field in the database table structure, an error will be reported by default.
//b. If it is configured to give up the right to maintain the association relationship, it cannot be deleted (it has nothing to do with whether the foreign key field is allowed to be null), because it will not update the foreign key field of the slave table at all.
//c. If you also want to delete, use cascading to delete references
/**
* Cascade operation:
* When we operate an object, let the code secretly operate another object in the background
* Cascade delete:
* When we delete a customer, let the code delete its associated contact attribute first, and then delete the main table data
*
* Configuration cascade: [use with caution] [Zhulian nine families]
* 1,We configure cascades where we operate. We delete customers now, so we configure cascades where customers are
* 2,Configure cascading in relationship annotations:
* @OneToMany(cascade=CascadeType.ALL) Cascade save update delete
* @OneToMany(cascade=CascadeType.PERSIST) Cascade save
* @OneToMany(cascade=CascadeType.MERGE) update cascade
* @OneToMany(cascade=CascadeType.REMOVE) cascading deletion
*
*/
customerMapper.delete(1L);
}
}
Summary
1. Relationship notes:
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "attribute name with @ JoinColumn annotation on the other side", targeenity = "", cascade = "")
@ManyToOne(targeEntity="",cascade = "") / / mappedBy cannot be configured. You cannot give up your foreign key maintenance
2. Maintain foreign key annotation: whoever has it can maintain foreign keys
@JoinColumn(name = "foreign key name", referenceColumnName = "primary key name of main table")
3. Operations: save and delete
Key point finding foreign key
5. Many to many mapping
1. Many to many save
1. Step 1
User: a user can have multiple roles
Role: you can have multiple users
Many to many relationship
2. Step 2
Find the middle table
User table
Role table
Intermediate table of user role, two columns, primary key of source user table and role table, and joint primary key
3. Step 3
A user has multiple roles:
A role contains multiple users:
User entity class
package com.xjggb.pojo;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
/**
*
* @author Johnny.Chen
*
*/
@Entity
//@Table(name="User") / / if the table name is the same as the class name, it can be omitted
public class User implements Serializable {
@Id
//@Column(name="userId") / / if the field name is the same as the property name, it can be omitted
@GeneratedValue(strategy= GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer userId;
private String name;
private String age;
private String pwd;
//A user contains multiple roles
// Relational annotation configuration many to many
@ManyToMany(targetEntity = Role.class)
// Maintain intermediate table notes
@JoinTable(
name = "T_user_Role_Ref" , //Intermediate table name
// Foreign key of the current intermediate table
joinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "u_id",referencedColumnName = "userId"),
// Foreign key of the opposite party in the middle table
inverseJoinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "r_id",referencedColumnName = "roleId")
)
private Set<Role> roles = new HashSet<>(0);
public Set<Role> getRoles() {
return roles;
}
public void setRoles(Set<Role> roles) {
this.roles = roles;
}
public Integer getUserId() {
return userId;
}
public void setUserId(Integer userId) {
this.userId = userId;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(String age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getPwd() {
return pwd;
}
public void setPwd(String pwd) {
this.pwd = pwd;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [userId=" + userId + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", pwd=" + pwd + "]";
}
}
Role class
package com.xjggb.pojo;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
@Entity
public class Role {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy= GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer roleId;
private String roleName;
//
// //A role contains multiple users
// @ManyToMany(targetEntity =User.class )
Maintain intermediate table notes
// @JoinTable(
// name = "T_user_Role_Ref", / / intermediate table name
Foreign key of the current intermediate table
// joinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "r_id",referencedColumnName = "roleId"),
Foreign key of the opposite party in the middle table
// inverseJoinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "u_id",referencedColumnName = "userId")
@ManyToMany(
mappedBy = "roles",
cascade = CascadeType.ALL //Cascade operation
)
private Set<User> users = new HashSet<>(0);
public Set<User> getUsers() {
return users;
}
public void setUsers(Set<User> users) {
this.users = users;
}
public Integer getRoleId() {
return roleId;
}
public void setRoleId(Integer roleId) {
this.roleId = roleId;
}
public String getRoleName() {
return roleName;
}
public void setRoleName(String roleName) {
this.roleName = roleName;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Role [roleId=" + roleId + ", roleName=" + roleName + "]";
}
}
4. Step 4
test
package com.xjggb.test;
import com.xjggb.mapper.CustomerMapper;
import com.xjggb.mapper.RoleMapper;
import com.xjggb.mapper.UserMapper;
import com.xjggb.pojo.Customer;
import com.xjggb.pojo.Role;
import com.xjggb.pojo.User;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.annotation.Rollback;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
//Specify operation period
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
//Load profile
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class JpaTest8 {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Autowired
private RoleMapper roleMapper;
/*
*
* */
@Test
@Transactional
@Rollback(false)
public void show(){
User user = new User();
user.setName("Mitsui Shou");
Role role = new Role();
role.setRoleName("dentist");
// Anyone who gives up can maintain an intermediate table with only one table, otherwise the error Duplicate entry '1-1' for key 'PRIMARY' will be reported
role.getUsers().add(user);
user.getRoles().add(role);
userMapper.save(user);
roleMapper.save(role);
}
}
2. Many to many deletion
Entity class
package com.xjggb.pojo;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
@Entity
public class Role {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy= GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer roleId;
private String roleName;
//
// //A role contains multiple users
// @ManyToMany(targetEntity =User.class )
Maintain intermediate table notes
// @JoinTable(
// name = "T_user_Role_Ref", / / middle table name
Foreign key of the current intermediate table
// joinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "r_id",referencedColumnName = "roleId"),
Foreign key of the other party in the middle table
// inverseJoinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "u_id",referencedColumnName = "userId")
@ManyToMany(
mappedBy = "roles",
cascade = CascadeType.ALL //Cascade operation
)
private Set<User> users = new HashSet<>(0);
public Set<User> getUsers() {
return users;
}
public void setUsers(Set<User> users) {
this.users = users;
}
public Integer getRoleId() {
return roleId;
}
public void setRoleId(Integer roleId) {
this.roleId = roleId;
}
public String getRoleName() {
return roleName;
}
public void setRoleName(String roleName) {
this.roleName = roleName;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Role [roleId=" + roleId + ", roleName=" + roleName + "]";
}
}
test
package com.xjggb.test;
import com.xjggb.mapper.CustomerMapper;
import com.xjggb.mapper.RoleMapper;
import com.xjggb.mapper.UserMapper;
import com.xjggb.pojo.Customer;
import com.xjggb.pojo.Role;
import com.xjggb.pojo.User;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.annotation.Rollback;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
//Specify operation period
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
//Load profile
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class JpaTest8 {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Autowired
private RoleMapper roleMapper;
/**
* delete
*/
@Test
//To resolve the exception: join the transaction first
@Transactional
//Because during the test phase, spring rolls back
@Rollback(false)
public void test3() {
//roleDao.delete(1); // If you have configured to discard the maintenance of intermediate tables, you cannot delete them
/**
* Cascade:
* 1)Unidirectional cascade:
* 2)Two way cascade: the relationship annotations on both sides are configured with cascade [disable] and [no grass]
*/
roleMapper.delete(1); //If you have configured to discard the maintenance of intermediate tables, you cannot delete them by default. If you have configured cascading, you can delete them
//At work: delete the user first, and then delete the role
/*userDao.delete(1);
roleDao.delete(1);*/
}
/*
*
* */
@Test
@Transactional
@Rollback(false)
public void show(){
User user = new User();
user.setName("Mitsui Shou");
Role role = new Role();
role.setRoleName("dentist");
// Anyone who gives up can maintain an intermediate table with only one table, otherwise the error Duplicate entry '1-1' for key 'PRIMARY' will be reported
role.getUsers().add(user);
user.getRoles().add(role);
userMapper.save(user);
roleMapper.save(role);
}
}
6. Object navigation query
Object navigation query: call management attribute query when managing objects
1) Query contact through customer navigation: customer getLinkmen() :
- The default is delayed loading
- You can change to load immediately: configure the fetch attribute in the relationship annotation
2) Contact navigation query customer: linkman getCustomer()
- The default is load now
- You can change to deferred loading: configure the fetch attribute in the relationship annotation
//The customer does not maintain foreign keys
@OneToMany(
mappedBy="customer",//mappedBy: the name of the attribute with @ JoinColumn annotation on the other side of the configuration
cascade = CascadeType.ALL//Cascade save update delete
,fetch = FetchType.EAGER //Configure immediate load LAZY load EAGER immediate load
)
The code is as follows
@Test
//To resolve the exception: join the transaction first
@Transactional
//Because during the test phase, spring rolls back
@Rollback(false)
public void show(){
//Query customer default delayed loading through contact navigation
//Query contact through customer navigation: lazy loading
Customer one = customerMapper.findOne(1L);//Check the customer first
System.out.println("one = " + one);
Set<Linkman> linkmans = one.getLinkmans();//Check the contact again
//iteration
for (Linkman linkman : linkmans) {
System.out.println(linkman);
}
}
summary
-
Introduction to jpa CRUD
-
Extraction of jpa tools
-
Interface method definition query
-
Use of Specification query
-
Mapping of one to many queries
-
Many to many mapping