JS advanced part
- judge
- Object reference type
- Research on undefined and null
- Distinguish between variable types and data types
- Data, variables and memory
- js function parameters are passed as values
- How does JS engine manage memory
- JS object
- JS function object
- this point in JS function
- JS semicolon problem
- Prototype object of function
- Display prototype and implicit prototype
- Prototype chain
- Attribute problem of prototype chain
- How is instanceOf judged
- summary
-
-
- Function object is the instance object of function, which also has implicit prototype properties, but generally we say that the instance object does not include function object
- The implicit prototype of an instance object points to the display prototype of the constructor object that constructs the instance object
- All the functions we define are instances of the Object constructor, except the Object itself
- The function constructor is used to construct the Object constructor Object, so the implicit prototype of the Object constructor Object points to fuction, and its display prototype is not function
- Test questions
-
- Variable promotion and function promotion
- Execution context
- Execution stack
- Scope
- closure
- JS object creation method
- inherit
- JS is single threaded
- Event cycle model
- Web Worker implements multithreading
- summary
judge

- instanceof is used to distinguish the specific types of objects, because all objects belong to Object type
- typeof returns a string
- "= =" will first try to convert the variables at both ends to the same type, and then compare; "= = =" It will directly compare whether the types are the same. If the types are the same, it will continue to compare whether the values are the same.
Object reference type

Both function objects and array objects belong to object objects. Object objects are a large range, and the latter two are two special objects
Research on undefined and null


Distinguish between variable types and data types

Data, variables and memory




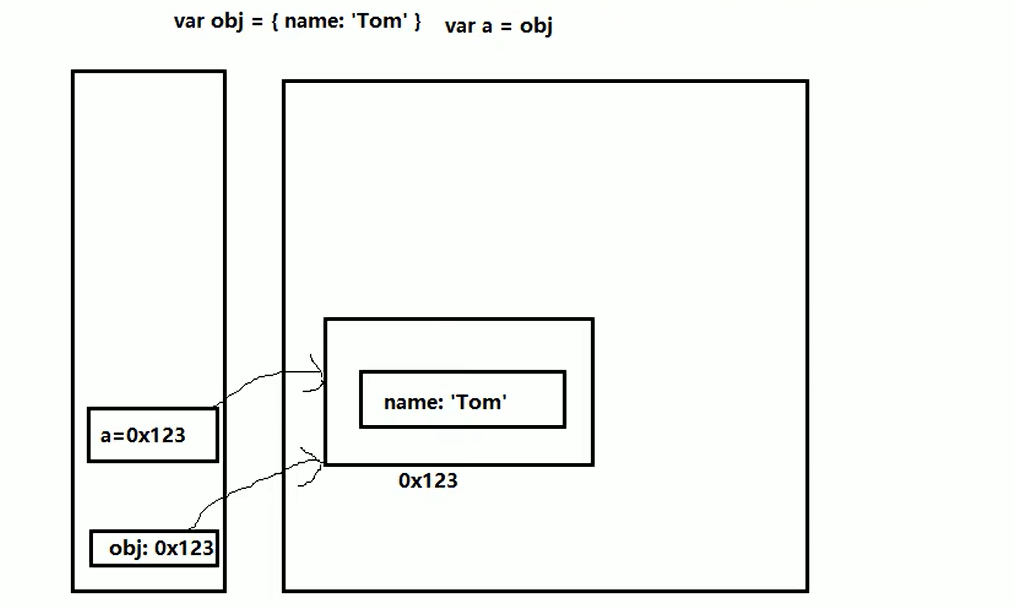
js function parameters are passed as values
When a parameter of basic type is passed in: it is just a copy of the content
When a reference type parameter is passed in: the address of the reference type parameter is copied
How does JS engine manage memory

JS object


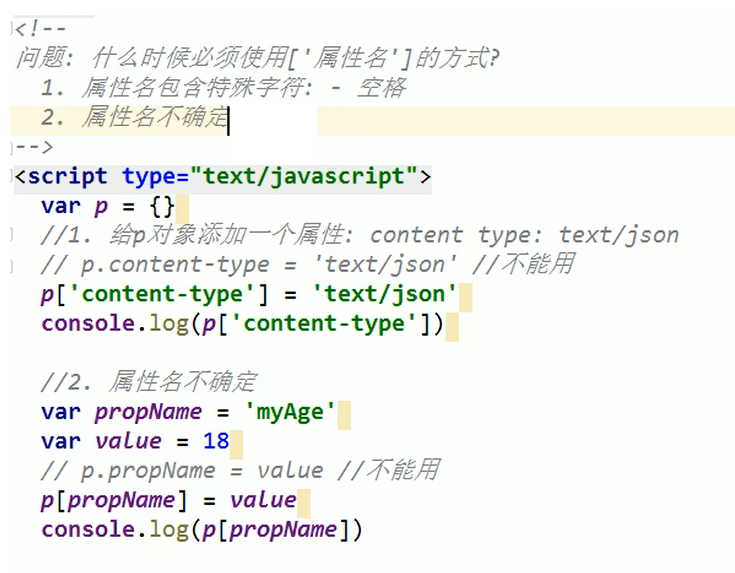
When to use ['attribute name'] and when to use it
JS function object

The difference between call and apply
Callback function

Execute function now


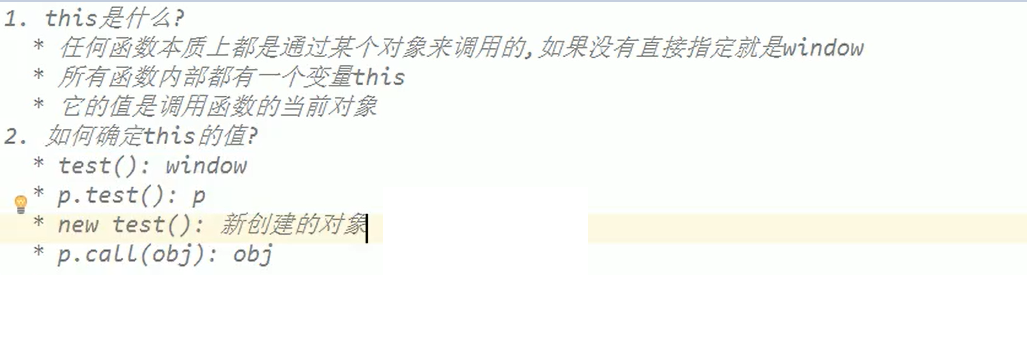
this point in JS function
JS semicolon problem


Prototype object of function


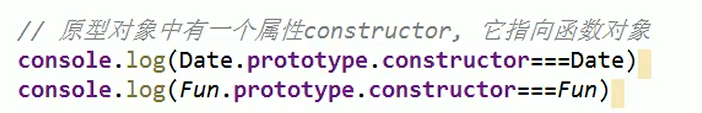

Display prototype and implicit prototype
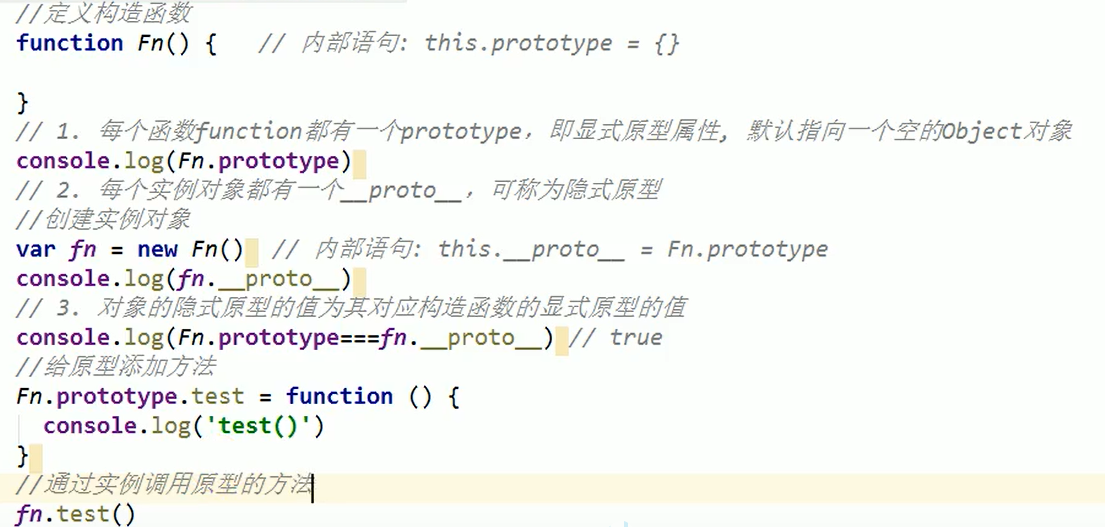
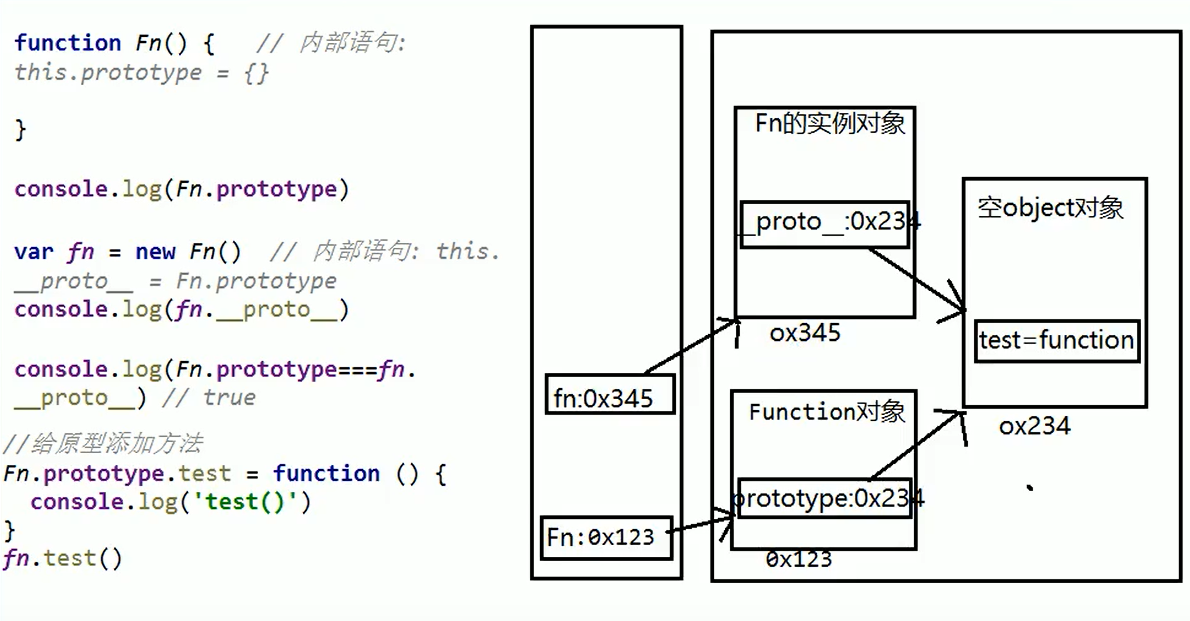

Prototype chain
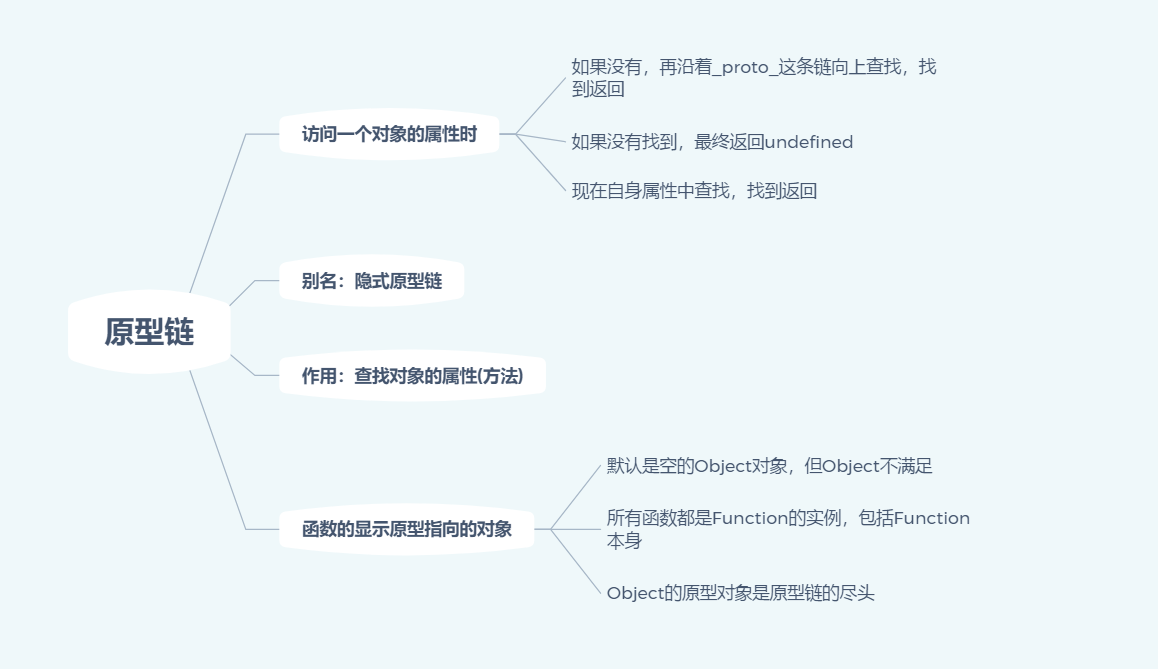
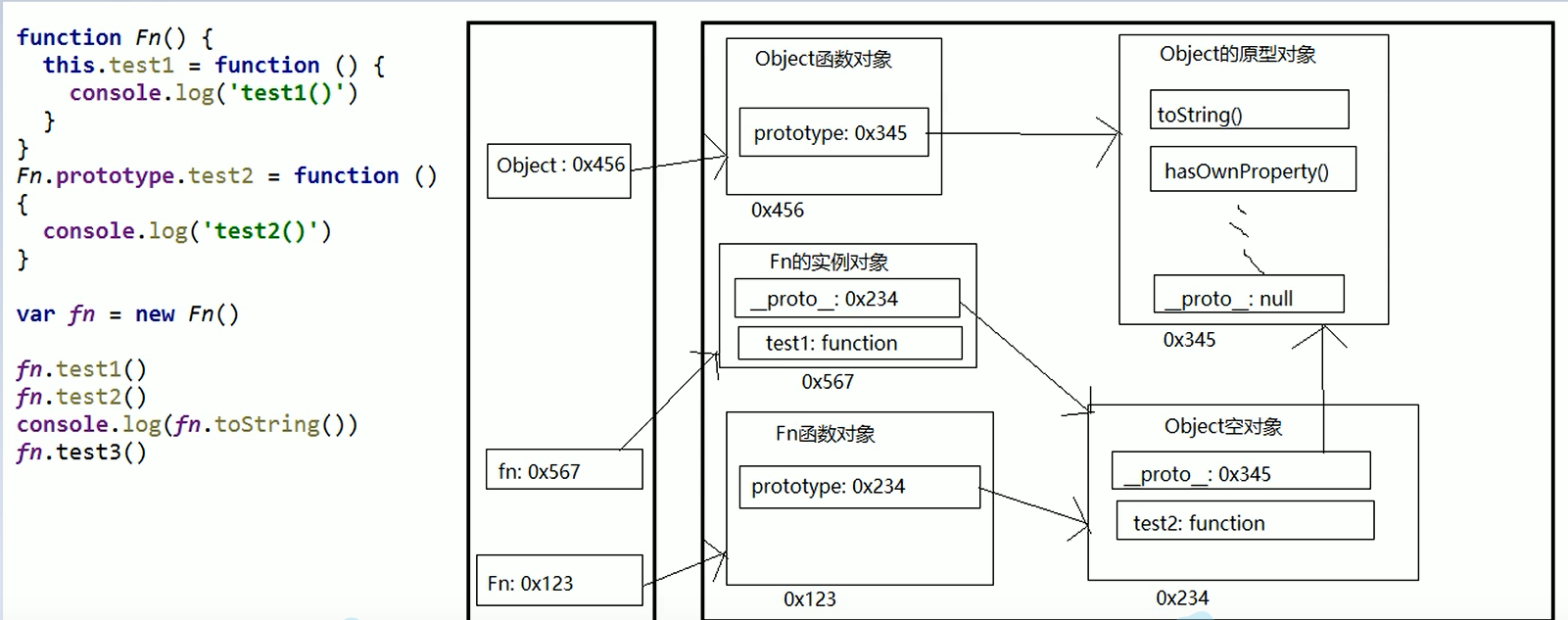


Attribute problem of prototype chain

The prototype chain is used to find attributes. Unless you add attributes to the prototype chain, setting the attribute value of the object will not take care of the prototype chain
How is instanceOf judged

summary
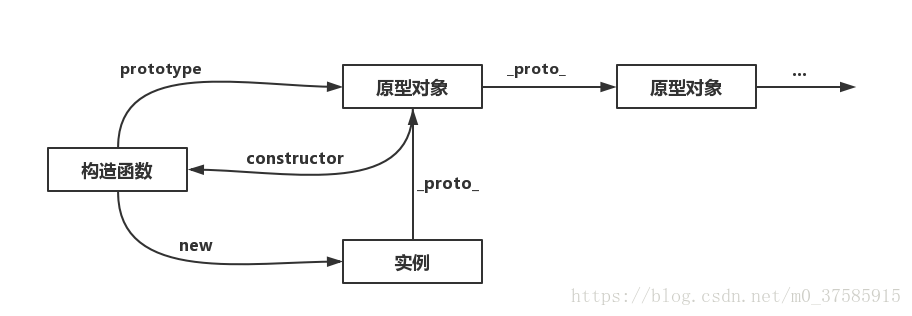
Prototype:
When talking about prototypes, we should first remember the following points, which are the key to understanding prototypes: 1,All reference types (arrays, functions, objects) can freely extend attributes (except null Other than). 2,All reference types have one'_ _ proto_ _'attribute(Also called implicit prototype, it is an ordinary object). 3,All functions have one'prototype'attribute(This is also called explicit prototyping. It is also a common object). 4,All reference types, its'_ _ proto_ _'Property points to its constructor'prototype'Properties. 5,When trying to get the property of an object, if the property does not exist in the object itself, Then I'll go to it'_ _ proto_ _'attribute(That is, its constructor'prototype'attribute)Look in the. 6.Any object has one constructor Property to the constructor that created this object 7.In prototype objects constructor Property, which also points to the constructor of the function object
Prototype chain:
When trying to get the property of an object, if the property does not exist in the object itself, Then I'll go to its constructor'prototype'Property. That's because'prototype'Property is an object,That is, the prototype object, so it also has one'_ _ proto_ _'Properties.
For example:
// Constructor
function Foo(name,age){
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
}
Object.prototype.toString=function(){
//What this is depends on who called this function during execution.
console.log("I'm "+this.name+" And I'm "+this.age);
}
var fn=new Foo('Xiao Ming',19);
fn.toString(); //I'm Xiao Ming And I'm 19
console.log(fn.toString===Foo.prototype.__proto__.toString); //true
console.log(fn.__proto__ ===Foo.prototype)//true
console.log(Foo.prototype.__proto__===Object.prototype)//true
console.log(Object.prototype.__proto__===null)//true
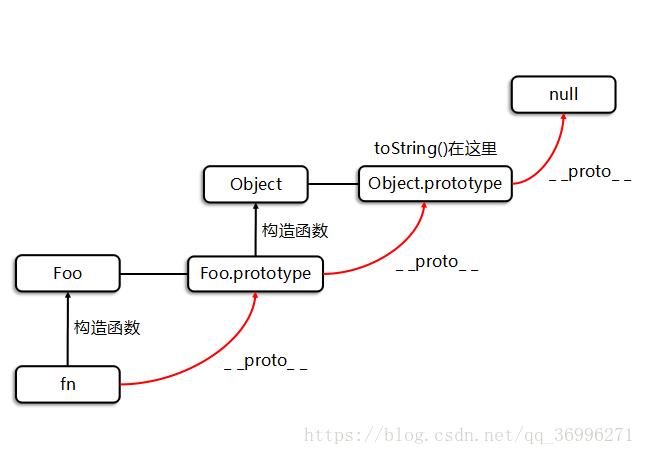
first, fn The constructor for is Foo(). So: fn._ _ proto _ _=== Foo.prototype And because Foo.prototype Is an ordinary object whose constructor is Object,So: Foo.prototype._ _ proto _ _=== Object.prototype Through the above code, we know this toString()The way is to Object.prototype Inside, When calling a method that does not exist in the object itself, it will look up layer by layer until null until. So when fn call toString()When, JS find fn There was no such method, so it went Foo.prototype Look for it in the, Find that there is still no such method, and then go Object.prototype Find it in, and call it when you find it Object.prototype Medium toString()method. This is the prototype chain, fn Can call Object.prototype Because of the mechanism of prototype chain. In addition, when using prototypes, it is generally recommended to write the methods to be extended in the constructor prototype Property, avoid writing in_ _ proto _ _Properties.
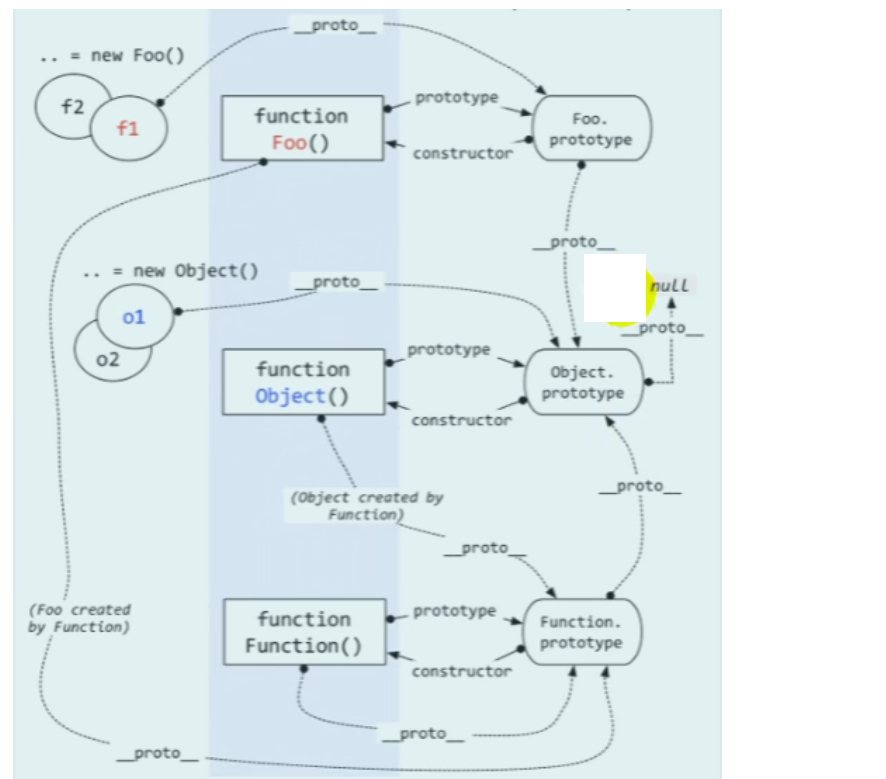
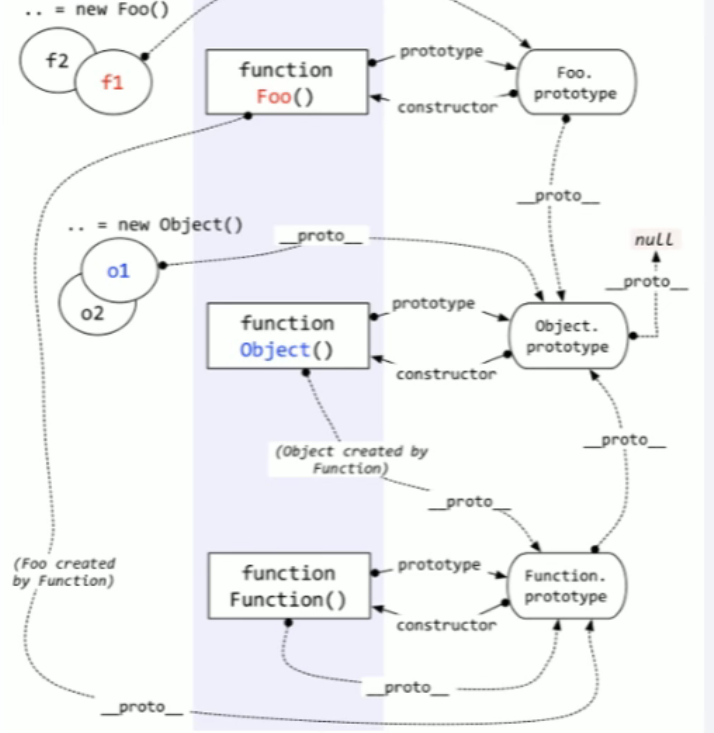
Function object is the instance object of function, which also has implicit prototype properties, but generally we say that the instance object does not include function object
The implicit prototype of an instance object points to the display prototype of the constructor object that constructs the instance object
All the functions we define are instances of the Object constructor, except the Object itself
The function constructor is used to construct the Object constructor Object, so the implicit prototype of the Object constructor Object points to fuction, and its display prototype is not function
Test questions
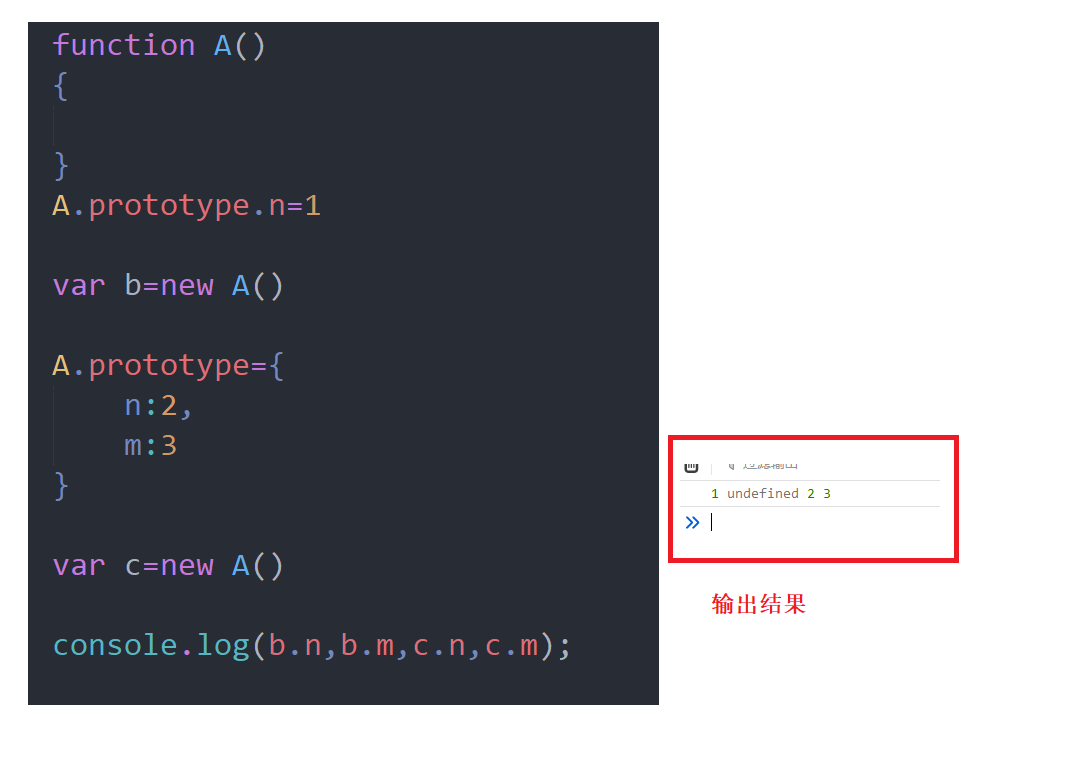
Explanation:
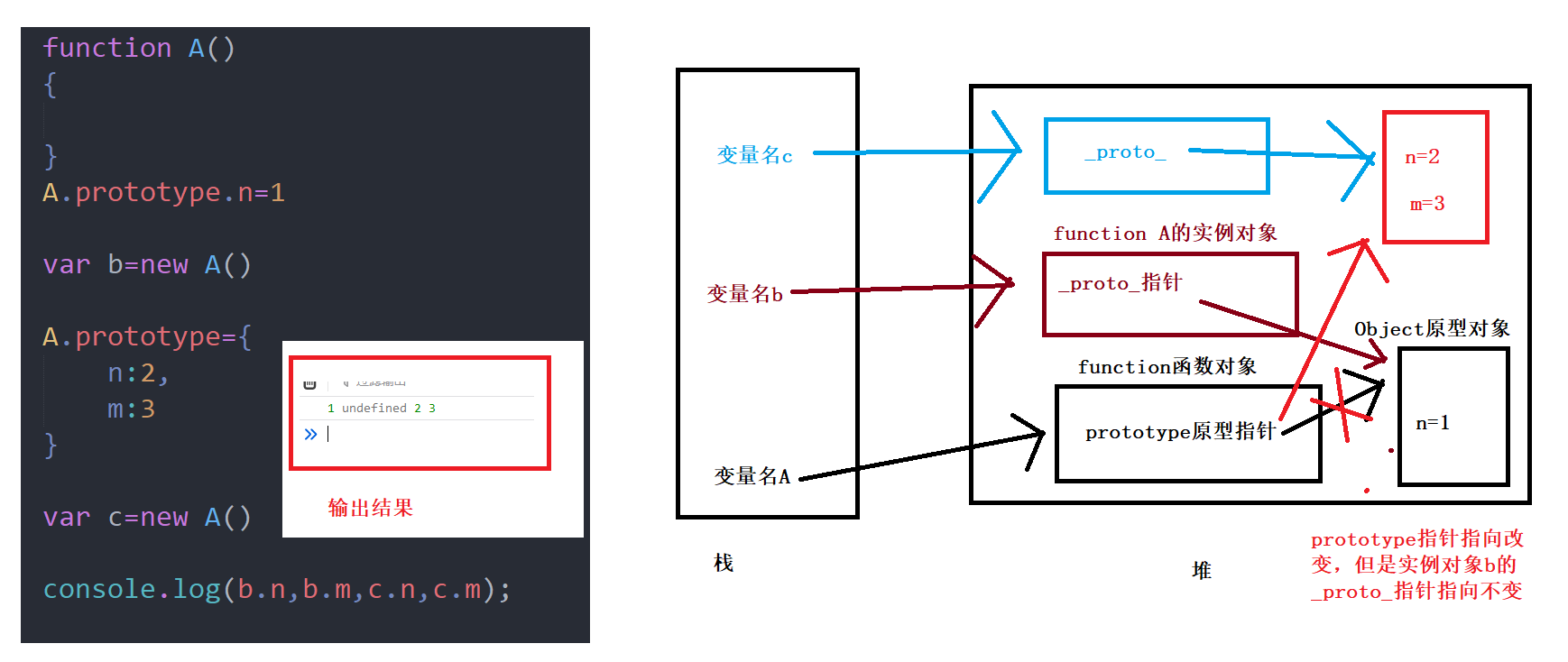
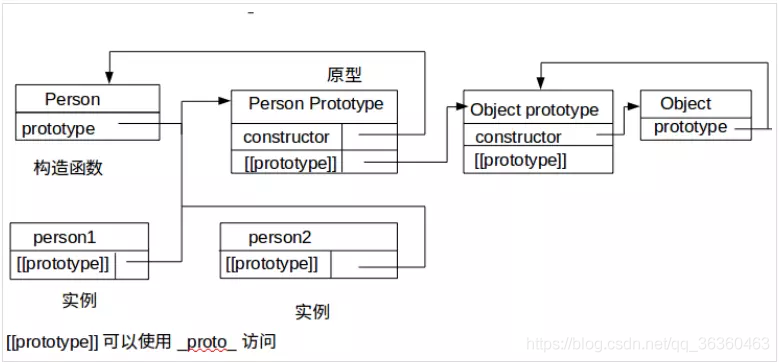
Understand an article_ proto_ Relationship and difference between and prototype
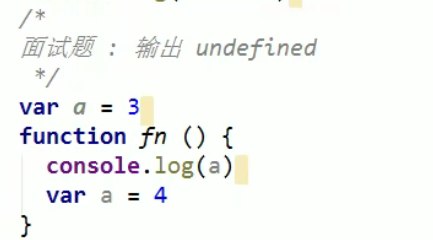
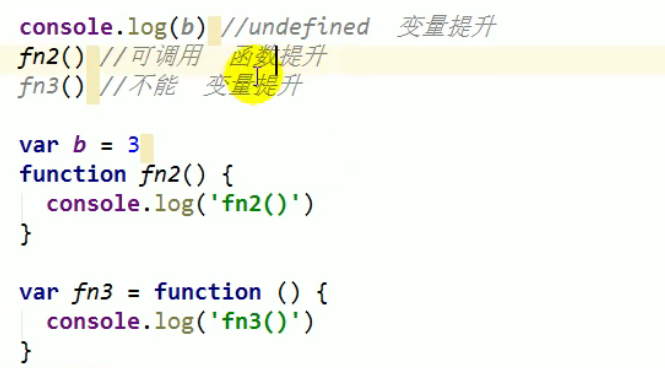
Variable promotion and function promotion

Execution context


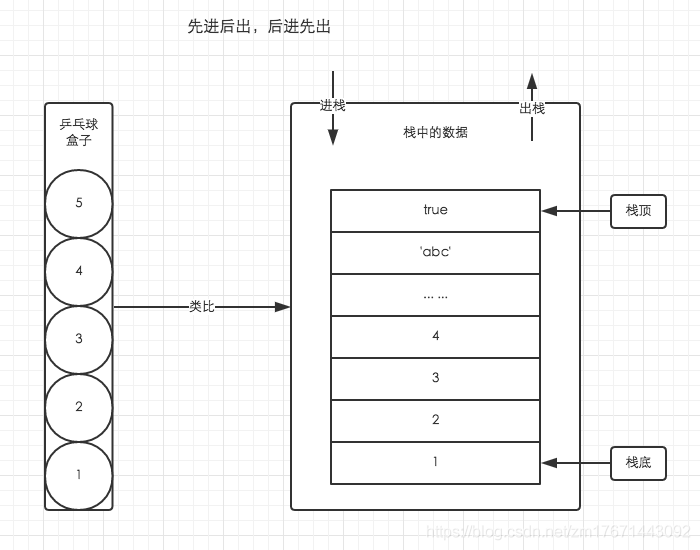
Execution stack
JavaScript On a single thread, all code is queued for execution. At the beginning, when the browser executes the global code, first create the global execution context and press it into the top of the execution stack. Each time a function is executed, the execution context of the function will be created, And push it into the top of the execution stack. After the execution of the current function is completed, the execution context of the current function is out of the stack and waits for garbage collection. Browser JS The execution engine always accesses the execution context at the top of the stack.
Scope

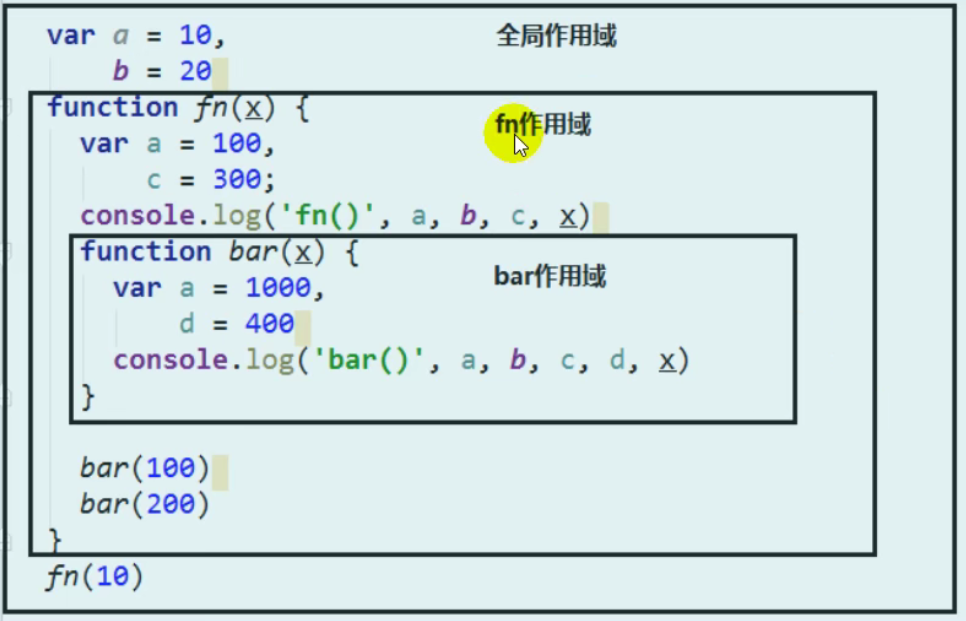
Scope chain

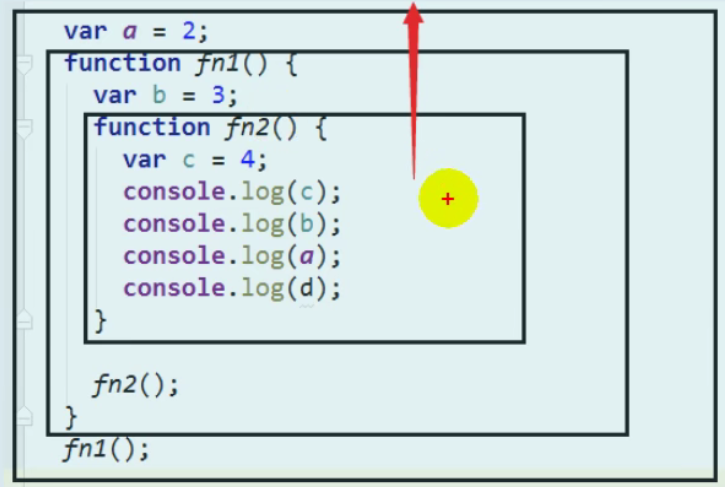
closure
Definition of closure

Advantages of closures
1. Make it possible for external access to internal variables of functions
2. Local variables reside in memory
3. The use of global variables can be avoided to prevent global variable pollution
4. It will cause memory leakage (a piece of memory space is occupied for a long time without being released)
Function of closure


Variable f gets the address value of the function returned by fn1. The variable name of fn3 is released, but the address it points to is received by F. therefore, the function object on this address is not garbage object and can be called through F
Closure lifecycle


Application of closures - JS module

JS module definition method 1:
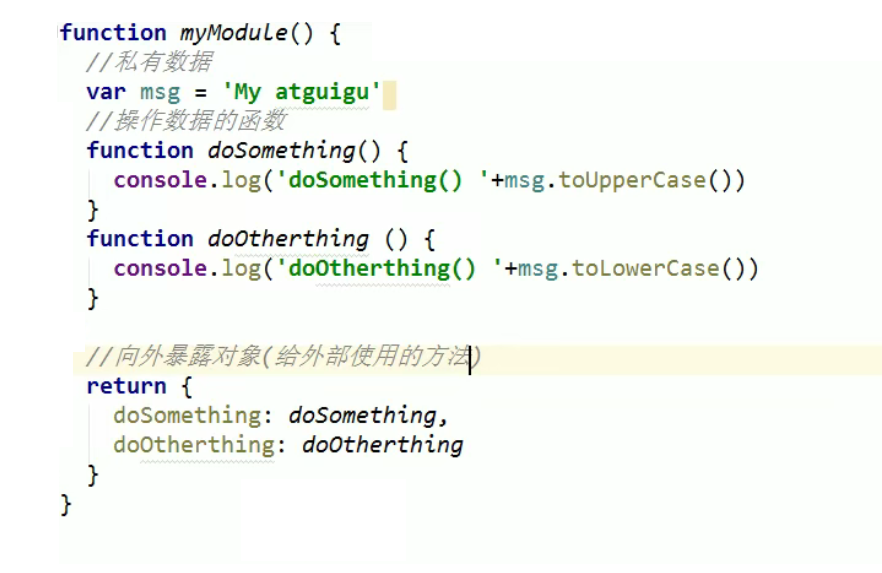
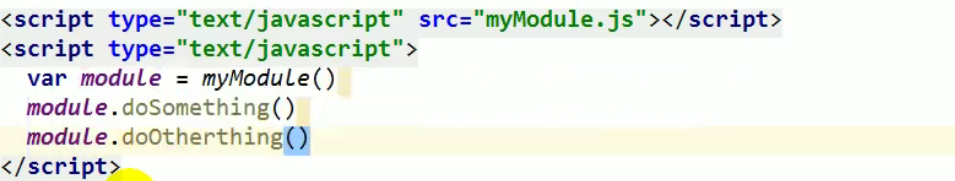
Write the above code into a js file. When the html page loads the js file, the code in the js file executes, and then the call returns to get the return value to execute.
JS module definition mode 2:
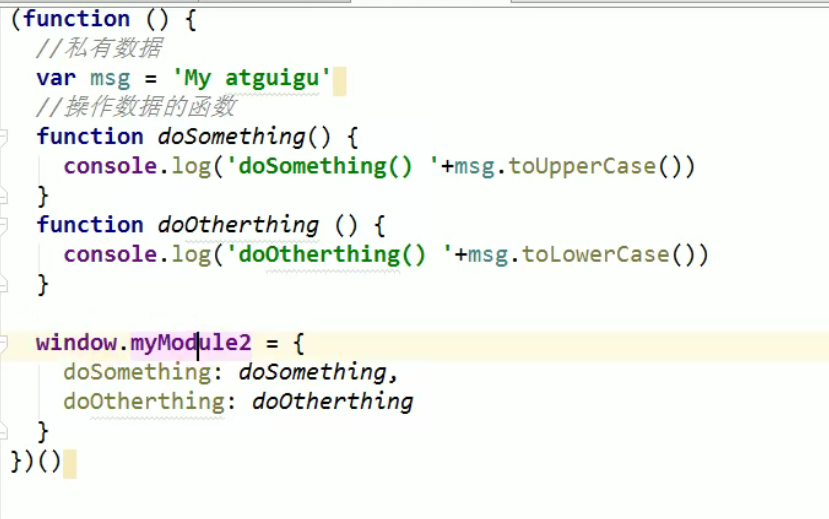
In this way, the js file is loaded through myMoudle2 Property name () can call the function directly
Disadvantages of closures


Memory overflow and memory leak

this variable saves the external
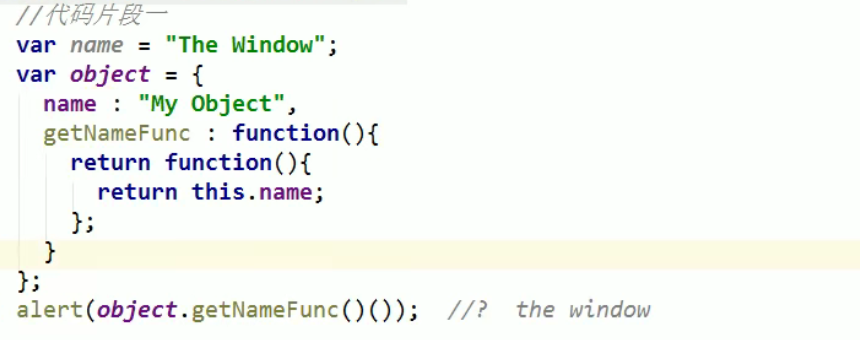

JS object creation method
Method 1: Object constructor mode

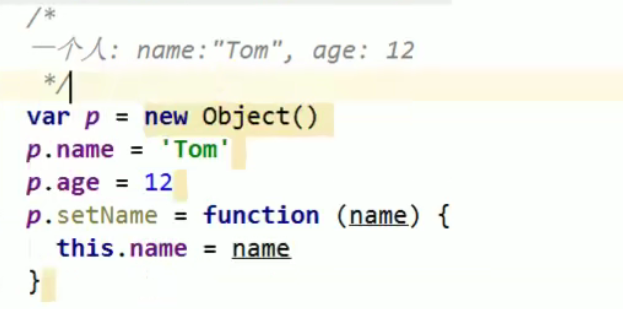
Mode 2: object literal mode


Mode 3: factory mode


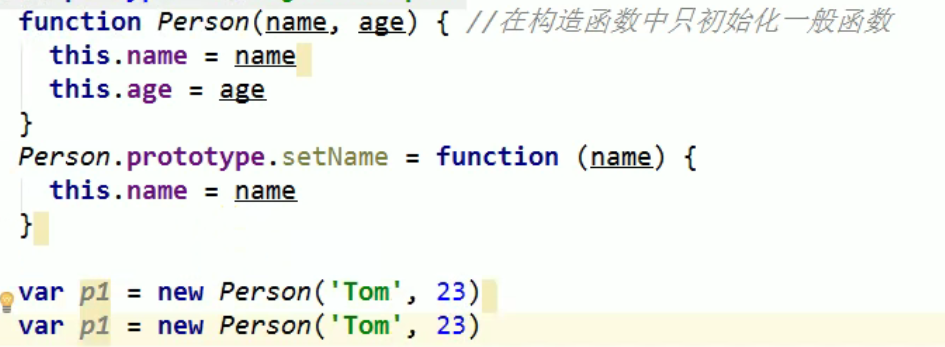
Mode 4: Custom constructor mode


Mode 6: combination mode of constructor + prototype

inherit
Inheritance of prototype chain
Key points of prototype chain inheritance: change the instance object of the corresponding parent type into the prototype object of the child type
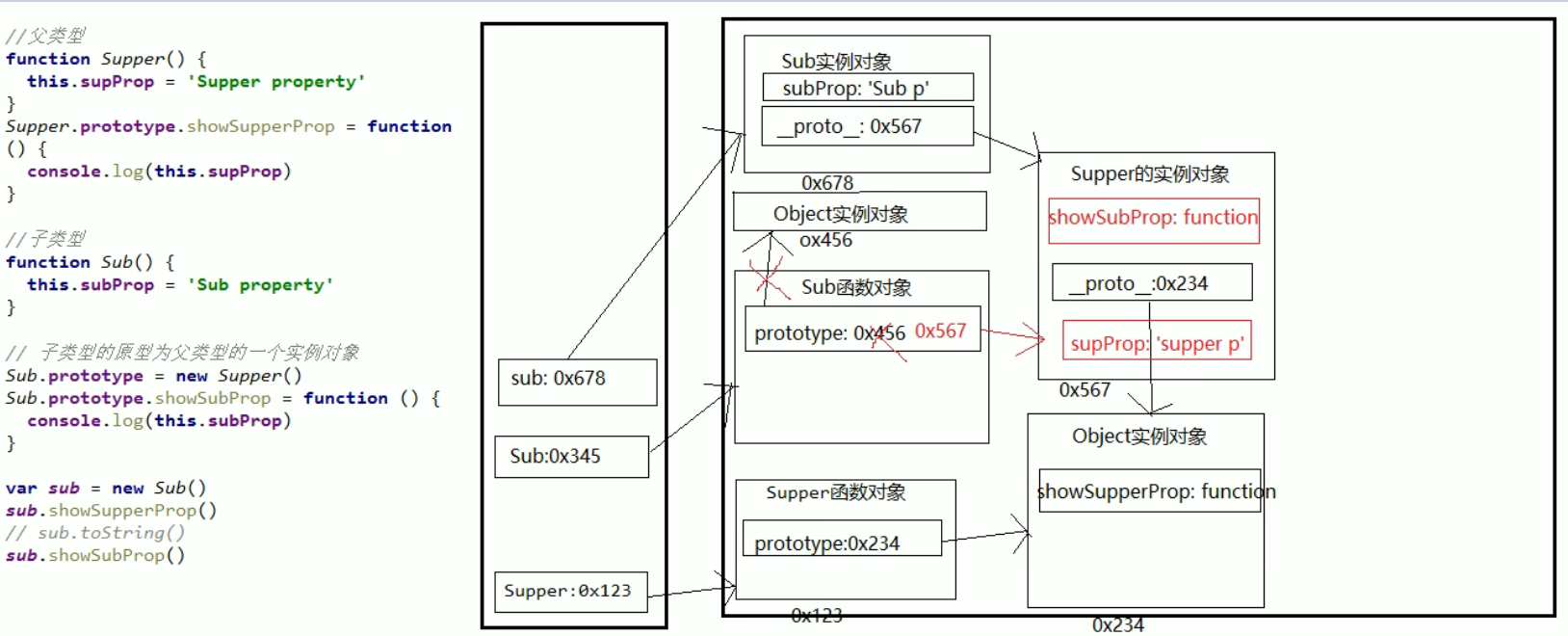
After the prototype chain inheritance effect is realized, the constructor of the subtype prototype points to the supplier just added to the prototype chain. We need to make the constructor of the subtype prototype point to the subtype

Borrow constructor to implement pseudo inheritance

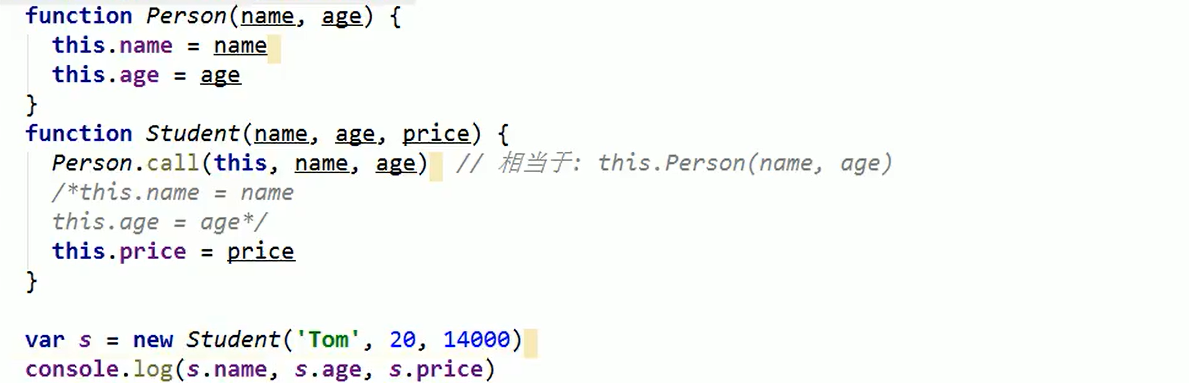
Combinatorial inheritance

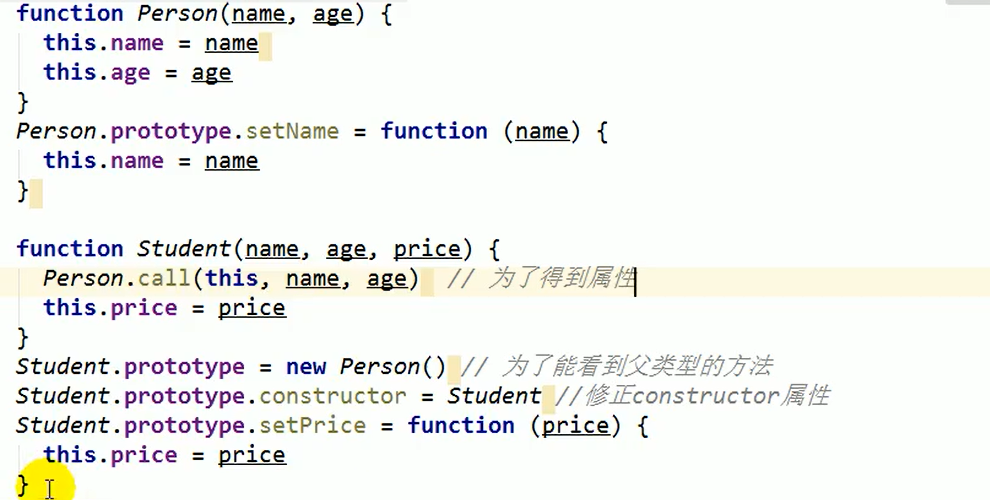
Here, call is used to get the attribute. Instead of calling the attribute through the prototype object, you can call it directly To call properties
JS is single threaded


Basic flow of code classification and JS code execution

Event cycle model

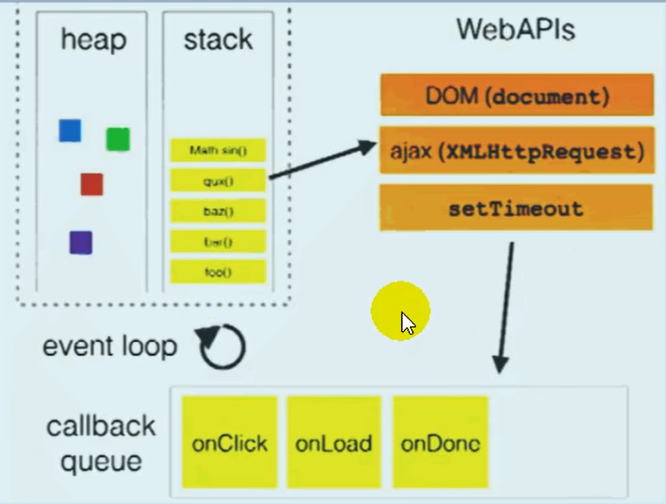

Web Worker implements multithreading
Detailed explanation of Web Worker
summary




