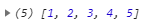A pen test, a nested array of flat processing.
Title
Convert [1,2, [3, [4,5]]] to [1,2,3,4,5].
▍ method 1: recursion
var arr = [1, 2, [3, [4, 5]]];
function flatten(arr) {
var res = [];
for(var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if(Array.isArray(arr[i])) {
res = res.concat(flatten(arr[i]));
} else {
res.push(arr[i]);
}
}
return res;
}
var result = flatten(arr);
console.log(result);Array.isArray(): determines whether a value is an array and returns a boolean type.
▍ method 2: reduce
var arr = [1, 2, [3, [4, 5]]];
function flatten(arr) {
return arr.reduce((result, item) => {
return result.concat(Array.isArray(item) ? flatten(item) : item);
}, []);
}
var result = flatten(arr);
console.log(result);Reduce is a method of array. It receives a function as an accumulator. Each value in the array (from left to right) starts to reduce and finally calculates to a value.
reduce contains two parameters: the callback function, which is passed to the initial value of total.
// To sum the values of an array:
arr.reduce((total, item)=> { // total is the previous calculation result, and item is the values of the array
return total + item;
}, 0);
▍ method 3: toString & split
var arr = [1, 2, [3, [4, 5]]];
function flatten(arr) {
return arr.toString().split(',').map(function(item) {
return Number(item);
})
}
var result = flatten(arr);
console.log(result);Because each item value of the array formed after split is a string, we need to traverse the array with a map method to convert each item to numeric type.
map(): run a callback function for each item in the array, and return the new array composed of the result of the function.
▍ method 4: join & split
var arr = [1, 2, [3, [4, 5]]];
function flatten(arr) {
return arr.join(',').split(',').map(function(item) {
return parseInt(item);
})
}
var result = flatten(arr);
console.log(result);join can also convert arrays to strings.
▍ method 5: extension operator
var arr = [1, 2, [3, [4, 5]]];
function flatten(arr) {
while(arr.some(item => Array.isArray(item))) {
arr = [].concat(...arr);
}
return arr;
}
var result = flatten(arr);
console.log(result);some(): run a callback function for each item in the array. If the function returns true for an item, then some returns true.
The extended operator of es6 can change a two-dimensional array into a one-dimensional one.
[].concat(...[1, 2, 3, [4, 5]]); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
Effect