What is design
- Silence is golden (don't output the wrong result)
- Each part is larger than the whole
- Seek 90% solutions instead of trying to meet 100% of users' needs
- Small is beauty
- Let each program do only one thing
- Rapid prototyping (first make a version for customers, and then continuously complete the requirements)
- Leverage software (reusable)
- Abandon efficiency for portability
- Use pure text to store data
- Use shell scripts to improve efficiency and portability
- Avoid mandatory user interfaces
- Make every program a filter
- Allow users to customize the environment
- Try to make the operating system kernel small and lightweight
- Use lowercase letters and keep them short
Five principles of design mode
- Opening and closing principle (open to extension, modify and close)
- Lee's replacement principle (where the parent class appears, the child class can appear)
- Principle of interface independence (keep the interface single and independent)
- Rely on the inversion principle, rely on abstraction rather than concrete
Frequent interview questions
First question
When taking a taxi, you can take a special bus or an express. Any car has a license plate number and name
The prices of different trains are different. The express train is 1 yuan per kilometer and the special train is 2 yuan per kilometer
Vehicle information is displayed at the beginning of the journey
At the end of the trip, the taxi amount is displayed
analysis
From the demand, we can get two categories, travel category and automobile category
uml design
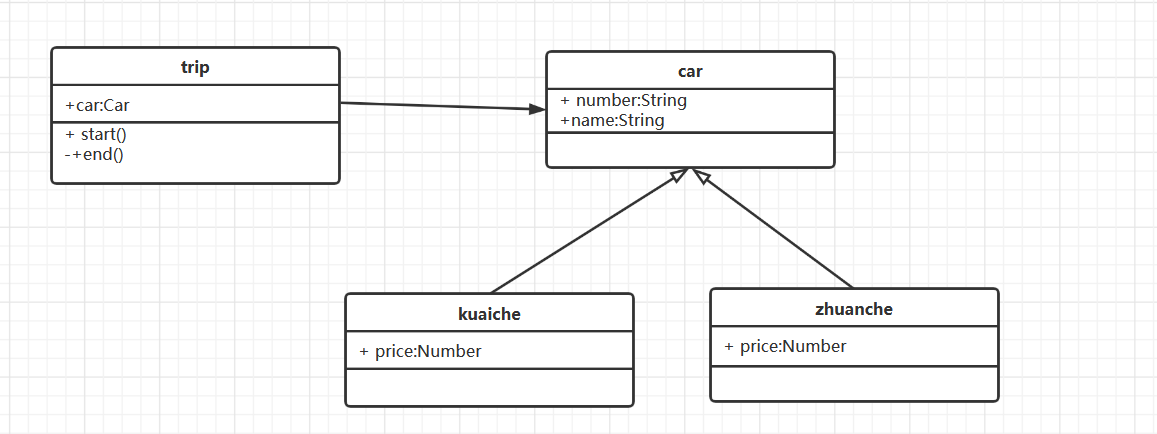
code
class Car {
constructor(name, number) {
this.name = name;
this.number = number;
}
}
class Kuaiche extends Car {
constructor(name, number) {
super(name, number);
this.price = 1;
}
}
class Zhuanche extends Car {
constructor(name, number) {
super(name, number);
this.price = 2;
}
}
class Trip {
constructor(car) {
this.car = car;
}
start() {
console.log(`this car name ${this.car.name} this car number ${this.car.number}`);
}
end() {
console.log(`total price ${this.car.price * 5}`);
}
}
let kuaiche=new Kuaiche('kuaiche','1001');
let trip=new Trip(kuaiche);
trip.start();
trip.end();
Second question
A parking lot is divided into three floors with 100 parking spaces on each floor
Each parking space can monitor the entry and exit of vehicles
Before the vehicle enters, display the number of vacant parking spaces on each floor
When the vehicle enters, the camera can recognize the license plate number and time
When the vehicle comes out, the exit display displays the license plate number and parking time
requirement analysis
From the demand, we can conclude that there are 7 categories: parking lot, floor, parking space, vehicle, camera, display and parking space
Class diagram
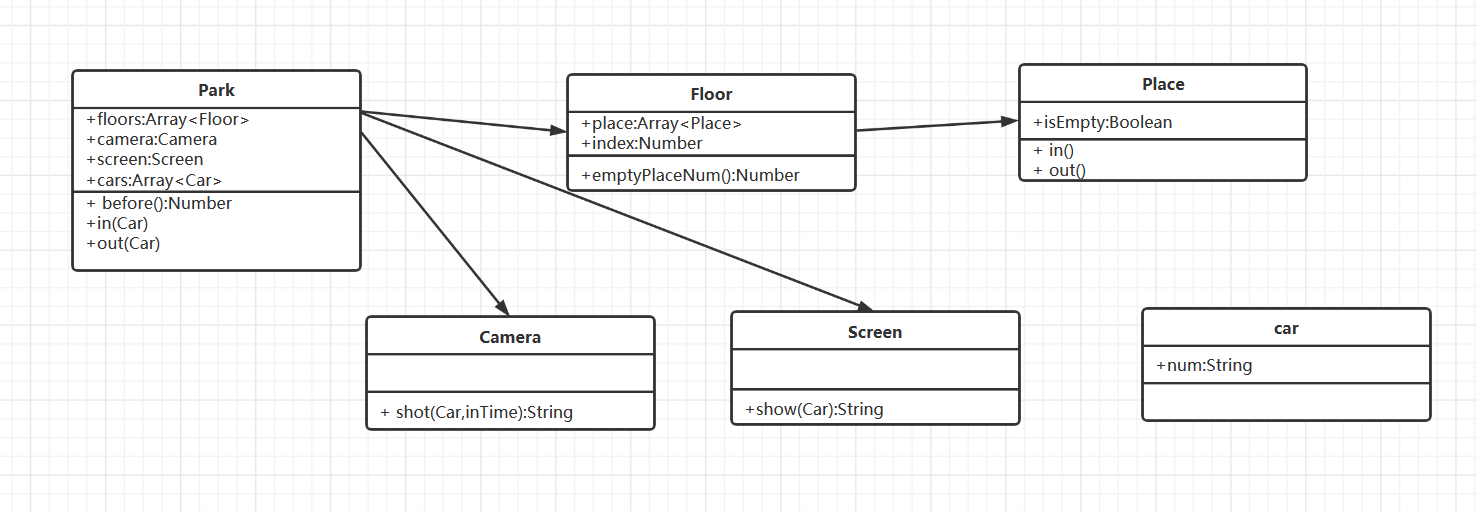
code
// vehicle
class Car {
constructor(num) {
this.num = num
}
}
// Entrance camera
class Camera {
shot(car) {
return {
num: car.num,
inTime: Date.now()
}
}
}
// Exit display
class Screen {
show(car, inTime) {
console.log('license plate number', car.num)
console.log('Parking Duration', Date.now() - inTime)
}
}
// Parking lot
class Park {
constructor(floors) {
this.floors = floors || []
this.camera = new Camera()
this.screen = new Screen()
this.carList = {}
}
in(car) {
// Get camera information: number and time
const info = this.camera.shot(car)
// Stop at a parking space
const i = parseInt(Math.random() * 100 % 100)
const place = this.floors[0].places[i]
place.in()
info.place = place
// Record information
this.carList[car.num] = info
}
out(car) {
// pick up information
const info = this.carList[car.num]
const place = info.place
place.out()
// Display time
this.screen.show(car, info.inTime)
// Delete information store
delete this.carList[car.num]
}
emptyNum() {
return this.floors.map(floor => {
return `${floor.index} Layer and ${floor.emptyPlaceNum()} Parking spaces`
}).join('\n')
}
}
// layer
class Floor {
constructor(index, places) {
this.index = index
this.places = places || []
}
emptyPlaceNum() {
let num = 0
this.places.forEach(p => {
if (p.empty) {
num = num + 1
}
})
return num
}
}
// parking lot
class Place {
constructor() {
this.empty = true
}
in() {
this.empty = false
}
out() {
this.empty = true
}
}
// Test code------------------------------
// Initialize parking lot
const floors = []
for (let i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
const places = []
for (let j = 0; j < 100; j++) {
places[j] = new Place()
}
floors[i] = new Floor(i + 1, places)
}
const park = new Park(floors)
// Initialize vehicle
const car1 = new Car('A1')
const car2 = new Car('A2')
const car3 = new Car('A3')
console.log('The first car enters')
console.log(park.emptyNum())
park.in(car1)
console.log('The second car enters')
console.log(park.emptyNum())
park.in(car2)
console.log('The first car left')
park.out(car1)
console.log('The second car left')
park.out(car2)
console.log('The third car enters')
console.log(park.emptyNum())
park.in(car3)
console.log('The third car left')
park.out(car3)