1, Event binding syntax
Grammatical form 1
Event listener} tag object addEventListener('click',function(){});
Grammatical form 2
The on syntax binds the} label object onclick = function(){}
On syntax is an event processing function bound by = equal assignment. In essence, the = equal assignment performs the overwrite assignment. The data after assignment will overwrite the previously stored data, that is, in on syntax, an event type with the same label object can only be assigned and bound to one event processing function. If the assignment is bound to multiple event processing functions, The post assigned event handler overrides the event handler stored between
Three elements of event binding
Tag object} event source is the tag object that binds the event
The 'click' event type is the type of event bound to the label object
function() {} event handler is the function program executed when the event is triggered
Is the syntax form of callback function, which can be function name or anonymous function
2, Delete syntax for events
1.on syntax binding event deletion
Because the on syntax is = equal to the assignment operation, as long as a null / empty function is assigned, the executed function program will not be called when the event is triggered, so as to achieve the effect of deleting the event
2. Delete event listening syntax
Special deletion function method is required: label object removeEventListener('event type ', event handler);
You can only delete event handling functions that are bound with function names. If you are bound with anonymous functions, you cannot delete them
be careful:
In practice, if you do not need to delete the event handler function, it is recommended to use the anonymous function syntax
In practice, if the event handler must be deleted, only the function name can be bound
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>I am div Label object</div>
<button>binding</button>
<button>delete</button>
<script>
//Get label object
var oDiv = document.querySelector('div');
var oBtn1 = document.querySelectorAll('button')[0];
var oBtn2 = document.querySelectorAll('button')[1];
oBtn1.addEventListener('click', function () {
//on syntax binding event
//oDiv.onclick = function(){console.log(111)};
//Event listening syntax binding
//Bound anonymous function
oDiv.addEventListener('click', function () { console.log(111) });
//Bound function name
oDiv.addEventListener('click', funA);
oDiv.addEventListener('click', funB);
oDiv.addEventListener('click', funC);
})
//Delete bound events
oBtn2.addEventListener('click', function () {
//Delete event bound by on syntax
//oDiv.onclick = null;
//oDiv.onclick = function(){};
//The bound anonymous function cannot be deleted because the memory addresses of the two anonymous functions are different
//Suppose the bound memory address is 00ff11
//The deleted memory address may be 00ffzz
//Unable to set the correct memory address for deletion
oDiv.removeEventListener('click', function () { console.log(111) });
//The bound function name stores the memory address
//The following can be deleted
oDiv.removeEventListener('click', funA);
oDiv.removeEventListener('click', funB);
oDiv.removeEventListener('click', funC);
});
function funA() {
console.log('aaa');
}
function funB() {
console.log('bbb');
}
function funC() {
console.log('ccc');
}
</script>
</body>
</html>3, Default event
The default event is the program effect executed by the html tag by default
There are: hyperlink click jump, form tab click jump, right mouse button
Block default events
Define a formal parameter in the event handler function. The formal parameter name is generally e / event
Label object addEventListener('event type '), function (E / event){
/ / prevent default event execution
Formal parameters prevenDefault();
})
Hyperlinks
Add click event to hyperlink tag
form label
Add a submit event to the form tag
Right mouse button
Add contextmenu right mouse button event to document
4, Prevent the propagation of events
The parent tag and the descendant tag add events of the same type, and the descendant tag triggers events. The parent tag will also trigger events of the same type. This implementation principle is called event propagation or bubble event
Prevent event propagation syntax
Label object Addevenlistener (event type, function(e/event){
e.stopPropagation();
})
Mode of event propagation
In previous versions, events were propagated in two ways
Bubble} child --- parent
Capture} parent - child
Now in the new version of browser, there is only bubbling mode by default and no capture mode
Event listening syntax binding event handler
Parameter 3 if set to true, the propagation execution capture method of the event
5, Common event types
1. window related event types
1.1 browser window size listening events
window.addEventListener( 'resize' ,function(){} )
1.2 page scrolling listening events
window.addEventListener( 'scrool',function(){} )
1.3 browser loading events
window.addEventListener( 'load',function(){})
1.5 new window open url connection
window.open(url address)
1.6 close the current window
window.close()
2. Mouse related event types
Click left click
dblclick# double click with the left mouse button
contextmenu # right click
mousedown mouse button press
mouseup; mouse button lift
mousemove mouse movement
mouseover mouse in mouseenter
mouseout mouseleave
3. Keyboard related event types
keydown keyboard key press
keyup , keyboard key lifting
keypress key press
4. Form related events
submit form submission event
Focus tag to get focus
blur , tags lose focus
change tag loses focus and data changes
Input input data
5. Mobile terminal events
touchstart
touchend
touchmove
6. Special events
Transition start
Transition end
Animation start
Animation end
An event can only be triggered when it is bound to the tag of the event, that is, within the scope of the event source
Full screen trigger event needs to be given
document
document.documentElement
document.body
Binding event
Some events can be supported, and some events can only be supported by an object
6, Event object
Event object (event), the data value stored in the parameter in the event handling function, is the object that triggers the event
The object that triggers the event and the object that binds the event are not necessarily the same object
When an event is triggered, the JavaScript program automatically stores the arguments in the formal parameters
That is to automatically store the data information related to the tag object that triggers the event in the event object
Event source Addeventlistener (event type, function {})
Event object target
Stored is the tag object that triggers the event
Supports all DOM operation syntax
7, Event delegate syntax
Instead of binding events directly to the tag object, bind events to the parent tag through the event object target determines different tag objects that trigger events and executes different function programs
Label object target is a DOM tag object
Label object target.tagName is the label name in uppercase English characters
Label object target executes DOM operation to determine what tag is clicked
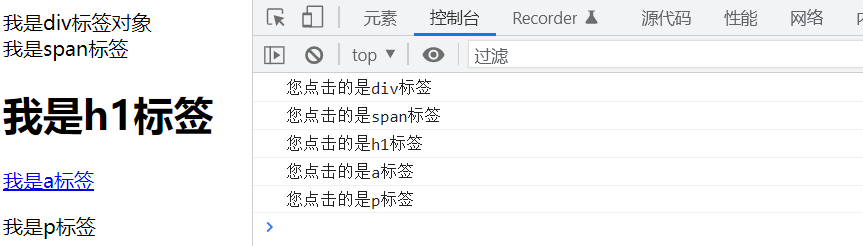
If div tag contains span tag h1 tag a tag p tag, add different click events to each tag
Generally, each tag object is obtained, and click events are bound to prevent the propagation of events
In practice, it is OK as long as different if judgments are triggered and different programs are executed according to different conditions
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
I am div Label object<br>
<span>I am span label</span>
<h1 id="h1">I am h1 label</h1>
<a href="JavaScript:;">I am a label</a>
<p>I am p label</p>
</div>
<script>
// Event delegation
// Add a click event to the parent div tag
// Through the event object target determines what tag triggers the event
// Different programs are triggered according to different tags
var oDiv = document.querySelector('div');
oDiv.addEventListener('click' , function(e){
// Event delegate click event will trigger
// The trigger event tag name is div, which proves that the div tag is clicked
if( e.target.tagName === 'DIV' ){
console.log( 'You clicked yes div label' );
}else if( e.target.tagName === 'SPAN' ){
console.log( 'You clicked yes span label' );
}else if( e.target.id === 'h1' ){
console.log( 'You clicked yes h1 label' );
}else if( e.target.getAttribute('href') === 'JavaScript:;' ){
console.log( 'You clicked yes a label' );
}else if( e.target.innerHTML === 'I am p label' ){
console.log( 'You clicked yes p label' );
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>Click each tab respectively, and the execution results are as follows: