Pod classification:
- Autonomous Pod: the pod will not be created after exiting
- Pod managed by the controller: maintain the number of copies of the pod throughout the life cycle of the controller
Controller type:
- Replication Controller and ReplicaSet
- Deployment
- DaemonSet
- StatefulSet
- Job
- CronJob
- Full name of HPA: Horizontal Pod Autoscaler
1.Replication Controller and ReplicaSet
ReplicaSet is the next generation of Replication Controller, which is officially recommended.
The only difference between ReplicaSet and Replication Controller is selector support, and ReplicaSet supports new set based selector requirements.
ReplicaSet ensures that a specified number of Pod replicas are running at any time.
Although ReplicaSets can be used independently, today it is mainly used by Deployments as a mechanism to coordinate Pod creation, deletion and update.
2.Deployment
Deployment provides a declarative definition method for Pod and ReplicaSet.
Typical application scenarios:
Used to create Pod and ReplicaSet
Rolling update and rollback
Expansion and contraction
Pause and resume
3.DaemonSet
The daemon set ensures that a copy of the Pod is running on all (or some) nodes. When nodes join the cluster, a Pod will also be added for them. When a node is removed from the cluster, these pods will also be recycled. Deleting a DaemonSet will delete all pods it creates.
Typical usage of DaemonSet:
Run the clustered storage DaemonSet on each node, such as glusterd, ceph.
Run the log collection daemon set on each node, such as fluent D and logstash.
Run monitoring DaemonSet on each node, such as Prometheus Node Exporter, zabbix agent, etc
A simple usage is to start a daemon set on all nodes, which will be used as each type of daemon.
A slightly more complex usage is to use multiple daemonsets for each daemon type separately, but with different flags, and different memory and CPU requirements for different hardware types.
4.StatefulSet
StatefulSet is an API object used to manage workload of stateful applications. Applications with unequal relationships between instances and instances dependent on external data are called "stateful applications"
Stateful set is used to manage Deployment and extend a group of pods, and can provide sequence number and uniqueness guarantee for these pods.
StatefulSets are valuable for applications that need to meet one or more of the following requirements:
Stable and unique network identifier.
Stable and persistent storage.
Orderly and elegant deployment and scaling.
Orderly and automatic rolling update.
5.Job
Execute the batch task only once to ensure the successful completion of one or more pods of the task.
6.CronJob
Cron Job creates Jobs based on time scheduling.
A CronJob object is like a line in a crontab (cron table) file. It is written in Cron format and executes jobs periodically at a given scheduling time.
7.HPA
Automatically adjust the number of pods in the service according to the resource utilization to realize the automatic scaling of Pod level
example
ReplicaSet controller example
Write the ymal file, verify the replica establishment and capacity expansion function, and the version cannot be upgraded or rolled back using this controller
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: ReplicaSet
metadata:
name: replicaset-example
spec:
replicas: 6
selector:
matchLabels:
app: myapp
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: myapp
spec:
containers:
- name: myapp
image: myapp:v1
Set the number of copies to 6:
- kubectl get pod view
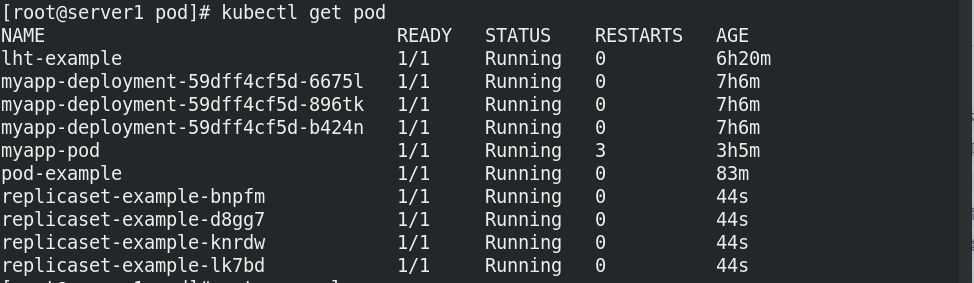
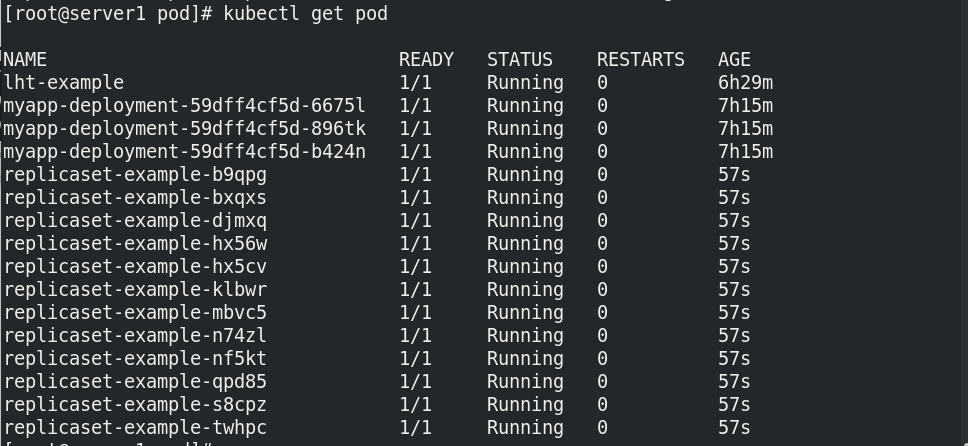
The copy is revised to 12:
Deployment controller example
It is used to create Pod and ReplicaSet, scroll update and rollback, expand and shrink capacity, pause and resume
- Create ymal file
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: myapp-deployment
labels:
app: myapp
spec:
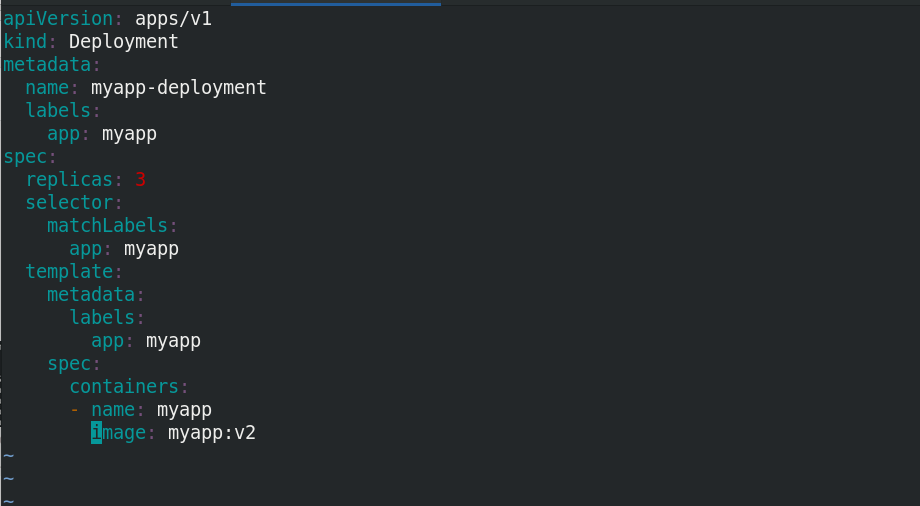
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: myapp
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: myapp
spec:
containers:
- name: myapp
image: myapp:v1
Run the deployment to view the container status
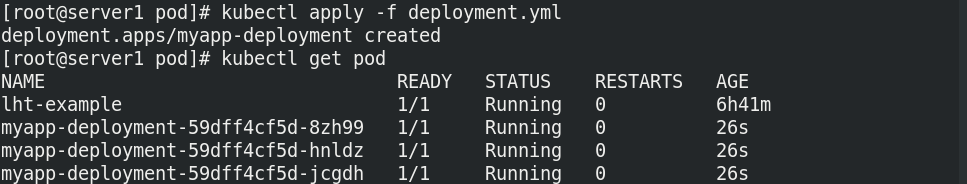
Change the image to v2 and rebuild the pod
- get pod -o wide
- curl 10.244.141.197
View found that the image was modified successfully:
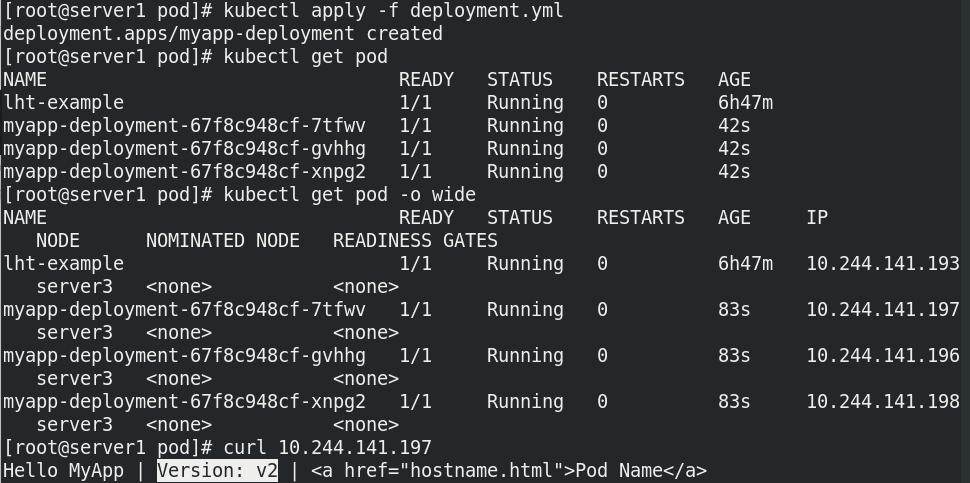
deployment will re-establish an rs controller to create a replica of v2. The rs of v1 will not be discarded for rollback
DaemonSet controller example
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: daemonset-example
labels:
k8s-app: zabbix-agent
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
name: zabbix-agent
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: zabbix-agent
spec:
containers:
- name: zabbix-agent
image: zabbix/zabbix-agent
Job and CronJob
job
$ vim job-example.yaml
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: pi
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: pi
image: perl
command: ["perl", "-Mbignum=bpi", "-wle", "print bpi(2000)"]
restartPolicy: Never
backoffLimit: 4
$ kubectl apply -f job-example.yaml
$ kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pi-6phk8 0/1 Completed 0 2m22s
$ kubectl logs pi-6phk8
$ kubectl delete job pi
cornjob
apiVersion: batch/v1beta1
kind: CronJob
metadata:
name: cronjob-example
spec:
schedule: "* * * * *"
jobTemplate:
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: cronjob
image: busybox
args:
- /bin/sh
- -c
- date; echo Hello from k8s cluster
restartPolicy: OnFailure